-
Basic atomic propositions notation and meaning
p, q, r... things that are either true or false
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from ¬φ∘
∘φ
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from ∘¬φ
φ∘
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from ψ∧φ∘
ψ, φ∘
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from ∘φ∧ψ
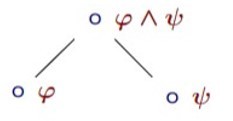
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from φ∨ψ∘
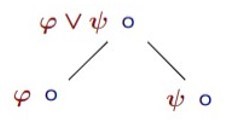
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from ∘φ∨ψ
∘ψ, φ
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from φ→ψ∘
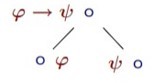
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from ∘φ→ψ
φ∘ψ
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from φ↔ψ∘
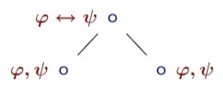
-
Propositional tableau: what follows from ∘φ↔ψ
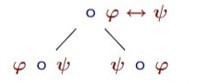
-
For an inference placed on the right side of a tableau to be valid, all branches must be _______
Closed
-
Each node of a tableau tree is called a ________
Sequent
-
A branch is closed if ___________________________
There's a formula that appears on both the left and right sides
-
is entails (⊨) a part of propositional logic?
No
-
Modus ponens definition
The reasoning that when the first part of an implication p->q holds (p), then the second must hold (q)
-
Refutation rule
Assume phi, and if after further steps you have a contradiction ⊥, phi cannot be true, therefore not phi is true.
-
Complete system definition
A set of rules that can be used to prove everything that is true within a certain type of logic
-
Three rules that make up a complete system for propositional logic
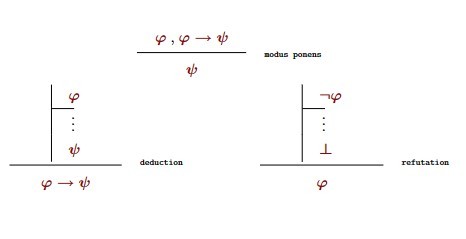
-
Modus ponens can also be referred to as __________
Elimination of implication
-
The deduction rule can also be referred to as ___________
Introduction of implication
-
The refutation rule can also be referred to as
Introduction/elimination of negation
-
Notes: conjunction rules for propositional natural deduction
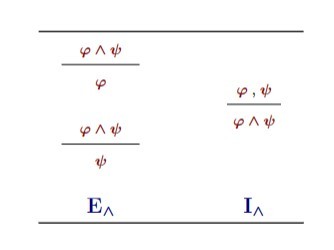
-
Notes: disjunction rules for propositional natural deduction
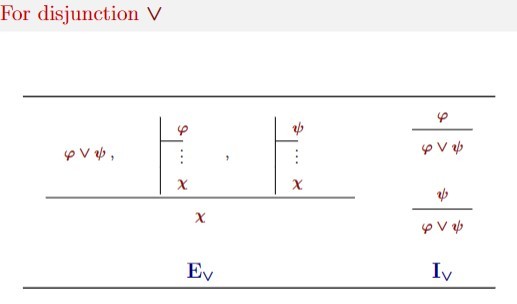
-
Syllogism definition
An inference that has the following characteristics: two premises and one conclusion, only of one of the following forms: (All A are B), (Some A are B), (All A are not B (no A is B)), (Some A are not B (not all A are B)).
-
In syllogistic reasoning, A and B are _________, which are similar to the role of classes in object oriented programming.
Predicates
-
How many predicates does a syllogism involve?
3
-
What does {x | φ(x)} mean?
“the set of things x that have the property described by φ”
-
P\S meaning
All objects in P that are not in S
-
Complement of P notation
P̄
-
A stroked out region in a syllogistic diagram means that that region is _____
empty, no objects belong to that region
-
predicate logic symbols for constants
a, b, c
-
predicate logic symbols for variables
x, y, z
-
predicate logic symbols for predicates
A, B, C, .... P, Q, R
-
In predicate logic, a term is a ________ or a _________
variable, constant
-
A formula is closed if ________
Every occurence of a variable in the formula is bounded.
-
Substitution of a variable inside a formula only affects the ____ occurrences of the variable
free
-
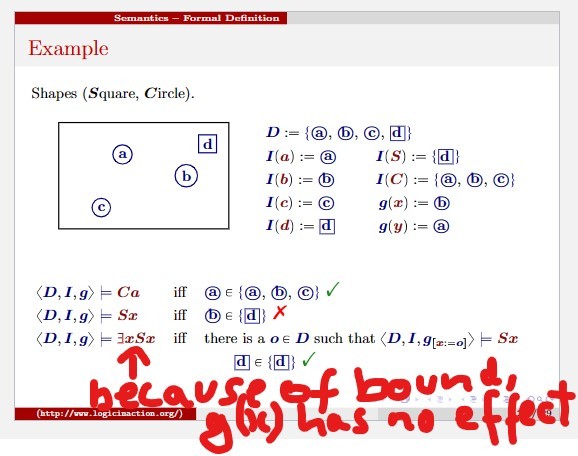
Model notation
M = <D, I, g>
-
What is the D in model notation
domain
-
What is the I in model notation
The interpretation function, basically like variable assignment but for constants and predicates. It assigns an object or a relation in the domain to each symbol for constants and predicates, respectively.
-
What is the g in model notation
variable assignment, basically like the interpretation function but for variables
-
Notes models
-
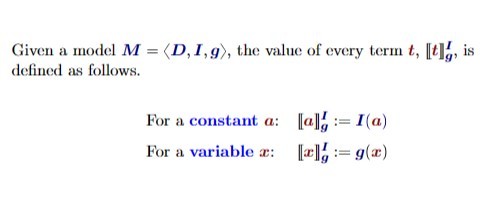
More notes models
-
Predicate logic is an extension of propositional logic with ________, _________ propositions and ____________
structured, basic quantification
-
Predicate tableau: what follows from ∃xφ(x)∘

