-
How many parts make up blood?
4
-
What are these parts? And what are their percentage amounts?
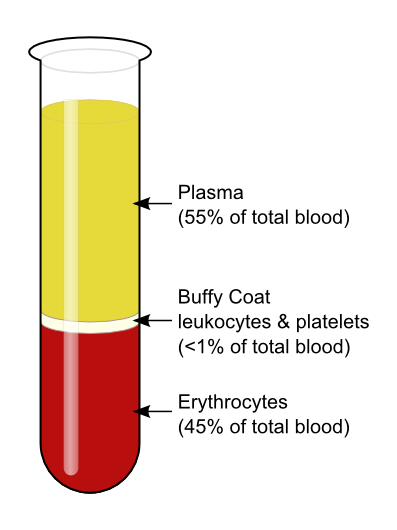
-Red blood cells (44%)
-White Blood cells (less than 1%)
-Platelets (less than 1%)
-Plasma (55%)
-
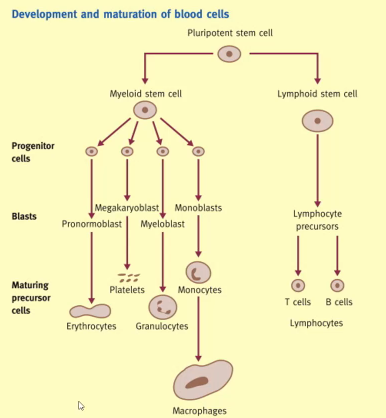
List the stem cells associated with each blast, associated with each matured precursor cell accordingly
-
What is the average life span of an RBC?
120 days
-
Hb binds to what?
Oxygen
-
Do RBCs (Erythrocytes) have nuclei? DNA, RNA or mitochondria?
No, none of these
-
What shape is an RBC (Erythrocytes)?
Biconcave discs
-
Haemoglobin is a protein... what?
-protein tetramer
-
