-
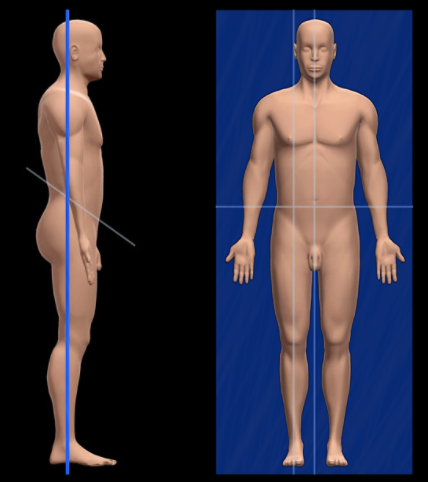
What is the Coronal Plane?
AKA Frontal Plane; it separates the body from the anterior and posterior
-
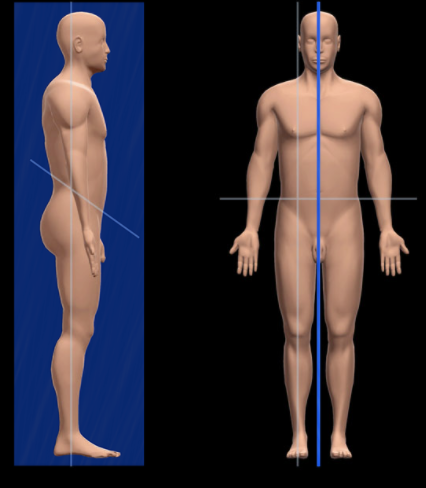
What is the Midsagittal Plane?
AKA Median Plane; Passes though the front to back through midline of body, dividing the body into the right and left
-
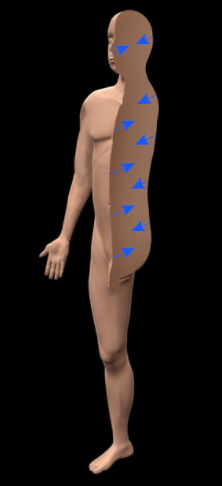
What does Deep mean?
Opposite of superficial; Away from the surface of the body
-
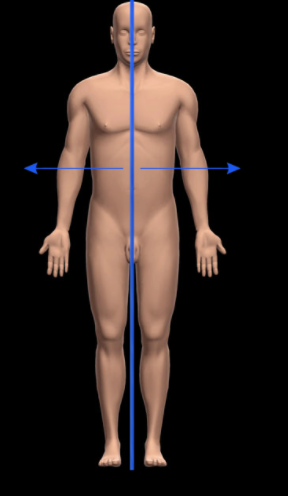
What does Lateral mean?
Opposite of medial; Away from the midline of the body
-
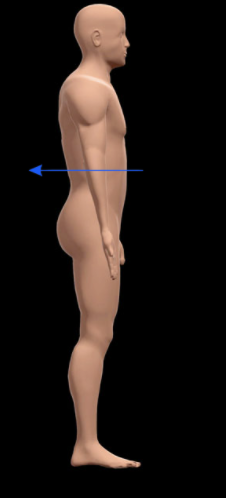
What does Posterior mean?
Opposite of Anterior; Toward the back of the body or relating to the back
-
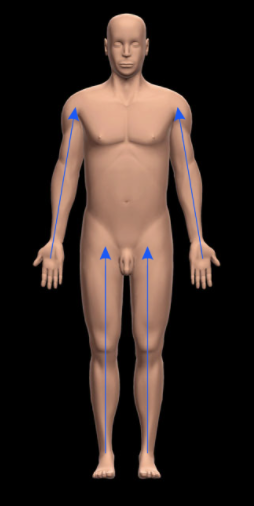
What does Proximal mean?
Opposite of Distal; Closer to Trunk or Origin of a structure
(Arms: Shoulder is Origin; Legs: Hips are the Origin)
-
Where is the Abdominal Cavity Located?
Abdominal Region
-
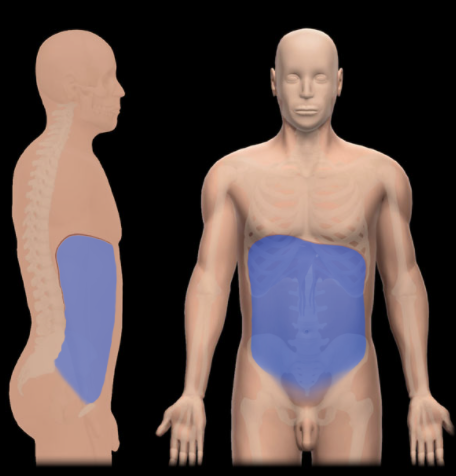
What is the Abdominal Cavity?
