-
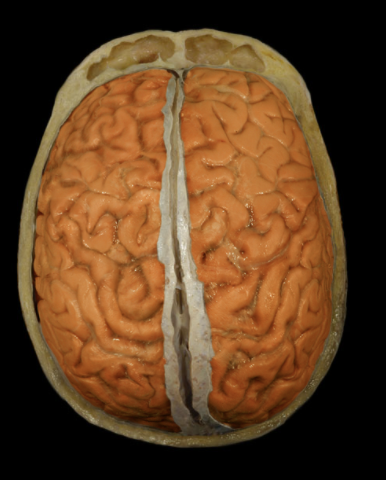
Where is the brain located?
Cranial cavity
-
What is the brain?
Major organ of central nervous system (CNS)
Composed of neurons and glia
-
What is the brain considered the seat of?
the seat of consciousness, intelligence, learning, emotion, and memory
-
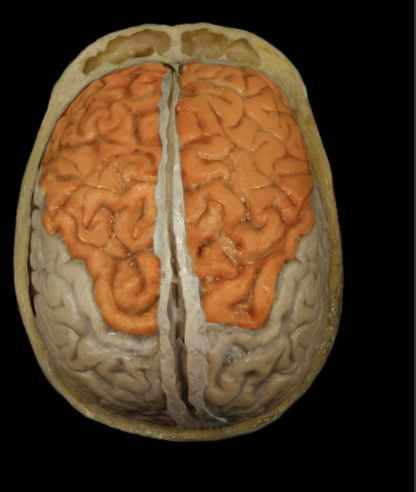
Where is the Frontal Lobe located?
Anterior portion of cerebral hemisphere
-
What is the Frontal Lobe?
Extends from anterior pole of brain to central sulcus
Contains precentral gyrus
-
What is the function of the Frontal Lobe?
Controls voluntary motor activity
Higher mental processing
Emotional behavior
Speech output (i.e., Broca's area - usually in left hemisphere)
-
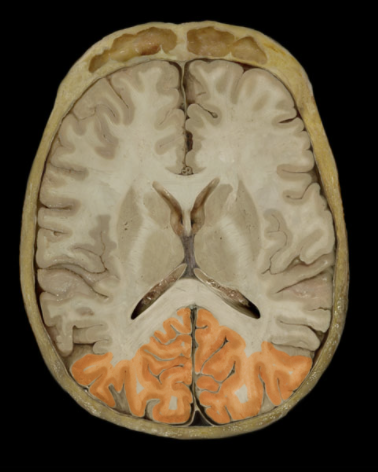
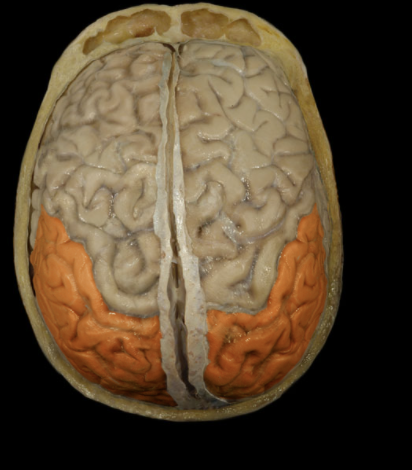
Where is the Occipital Lobe located?
Posterior portion of each cerebral hemisphere
-
What is the Occipital Lobe?
Extends from parieto-occipital sulcus to posterior pole of brain
Contains lingual gyrus
-
What is the function of the Occipital Lobe?
Primary visual area
-
Where is the Parietal Lobe located?
Lateral surface of each cerebral hemisphere of brain
-
What is the Parietal Lobe?
Extends from central sulcus (rostral) to parieto-occipital sulcus (caudal)
Includes postcentral gyrus
-
What is the function of the Parietal Lobe?
