
Introduction to the CVS (Physiology)
Session summary This lecture will introduce some ideas about why we need a cardiovascular system. Some principles on how blood is transported and allocated to the different areas of the body will be covered. Important fundamental concepts such as cardiac output, blood flow and the pressure profile of blood as it flows through the system will be considered. Finally, basic outlines concerning the structure and functions of blood vessels and exchange of gasses and nutrients will be presented. Learning outcomes At the end of this session you will be able to: Explain the purpose of the cardiovascular system Understand the relationship between cardiac output and blood flow Appreciate the importance of blood pressure and changes of flow through the circulation Understand the basic structure & function of blood vessels
-
How much % of deaths is Cardiovascular disease responsible for in the UK?
27%
-
How many % of people in the UK suffer with cardiovascular disease?
7.6%
-
What is the annual cost of treating cardiovascular disease?
10 billion
-
As early as 1961, CVS disease made up ____% of total deaths
50%
-
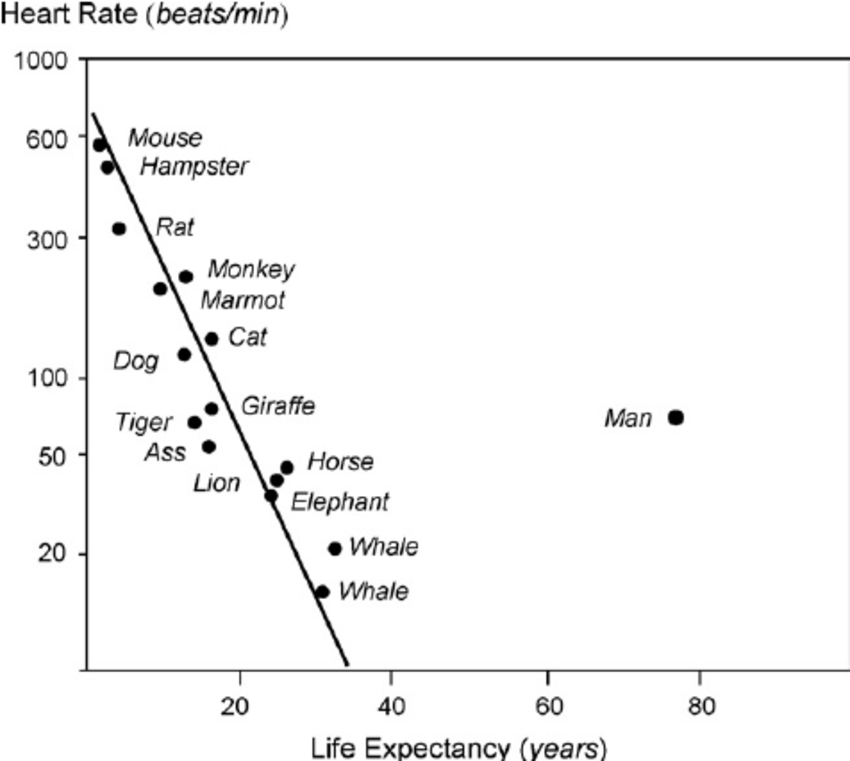
Why are humans an outlier when it comes no.of heart beats a second against other species of animal?
Humans have evolved to be highly efficient in terms of energy usage
-
What does 'Cardio' of the word cardiovascular mean?
Heart
-
What does 'Vascular' of the word cardiovascular mean?
Vasculature (blood vessels)
-
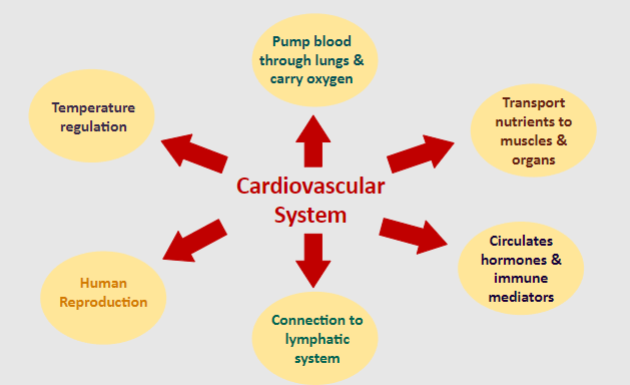
What are the main responses of the cardiovascular system?