- Bounded by abdominal walls, thoracic diaphragm (superior), and pelvic brim (inferior)
- Major organs include: stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and ureters, suprarenal glands, aorta, inferior vena cava, and lumbar nerve plexus
-
What is the inferior part of the abdominal cavity called?
the greater (or false) pelvis (i.e., between iliac fossae, superior to pelvic inlet)
-
What does the Abdominal cavity combine with to form a continuous abdominopelvic cavity?
Pelvic Cavity
-
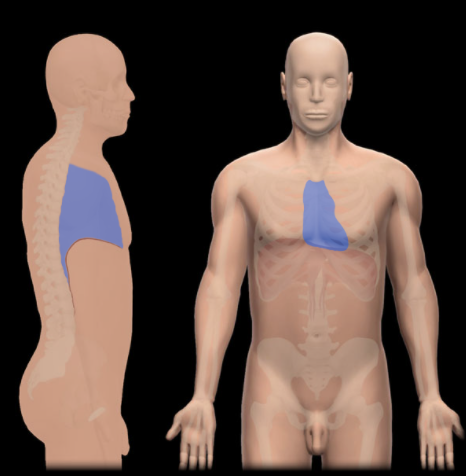
Where is the Mediastinum located?
Thoracic Cavity
-
What is the Mediastinum?
Middle region of thorax
Lies between sternum and thoracic vertebral bodies
Separates right and left pulmonary cavities
Divided into superior and inferior parts
Inferior mediastinum subdivided into middle, posterior, and anterior part
-
What does the Superior Mediastinum include?
Great vessels, thymus (remnant in adult), thoracic duct, and parts of trachea and esophagus
-
What does the Middle Mediastinum include?
Heart, pericardium, and roots of great vessels
-
What is the Thoracic Cavity divided into?
Mediastinum and right and left pulmonary cavities
-
What does the Posterior Mediastinum contain?
Thoracic aorta, esophagus, and thoracic duct
-
What does the Anterior Mediastinum contain?
loose connective tissue (may include thymic remnant in adult)
-
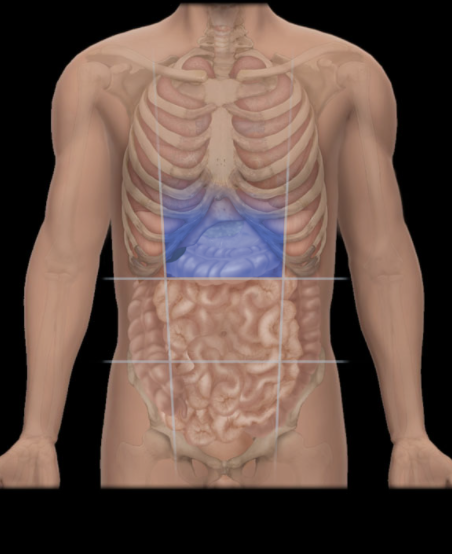
Where is the Epigastric Region located?
abdominal wall (anterior)
-
What is the Epigastric Region?
One of nine regions of abdominal cavity
Upper median region (flanked by right and left hypochondriac regions)
Contents include suprarenal glands and parts of stomach, large intestine, liver and gallbladder, and pancreas
-
What is the function of the Epigastric Region?
Used in clinical practice to describe location of abdominal organs
-
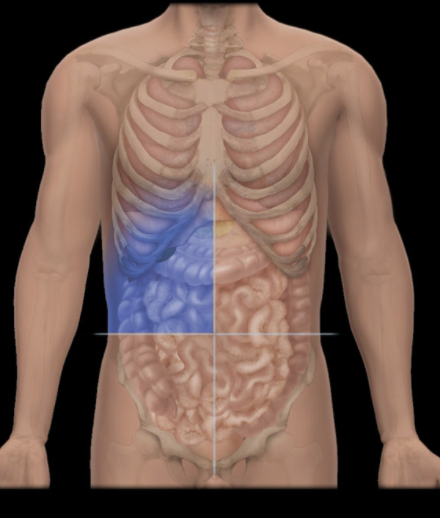
Where is the Upper Right Quadrant Located?
Right of midline, superior to transverse plane through umbilicus
-
What is the Upper Right Quadrant?
Upper right lateral area of abdominopelvic cavity
Contents include right kidney and suprarenal gland, gallbladder, and parts of liver, stomach, pancreas, and small and large intestines
-
What is the function of the Upper Right Quadrant?
