Lab 3, histology, facial muscles, skull
Histology of bone and cartilage, then also covers facial muscles, the skull, and the cervical vertebrae
-
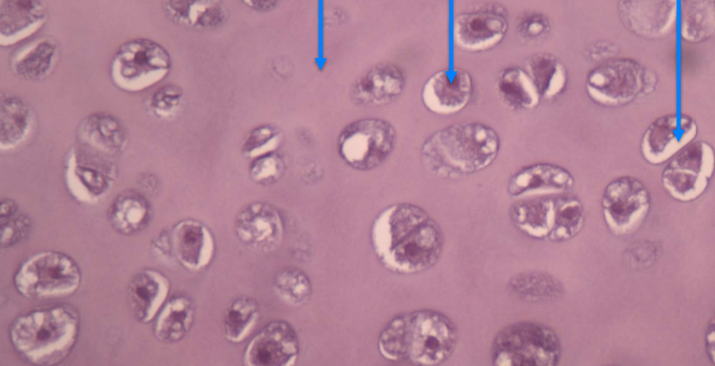
What tissue is this? What are the arrows pointing to (in order)?
- its hyaline cartilage
Arrows: the Ground substance, chondrocyte, and lacuna
-
What are the components of the extracellular matrix in hyaline cartilage?
Ground substance: hylaronic acid + chondroitin sulphate + water
fibres: collagen
-
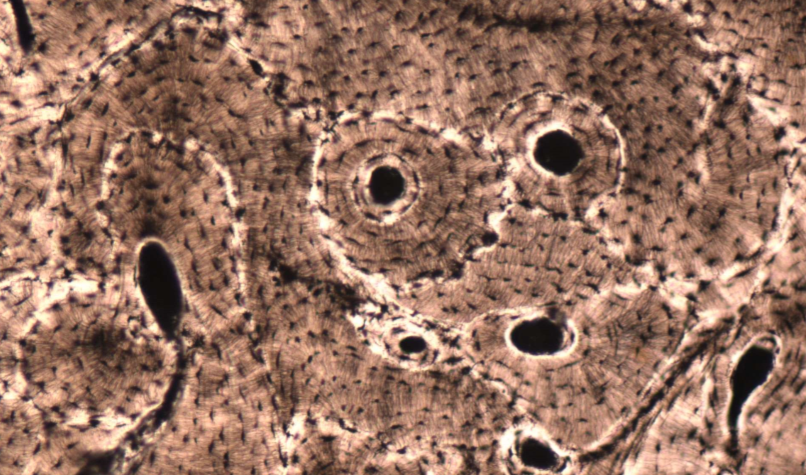
What type of tissue is this? Whats the components of its extracellular matrix?
- Compact bone
Ground substance: hydroxyapetite (calcium phosphate salts) + water
Fibres: collagen
-
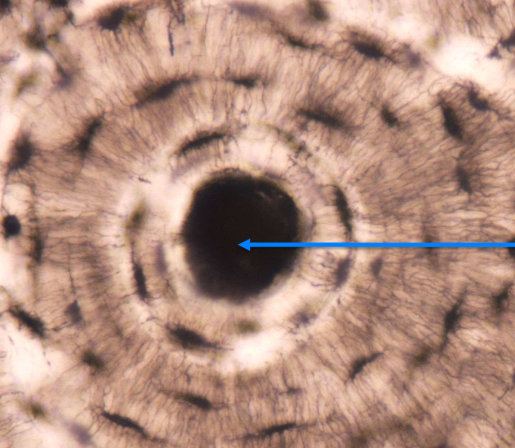
What is this area of this tissue?
The central/osteonic/haversian canal
-
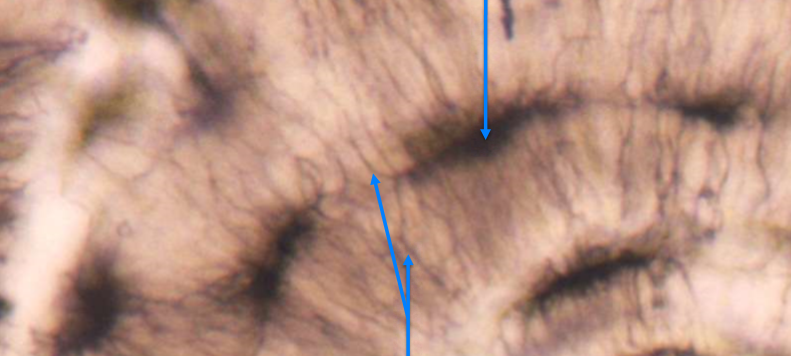