Reception of general sensory information from body
Tactile object recognition
Language, verbatim repetition of terms (i.e., Wernicke's area - usually in left hemisphere)
-
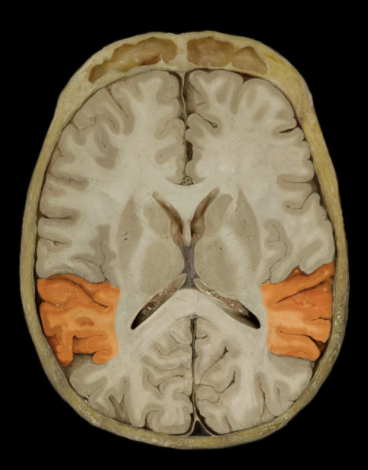
What is the location of the Temporal Lobe?
Lateral and inferior portion of each cerebral hemisphere
Inferior to lateral sulcus
-
What is the Temporal Lobe?
Lateral surface has three parallel gyri
-
What is the function of the Temporal Lobe?
Primary hearing and smell areas
Memory
Speech perception and recognition (i.e., Wernicke's area - usually in left hemisphere)
-
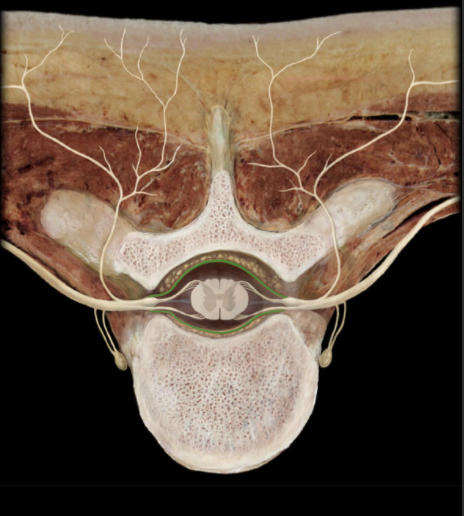
What is the location of the Dura Mater?
Surrounds brain and spinal cord
-
What is the Dura Mater?
Tough, dense irregular connective tissue layer
Most external of three layers of meninges (dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater)
Cranial dura mater has periosteal (outer) and meningeal (inner) parts
Cranial dura mater contains dural venous sinuses
-
What is the function of the Dura Mater?
Protection of brain and spinal cord
-
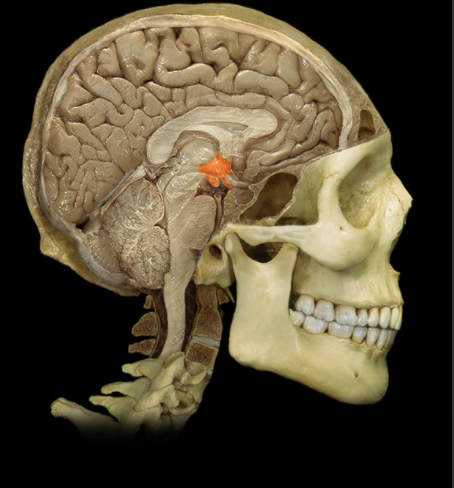
Where is the Hypothalamus located?
Ventral diencephalon
-
What is the Hypothalamus?
Collection of nuclei located inferior to thalamus
Includes infundibulum and mammillary bodies
-
What is the function of the Hypothalamus?
Considered master control center for endocrine system
Secretes releasing and inhibiting hormones that control anterior pituitary gland
Produces hormones that are transported to and stored in posterior pituitary gland
Controls autonomic nervous system
Regulates body temperature, food, and water intake
Regulates emotional behavior
Maintains sleep/wake cycle
-
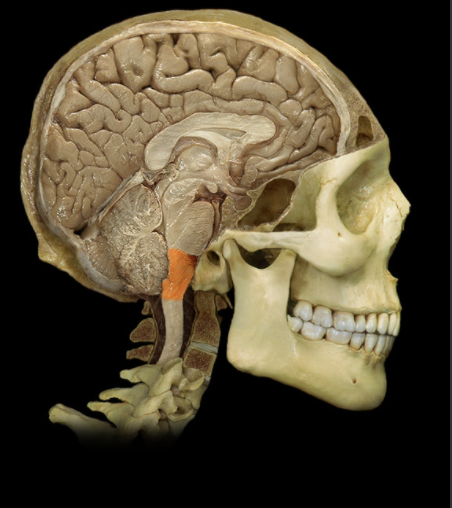
Where is the Medulla Oblongata located?