Used in clinical practice to describe location of abdominal organs and abdominal pain
-
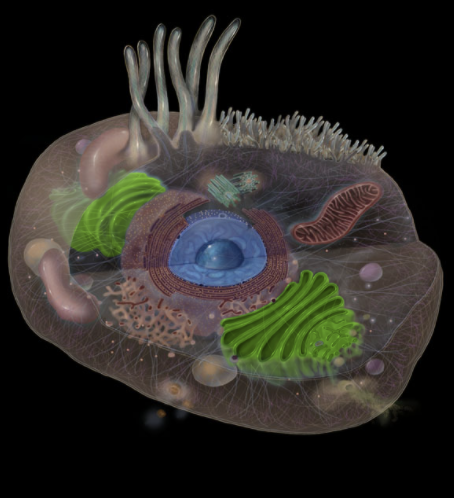
Where is the Golgi Apparatus located?
Cytoplasm
Adjacent to rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
-
What is the Golgi Apparatus?
Membrane-bound organelle
Series of flattened sacs (cisternae)
Three subdivisions: (1) cis-face (closest to, and contiguous with RER), (2) intermediate face, and (3) trans-face (farthest from RER)
-
What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus?
Transport vesicles, containing newly synthesized proteins from RER, fuse with cis-face
Modifies, packages, and sorts newly synthesized proteins
Modified proteins packaged at trans-face into vesicles that become: lysosomes (contain hydrolytic enzymes), secretory vesicles (undergo exocytosis), or vesicles that add new plasma membrane
-
Difference between the cis-face and trans-face?
cis-face also known as receiving region
trans-face also known as "transport" or "shipping" region
-
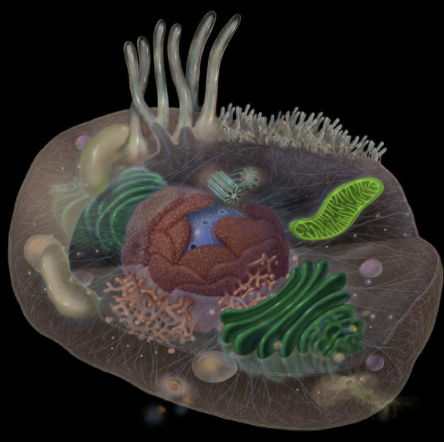
Where is the mitochondria located?
Cytoplasm
-
What is the Mitochondria?
Rod-shaped, membrane-bound organelle (0.5-1.0 µm in diameter; up to 7 µm in length)
Has double membrane (i.e., two lipid bilayers): outer membrane is smooth, inner membrane has complex folds called cristae
Intermembrane space between outer and inner membrane
Matrix space enclosed by inner membrane
-
What is the function of the Mitochondria?
"Powerhouse" of cell (most cells contain numerous mitochondria)
Synthesizes adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which provides chemical energy for cellular respiration (through oxidative phosphorylation)
-
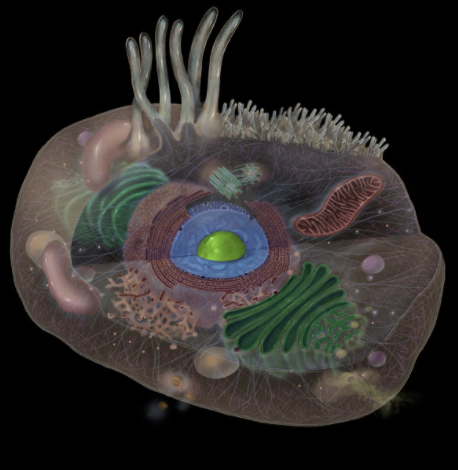
Where is the Nucleolus located?
Nucleus
-
What is the Nucleolus?
Dark staining, granular region of nucleus (1-3 µm in diameter)
Usually spherical in shape
1-3 nucleoli present depending on synthetic activity of cell
-
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly
-
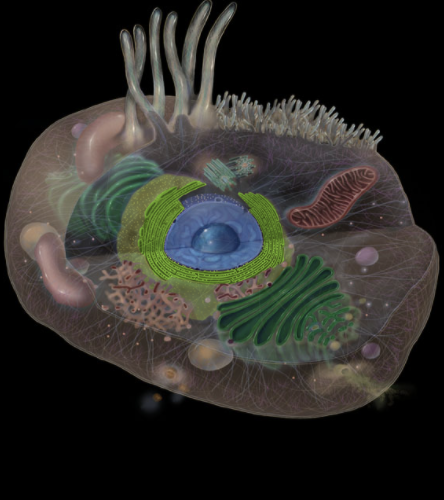
Where is the RER located?
