-
what is cranial?
in reference to the head
-
what is the anatomical position?
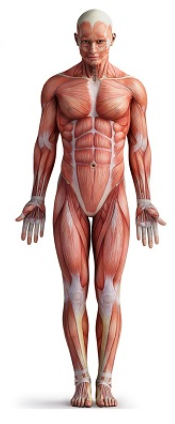
universal reference with the hands and feet both forward
-
what is superior/inferior?
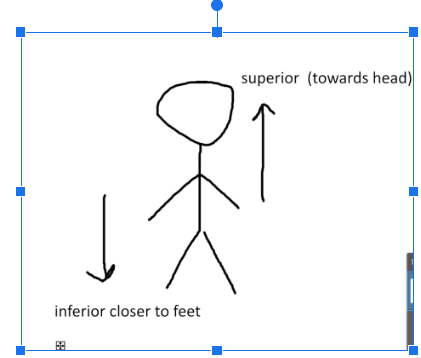
-
what is anterior/posterior?
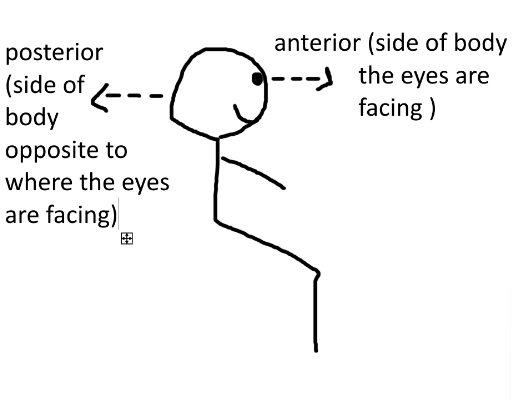
-
what is ventral/dorsal?
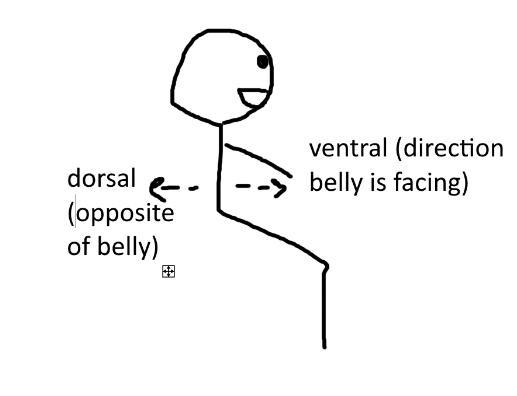
-
what is medial/lateral?
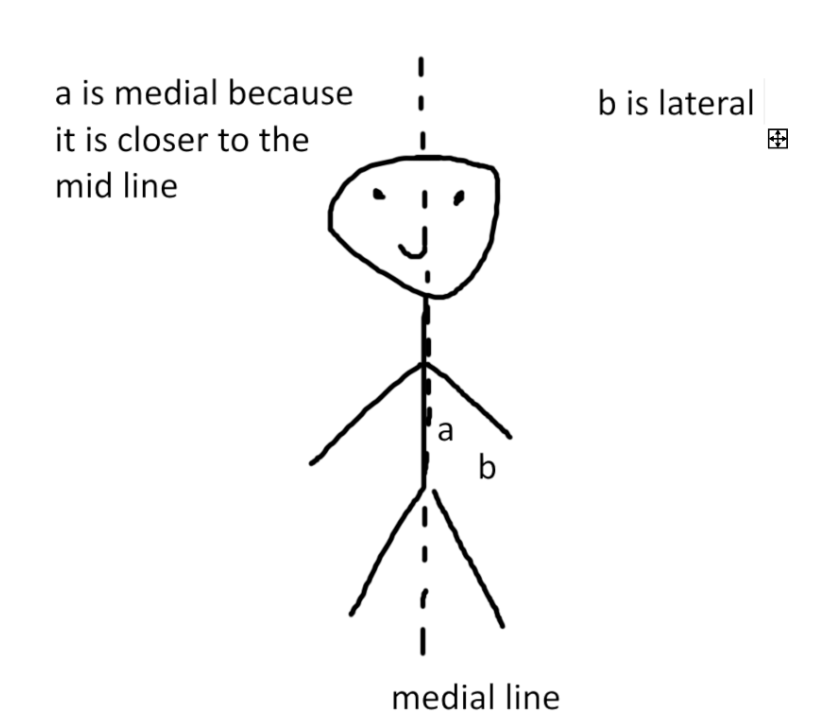
-
what is cephalad/caudal?