Most caudal portion of brain
-
What is the Medulla Oblongata?
Extends from pons to spinal cord
Associated with cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII
-
What is the function of the Medulla Oblongata?
Contains respiratory, cardiac, and vasomotor centers
-
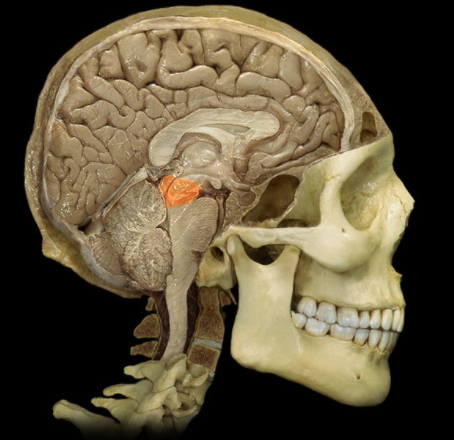
Where is the Midbrain located?
Brainstem
Between diencephalon and pons
-
What is the Midbrain?
Composed of white matter tracts and gray matter nuclei
Associated with cranial nerves III and IV
Prominent features include superior and inferior colliculi, cerebral peduncles, substantia nigra, and cerebral aqueduct
-
What is the function of the Midbrain?
Coordinates movements in response to visual and auditory stimuli
Conveys motor information from cerebral cortex to pons
Conveys sensory information from spinal cord to thalamus
-
Where are the Pons located?
Ventral aspect of brainstem
Between midbrain (rostral) and medulla oblongata (caudal
-
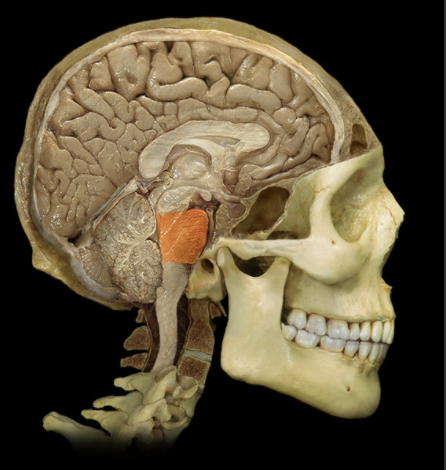
What are Pons?
Characterized by distinct ventral "bulge"
Attached to cerebellum by middle cerebral peduncle
Associated with cranial nerves V, VI, VII, and VIII
-
What is the function of the Pons?
Involved in control of sleep and respiration
Transfer of information to and between cerebellar hemispheres
-
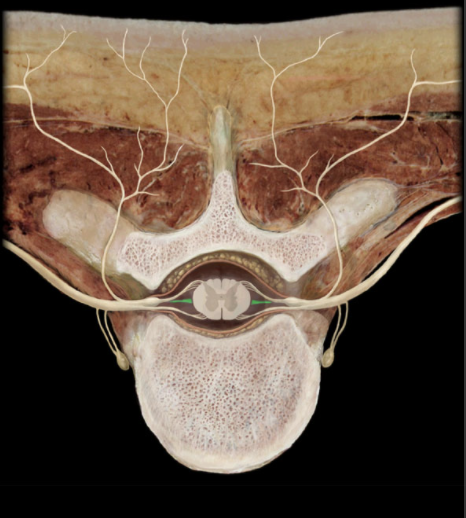
Where is the the Denticulate Ligament located?
Vertebral canal within dural sac
-
What is the Denticulate Ligament?
Lateral extension of pia mater between dorsal and ventral roots
Attach to inner surface of dura mater
-
How man Denticulate Ligaments are on each side of the spine?
20-22 on each side of spinal cord
-
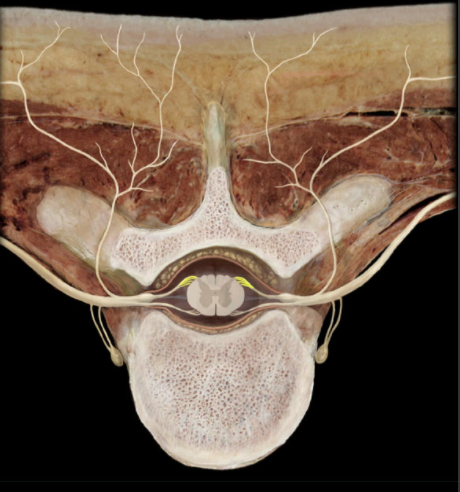
Where are the Dorsal Roots located?