-
What is the definition of passive diffusion?
Is the random, undirected thermal movement of molecules
-
The time needed to diffuse a given distance is proportional to what?
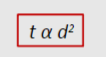
The square of the distance
-
A picture summary of the distance, time and example of systems:

-
Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart from the ______ via what? And is pumped through ________, how?
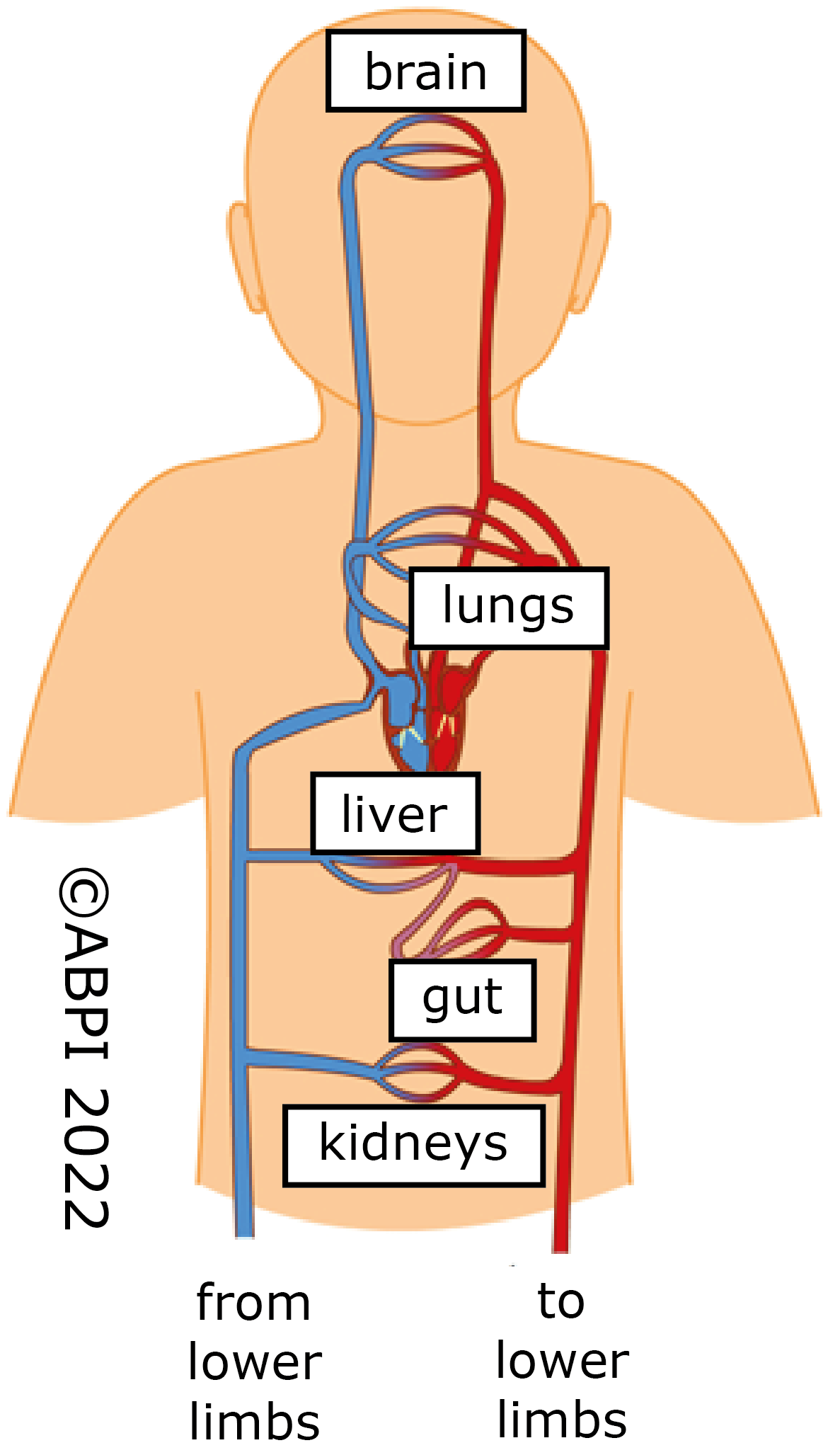
-From the veins via the right atrium
-Pumped through the lungs by the right ventricle
-
Oxygenated blood returns to the heart from the ______ via what? And is pumped through ________, how?
