-
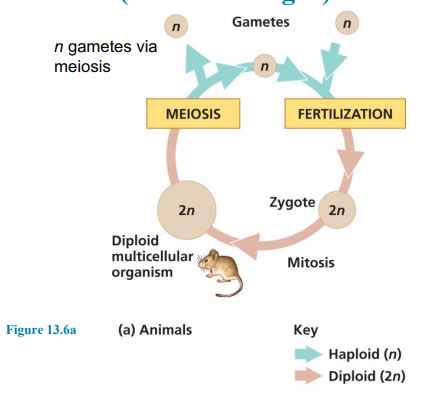
animals (and some algae)
-

fungi (and some animals)
-
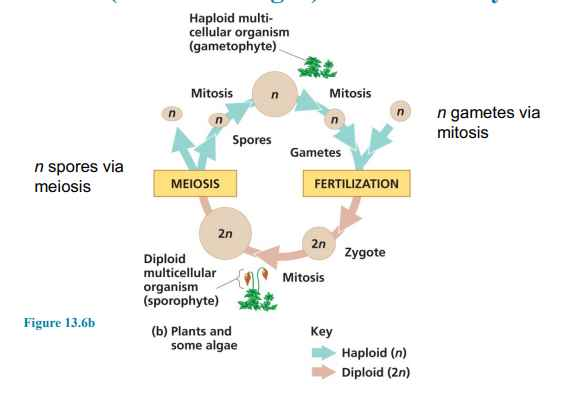
plants (and some algae)
-
land plants shared traits with charophytes
Rings of cellulose-synthesizing proteins (see figure), Structure of flagellated sperm, Formation of a phragmoplast
-
gametophyte
haploid and produces haploid gametes by mitosis
-
sporophyte
diploid, fusion of gametes and produces haploid spores by meiosis in sporangia
-

alteration of generations
-
gametangia
origin of gamete production; are haploid
-
female gametangia
archegonia
-
male gametangia
antheridia
-
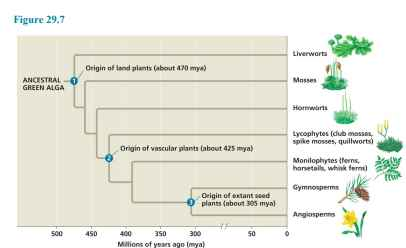
liverworts, mosses, and hornworts
non-vascular plants
-
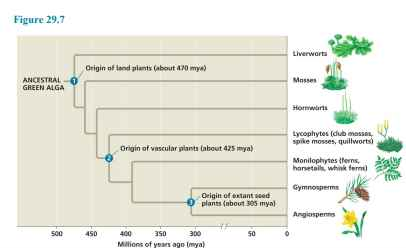
lycophytes, monilophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms
vascular plants
-
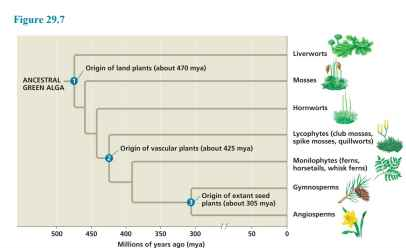
lycophytes and monilophytes
seedless vascular plants
-
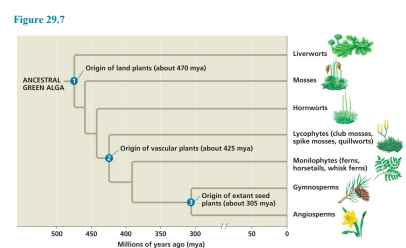
gymnosperms and angiosperms
seed plants
-
non- vascular plants (bryophyta)
gametophyte dominant
-
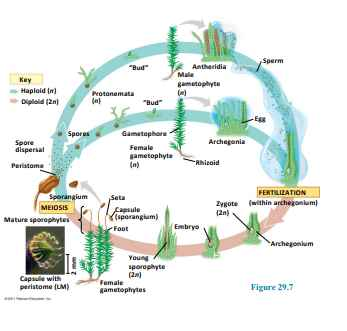
moss life cycle
-
bryophyte gametophytes
mature gametophytes produce flagellated sperm in antheridia and an egg in each archegonium
-
bryophyte sporophytes
grow out of archegonia; consists of a foot, seta (stalk), and sporangium (capsule) which discharges spores through a peristome
-
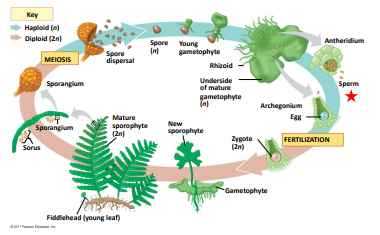
fern life cycle (seedless vascular plants)
-
sporophylls
modified leaves with sporangia
-
sori
clusters of sporangia on the underside of sporophylls
-
strobili
cone-like structures formed from groups of sporophylls
-
homosporous
produces one type of spore that develops into a bisexual gametophyte
-
heterosporous
produce megaspores (female gametophytes) and microspores (male gametophytes)
-
homosporous spore production
sporangium on sporophyll-> single type of spore-> typically a bisexual gametophyte-> eggs+sperm
-
heterosporous spore production
megasporangium on megasporophyll-> megaspores -> male gametophyte -> eggs (in archegonia)
microsporangium in microsporophyll -> microspore -> male gametophyte -> sperm (in antheridia)
-
the two clades of seedless vascular plants
phylum lycophyta and phylum monilophyta
-
phylum lycophyta
small herbaceous plants; many are epiphytes; microphylls
-
phylum monilophyta
ferms, horsetails, and whisk ferns
-
traits of seed plants
reduced gametophytes, heterospory, ovules, pollen
-
seed plant gametophytes
microscopic; remain withing the sporangia of parental sporophyte, and depend on sporophyte for nutrition
-
female gametophyte (seed plants)
develops within an ovule
-
male gametophyte (seed plants)
develops within a pollen grain
-
ovule
consist of a mega sporangium, megaspore and one or more integuments
-