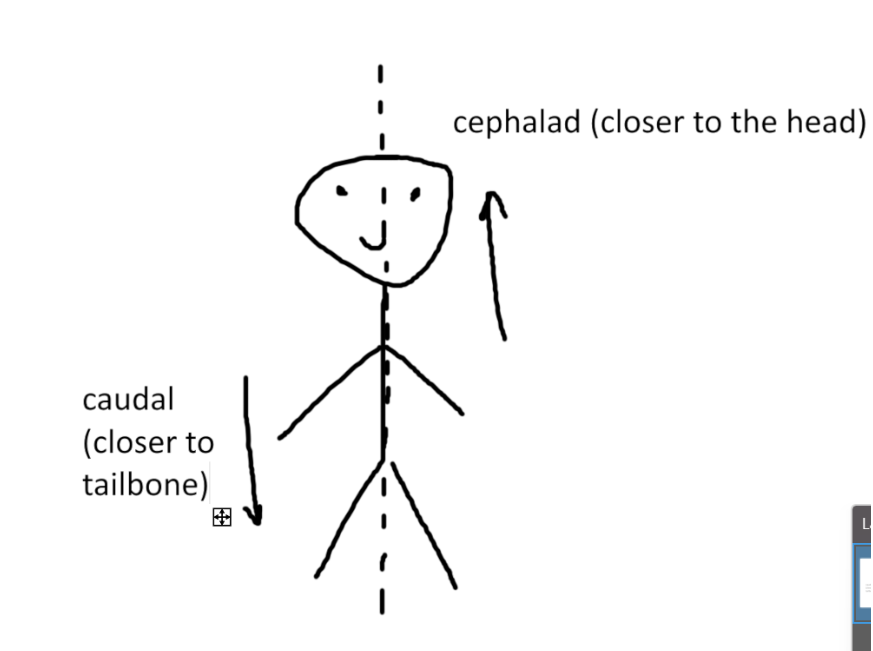
-
what is superficial/deep?
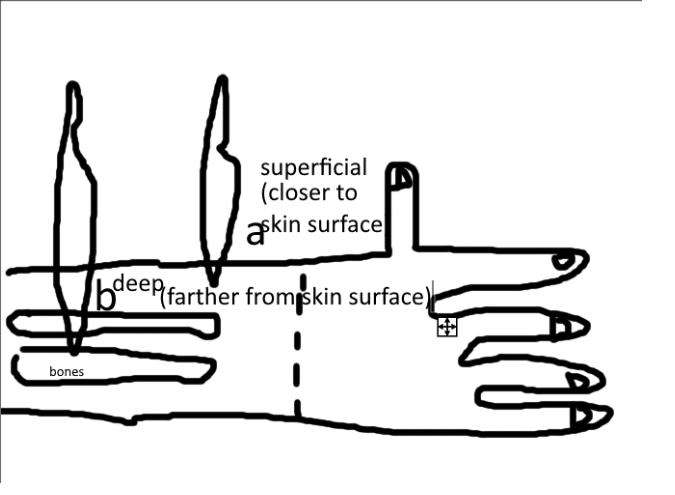
-
what is proximal/distal?
