-
When a magnetic field is perpendicular to a current-carrying wire, does the wire feel a force?
Yes
-
equation for force when a magnetic field is perpendicular to a current-carrying wire
BIl
B - magnetic flux density
I - current in the wire
L - length of the wire
-
Fleming’s left hand rule for motors represents what properties on what fingers
Thumb - force
First finger - field
Second finger - current
-
What is magnetic flux density?
Flux density measured in Tesla(T) or Webers/meters^2(Wb/m^2), flux per metre^2
The amount of magnetic flux in an area taken perpendicular to the magnetic flux’s direction
-
A charged particle moving through a field feels a force travelling along the field lined or perpendicular to them
Perpendicular
-
What is the equation for the force felt by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
F=BQv
-
Is the force applied to the particles applied perpendicular to the particles motion or in one direction?
Perpendicular to its motion, causing it to move in a circular motion
-
Which fields to cyclotrons use
Electric and magnetic
-
How does a cyclotron work and what’s the electric and magnetic fields purpose in a cyclotron?
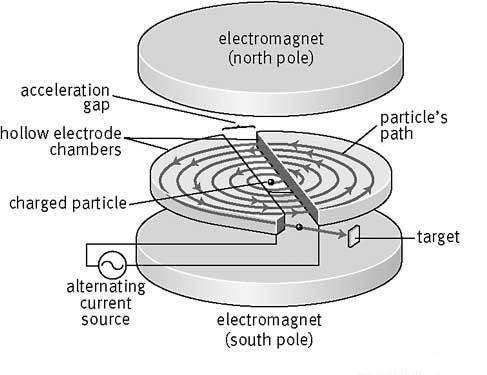
A cyclotron is made up of 2 semicircular electrodes called ‘Dees’ with a magnetic field applied perpendicular to the Dees and an alternating potential difference applied between the Dees
Each Dee is a metal electrodes with opposite charges, this creates an electric field in the gap between the two Dees. This is what accelerates the particles.
The magnetic field causes the particles to move in a circular motion, which allows it to gain speed whilst minimising space. As they speed up the radius of their motion increases, until it breaks free tangential to one of the Dees.
-
What is magnetic flux (quantative)

-
What is flux linkage?

-
What is the flux linkage of a rectangular coil rotating through a magnetic field?

-
What is faraday’s law?
The induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage
-
What is Lenz’s law?
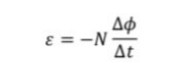
The direction of the induced emf is such as to oppose the change that induces it
-
What happens when you move a straight conductor through a magnetic field?
The electrons experience a force pushing them to one end of the conductor creating an emf across the conductor
The rod bey faraday’s law, it is changing flux as it moves through the field hence an emf is induced
-
What would be the emf produced when rotating a coil at a constant rate in a magnetic field

-
Describe how one would use an oscilloscope
Oscilloscopes are used to displace AC waves, the x axis is called the time base and shows how long it takes the wave to move 1 division and the y axis shows how much PD is needed to move tye wave up 1 division,
Using this we find the peak voltage, time period and frequency
-
What is magnetic flux?
It is a measurement of the total magnetic field lines that passes through a given area measured in Wb
-
How does a transformer work?
A primary coil wrapped around an iron core with an alternating potential difference creates an alternating magnetic field, this magnetic field induces an emf in a secondary coil also wrapped around the core, this makes a I in the secondary coil
-
What kind of current is produced by a transformer and why?
Alternating current
-
How is current produced in a transformer
An emf is induced by a changing magnetic field and so the emf induced is alternating producing an alternating current
-
Why are transformers used?
By changing the number of coils, the transformers can be used to increase the voltage and reduce current when transporting power with minimal energy loses
The voltage is then dropped again locally to ensure safe usage in households
-
What equation links the number of coils in a transformer with their voltages?
Ns/Np = Vs/Vp
-
What is transformer efficiency?
The ratio of output power in the transformer to input power
IsVs/IpVp
-
In a step-up transformer does the secondary coil or primary coil have more coils
Secondary
Step-up transformers increase voltage so more coils need to be in secondary coil for larger p.d.
