-
Give a summary of each of the major sympathetic effects and what neurotransmitter they use (7)
-Increase cardiac rate+force (Noradrenaline/NA)
-Vascular smooth muscle contraction (NA)
-Vascular dilatation/ airway relaxation/ bladder relaxation (NA)
-Inhibition of transmitter release in sympathetic nerves (NA)
-Pupil dilation (NA)
-Metabolism/ increase in glucose (NA)
-Sweat (Acetylcholine/AC)
-
How is noradrenaline made, where does it bind and what are the Adrenoreceptors?
Noradrenaline is made and released by the sympathetic nerves.
Binds to the Adrenoceptors to produce an effect
The Adrenoceptors are: (alpha and beta)
a1
a2
b1,b2,b3
-
All receptors that produce an autonomic effect are?
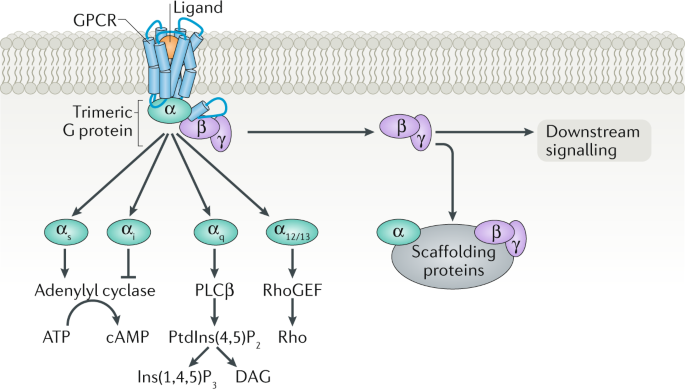
G protein coupled receptors AKA GPCRS
-
Effects on Heart? And what receptor(s) and/ neurotransmitter cause them? (3)
b1 RECEPTOR (relaxation and contraction) + NORADRENALINE INCREASES:
-Force of contraction (positive inotropy)
-Rate of contraction (positive chronotropy)
-Rate of relaxation (positive lusitropy)
-
Effects on Blood Vessels? And what receptor(s) and/ neurotransmitter cause them? (1)
a1 RECEPTOR (contraction) + NORADRENALINE or ADRENALINE
-Produce smooth muscle contraction artery narrowing
-
Effects on some Arteries and Smooth Muscle (Relaxation)? And what receptor(s) and/ neurotransmitter cause them? (2)
b1 or b2 RECEPTOR (relaxation for both) + ADRENALINE
-Certain arteries like coronary and the skeletal muscle RELAX to adrenaline
-Bladder, uterus and GI smooth muscle relaxes to sympathetic nerve activation
-
Effects on Kidney? And what receptor(s) cause them? (4) What about Renin specifically?
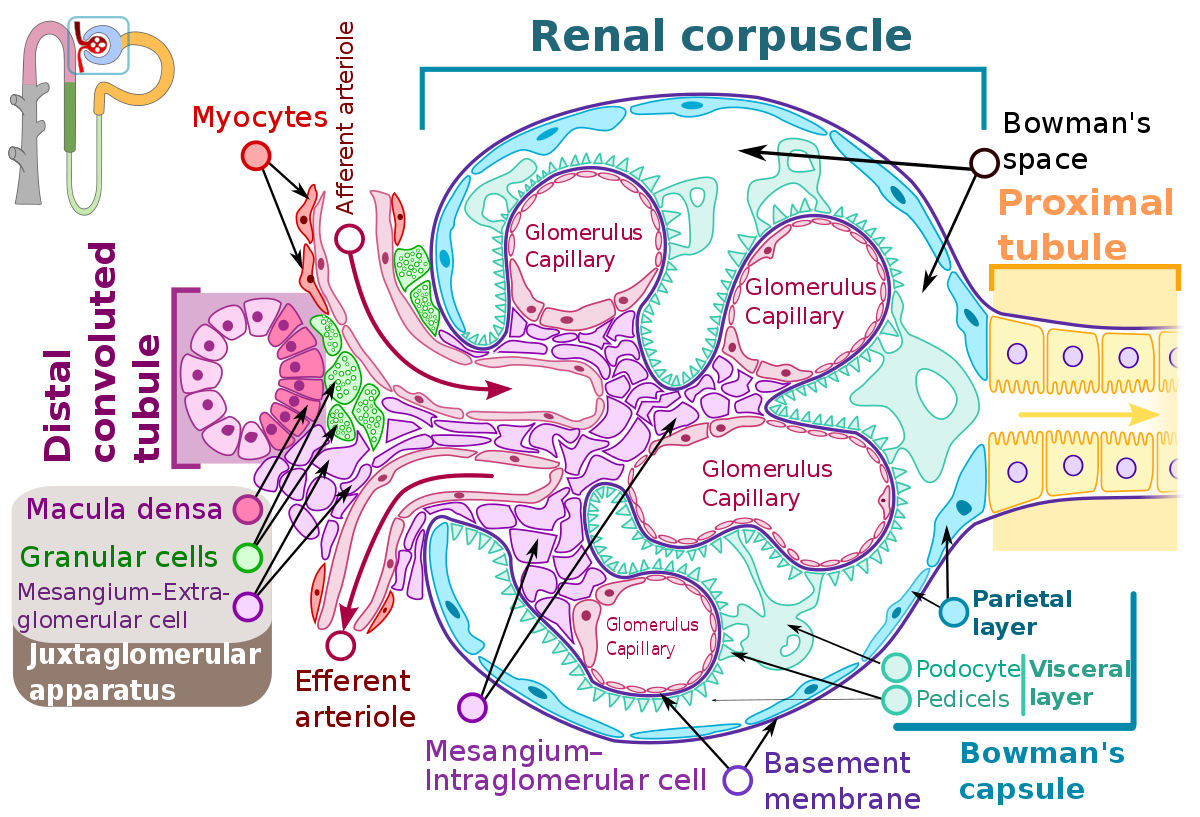
b1 RECEPTOR + NORADRENALINE
