-
drug and receptor
the interaction between what two things is ultimately responsible for pharmaceutical effect- pharmacodynamics ?
-
receptor
-protein-molecule that recognizes and responds to endogenous chemical signals
-
low
The driving force or drug-receptor complex is at what energy state?
-
Kd
-measures the affinity of a receptor to a drug
-represents concentration of the drug that gives 50% drug-receptor complex
-
larger concentration of drug-receptor complex; greater affinity for the drug
A smaller Kd tells us what about the receptor?
-
Ionic (electrostatic) interaction
-when a full charge interacts with another full charge
-
histamine, lysine, arginine
Basic groups involves with ionic interactions? (gives us a positive charge)
-
aspartic acid, glutamine
Acidic groups that give us a negative charge?
-
ionic
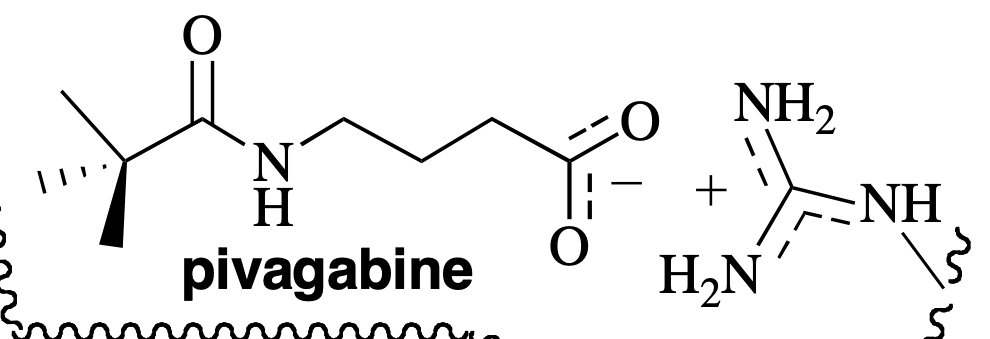
What type of interaction is occuring?
-
ion-dipole
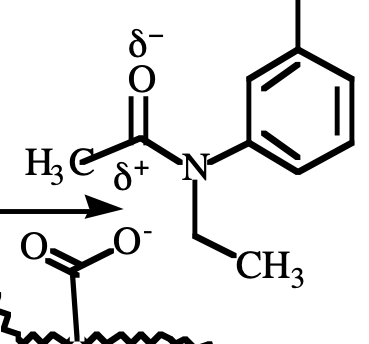
What type of reaction is this?
-
dipole-dipole
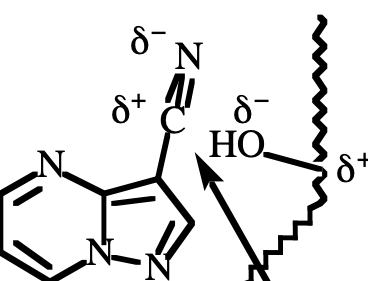
What type of reaction is this?
-
hydrogen bonding
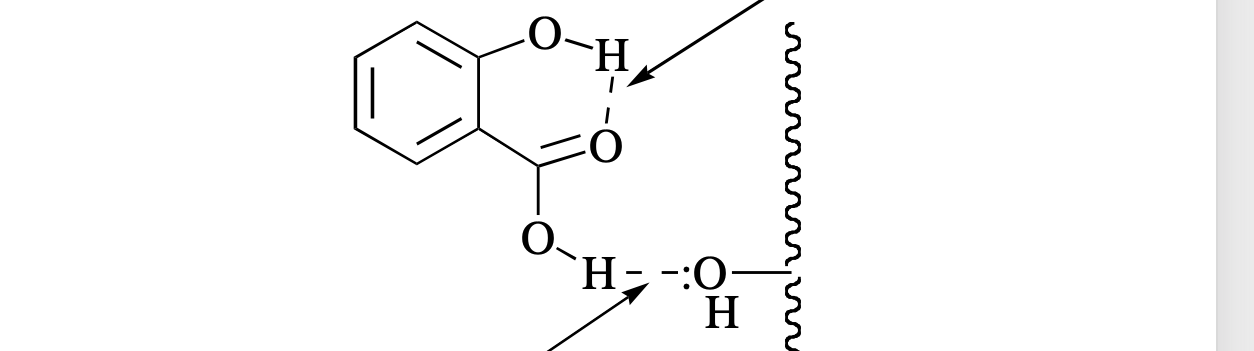
What type of reaction is this?