How many polypeptide chains make up haemoglobin, and what are these chains?
-4 chains
-2x alpha
-2xbeta
-
Each globin chain carries a what?
Haem molecule
-
Haem holds what molecule?
A ferrous (Fe++) iron atom
-
When it comes to oxygen binding with the ferrous iron atom, is it reversible or irreversible?
reversible
-
What are the granulocytes? And what cells are granulocytes?
Granulocyte-Prominent cytoplasmic granule
-Neutrophil
-Eosinophil
-Basophil
-
What proportions of the granulocytes make up the WBC (white blood cells)?
-Neutrophil (40%-60% of wbc)
-Eosinophil (1-4% of wbc)
-Basophil (<1% of wbc)
-
What are the characteristics of the Neutrophil? (2)
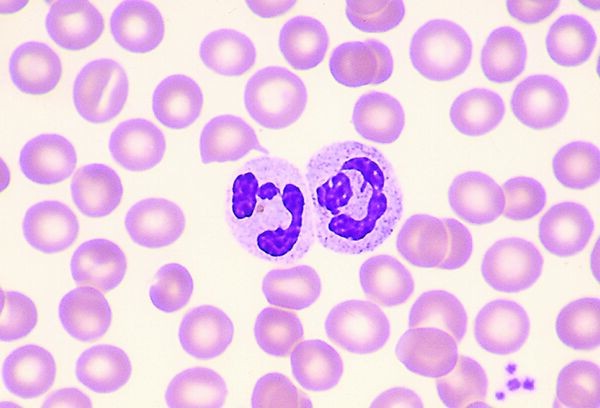