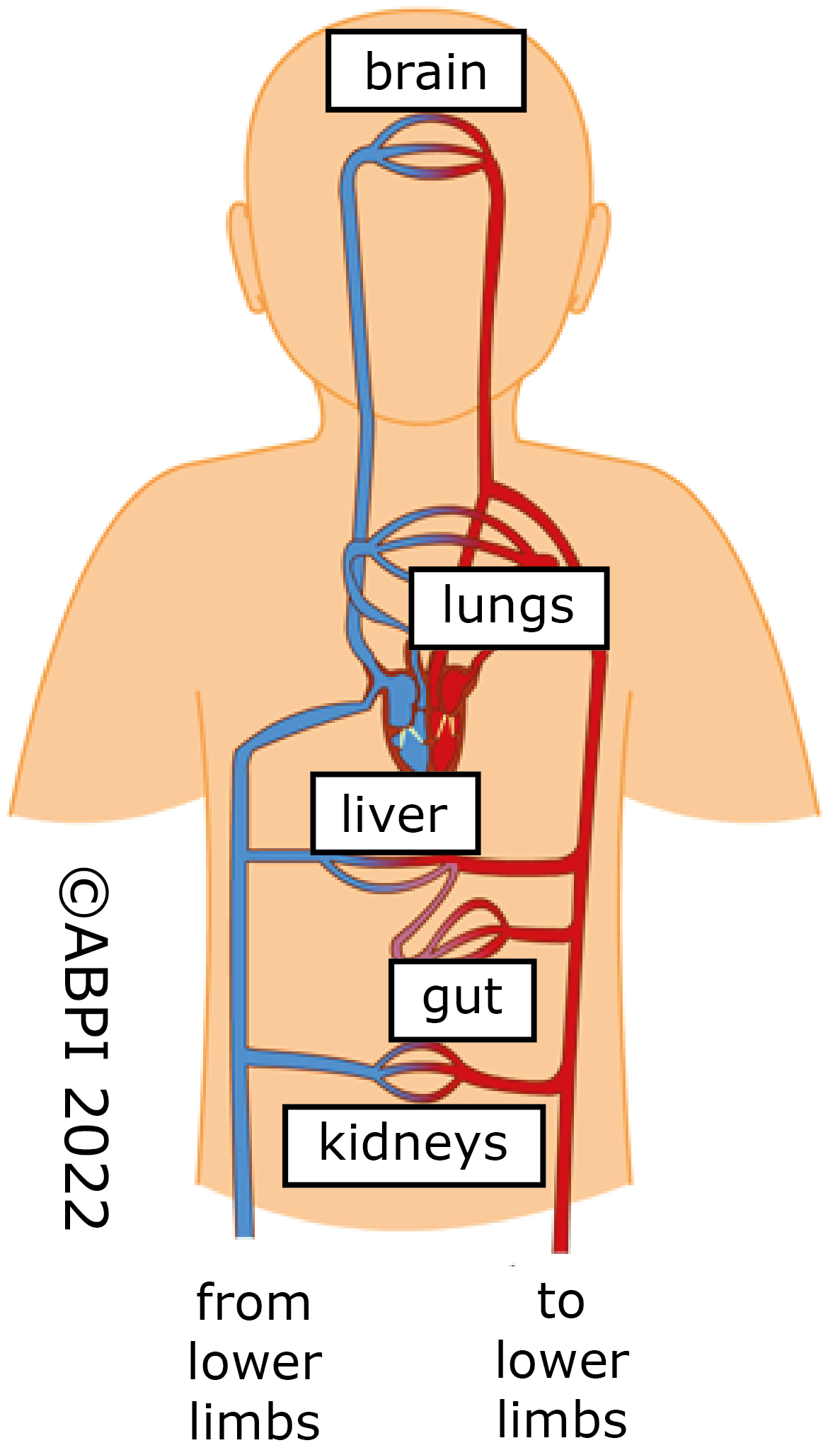
-From the lungs via the left atrium
-Pumped through the body by the left ventricle
-
Output of blood at high pressure creates a pressure difference with distant blood vessels.... such as the Aorta and Large veins
State the estimated mmHg value of the aorta and large veins at high blood pressure
Aorta >100 mmHg
Large veins 5-10 mmHg
-
Picture demonstrating the systolic and diastolic format in study of the CVS
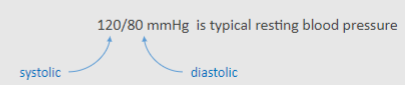
-
What is the equation for cardiac output?
Cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume
-
How do we figure out the maximum heart rate typically?
Maximum heart rate = 220 – Age
-
What are the 3 general steps of cardiac output?
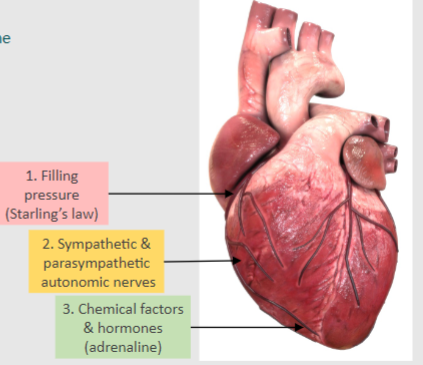
1. Filling pressure (Starling’s law)
2. Sympathetic & parasympathetic autonomic nerves
3. Chemical factors and hormones (adrenaline)
-
How much blood flows through the heart at rest, a minute?
70/min x 70 ml = 5 litres/min
-
How much blood flows through the heart at exercise, a minute?
180/min x 120 ml = 20 litres/min
-
Blood flow is proportional to what?

To pressure across blood vessel
-
Blood flow is inversely proportional to what?

To resistance of blood vessel
-
Blood proportionality basically means that an increase of resistance leads to a.....?
Decrease in blood flow
-
What is the equation of blood flow that includes resistance?
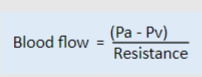
-
What does mmHg mean? And is a measurement for what?
-Millimetres of mercury
-Unit of pressure measurement
-
Venous pressure (Pv) varies with location & posture, and is generally around a value of what mmHg?
3-12 mmHg
-
What do Arterioles (resistance vessels) Control?
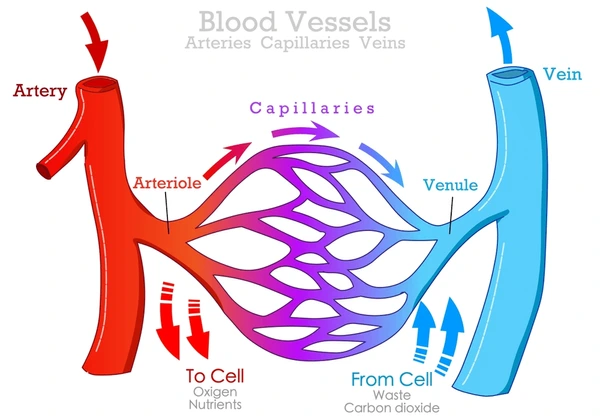
Control arterial BP and regulate local blood flow
-
What do Arteries (elastic vessels) Control?
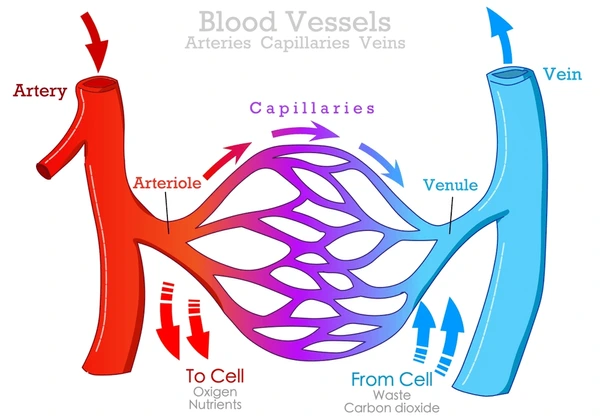
Accommodate stroke volume to convert ejection into continuous flow
-
What do Venules & Veins (capacitance vessels) Control?