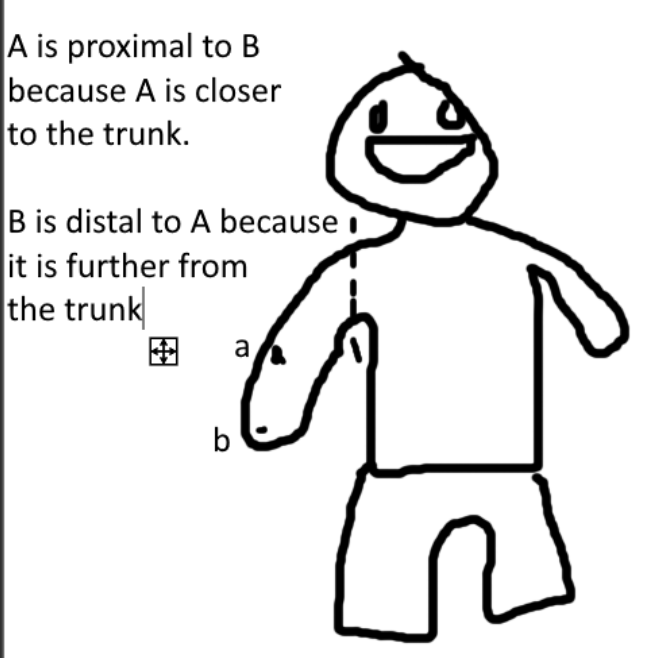
-
what is a transverse sectional plane?
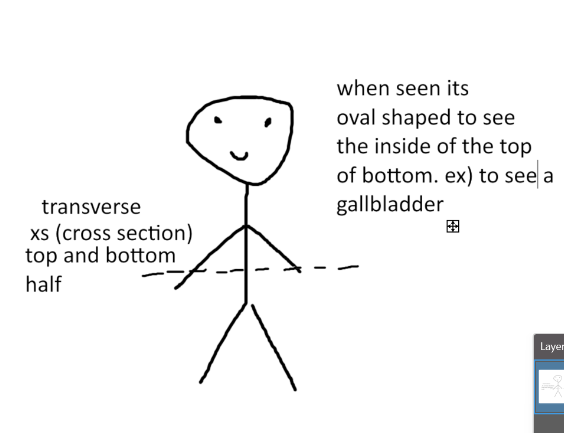
-
what is a sagittal sectional plane?
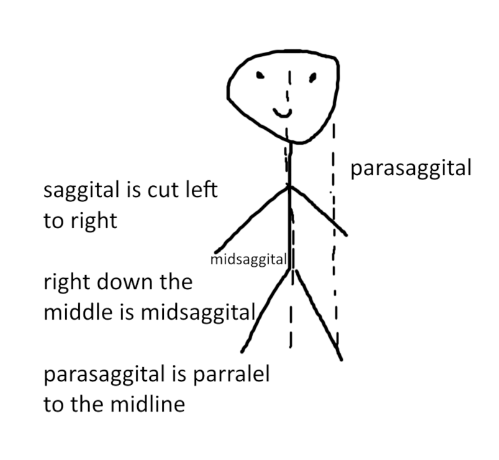
-
what is a frontal sectional plane?
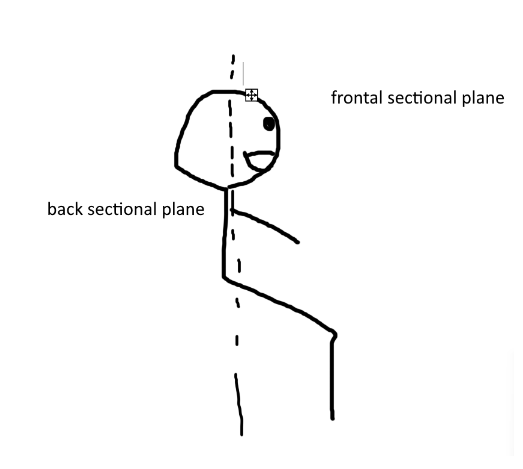
-
what cavities are in the dorsal body cavity?
-cranial cavity
-vertebral cavity
-
what does the cranial cavity contain?
-brain
-
what is in the vertebral cavity?
-spinal cord
-
what is in the ventral body cavity?