-Polymorphonuclear:irregular, multi-lobed nucleus (increases with age)
-Weakly staining cytoplasmic granules
-
What are the characteristics of the Eosinophil? (2)
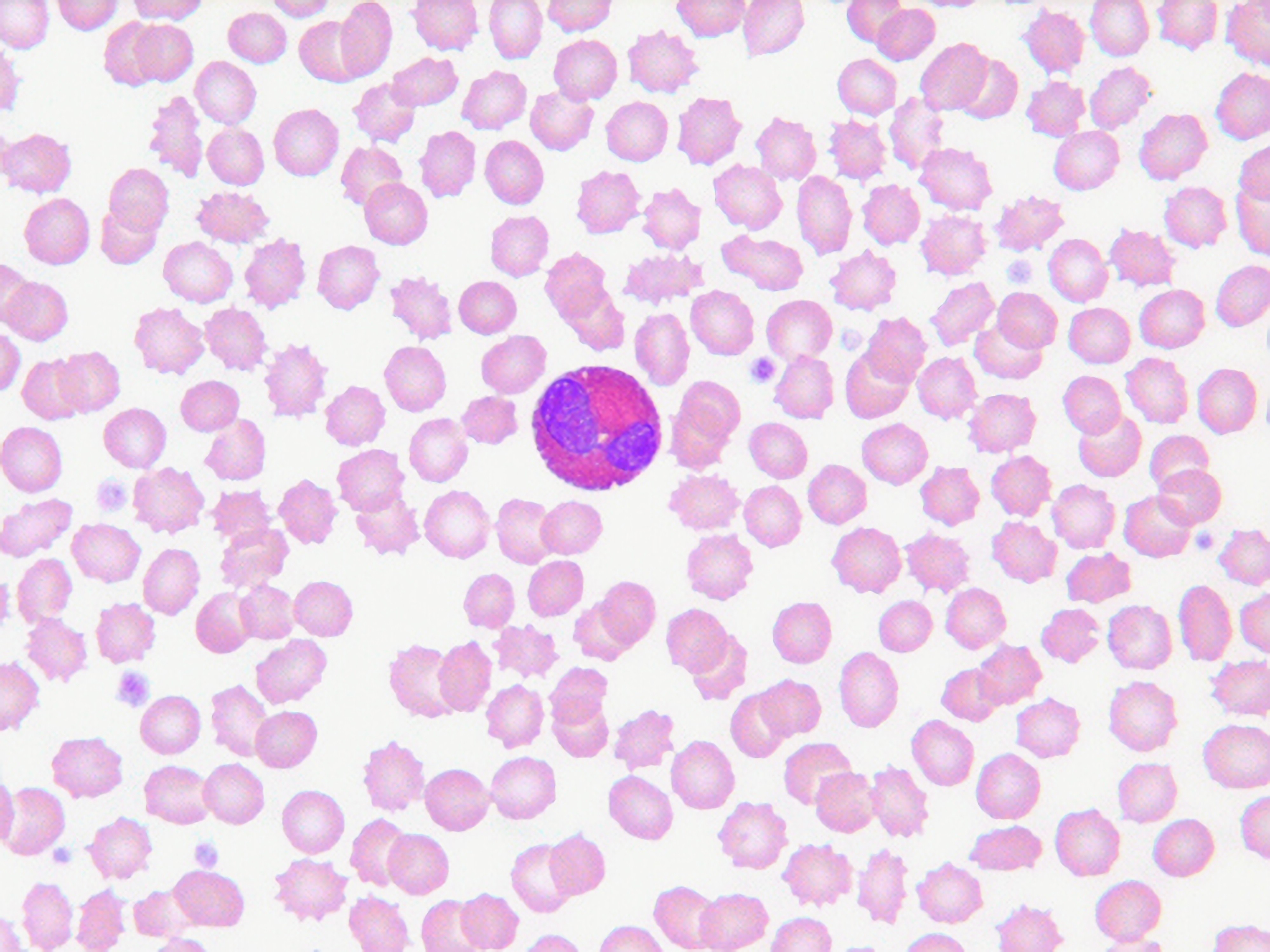
-Cytoplasmic granules stain red with eosin
-Generally have two-lobed nucleus
-
What are the characteristics of the Basophil? (2)
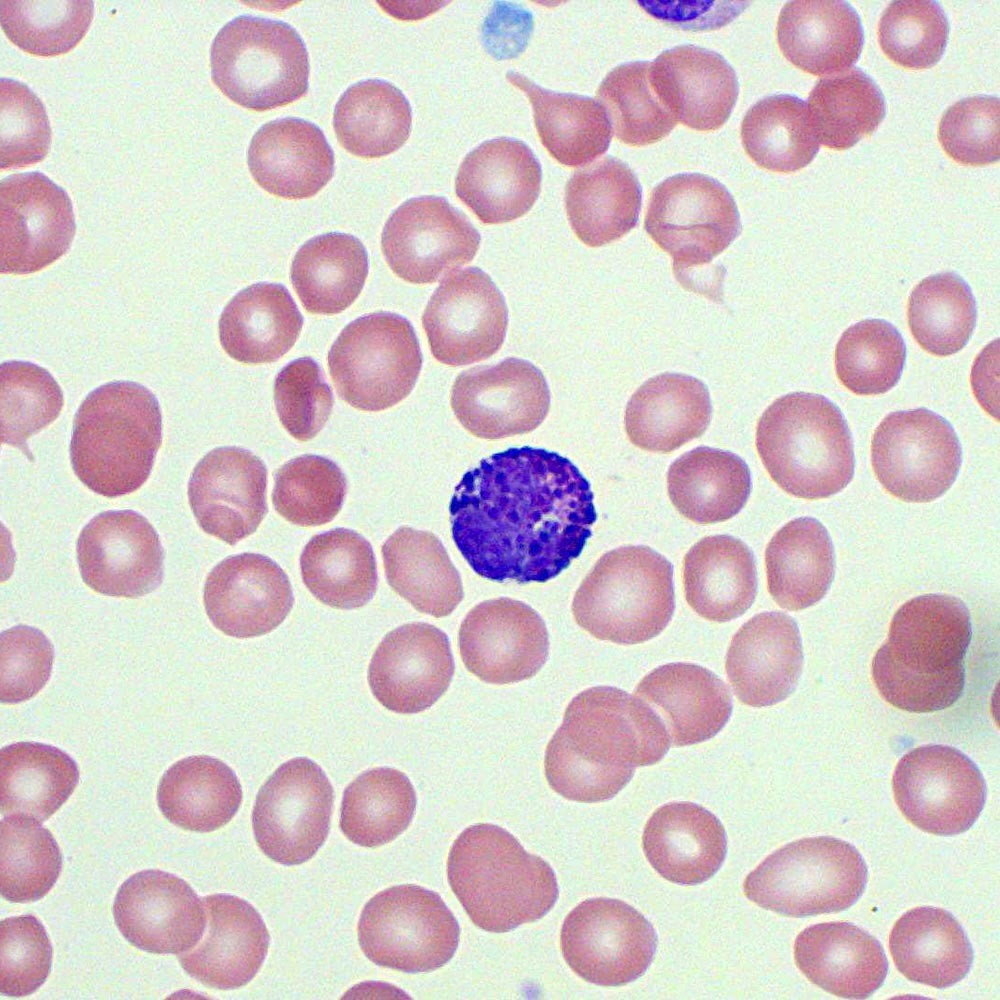
-Cytoplasmic granules stain blue/purple with basic dyes
-Nucleus generally two-lobed but difficult to see
-
What are the agranulocytes? And what cells are agranulocytes?
Agranulocytes-lack visible cytoplasmic granules
-Lymphocytes
-Monocytes
-
What proportions of the agranulocytes make up the WBC (white blood cells)?