Top is osteocyte in lacuna
bottom is the canaliculi
-
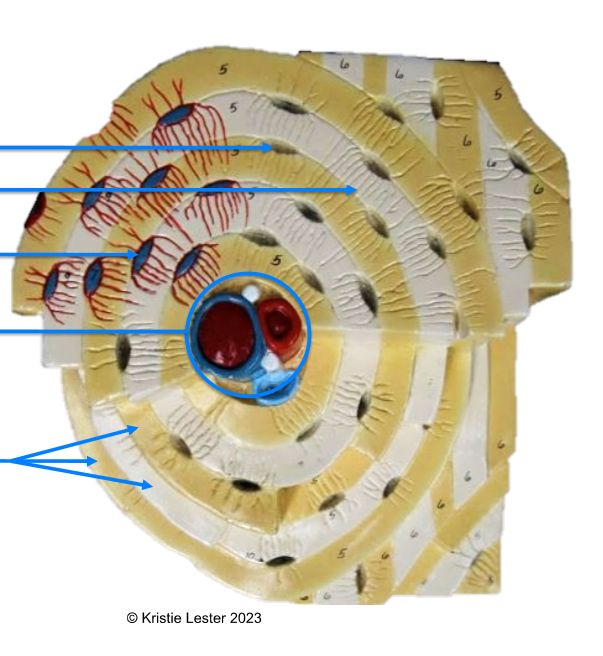
Lacuna, canaculi, Osteocyte, central/osteonic canal, lamellae
-
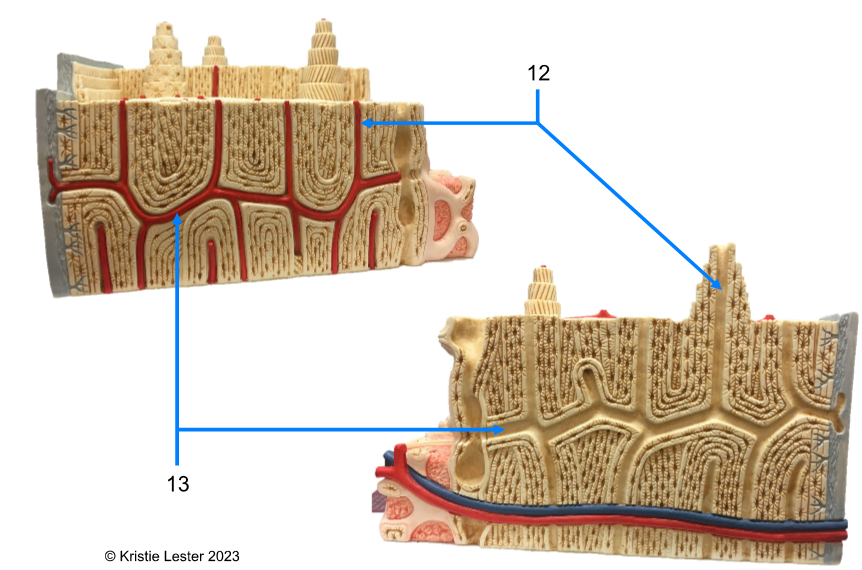
12. Central/osteonic canal
13. Transverse (perforating) canals
-
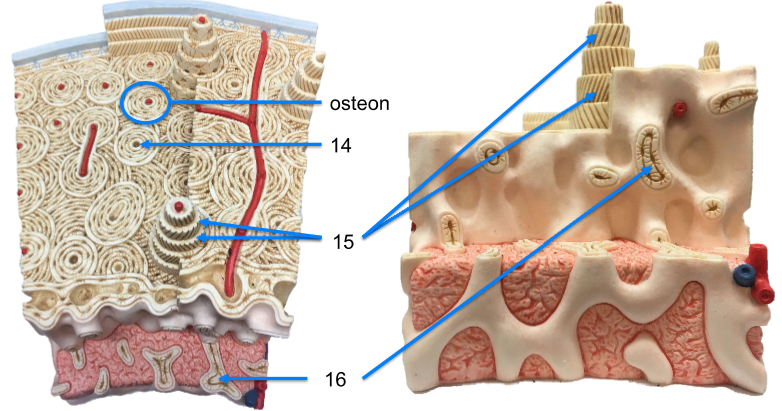
14. central/osteonic/haversian canal
15. lamellae
16. spongy bone (trabeculae)
-
What can be found in both spongy and compact bone?
Osteocytes, lacunae, canaliculi, lamellae
-
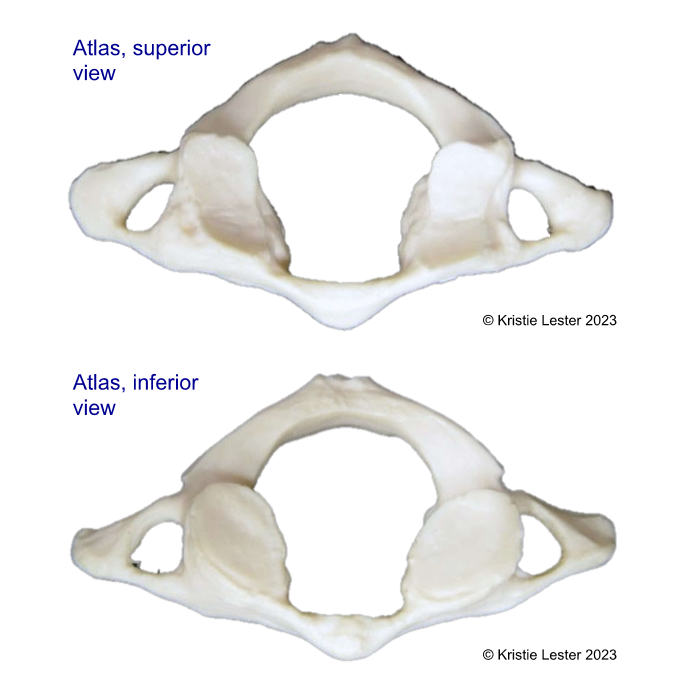
What vertebrae is this? What defining features does it have that the other two groups of vertebrae dont?
Cervical vertebrae
- Transverse foramina (all), bifurcated (bifid), and spinous processes (C2-C6)
-
What are the three types of vertebrae?
Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar
-