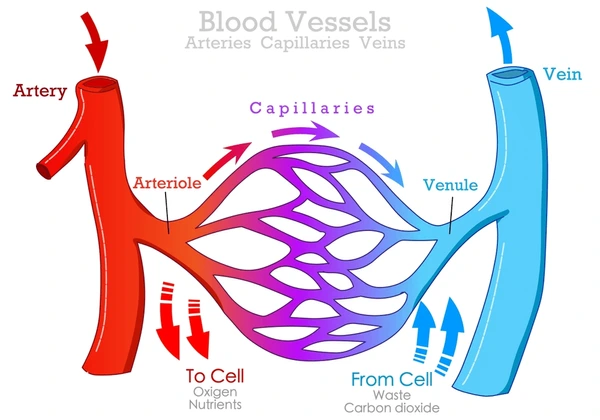
Control filling pressure of the heart & provide a reservoir of blood
-
What do Capillaries (exchange vessels) Control?
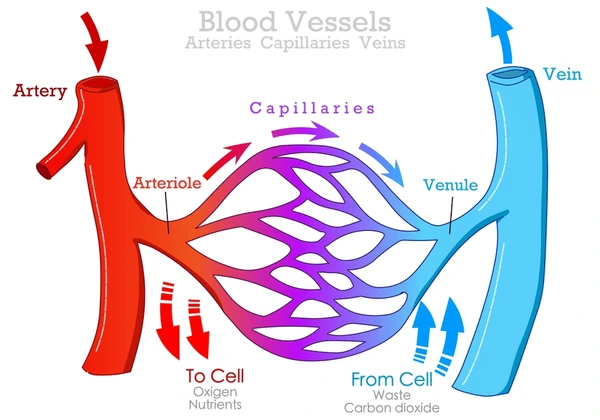
Nutrient delivery to cells tissue water & lymph formation removal of metabolic waste
-
Picture demonstrating Cardiac output distribution at rest of the components of the body:
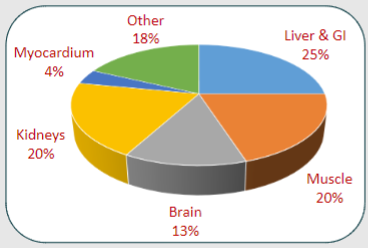
-
Picture demonstrating Oxygen consumption at rest of the components of the body:
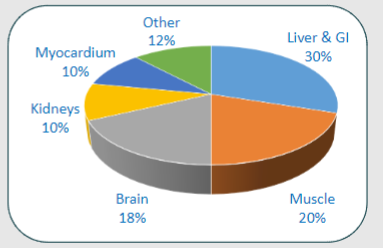
-
Arterioles are resistance vessels and control arterial BP by....
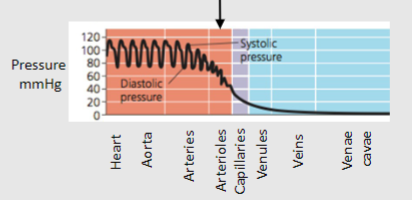
Determining total peripheral resistance (TPR)
-
TPR stands for Total Peripheral Resistance, what does it refer to?
It refers to the overall resistance to blood flow offered by the entire systemic circulation, excluding the pulmonary circulation
-
Why does blood slow down in capillaries?
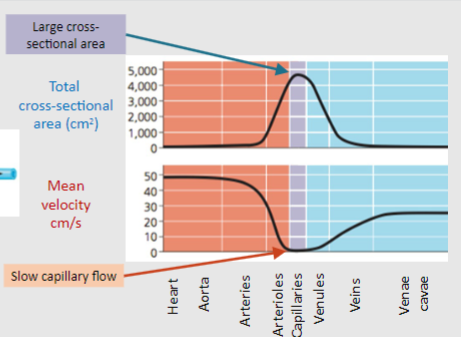
Allows gaseous/nutrient exchange to occur
-
What is the Equation for blood velocity?