Cytoplasm (perinuclear)
Between nucleus and Golgi apparatus
-
What is the RER?
Membrane-bound organelle
Subdivision of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), an interconnected system of tubules and flattened sacs (cisternae)
Has attached ribosomes
Continuous with smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
-
What is the function of the RER?
Synthesizes protein for secretion, insertion into plasma membrane, and lysosomal enzymes and other proteins packaged in vesicles
-
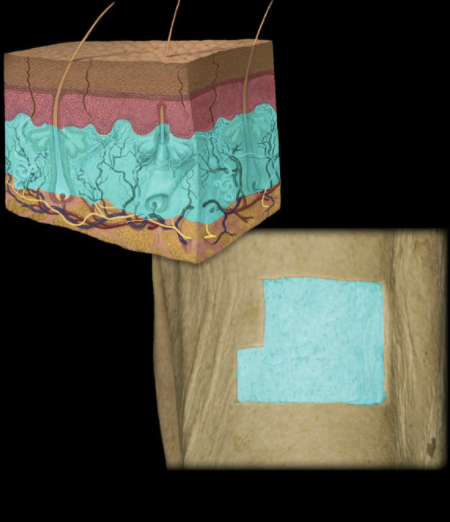
Where is the Dermis Located?
Skin (between epidermis and hypodermis)
-
What is the Dermis?
Two layers: papillary (superficial), composed of areolar connective tissue; and reticular (deep), composed of dense irregular connective tissue
Contains appendages of skin: hair follicles and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
Contains sensory nerve endings and dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
Includes part of hair follicle (which develops as invagination from epidermis)
-
What is the function of the Dermis?
Supports epidermis
Dense concentration of collagen and elastin gives skin strength
Receives general sensory stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) via nerve endings and specialized receptors
Regulates body temperature
-
what is inserted on the dermis?
Muscles of facial expression
-
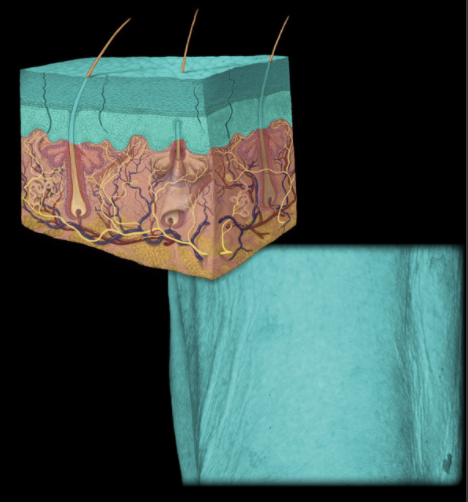
Where is the epidermis located?
Superficial to the dermis
-
What is the epidermis?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness
Avascular
Major cell type is keratinocyte
Thick skin has five layers (superficial to deep): stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
Thin skin has four layers (stratum lucidum is missing)
Cells of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum lack nuclei
-
What is the function of the epidermis?
Physical barrier
Protection of underlying structures
-
What does the epidermis contain?
Also contains stem cells, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and dendritic cells
-
What does the epidermis depend on?
Depends on underlying dermis for nutrients (i.e., vascular supply)
-
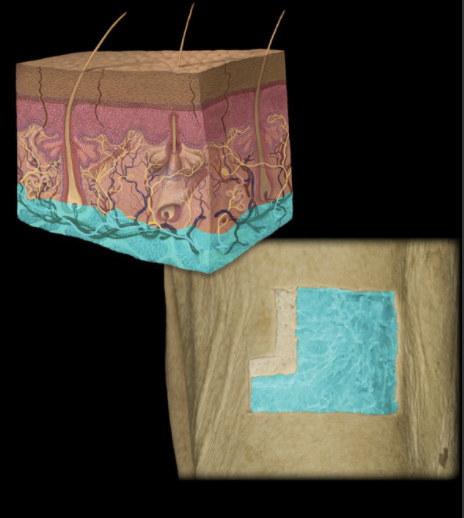
Where is the hypodermis located?
Deep to skin
-
What is the hypodermis?
Layer of loose areolar connective and adipose tissue
Contains cutaneous nerves and blood vessels, and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
Contains lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscle (pressure receptor)
Contains portions of hair follicles associated with thin skin
-
What is the function of the hypodermis?
Fat storage
Thermal regulation
Permits movement of skin
-
What is the hypodermis also referred as?
Subcutaneous tissue or superficial fascia