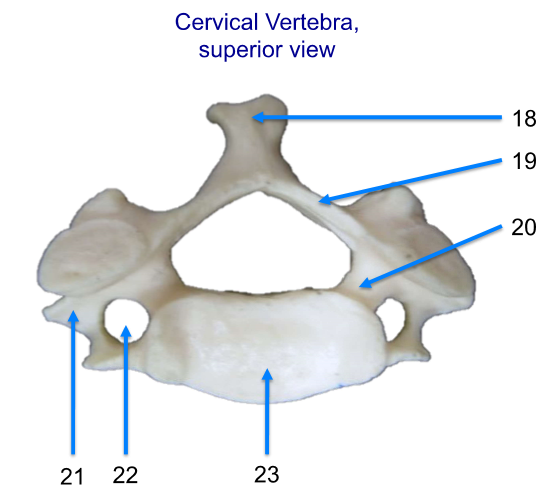
Label the areas! Name the vertebrae
18. spinous process
19. lamina
20. pedicle
21. transverse process
22. transverse foramen
23. body
-
20-30

-
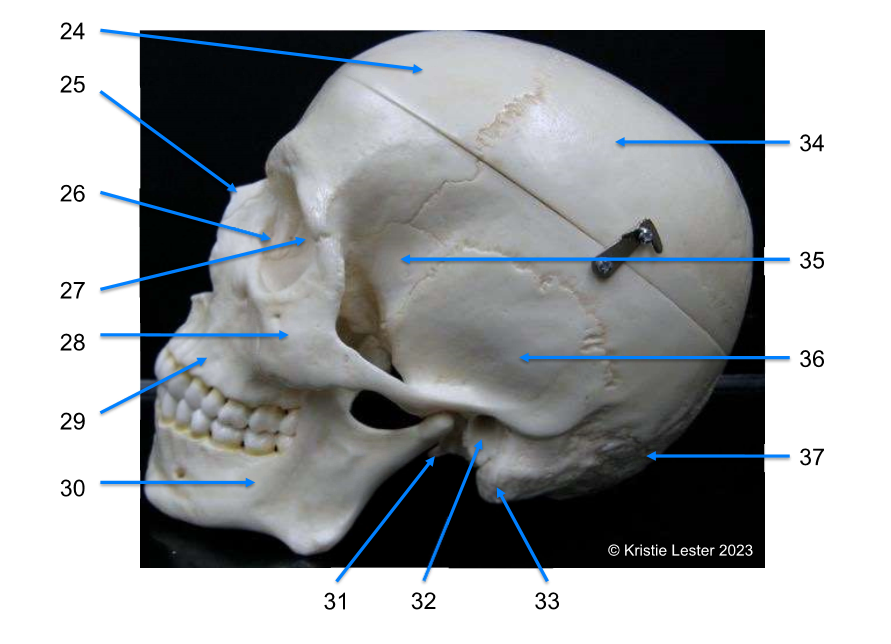
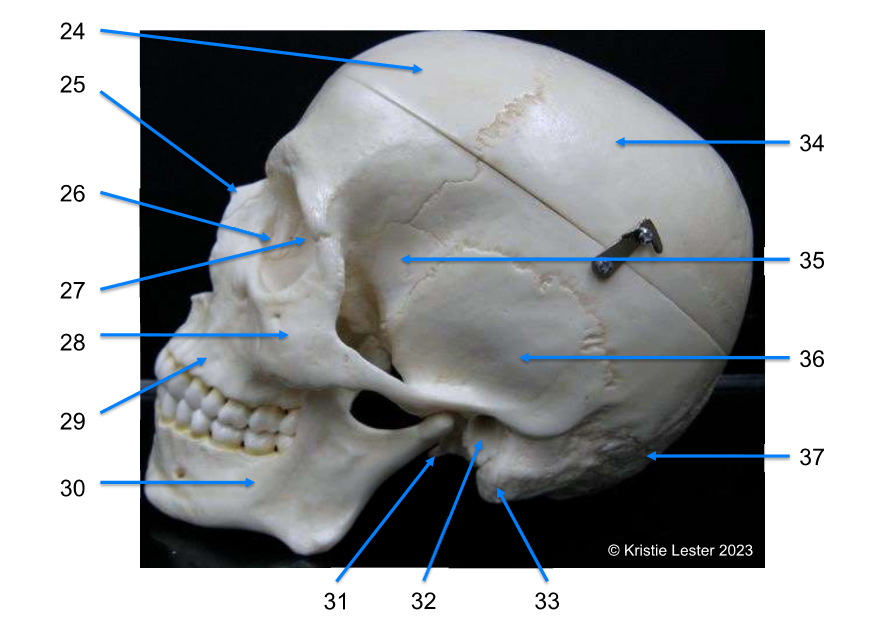
31-34
31. styloid process
32. external acoustic (auditory) meautus
33. mastoid process
34. parietal
-
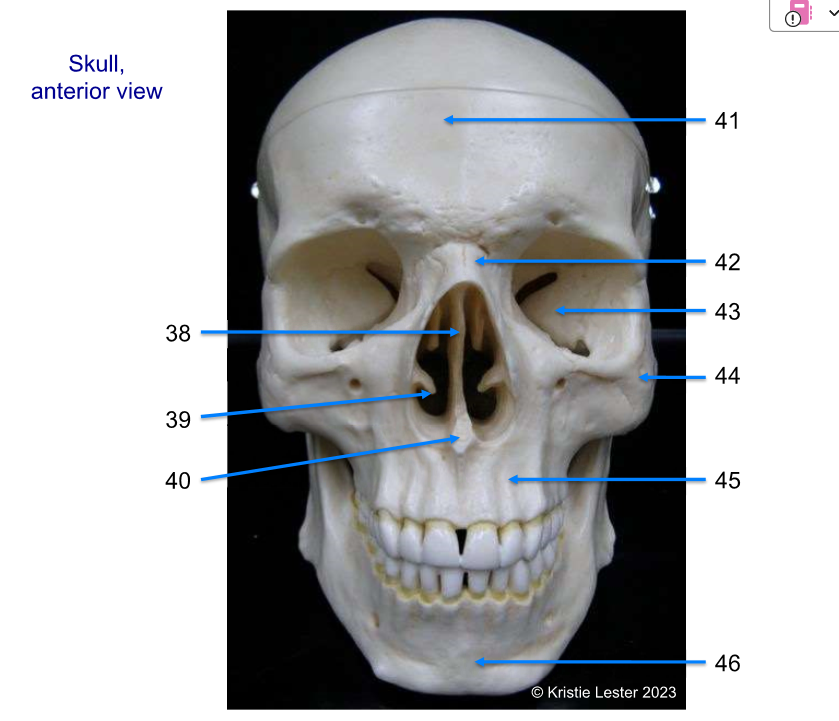
38 to 42
38. ethmoid (vertical piece behind nose)
inferior nasal conchae (hooks behind nose)
vomer (bone at nostril)
frontal (forehead area)
nasal (bridge of nose, between eyes)
-
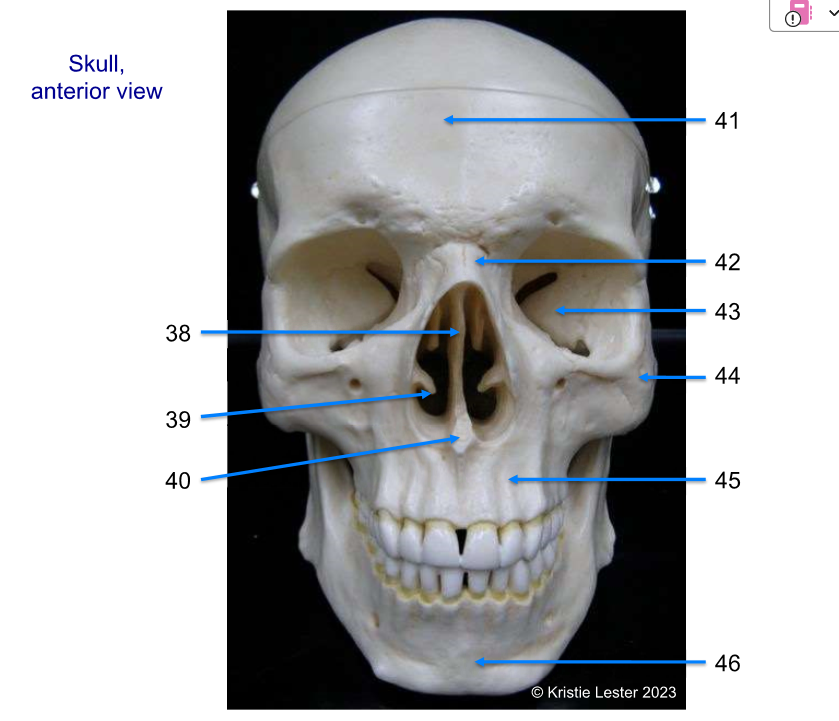
43-46
43. sphenoid (behind eyes)
zygomatic (cheek bones)
maxilla (top jaw)
mandible (bottom jaw)
-
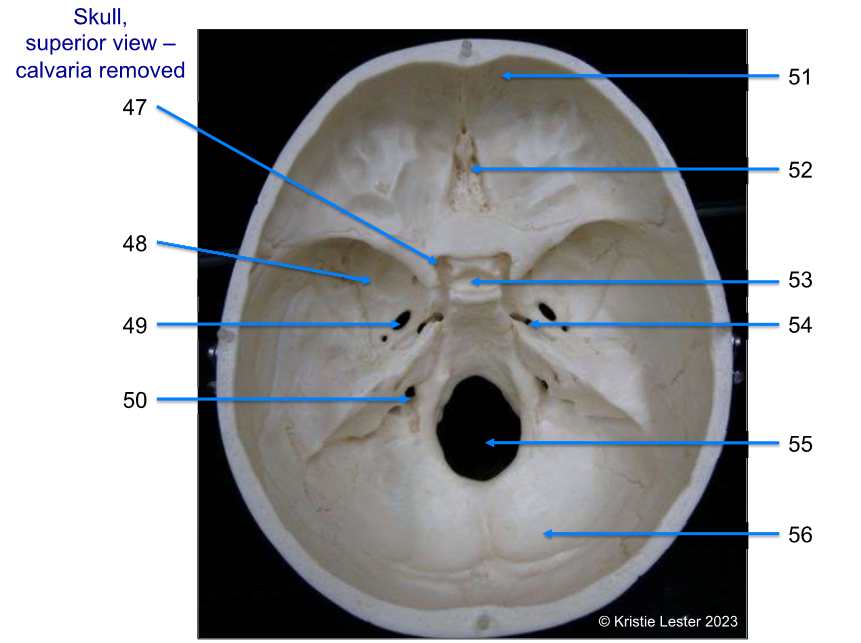
47-51
47. optic canal (two canals at top of slope)
sphenoid (behind eye holes)
