-
Hooke's LawHooke's law says that the force applied is directly proportional to the extension
-
Force equationForce = spring constant x change in length
-
Limit of proportionalityThe limit of proportionality is the point beyond which Hooke's law no longer applies
-
The elastic limitThe elastic limit is the maximum stress that can be applied without plastic deformation which is when it does not return to its original shape
-
elastic deformationmaterial returns to its original shape andf has no permenant extension, energy is stored as elastic strain energy
-
plastic deformationmaterial is permanently stretched because the atoms have physically moved relative to one another, energy is used to deform it
-
force vs extension graph

-
Tensile stressthe force applied per unit cross sectional area, measured in Pa/Nm^-2
-
Tensile strainthe extension per unit original length, a ratio so has no unit
-
stress equationForce/cross sectional area
-
strain equationextension/original length
-
Breaking stressIf enough stress is applied to the material it can fracture
-
the ultimate tensile srtressthe maximum stress it can withold
-
how does a brittle material fracture?witout showing any plastic behaviour
-
How does a ductile material fracture?can be stretched into long wires and stays permentanly stretched, shows plastic behaviour
-
what is the strength of the material?the ultimate tensile stress?
-
if hooke's law is obeyed the energy stored is...the area under the force extension graph
-
work done equations
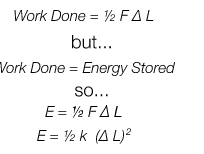
-
what can the energuy in a spring be transformed to?kinetic and gravitational potential energy
-
What happens up to the limit of proportionality?stress and strain are directly proportional to each other
-
What is young modulus?a constant measure of stiffness
-
young modulus equationtensile stress/tensile strain (Pa, Nm^-2)
-
What is the gradient of a stress strain graph?young modulus
-
What is the area under the stress strain graph equivalent to?strain energy per unit volume
-
energy per unit volume equation1/2 x stress x strain
-
The smaller the cross-sectional area...the greater the stress- meaning that the breaking point can be reached faster than expected
-
springs in series force and extensionThe force acting on the springs must be the same The extension of each spring must add to the total extension
-
springs in parallel force and extensionthe extension of each spring must be shared by the springs and must add up to the total force
-
springs in parallel springs constant equationkT = k1 + k2 ...
-
springs constant for springs in series1/kT = 1/K1 + 1/k2
-
what is elastic strain energy?the energy store for when work is done on a material to stretch or compress it
-
elastic energy stored in a stretched wire equation1/2 x T x e
-
the spring constanta measure of stiffness of an object, up to its limit of proportionality, Nm^-1
-
why does a spering recoil after weight has been exerted onto it?The spring will exert an equal and opposite force to the force stretching it in order to restore equilibrium/remain at rest again As springs have a restorative force
-
The forece exctension graph for a rubber band
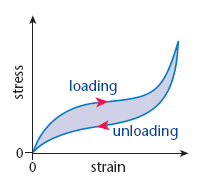 The loading curve is the c urve produced when the force applied is increasing The unloading curve is the curve produced when the force applied is decreasing As the unloading curve is under the loading curve this shows that the rubber gives up less energy than it originally took in
The loading curve is the c urve produced when the force applied is increasing The unloading curve is the curve produced when the force applied is decreasing As the unloading curve is under the loading curve this shows that the rubber gives up less energy than it originally took in -
Neckingthe material shows 'necking' one part of it narrows considerably. The stress dramatically increases compared to strain / extension increases daramitally fompared to force locally in the necking region