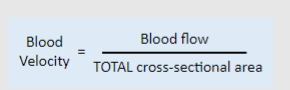
-
Picture demonstrating the Distribution of blood volume across the body:
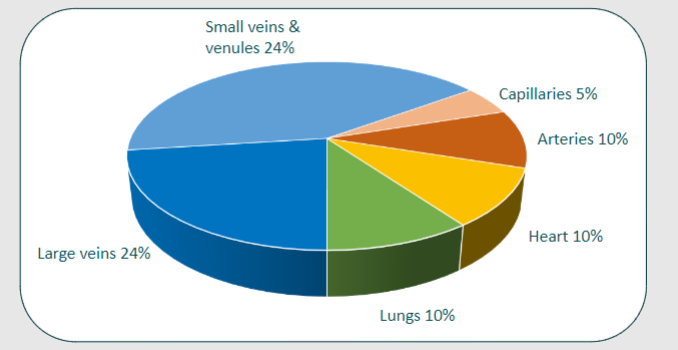
-
Systemic veins & venules serve as a reservoir holding how much volume as a percentage?
65%
-
Sympathetic nerves in the tunica adventitia release noradrenaline, which stimulates what receptor and leads to what?
α1 receptors leading to vasoconstriction
-
Endothelium releases nitric oxide which relaxes the vesselsleading to what?
Vasodilation
-