-Lymphocytes (25% of wbc)
-Monocytes (10% of wbc)
-
What are the characteristics of the Lymphocytes? (3)
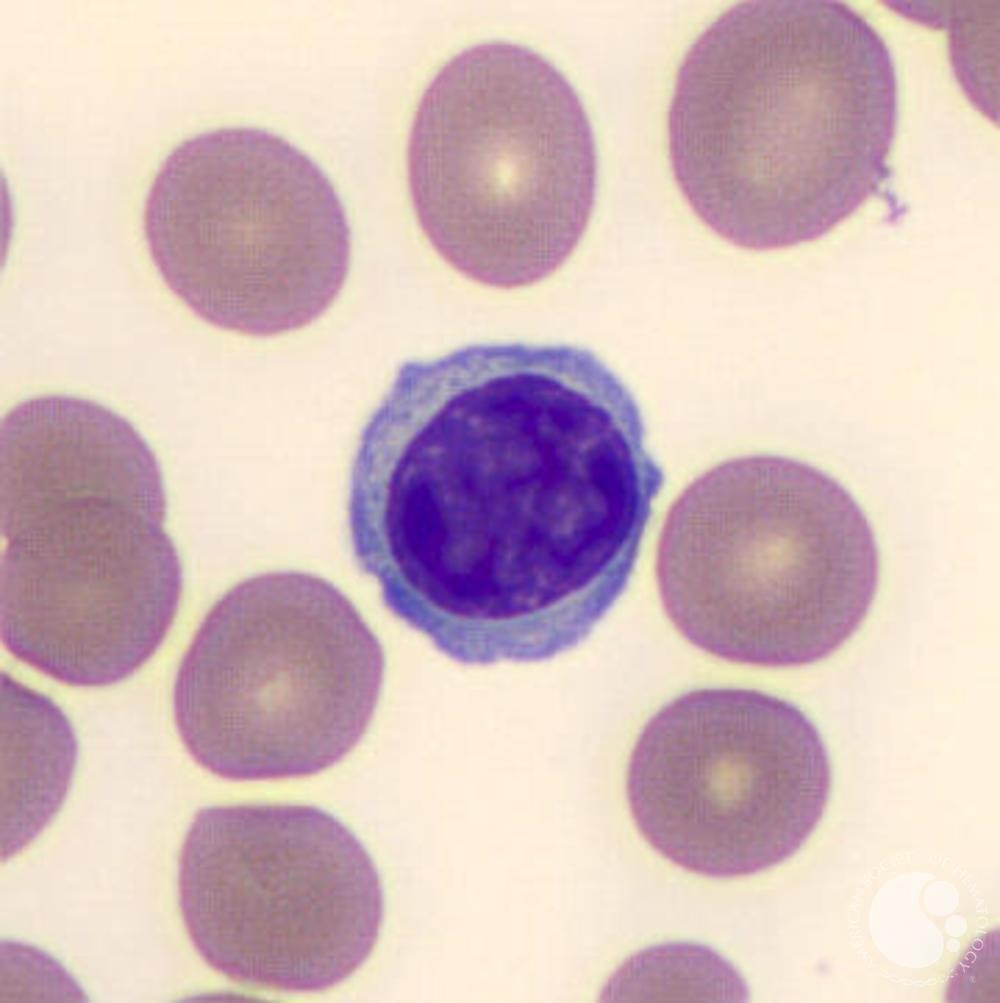
-They are part of the immune system
-2 main types - T- and B- Lymphocytes
-Spherical cells with a single, often large nucleus which occupies much of the cells volume
-
What are the characteristics of the Monocytes? (3)
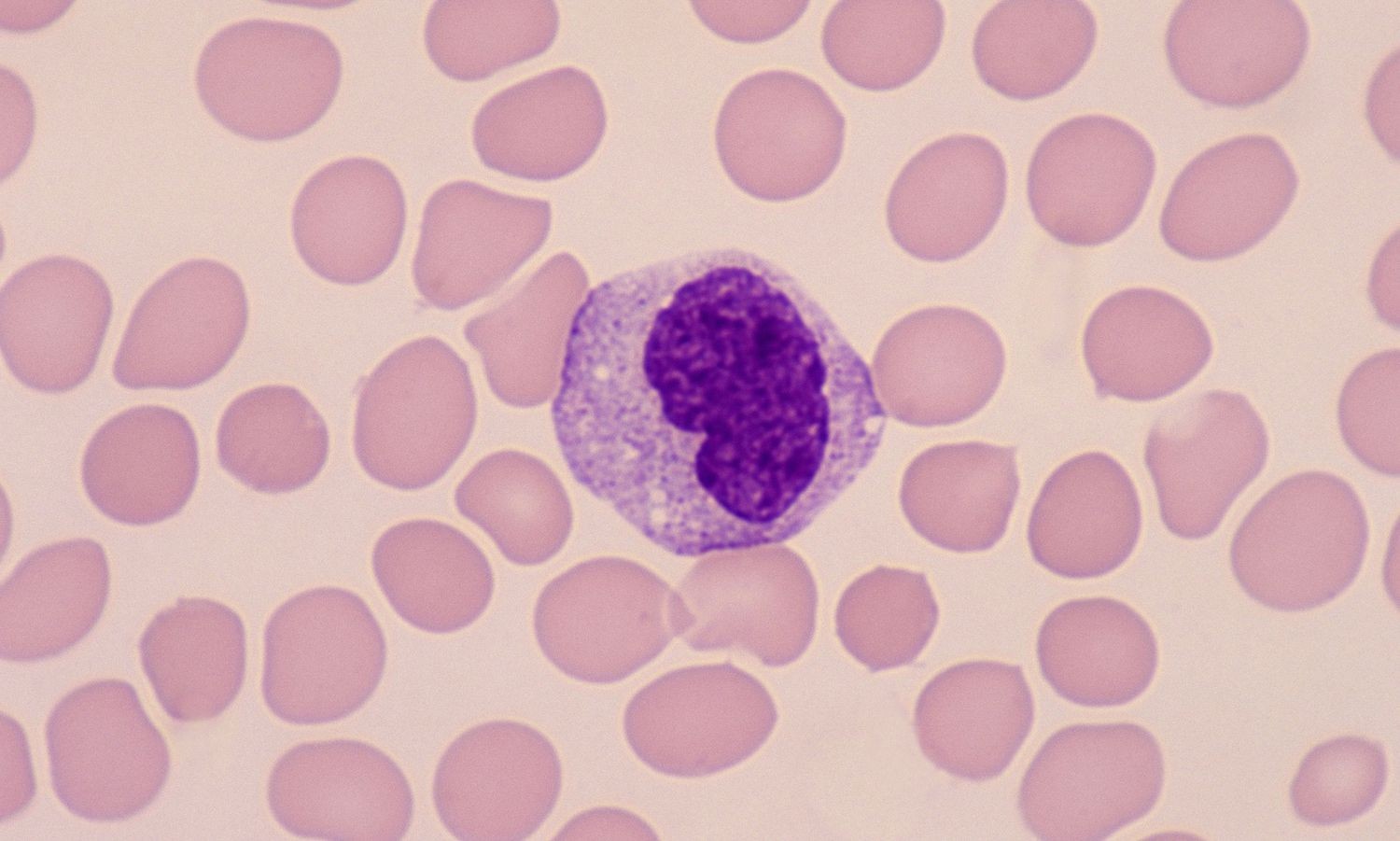
-Largest type of wbc
-Large regular nuclei
-Has indented horseshoe-shaped nucleus
-
Are leukocytes colourless?
Yes
-
What's another name for platelets?
Thrombocytes
-
What are considered leukocytes?
-Lymphocytes
-Monocytes
-Neutrophil
-Eosinophil
-Basophil
-
Do platelets have... nuclei, membranes or granules?