-thoracic cavity
-abdominopelvic cavity
-
what is in the thoracic cavity?
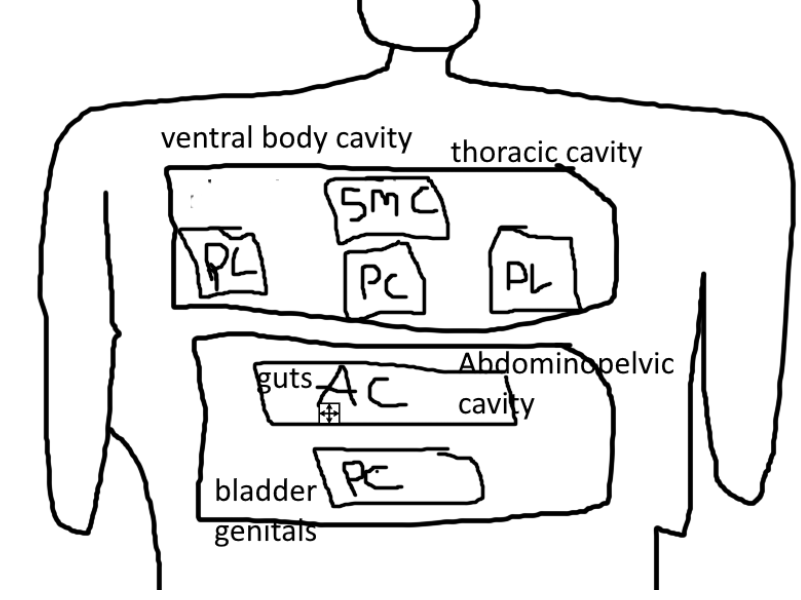
-pleural cavity
-superior mediastinal cavity
-pericardial cavity
-
what is in the Pleural Cavity?
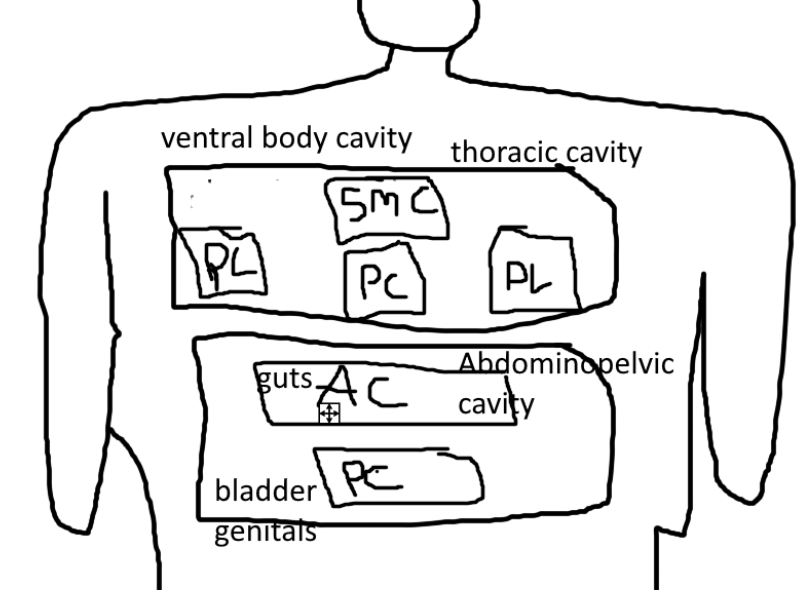
-lungs
-
what is in the Superior Mediastinal Cavity?