State the parts of the artery and vein:
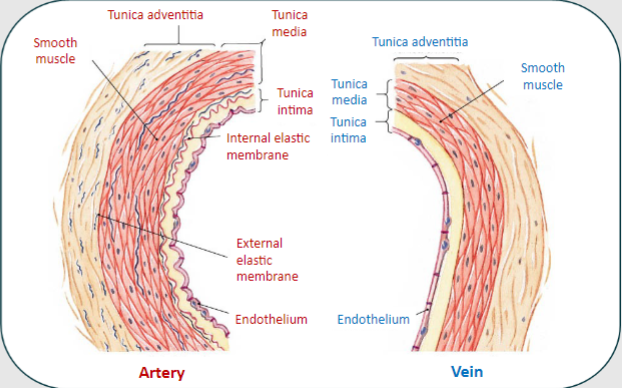
-Tunica intima
-Tunica media
-Tunica Adventitia
-
What is the tunica intima?
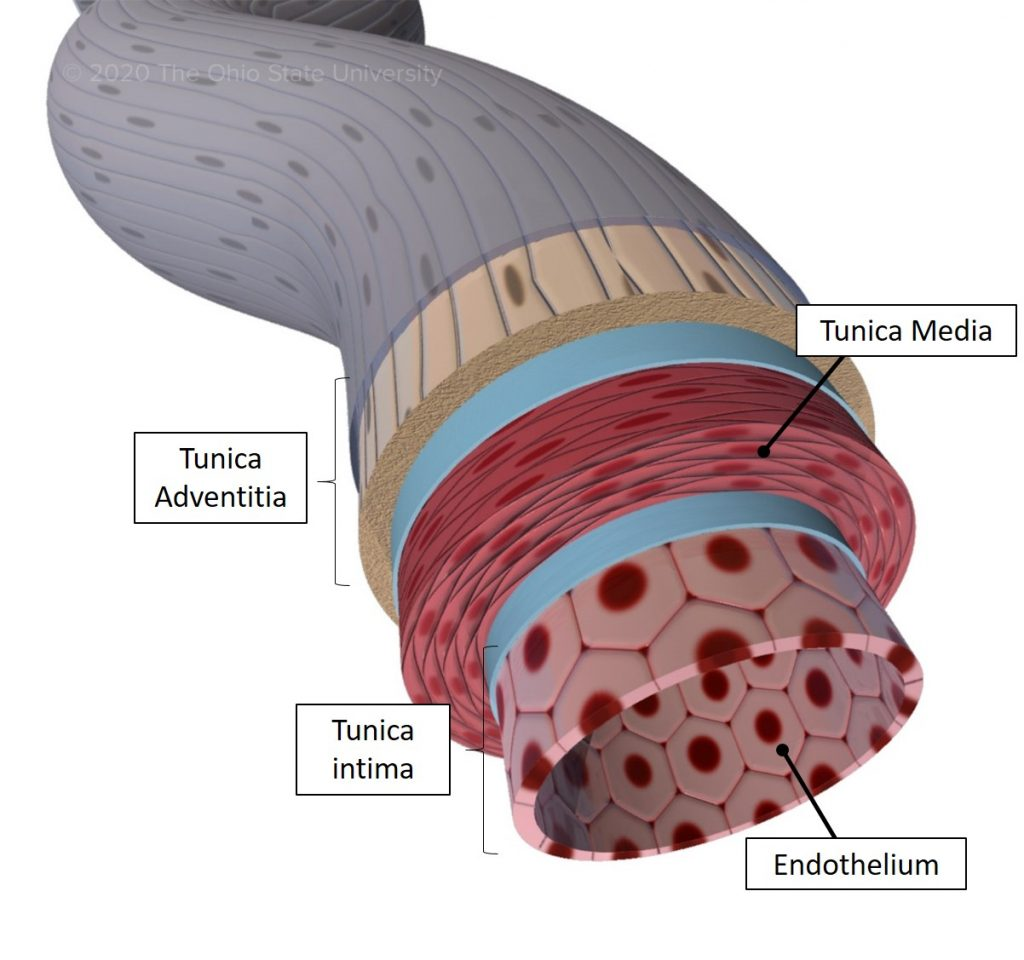
– Endothelial layer
Controls vascular permeability, modulates vasoconstriction, site of angiogenesis, regulates coagulation
-
What is the tunica media?
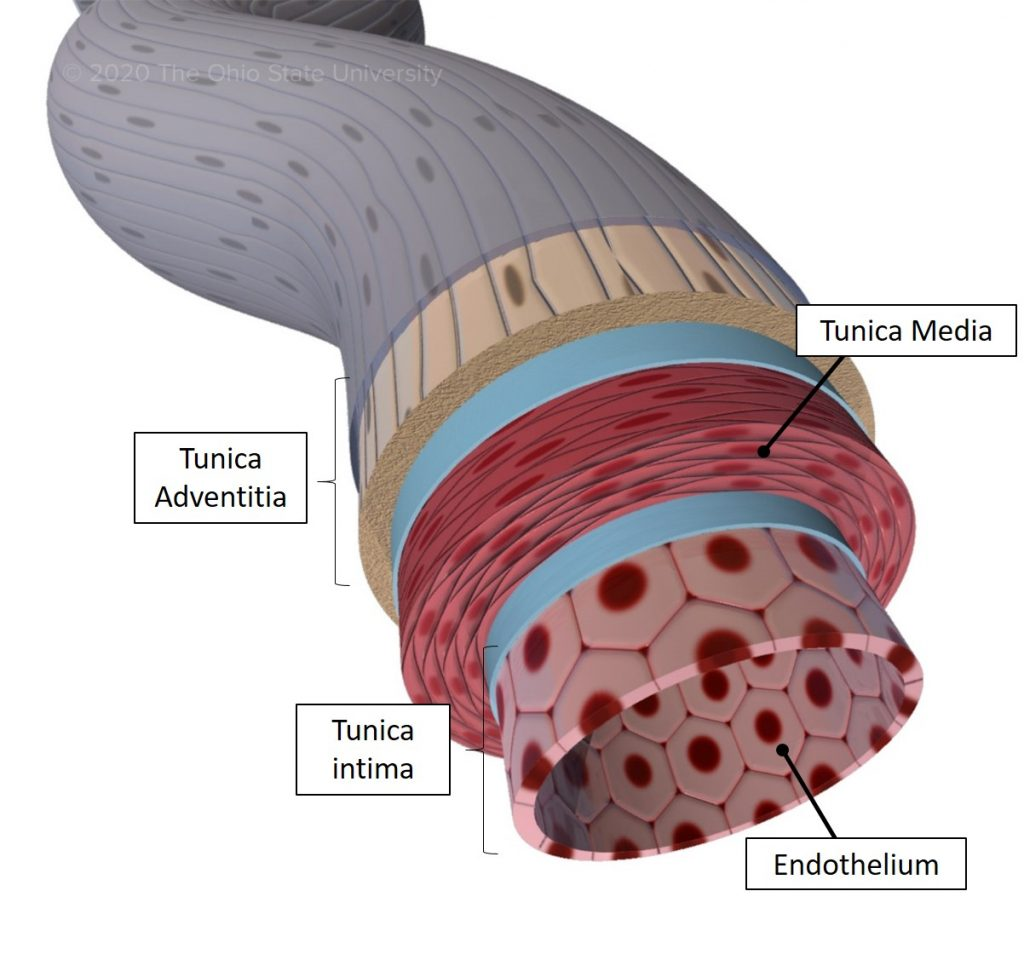
– Smooth muscle
Embedded in extracellular matrix regulates vasoconstriction and vasodilatation of vessels
-
What is the tunica adventitia?
