-
MSNPD - Idea Generation
Systematic search for new product ideas
• Internal idea sources:
– Internal social networks
– Intrapreneurial programs
• External idea sources:
– Distributors and suppliers
– Competitors
– Customers
-
MSNPD - Idea Screening
Screening new product ideas to spot good ones and
drop poor ones as soon as possible
• Ways of screening new ideas:
– New idea write-up reviewed by a committee
– R-W-W framework—Real, win, worth doing
-
MSNPD - Concept Development & Testing
Developing a new product into alternative product
concepts
– Find out how attractive each concept is to customers
– Choose the best one
• Testing new product concepts with groups of target
consumers
• Methods:
– Presenting the concepts to consumers symbolically or
physically
– Asking customers to respond by answering questions
about their reactions to the concepts
-
MSNPD - Marketing Strategy Development
• Initial marketing strategy for a new product
• Three parts of the marketing strategy statement:
– Describes the target market, planned value proposition,
sales, market-share, and profit goals
– Determines product’s planned price, distribution, and
marketing budget
– Develops long-run sales, profit goals, and marketing mix
strategy
-
MSNPD - Business Analysis
A review of the sales, costs, and profit projections for a new product
– To find out whether these factors satisfy the company’s
objectives
-
MSNPD - Product Development
Developing the product concept into a physical product
– To ensure that the product idea can be turned into a
workable market offering
-
MSNPD - Test Marketing
• Introduces the product and its proposed marketing
program into realistic market settings
• Gives the marketer an experience with marketing a
product before full introduction
• Tests the product and its marketing program
• Testing takes time, and costs can be high.
Alternatives to standard test markets
– Controlled test markets
– Simulated test markets
• Reasons for using alternative test markets
– Reducing the costs
– Speeding up the process
-
MSNPD - Commercialization
• Introducing a new product into the market
• Considerations for launching a new product
– When to launch
– Where to launch
Single location, region, national market, or international
marke
-
Product life cycle and stages
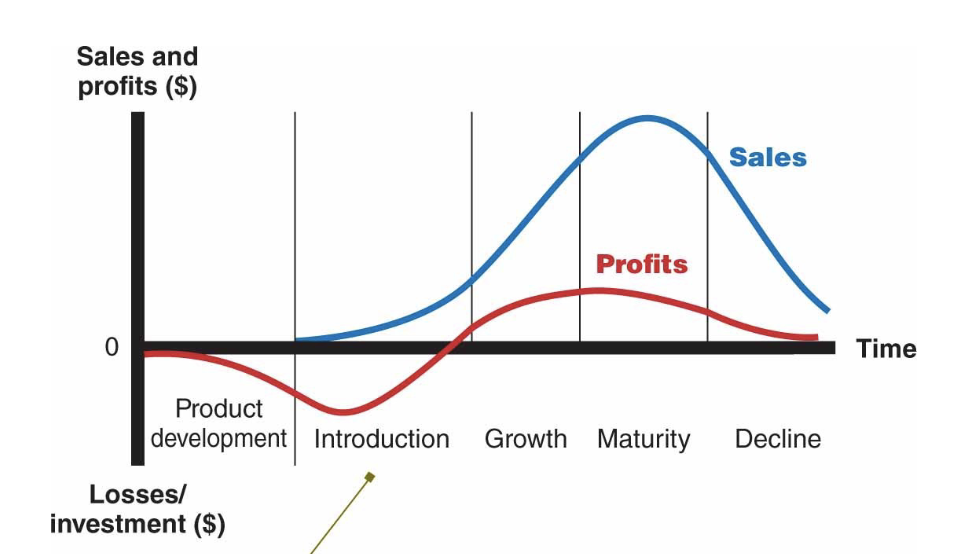
Product development
Introduction
Low sales, High cost per customer, Offer a basic product, use cost-plus
Build product awareness among early adopters and dealers. Use heavy sales promotion to entice trial
Growth
Rapidly rising sales, Average cost per customer, Offer product
extensions, Price to penetrate market
Build engagement and interest in the mass market, Reduce to take advantage of heavy consumer demand
Maturity
Peak sales, Low cost per customer, Diversify brand and models, Price to match or beat competitors
Stress brand differences and benefits, Increase to encourage brand switching
Decline
Declining sales, Low cost per customer, Phase out weak
items, cut price
Reduce to level needed to retain hard-core loyals, Reduce to
minimal level