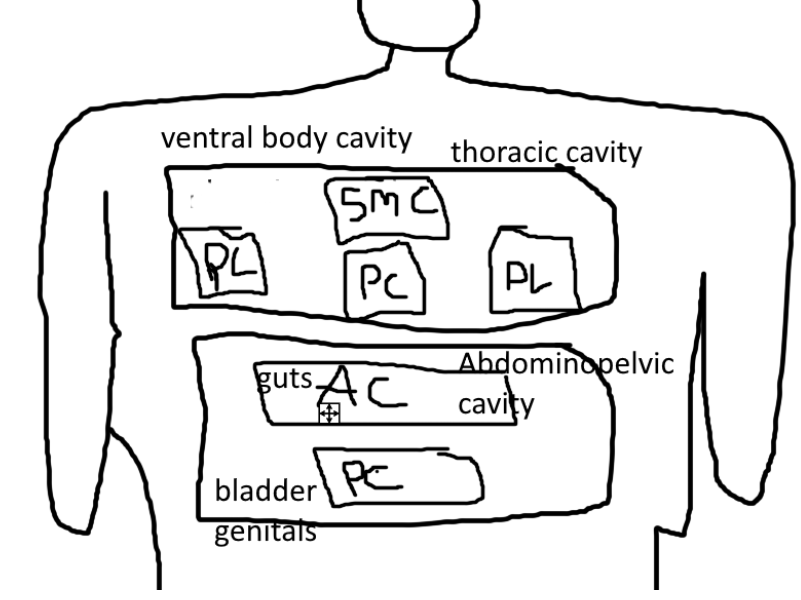
-esophagus
-blood vessels
-
what is in the Pericardial Cavity?
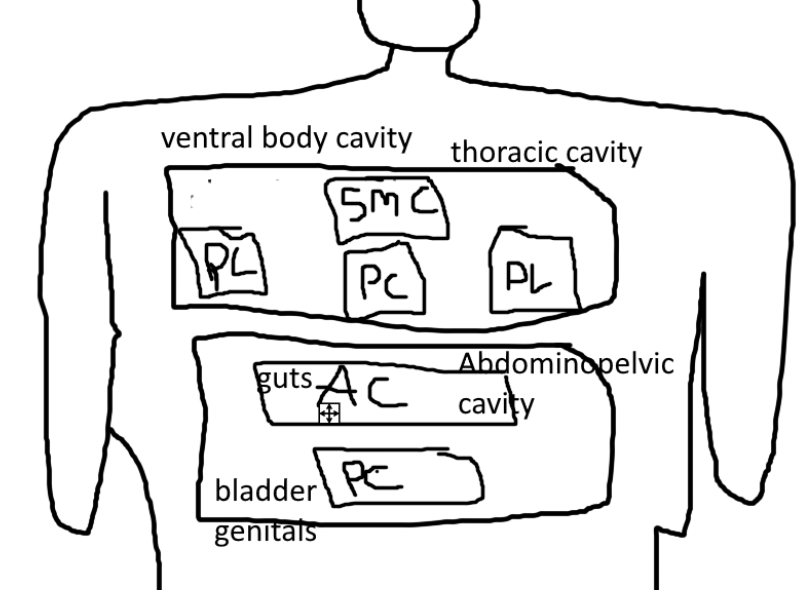
-heart
-
what is in the Abdominopelvic Cavity?
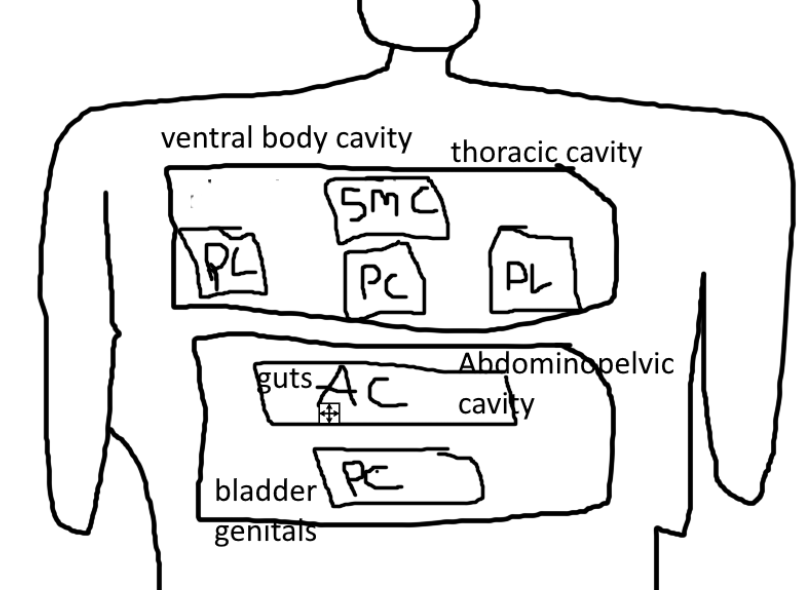
-abdominal cavity
-pelvic cavity
-
what is in the abdominal cavity?