unfertilized ovule
-
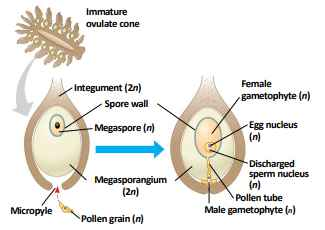
fertilized ovule
-
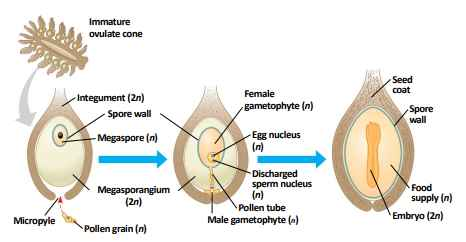
gymnosperm seed
-
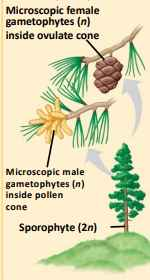
gymnosperm
-
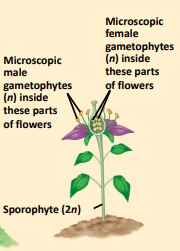
angiosperm
-
gymnosperm extant phyla
cycadophyta (cycads), ginkgophyta, gnetophyta, coniferophyta
-
phylum cycadophyta
large cones and palmlike leaves; flagellated sperm
-
phylum ginkgophyta
single living species; flagellated sperm; high tolerance to air pollution
-
phylum gnetophyta
comprises three genera: gnetum, ephedra and welwitschia
-
phylum coniferophyta
largest gymnosperm phyla, mostly evergreens
-
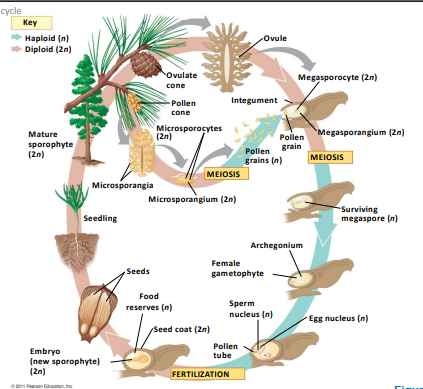
pine life cycle