-Effects the Juxta glomerular apparatus (JGA)
-Located between afferent and efferent renal arteries
-When Sympathetic nerves stimulated
-Increase RENIN release
RENIN CAUSES:
Angiotensinogen (inactive)
TO
Angiotensin I (active)
-
Effects on Liver and Skeletal Muscle? And what receptors and/ neurotransmitter cause them? (3)
b2 or b3 RECEPTOR + NORADRENALINE
Sympathetic nerve activation causes;
-Increased glycogenolysis
-Increased lipolysis
-Increased glucose and TCA cycle intermediates
-
Effects on Eyes? And what receptors and/ neurotransmitter cause them? (2)
a1 or b1 RECEPTOR + NORADRENALINE
-Contracts radial muscle=wide pupil/dilation
-Increases aqueous humour production
-
Effects on Sweat and Hair? And what receptors and/ neurotransmitter cause them? (2)
a1 RECEPTOR + ACETYLCHOLINE
-Sympathetic nerve causes piloerection
-Increases sweat production
-
In Conclusion-A Summary of the Receptors (6)
1)Cardiac Output Increases (b1)
2)Blood Flow in Skeletal muscle improves (a1)
3)Other Circulations reduced (b1 or b2)
4)Digestion and Bladder function reduced (b1 or b2 or b3)
5)Fuel Mobilized (b2)
6)Eyes widen (a1)
-
What are the expected mediated responses adrenoceptor a1? (3)
-Arterial narrowing
-Seminal vesicular contraction
-Radial muscle contraction
-
What are the expected mediated responses adrenoceptor a2? (1)
-Reduction of transmitter released from the sympathetic nerves
-
What are the expected mediated responses adrenoceptor b1? (1)
-Increased heart rate and force of contraction
-
What are the expected mediated responses adrenoceptor b2? (2)
-Airway and artery relaxation
-Glycogenolysis
-
What are the expected mediated responses adrenoceptor b3? (2)
-Bladder and Uterus relaxation
-Lipolysis