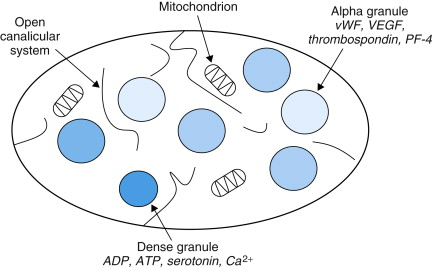
-No nuclei
-They are membrane bound
-Contain granules
-
What are the functions of RBC when related to transport? (4)
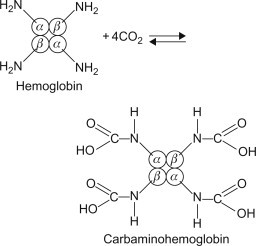
-RBC transport oxygen bound to Hb from lungs to body tissues
-Help in the removal of CO2 from body tissues to lungs
-Buffering action, maintains blood pH as it changes from oxyhaemoglobin (carrying o2) to deoxyhaemoglobin (without o2)
-Carbaminohaemoglobin (HbCO2)-CO2 binds non-covalently to globin chain of Hb and transports CO2 in blood (20%)
-
What is the colour of haemoglobin when fully saturated with O2?
Bright red
-
What is the colour of deoxyhaemoglobin when lost all O2?
Dark red
-
What is pulse oximetry?