-
Eddy current
As the primary coils magnetic field induces emf in the secondary coil, it also induces emf hence the mini currents in the iron core
-
Eddy currents problem
By lenz’s law the emf created snd its field opposes that of the primary coil. Causes energy loss via resistive heating of the iron core by the eddy current - reducing efficiency
-
Reduce eddy current losses
A laminated core
Thin sheets of iron with an electrical insulator between, reducing the eddy current
-
peak voltage V0
Distance from the equilibrium to the highest/ lowest point
-
Peak to peak voltage
Distance from the minimum point to the maximum point
-
Root mean square voltage
The average of all the squares of the possible voltages
Gives the average value of voltage output of the supply
-
Root mean square current
Irms = I0/root two
-
Root mean square voltage
Vrms = V0/root two
-
What is magnetic flux linkage
Product of flux and number of turns
The total amount of magnetic field lines passing through a number if loops
Wb
-
Why are transformers not 100 percent efficient
Flux leakage - magnetic field does not follow the intended oath fully
Heating in iron core and copper wires
-
Why does speed not change in centripetal motion
Force acts inward
Velocity is tangential to object
Work is not done so no change in ke so no change in speed
-
Radius of curvature
R = mv/Bq
-
In a transformer that is not completely efficient the output voltage …. The current ….
The output voltage remains the same as if it was completely efficient current is altered
-
Graph of emf and magnetic flux
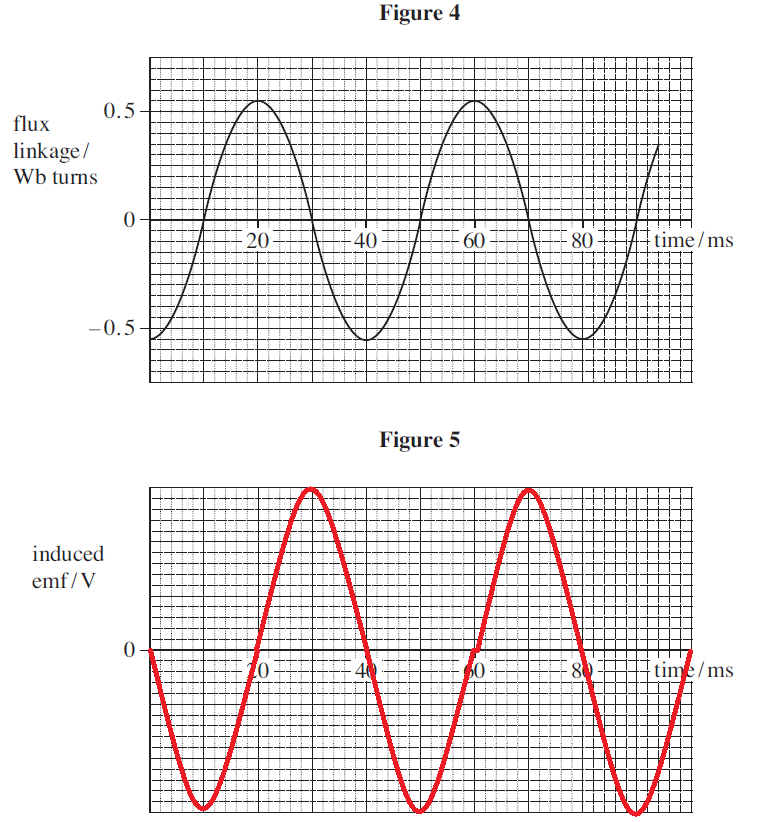
-
To produce a magnetic field
Motion of charged particles or permanent magnet made of a magnetic material like iron
-
Magnetic field into out of paper symbol
X into
O out of
-
Solenoid
Long coil of wire with a large number of loops
-
Magnetic field increases
The closer to the source of the field
-
Magnetic flux density
T the measure of the strength of the magnetic field , B
-
Flemmings left hand rule for neg charge
Use right hand
-
The movement of a charged particle in a amgnetic field
makes it experience a force
-
Electromag induction
Induces a flow of current using relative motion between conductor and magnetic field
-
Under what conditions increases emf induced
increase speed of conductors movement relative to the magnet And vice versa