-
intermolecular
hydrogen bonding that occurs between two molecules
-
intramolecular
hydrogen bonding that occurs within the same molecule
-
decreases free energy; stabilizing
Increase in entropy of H2O molecules _______. Leads to _________ the complex
-
pi stacking
What type of hydrophobic interaction is this?
-
Van der Waals forces
-as molecules approach, temporary dipoles in one atom induce opposite dipoles in another; therefore, producing an intermolecular attraction
-
full agonist
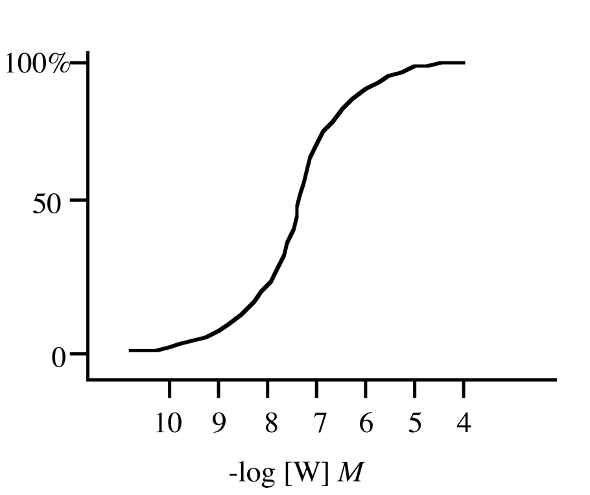
What is this a representation of ?
-
partial agonist
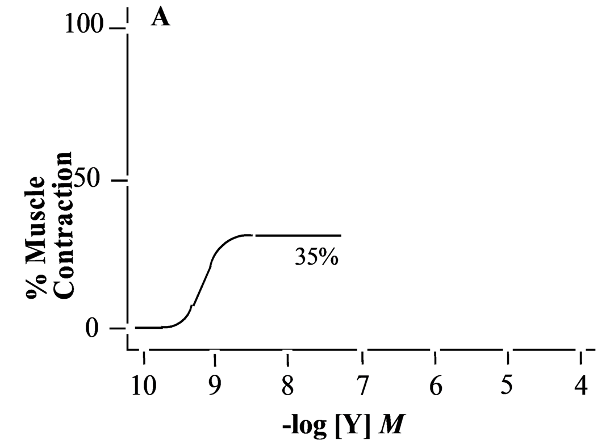
What is this a representation of?
-
agonist
To effect a certain response of a receptor, design a(n) ____
-
antagonist
To block a particular response of a natural ligand of a receptor, design a(n)
-
inverse agonist
To produce the opposite affect of the natural ligand, design a(n)
-
agonist
Which shows structural similarity to natural ligand; agonist or antagonist?
-
agonist
What type of drug is this?
-
antagonist
What type of drug is this?
-
enantiomer
What type of drug is this?
-
equilibrium; basal activity
R and R* are in _______ which defines the _________ of the receptor.
-
Full agonist
______ bind only to R*- lead to an increase in basal activity
-
Partial agonist
________ bind preferentially to R* (some still bind to R)
-
Full inverse agonist
__________ bind only to R (decrease in basal activity)
-
Antagonist
__________ have equal affinities for both R & R* (no effect on basal activity)
-
eutomer
more potent enantiomer
-
distomer
less potent enantiomer
-
eudismic ratio
the ratio of eutomer/distomer potencies of enantiomers
-
d
Distomers are usually ______
a. more potent
b. less potent
c. equally efficacious
d. impure
-
chiral
What is the typical stereochemistry of drugs? Chiral or racemic ?
-
3
How many binding sites must the receptor have in order for the drug to bind?

