-
Shelf life
-based on time required for the drug content to decrease to 90% of the label claim (t90 ) at the recommended storage temperature.
-
Expiration date
-the date placed on the container label of a drug product designating the time prior to which a batch of the product is expected to remain within the approved shelf life specification if stored under defined conditions, and after which it must not be used.
-
shelf life (expiration dating period)
-the time period during which a drug product is expected to remain within the approved shelf-life specification, provided that it is stored under the conditions defined on the container label
-
hydrolysis, oxidation, photolysis, thermal degradation, racemization
List some mechanisms of degradation?
-
rate law
The order of a chemical reaction is determined by ______
-
zero order
A ______ reaction is one in which the rate is independent on the concentrations of the reactants.
-
half-life
The _______ of a zero order reaction is dependent on initial concentration.
-
a
Fraction of drug lost changes over time.
a. zero order
b. first order
c. third order
-
a, c
Amount of drug lost over time is constant .
a. zero order
b. first order
c. second order
-
zero order
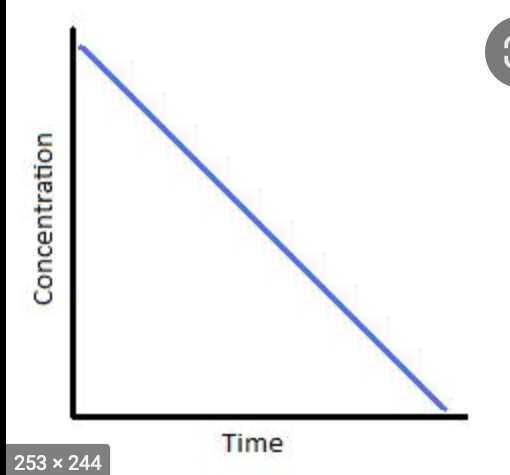
what reaction is this graph depicting?
-
first-order
A _____ reaction is one where the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of one of the reactants
-
first order
this unit applies to what reaction, time-1
-
zero order
concentration/time applies to what reaction?
-
first order
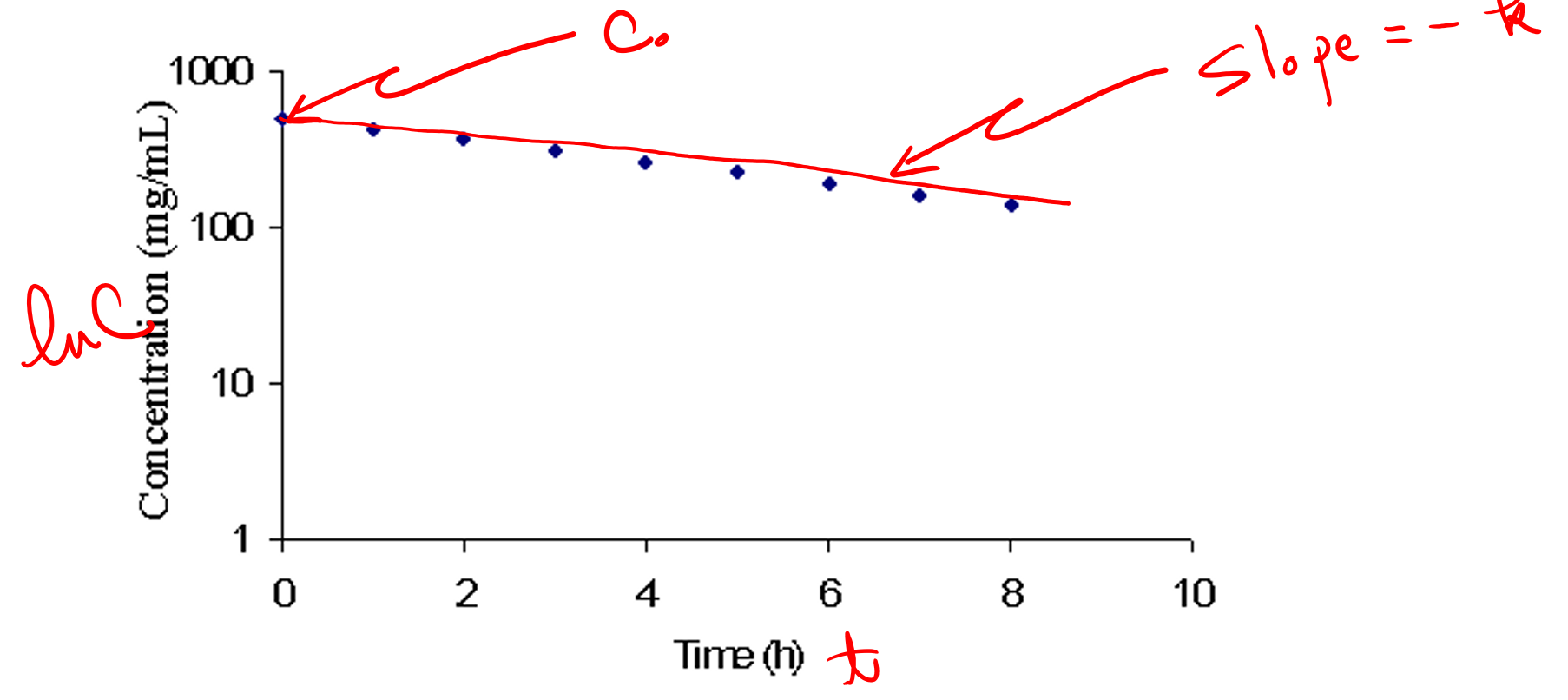
this graph applies to what reaction?
-
b
Amount lost over time is changing.
a. zero order
b. first order
c. second order
-
b
Fraction of drug lost over time is a constant.
a. zero order
b. first order
c. second order
-
b
Half life is independent of concentration and is thus a constant over time.
a. zero order
b. first order
c. second order
-
pseudo-first order; concentration of A doesn't change much
If the initial concentration of reactant A is much larger than concentration B, what type of reaction is this and why does this occur?
-
c
Drug loss over time remains constant as long as the reservoir has enough drug remaining.
a. pseudo- first order
b. second order
c. pseudo-zero order
-
pseudo zero order
The reaction kinetics are first order process but it mimics a zero order rate of drug loss
-
returns to 1st order
In regards to Pseudo-zero order, after all drug in reservoir is consumed, the reaction _____
-
second order
-reaction rate depends on the concentration of two reactants