foramen ovale (two hole pairs, more lateral than other pair its beside)
jugular foramen (small symetrical set of holes by magnum)
frontal (front piece of skull)
-
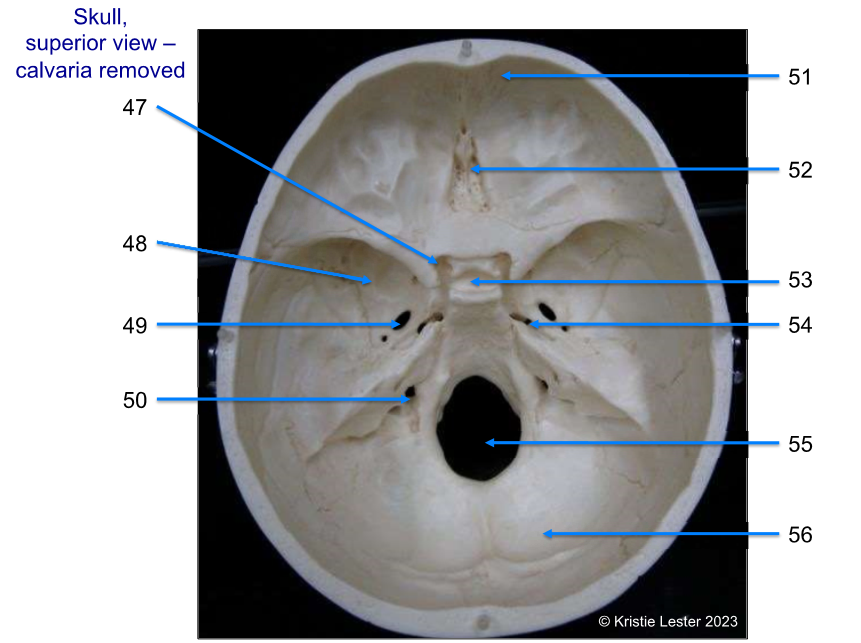
52-56
52. ethmoid (top of it, iternal above nose)
sella turcica (at top of slope to magnum)
foramen lacerum (small hole, symetrical pair, smaller of the two sets that are more anterior)
foramen magnum (big hole in middle)
occipital (back of skull)
-
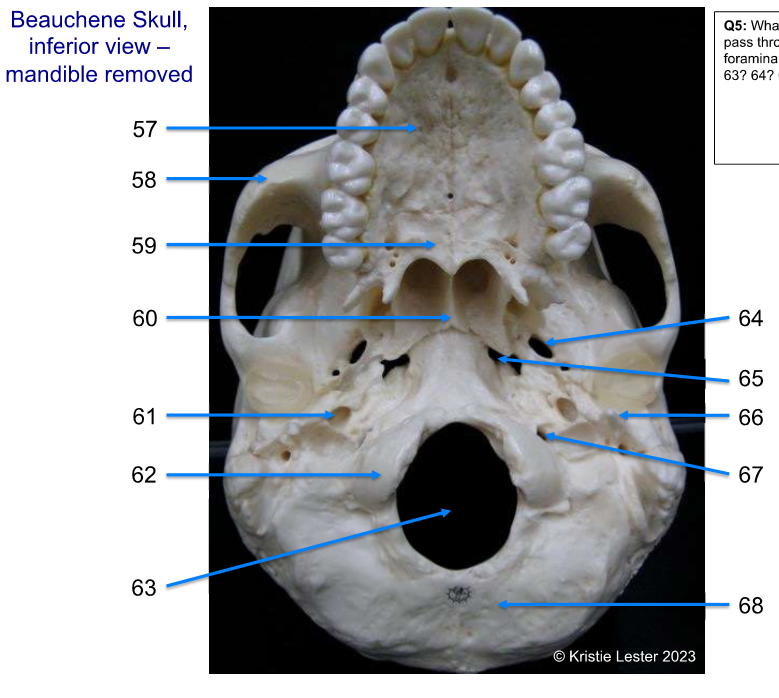
57-62
57. Maxilla (upper jaw bone, that teeth are in, including anterior area in mouth)
58. zygomatic (cheek bone)
59. palatine (posterior area of upper bone in mouth)
60. vomer (bottom of vomer, below nose)
61. carotid canal
62. occipital chondyle
-
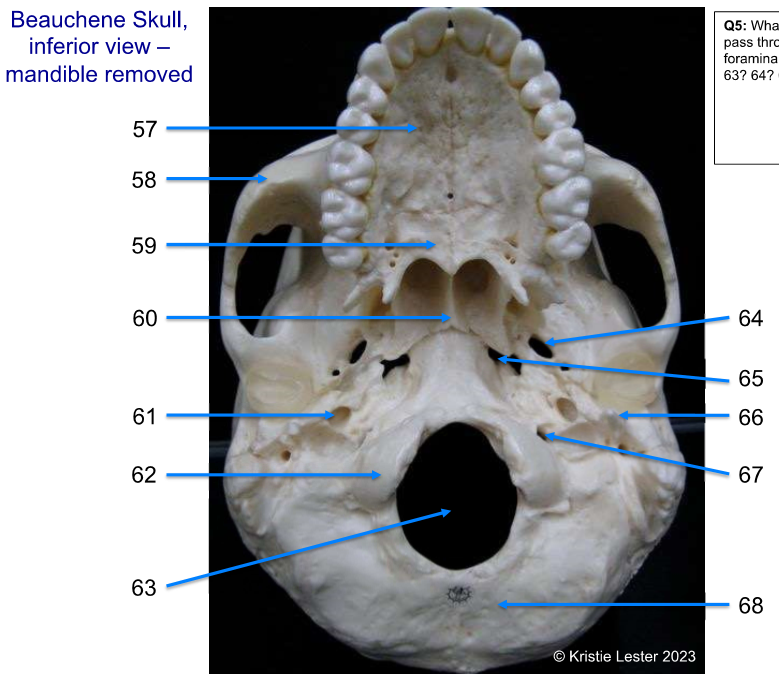
63-68
63. foramen magnum (big hole in middle)