Vertebral canal
-
What are Dorsal Roots?
Series of small nerves branching from dorsal spinal cord
Several rootlets unite to form a dorsal root
-
What is the function of Dorsal Roots?
Conduct afferent (sensory) impulses
-
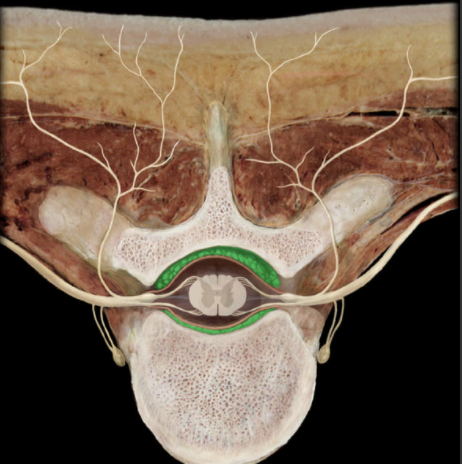
Where is the Epidural Space?
Space or potential space external to dura mater
-
What is the Epidural Space?
Spinal: contains loose connective tissue, fat, and venous plexus
Cranial: potential space
-
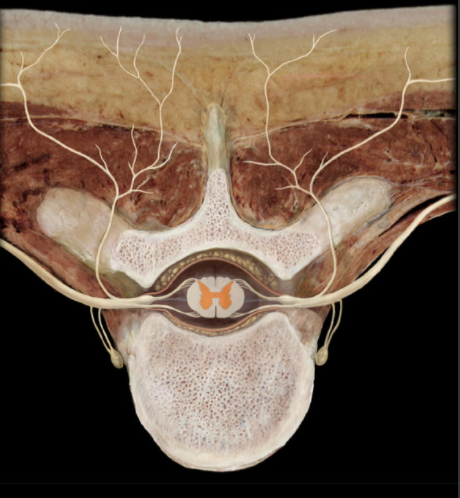
Where is Gray Matter?
"Core" of spinal cord
-
What is Gray Matter?
Unmyelinated nervous tissue shaped like the letter "H"
Limbs of "H" are termed ventral horns and dorsal horns
Collections of neuronal cell bodies neuronal cell processes, and glial cells
Ventral horns associated with motor neurons
Dorsal horns associated with sensory neurons
-
What composes the inner and outer coat of the spinal cord
inner: Gray Matter
Outer: White Matter
-
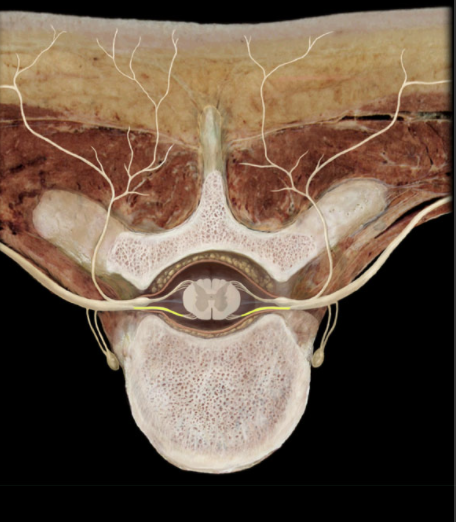
Where is the Ventral Root?
Vertebral canal
-
What is the Ventral Root?
Efferent (motor) limb of each spinal nerve
Formed by union of several ventral rootlets
Unite with dorsal root of same spinal cord level to form spinal nerve
-
What is the function of the Ventral Root?