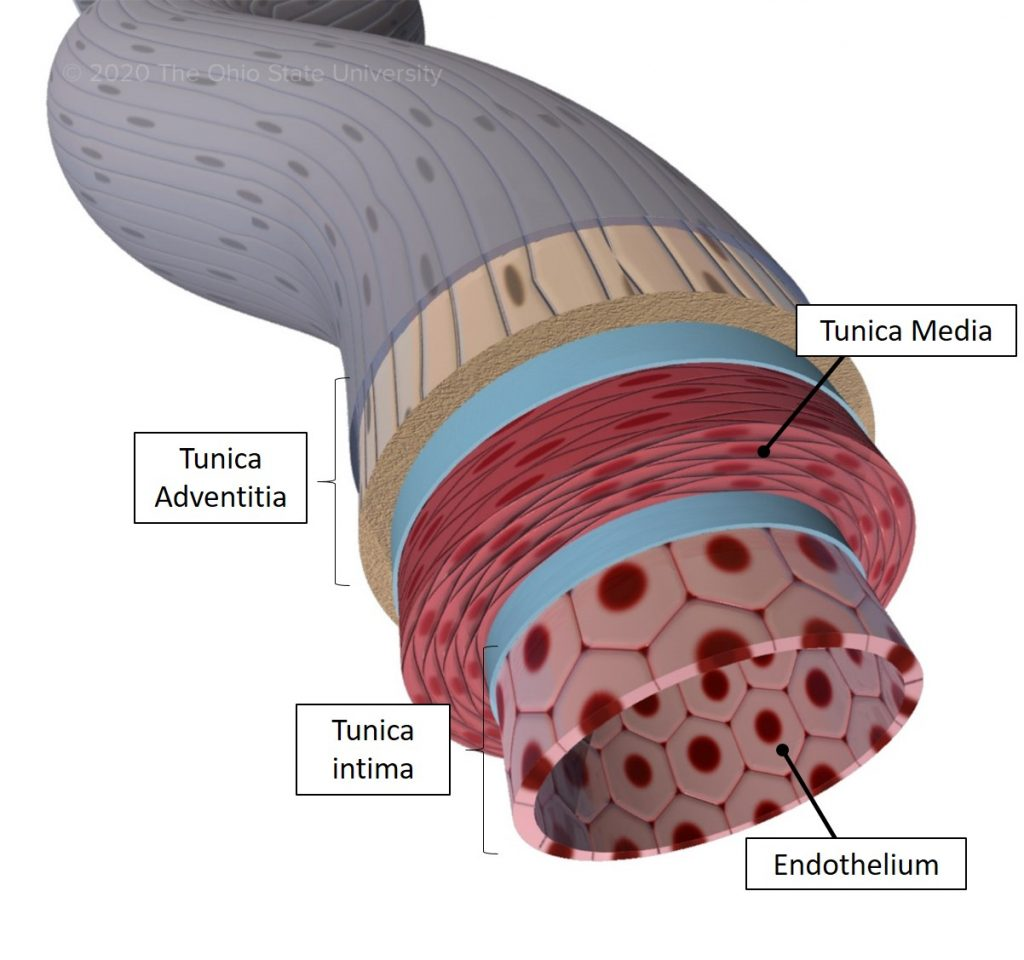
– Collagenous material
Fibroblasts, innervated layer