64. foramen ovale (two symetrical holes more lateral and anterior
65. foramen lacerum (two symetrical holes more medial and anterior)
66. styloid process (process beneath and more medial than ear hole)
67. jugular foramen (two symmetrical holes beside magnum)
68. occipital (back of skull)
-
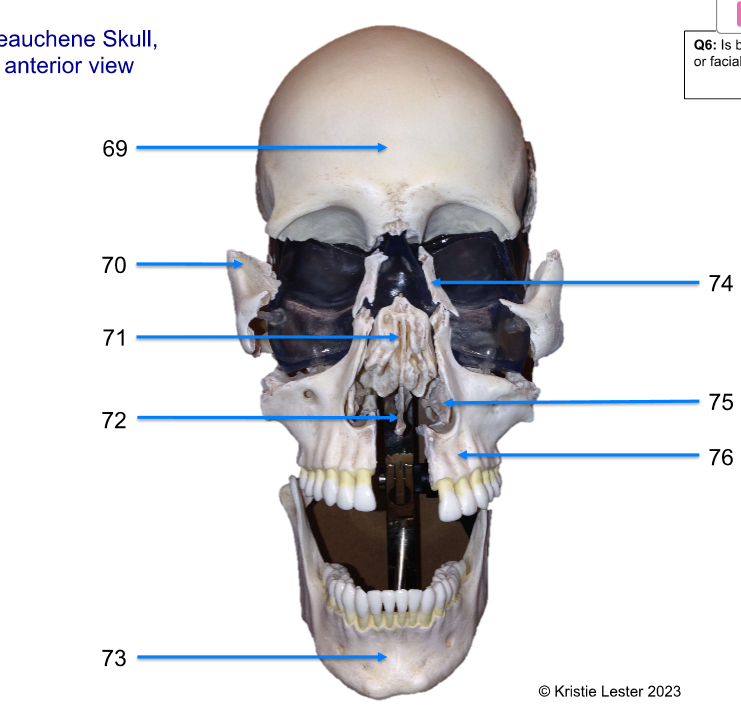
69 - 72
69. frontal
70. zygomatic
71. ethmoid
72. vomer
-
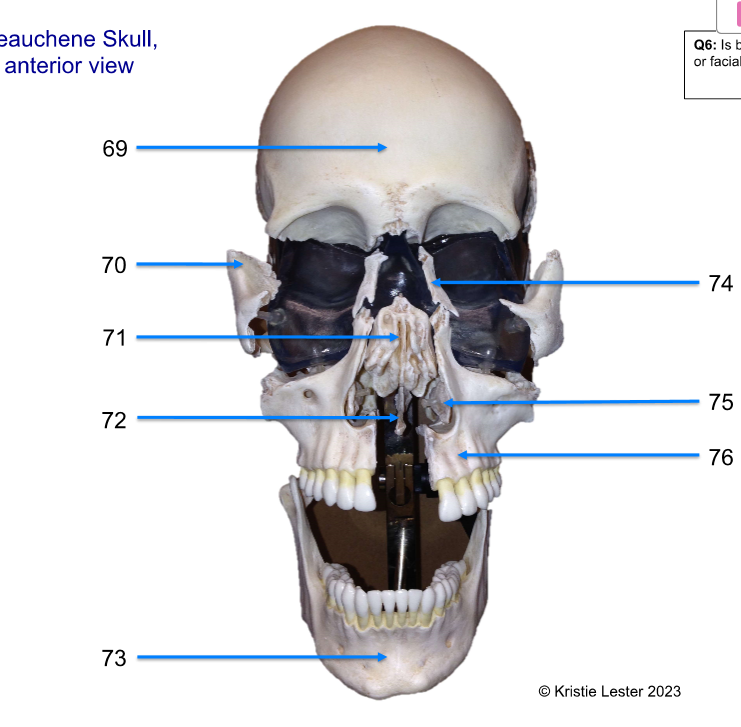
73 - 76
73. mandible
74. nasal
75. inferior nasal conchae
76. maxilla
-
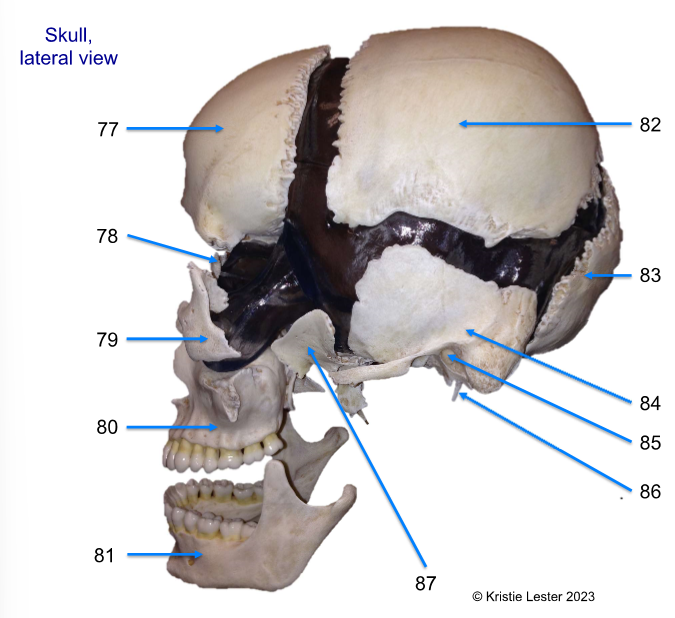
77 - 82
77. frontal
78. nasal
79. zygomatic
80. maxilla
81. mandible
82. parietal (superior posterior of skull)
-
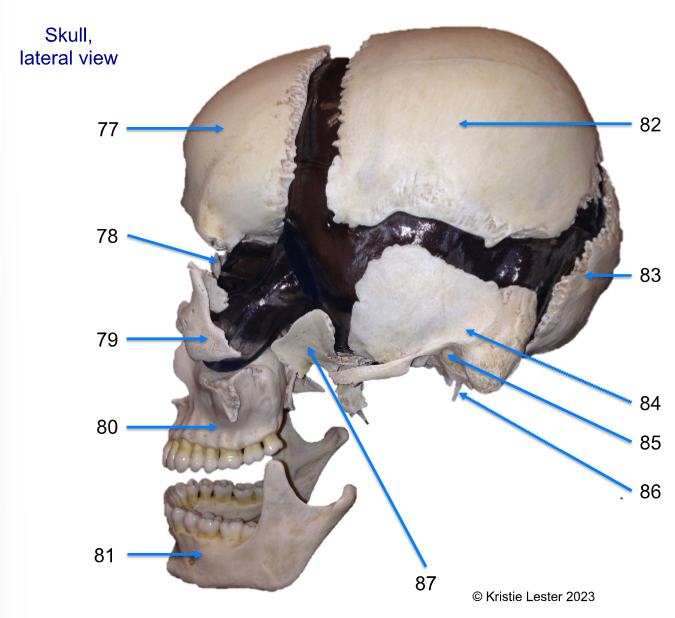
Label 83 - 87
83. occipital
84. temporal (on sides of the skull)
85. external acoustic (auditory) meatus
86. styloid process (under the ear)