Conduct efferent (motor) impulses
-
Location of the Spinous Process
Posterior aspect of vertebrae
-
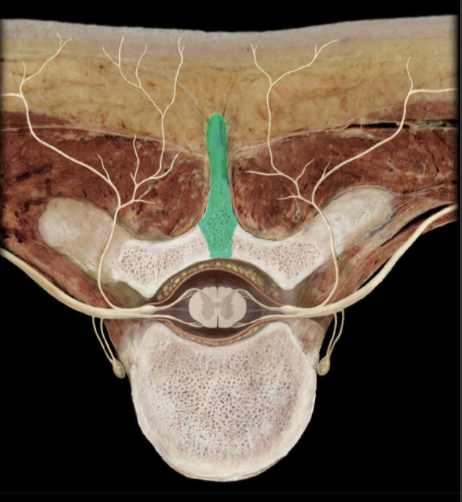
What is the Spinous Process?
Unpaired posterior midline projection from vertebral arch
-
The Spinous Process presents all the vertebrae except which two?
the atlas (C1 vertebra) and coccygeal vertebrae
-
Function of the Spinous Process?
Provides attachment for muscles and ligaments
-
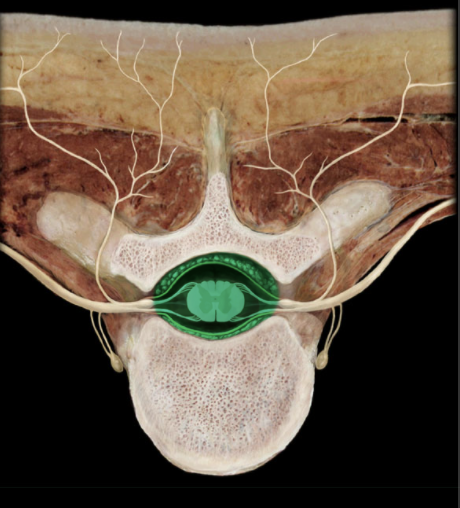
Location of the Vertebral Canal?
Vertebral column
-
What is the Vertebral Canal?
Canal formed by combined vertebral foramina
-
What does the Vertebral Canal contain?
Contains spinal cord, meninges, spinal nerve roots, blood vessels, and fat
-
Location of facial nerves?
Posterior cranial fossa
Facial canal
Middle ear
Face
Infratemporal fossa
Oral cavity
-
Composition of the facial nerves?
Motor
General sensation
Special sensation
Parasympathetic
-
What is the motor portion of the facial nerve?
Muscles of facial expression
Posterior belly of digastric muscle
Stylohyoid muscle
Stapedius muscle
-
What is the general sensation of the facial nerve?
Small area of skin of auricle of ear
-
What is the special sensation of the facial nerve?
Taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue
Taste from palate
-
What is the parasympathetic portion of the facial nerve?
Lacrimal gland
Submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
Mucous glands of nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and palate
-
What is the CNS connection of the facial nerve?
Motor: pons (motor nucleus of facial nerve)
General sensation: medulla oblongata (spinal trigeminal nucleus)
Special sensation: medulla oblongata (nucleus of solitary tract)
Parasympathetic: medulla oblongata (superior salivatory nucleus
-
What is the sensory ganglion of the facial nerve?
Genculate
-
What is the cranial Foramina of the facial nerve
Internal acoustic meatus
Pterygomaxillary fissure
Stylomastoid foramen
-
The facial nerve is also known as...
CN VII
-
Extra functions of the Facial Nerve
Special sensory and parasympathetic axons, together, form the chorda tympani nerve
Postganglionic parasympathetic nerve cell bodies located in pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia
-
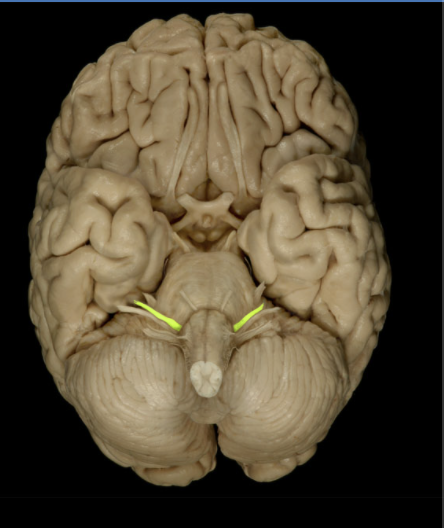
Location of the Oculomotor nerve?