the LUQ?
the RUQ?
the RLQ?
THE LLQ?
-guts
-stomach
-cecum
-small intestine
-
whats in the pelvic cavity?
-bladder
-genitals
-
which cavity is the nervous system in?
-dorsal body cavity
-
which cavity is the integumentary system in?
-ventral and dorsal
-
which cavity is the skeletal system in?
-ventral and dorsal
-
which cavity is the muscular system in?
-ventral and dorsal
-
which cavity is the brain and nervous system in?
-dorsal
-
which cavity is the endocrine system in?
-cranial cavity
-pelvic cavity
-
identify the location of the four abdominal quadrants
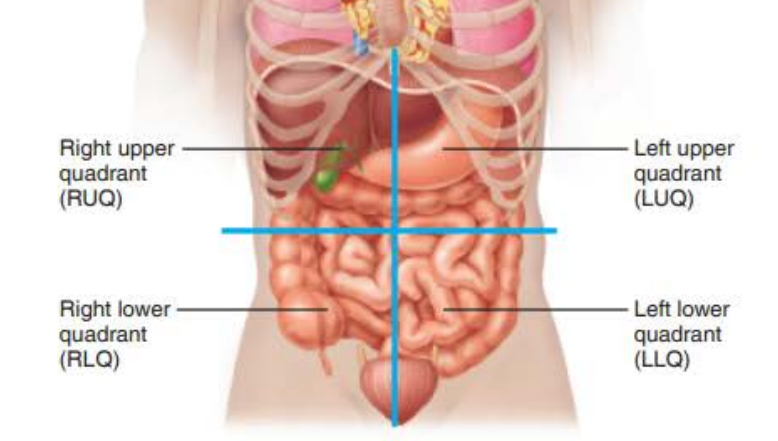
RUQ
LUQ
RLQ
LLQ
-
state the medical significance of the abdominal quadrant system
-the abdominopelvic cavity is large and houses several organs
-
name the stages of the cell cycle
-prophase
-metaphase
-anaphase
-telophase
-
what happens during prophase?
chromosomes are visibly condensed, nucleolus disappears, centrioles separate
-
what happens during metaphase?
chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
-
what happens during anaphase?
spindle fibers split the sister chromatids apart towards opposite poles of the cell
-
what happens during telophase?
nuclear envelope begins to reform around the chromosomes at opposite poles, spindle fibers disappear
-
distinguish between mitosis and cytokinesis
-mitosis is the division of the nucleus
-cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm
-
define meiosis
-a single cell divides twice to produce four cells with half the amount of genetic information
-
what is a chromatin?
-DNA and protein
-the material that composes the chromosomes of organisms
-
what is a centromere?
region of the dna where chromatids attach
-
what is the equator?
-imaginary line located centrally within a cell
-chromosomes align on the equator during metaphase
-
what is the cleavage furrow?
indentation that appears due to the pinching of the cytoplasm and membrane during the late stages of cell division
-
what is a chromatid?
one of the two strands that compose a chromosome
-
what is a kinetochore?
a protein complex that gathers on the centromere for the spindle to attach to
-
what is an aster?
star shaped microtubule structure that positions that spindle
-
what is a chromosome? how many do humans have?
-thread-like structure that contains the genetic material of an organism
-46 arranged in 23 pairs
-
what are spindle?
-microtubules
-splits chromosomes during mitosis
-
what is the centriole pair?
-microtubules
-produces spindle fibers