87. sphenoid (the bone behind eye, also from other pov of it)
-
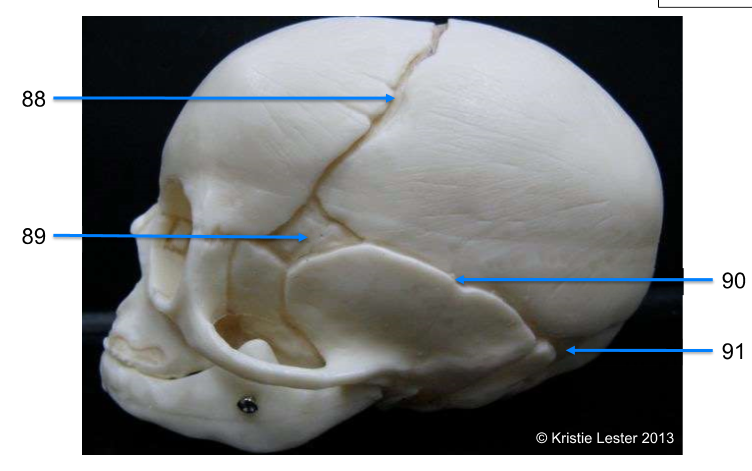
88. coronal suture
89. shenoidal fontanelle
90. squamous suture
91. mastoid fontanelle
-
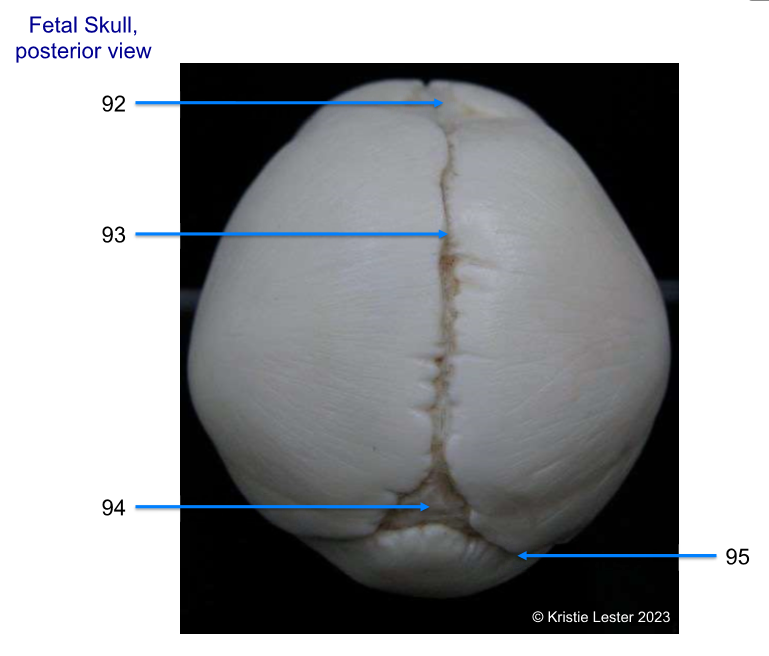
92. frontal fontanelle
93. sagittal suture
94. occipital fontanelle
95.lambdoid suture
-
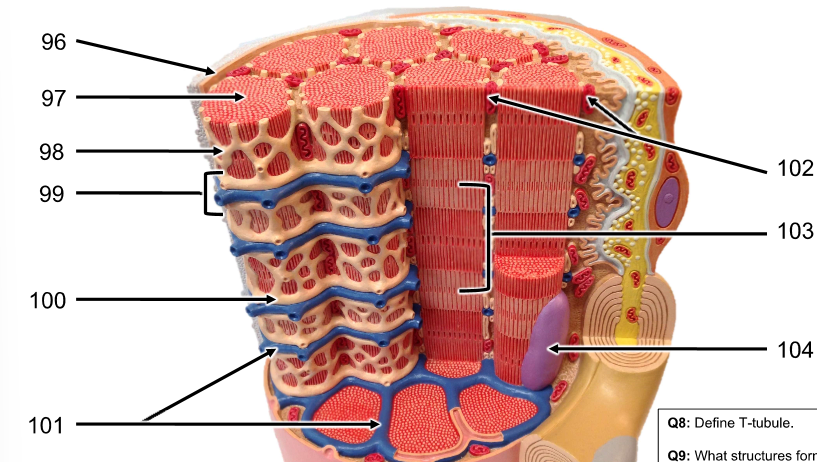
96 - 100
96. Sarcolemma (cell membrane)
97. myofibril (columns of sarcomere, many make up muscle)
98. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR, criss-cross around myofibrils)
99. Triad (2 Terminal cisterna of SR & T-tubules)
100. terminal cisterna of SR (SR that borders T-tubules)
-
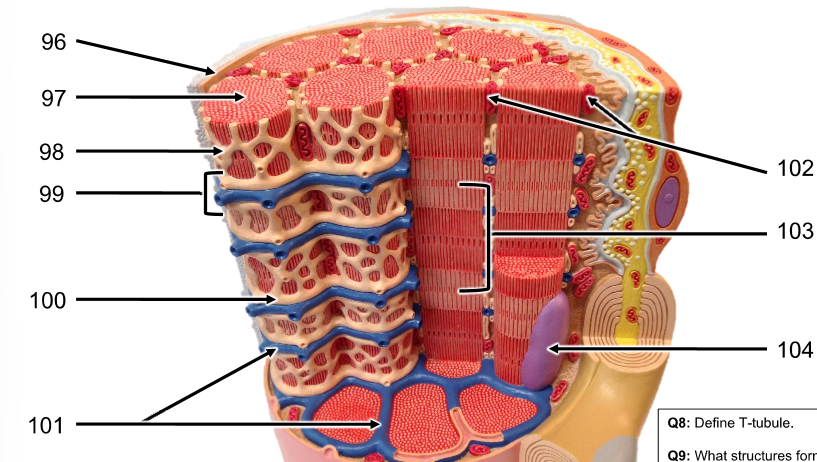
101 - 104
101. T-tubules (like plastic that keeps cans together, cans are myofibrils)
102. mitochondria
103. sarcomere (makes up myofibril)
104. nucleus (much bigger than mitochondria)
