-
sound waves
are produced by the vibrations of matter
-
Sound
can be produced by vibrating strings (such as in a piano, a violin, or a guitar), the oscillating diaphragm of a stereo speaker, or the vibration of your vocal cords
-
compressions
Regions of the medium having high density and pressure
-
rarefactions
regions of low density and pressure
-
sound
is a pressure wave and a longitudinal wave
-
speed of sound
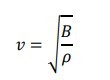
-
sound travels faster in a ______ than one with higher density
fluid with lower density
-
For an ideal gas, the ratio_______ depends on the gas temperature, so the speed of sound depends on temperature
B/ρ
-
At other air temperatures TC (measured in Celsius), the speed of sound is given by
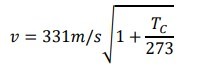
-
Intensity I
is defined as the average power Pav per unit area A perpendicular to the direction of propagation:
-
Formula of Intensity is
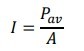
-
the intensity of a point source decreases as the distance r from the source increases
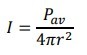
-
The intensity range of human hearing spans ____ orders of magnitude
12
-
sound level in terms of base 10 logarithms is
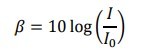
-
Sound level is measured in decibels (dB), although the quantity defined is actually dimensionless. The threshold of human hearing is ____ dB and sound is painful at _____ dB.
0 , 120
-
Sound waves are divided into three categories:
: (1) Audible waves lie within the range of sensitivity of the human ear (from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz)
(2) Infrasonic waves have frequencies below the audible range (f < 20 Hz)
(3) Ultrasonic waves have frequencies above the audible range (f > 20,000 Hz)
-
Doppler Effect
indicates the change in frequency due to relative motion between the wave source and the observer
-
For sound waves, the observed frequency is (formula)
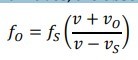
-
When the observer moves toward the source
a positive (+) speed is substituted for vO
-
When the observer moves away from the source
a negative (–) speed is substituted for vO
-
When the source moves toward the observer
a positive (+) speed is substituted for vS
-
When the source moves away from the observer
a negative (–) speed is substituted for vS
-
Superposition Principle, superimposing
When two (or more) waves travel in the same medium, the resulting wave function is found by __________ (adding) the individual wave functions.
-
in Superposition Principle, The resultant wave is the __________ of the individual waves
superposition
-
Interference, interfere
When two waves exist in the same medium, they don’t collide; they _______ with each other
-
When the resulting pulse’s height is greater than that of both original waves, the result is __________
constructive interference
-
When the resulting pulse’s height is smaller than that of each original wave, the result is _________
destructive interference
-
. If the two pulses have the same amplitude but one is inverted with respect to the other, the resulting wave profile is __________
momentarily flat
-
When you shout into a gorge or at a large wall, you hear your voice echo because when a wave travels to the end of a medium—in this case, the air—the wave is
reflected back into the medium
-
resonance
If a periodic force is applied to a system, the amplitude of the resulting motion is greatest when the frequency of the applied force is equal to one of the natural frequencies of the system
-
The profile of a wave reflected from a fixed end is
inverted
-
The profile of a wave reflected from a free end is
upright
-
resonance frequencies
Because an oscillating system exhibits a large amplitude when driven at any of its natural frequencies, these frequencies are often referred to as
-
beating
_____ is the periodic variation in intensity at a given point due to the superposition of two waves having slightly different frequencies
-
beat frequency (formula)
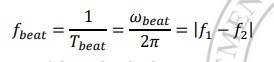
-
Light and other forms of radiation are _________ in the form of waves that propagate according to the laws of electricity and magnetism
electromagnetic disturbances
-
The behavior of these _______ has clear similarities with mechanical waves. However, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium; they can propagate through empty space
electromagnetic waves
-
frequency and wavelength of any electromagnetic wave in a vacuum are given by
c = fλ
-
electromagnetic spectrum
refers to the continuum of electromagnetic waves arranged in order by frequency (and wavelength)
-
electromagnetic waves do not need a medium, the Doppler effect for EM waves is simply a
relative-velocity phenomenon
-
If the source emits EM waves that have a frequency fS, the observed frequency fO is given by
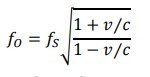
-
When a light source moves away from an observer, the wavelength is longer and the light looks redder
redshift
-
When a light source moves toward the observer, the wavelength is shorter and the light looks bluer
a blueshift
-
Radar and sonar
____ and ______ are sensor systems that use the propagation of waves to detect and localize targets
-
echo
_____ is the reflection of sound waves off of some distant object
-
echolocation
When bats, dolphins and other animals use sonar naturally, usually to find prey
-
Sound Navigation and Ranging
is a system for the detection of objects and for measuring the depth of water. It works by emitting sound pulses and measuring how long it takes the echoes to return.
-
Radio Detection and Ranging
is a system for calculating the position, distance or other important characteristic of a distant object
-
Detection (or navigation)
refers to locating objects
-
in ______ a transmitter with an oscillator is used to generate radio waves, and a waveguide links the transmitter to the antenna
radar
-
in _______ a electrical energy is supplied directly to a hydrophone array which converts it to sound waves
a sonar
-
_____ the received signals normally go through a low noise amplifier before being down-converted to an intermediate frequency
radar
-
the received signals for ______ go through a pre-amplifier to shape the signal (front-end conditioning) prior to being sent to the signal processing unit
a sonar
-
Three distinct types of radar systems are
[1] the static early warning area surveillance platform, [2] the targeting and fire control platform, and [3] the battlefield reconnaissance detection and search platform
-
Active radar
a type of radar at which a radio wave is emitted from an antenna and reflects off objects the wave encounters
-
passive radar
system relies on a signal transmitted from a different location. This type of radar system is called bistatic.
-
Active sonar
is emitting pulses of sound and listening to echoes.
-
Passive sonar
is essentially listening for the sound or “noise” made by marine objects (such as submarines or ships) and marine animals (such as whales)
-
Radar and sonar are capable of distance measurement through the timing method
Range R = vt/2
-
Radar and sonar are also capable of measuring the speed of the target in the following ways:
[1] Measuring distance and recording where the target was located a set time ago;
[2] Analyzing the Doppler signal where the target’s motion relative to the transmitter and receiver produces a change in frequency.
-
Passive sonar systems
able to determine the range and bearing of an acoustic target without giving away the location of its source