Will determine is a patient is hypoxic (does not have enough O2), by measuring the colour of haemoglobin
-
How many Hb molecules are there in each RBC?
300,000,000 Hb
-
What are the functions of WBC when related to defence (immunity) for Neutrophils? (2)
-Phagocytose and kill bacteria and fungi
-They are the main mediators of innate immunity
-
What are the functions of WBC when related to defence (immunity) for Lymphocytes? (3)
-They are the main mediators of adaptive (acquired) immunity
-Produce antibodies
-Kill virus infected cells
-
What are the functions of WBC when related to defence (immunity) for Monocytes? (1)
-Phagocytosis of dead cells and pathogens
-
What are the functions of WBC when related to defence (immunity) for Eosinophils? (2)
-Kill parasites
-Involved in allergic responses
-
What are the functions of WBC when related to defence (immunity) for Basophils? (3)
-Kill parasites
-Involved in allergic responses
-Involved in inflammation
-
What are the functions of WBC when related to defence (haemostasis) for platelets? (5)
-Major role:primary haemostasis
-Recognise damage at a blood vessel wall
-Form a platelet plug
-Prevent/stop bleeding
-Platelet plug stops bleeding-but insecure and temporary
-
What is plasma?

The fluid component of the blood
-
What are the components of plasma and state their proportions %? (4)
-Water (92%)
-Plasma proteins (6-8%) (e.g. albumin, globulin)
-Electrolytes (Na+. Cl-) (<1%)
-Other components:glucose, amino acids, hormones (thyroxine, cortisol); waste (urea); blood gases (e.g. CO2) all make up <1%
-
What is serum?
The fluid left after blood clotting
-
What should be used if a blood test requires unclotted blood?
-An anticoagulant r.g. EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)
-
Other tests work better with plasma than serum......... Is this true?
No, tests usually work better with serum rather than plasma. e.g. protein electrophoresis
-
What are the functions of Plasma when related to transport? (4 +examples)
-Plasma proteins transport nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and vitamins absorbed from the digestive tract to different parts of the body.
-Transport of respiratory gases
-Removes nitrogenous waste products produced after cellular metabolism for excretion
-Carry substances which are poorly soluble in water, bound to albumin;
Examples:
+Albumin acts as a general purpose carrier
+Globulin also acts as a specialised carrier for metal ions e.g. Ca++, Fe++, Cu++, and hormones released into the blood to their target organs- e.g. TBG transports thyroxine
+Transferrin transports iron
-
What are the functions of Plasma when related to defence (immunity)?
-Contain Immunoglobulins (lg)
+Made by B-Lymphocytes act as body's defence against bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites
-Complement proteins
+Kill bacteria and other pathogens
-
What are the functions of Fibrinogen when related to defence (Haemostasis)?
+Fibrinogen plays a major role in blood clotting along with other procoagulants like thrombin and factor X
-
What is homeostasis?
Keeping the internal environment of the body constant
-
What is regulated by the plasma in terms of homeostasis? (2)
-Regulation of acid-Base balance:
(Through their buffering action, maintaining a pH at 7.4)
-Regulation of body temperature:
-
LFTs are an abbreviation of?
Liver Function Tests
-
U and Es are an abbreviation of?
Urea and Electrolytes
-
How do you find packed cell volume (PCV/ haematocrit (Ht)), and what is the normal value?
PVC= vol of cells / total volume
normal value=0.4-0.5
-
What does the Full Blood Count (FBC) include? And what are do they mean? (4)
-Haemoglobin concentration (Hb in g/l)
+Overall concentration of haemoglobin in the blood (used to diagnose anaemia)
-Mean (red) cell volume (MCV)
+Size of RBCs
-Mean (red) Cell Haemoglobin Content (MCHC)
+How much Hb in each red cell
-Haematocrit (Ht or Hc)
+Low Ht may indicate anaemia, large number of WBC due to infection
+Higher Ht-dehydration, polycythaemia Vera
-
What percentage of total plasma proteins are globulins?
38%
-
What percentage of total plasma proteins are albumins?
55%
-
What percentage of total plasma proteins are fibrinogens?
7%