-
What is a T-tubule? What does it do?
T-tubules (transverse tubules) wrap around the myofibril colomns consistenly. This ensures the center of muscle cell is in contact with interstitial fluid (contained in the T-tubule and important for skeletal and cardiac muscle physiology)
-
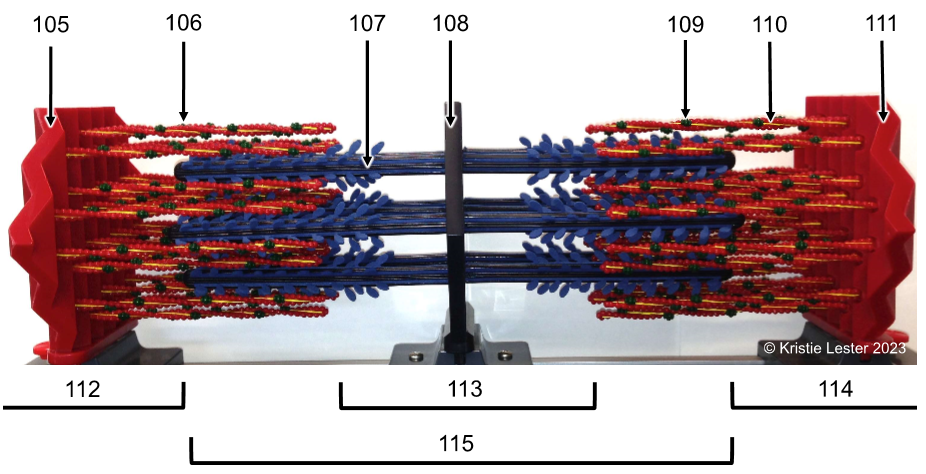
105. Z-disc (at either end)
106. Actin (part of thin filament)
107. Myosin (part of thick filament)
108. M-line (in middle)
-
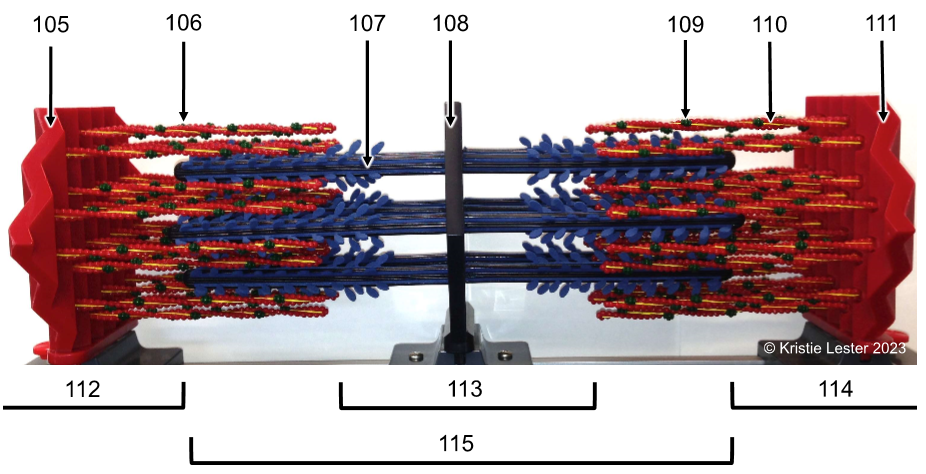
109. troponin (part of thin filament, a protein)
110. tropomyosin (part of thin filament, a protein)
111. Z-disc (on either end)
-
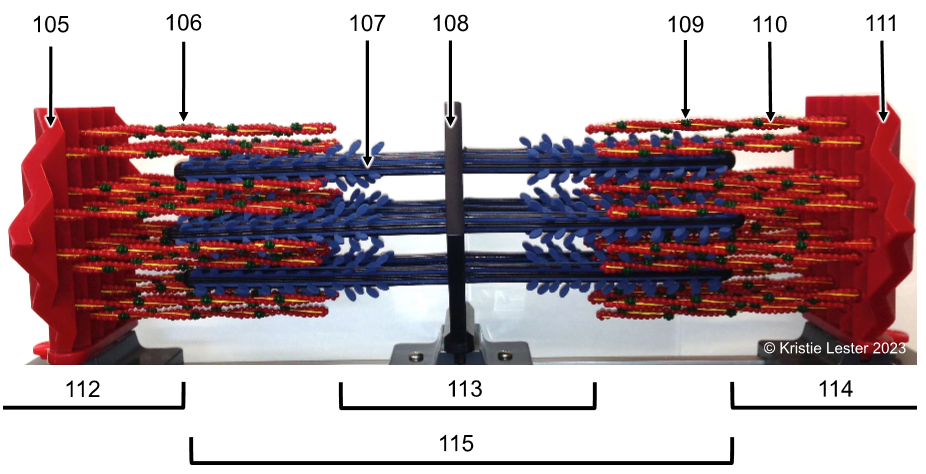
112 & 114. I-band (only think filaments)
113. H-zone (only thick filaments)
15. A-zone (thin & thick filaments, including H-zone tho)
-
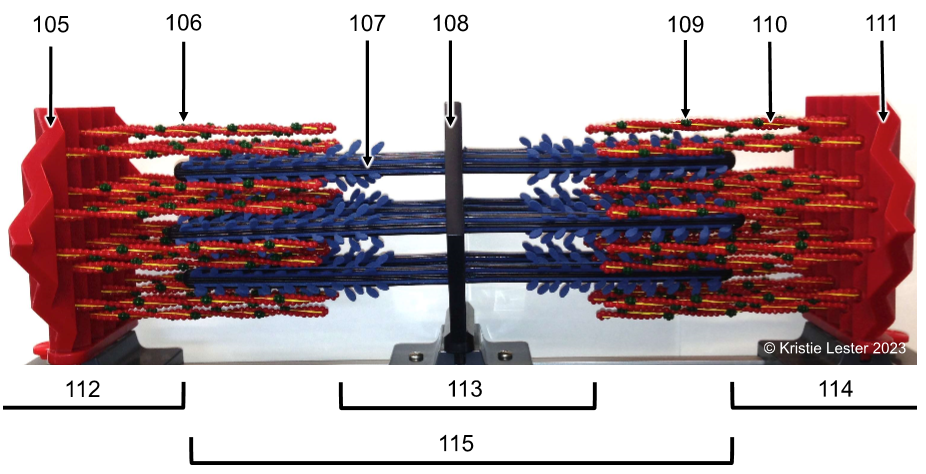