Increase the loops in the conductive wire
-
A solenoid large enough
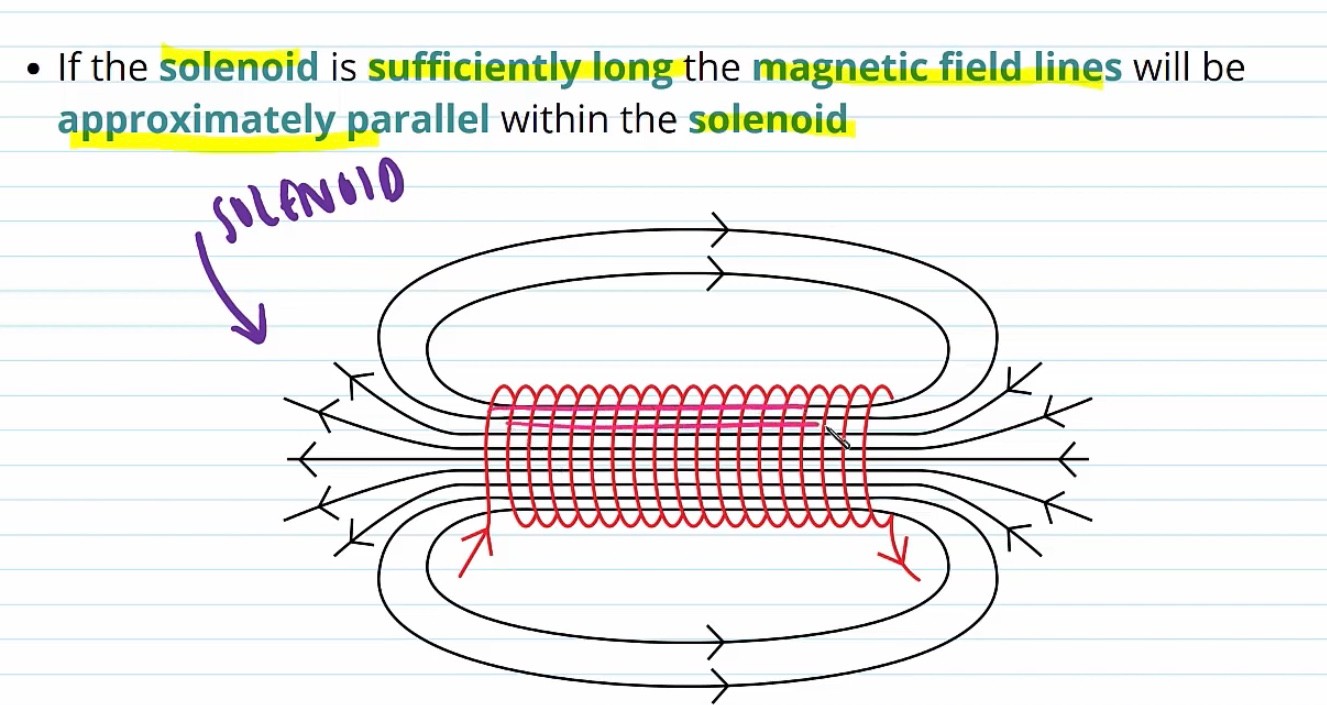
-
Electron diffraction tube

Anode supplied with a high voltage - thermionic emission
-
When an emf is induced
There is relative movement between the magnetic field and the conductor
Corresponds to the conductor cutting through the lines of flux so there is a change in magnetic flux linkage through the conductor - farradays law
-
Magnetic flux linkage can be varied by
Varying the area of the conductor
-
One control setting in the oscilloscope that reduces unvertsinty in the time constant
Reduce time base setting as uncertainty due to the size of time base setting so will stretch it out more
-
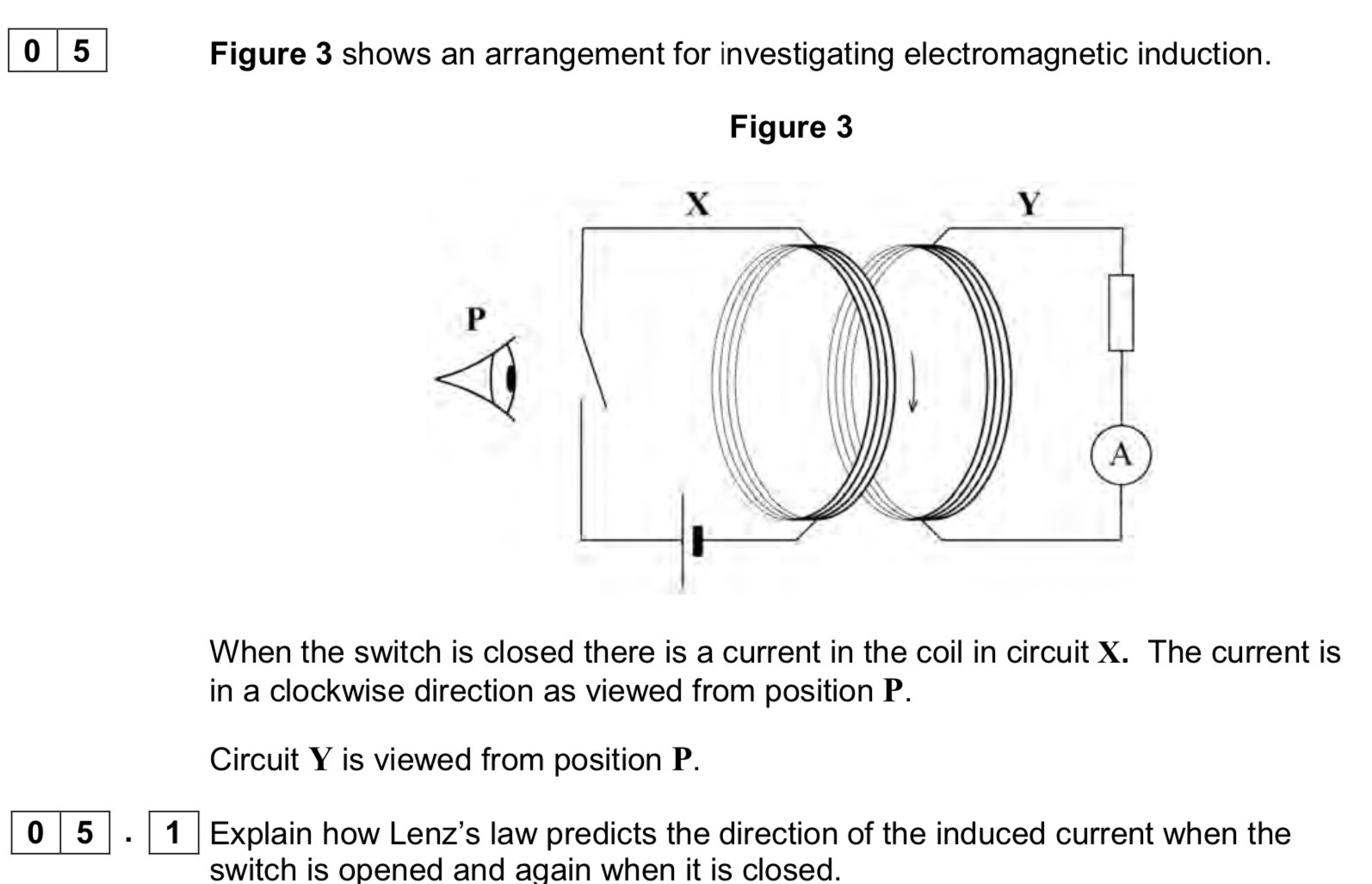
Induced current as such to appose the change inducing it , lenz’s law
Switch on current increases flux in y
Current in opposite direction to oppose the flux
Switch off, flux in y due to x decreases so current travels in the opposite direction to previous to oppose the change
-
what do gravitational field lines represent
The direction of force acting on a mass places there