-
Predicate tableau: what follows from ∘∃xφ(x)
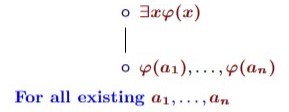
-
Predicate tableau: what follows from ∀xφ(x)∘

-
Predicate tableau: what follows from ∘∀xφ(x)
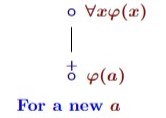
-
What must be done every time a new constant is introduced to a predicate tableau?
Reactivate all of the previous universal statements
-
Elimination of universal quantifier predicate natural deduction

-
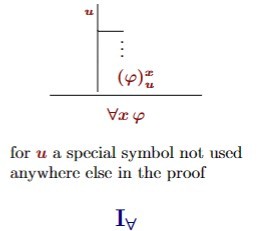
Introduction of universal quantifier predicate natural deduction
-
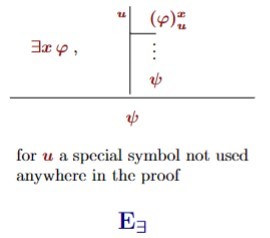
Elimination of existential quantifier predicate natural deduction
-
Introduction of existential quantifier predicate natural deduction

-
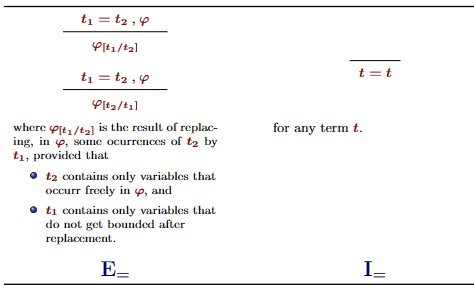
Elimination/introduction of identity symbol predicate natural deduction
-
PDL composition of relations notation, for binary predicates Ra and Rb
Ra ∘ Rb
-
Composition of two relations Ra and Rb definition
Say that there are three states, x, y and z. if x is related to y via Ra and y is related to z via Rb, then x is related to z via Ra ∘ Rb
-
PDL union of two relations notation, for binary predicates Ra and Rb
Ra ∪ Rb
-
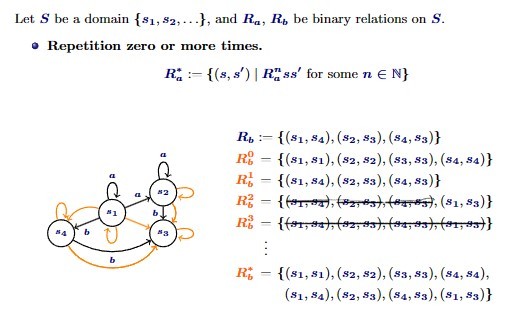
PDL repetition of a relation notation
-
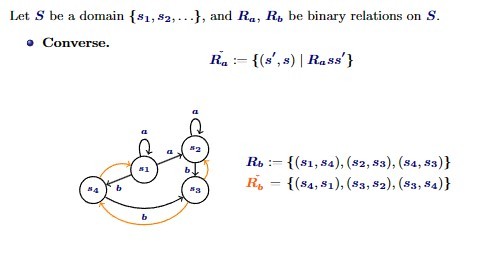
PDL converse of a relation notation
-
Converse of a relation definition
Undoing an action, essentially the reversed arrow of a relation
-
More notation pdl
-
More notation pdl

-
Square brackets vs spiky brackets PDL
[ ] = for ALL possible executions. <> = for any (one or more) execution
-
PDL: what does LTS stand for
Labelled transition system
-
An LTS with a designated (root) state is called a ______ LTS or a _______
pointed, process graph
-
3 components of LTS
S (set of states), V (valuation function, which atomic propositions are true and/or false in each state), A binary relation Rₐ for every basic action a
-
If x = y .〈a〉.k is prefix, then we will use sˣ to denote the state __
k
-
More notes PDL
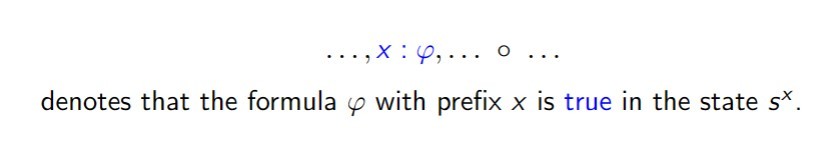
-
In hoare logic, if the execution never terminates because of an infinite while loop, the triple is considered __________
correct/partially correct
-
When do auxiliary variables change their value?
Never