What proteins make up the thin vs. thick filaments of the model?
Thin filement proteins are actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
Thick is myosin
-
If the sarcomere contracted, which areas/bands would get smaller/disappear?
I-band and H-zone, so it'd all have overlapping filaments
-

116. Temporalis
117. occipitofrontalis - occipital belly
118. Buccinator
119. Masseter
120. Trapezius
-
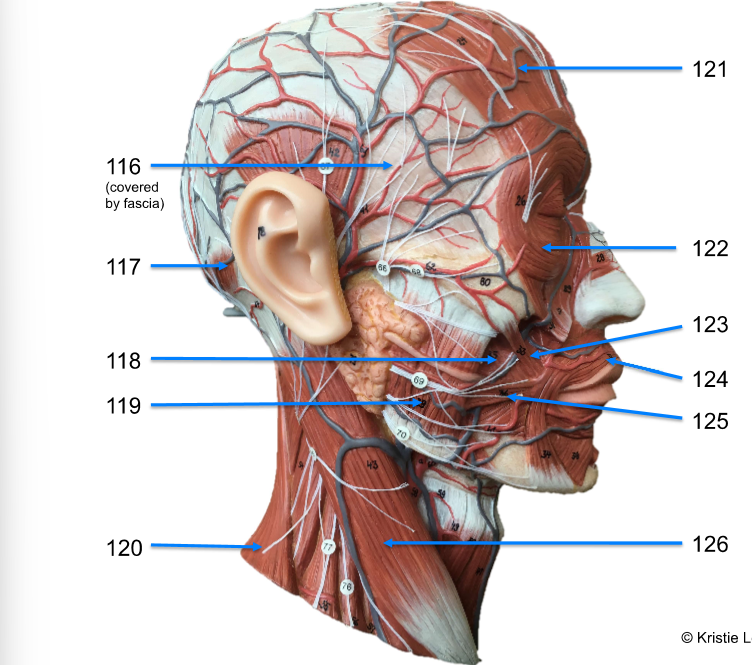
121. Occipitofrontalis - frontal belly
122. orbicularis oculi
123. zygomaticus major
124. orbicularis oris
125. risorius
126. sternocleidomastoid
-
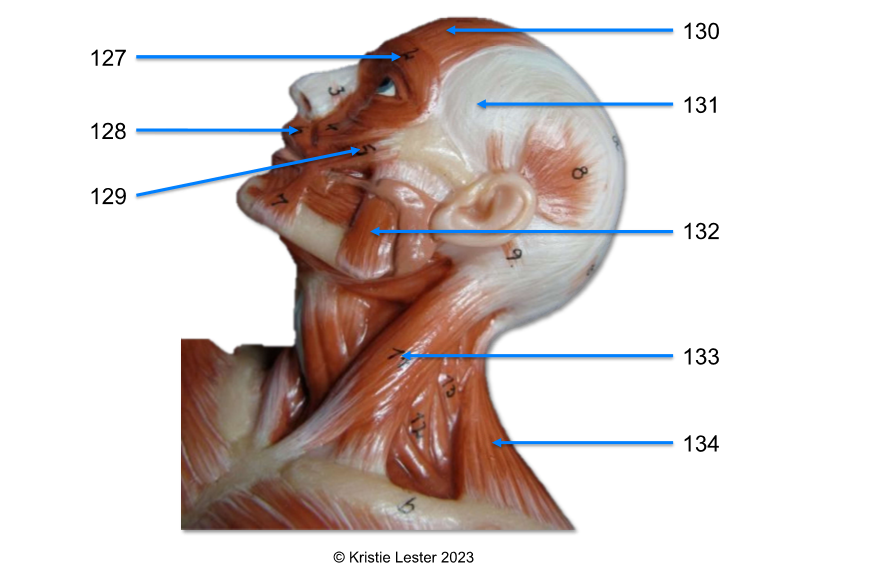
127. orbicularis oculi
128. orbicularis oris
129. zygomatic major
-

130. occipitofrontalis - frontal belly
131. temporalis (under the fascia)
132. masseter
133. sternocleidomastoid
134. trapezius