Middle cranial fossa
Orbit
-
Composition of the Oculomotor nerve?
Motor
Parasympathetic
-
What the Motor portion of the Oculomotor nerve consists of?
Medial rectus muscle
Superior rectus muscle
Inferior rectus muscle
Inferior oblique muscle
Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
-
What the parasympathetic portion of the Oculomotor nerve consists of?
Pupillary sphincter muscle (constriction of pupil)
Ciliary muscle (permits lens to thicken for accommodation)
-
What the CNS connection portion of the Oculomotor nerve consists of?
Midbrain (oculomotor and accessory oculomotor nuclei)
-
What the Cranial Foramina portion of the Oculomotor nerve consists of?
Superior orbital fissure
-
Extra information of the Oculomotor Nerve
Rectus and oblique muscles are extrinsic eye (extra-ocular) muscles
Postganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies located in ciliary ganglion in the orbit
Oculomotor nerve also known as CN III
-
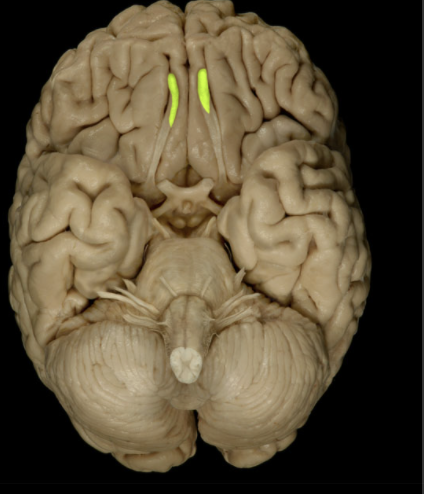
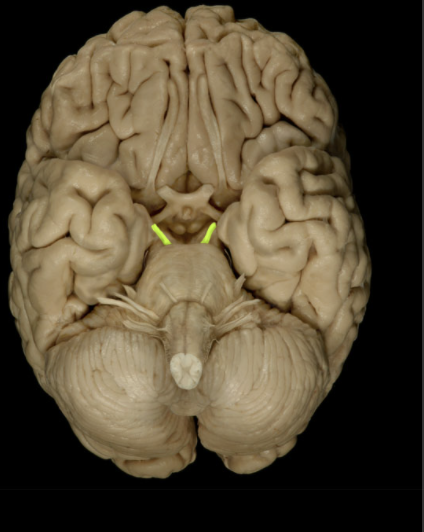
Where is the Olfactory Bulb located?
Lies on cribriform plate of ethmoid bone in anterior cranial fossa
Ventral aspect of frontal lobe of brain
-
What is the Olfactory Bulb?
Expanded anterior end of olfactory tract
Site of synapse for olfactory neurons (CN I) after their axons pass through cribriform plate
-
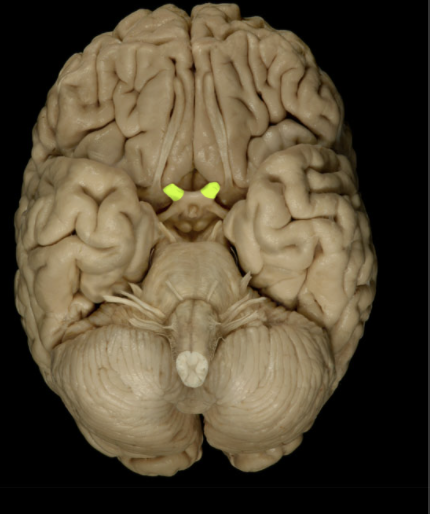
Location of the Optic Nerve
Orbit
Middle cranial fossa
-
Optic Nerve composition
Special sensation
-
Special Sensation of the Optic Nerve
Vision
-
Cranial Foramina of the Optic Nerve
Optic canal
-
What does the special sensation of the Optic Nerve include?
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
-
How are optic nerves formed?
by axons of retinal ganglion cell
-
What is the Retinal Ganglion cell axon pathway
optic nerve > optic chiasm > optic tract > brainstem nuclei (including lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus)
-
What is the optic nerve also known as?
CN II
-
CNS connection of the Optic Nerve?
Lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus

