-
What is histology?
The study of tissues and their structure
-
What is Tissue structure?
How cells combine together with extracellular material and each other to form a tissue
-
What is Cellular structure?
How a cell is shaped, and how the components inside cells are organised to support that cells specific function
-
What is subcellular structure?
Detailed analysis of organelles and inclusions
-
What is Histochemical structure?
Molecular analysis of cellular structure
-
What are the four basic tissues of the human body?
-Epithelial tissues
-Connective tissues
-Muscle tissues
-Nerve tissues
-
All tissues of the body develop from the three primary cell layers that form the embryo....what are these three layers?
-Ectoderm
-Mesoderm
-Endoderm
-
Ectoderm develops into what tissue?
-Nervous tissue and Epithelial tissue
-
Mesoderm develops into what tissue?
-Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue and Muscle tissue
-
Endoderm develops into what tissue?
-Epithelial tissue
-
What is Epithelial tissue, and what are the characteristics?
-Epithelial tissue is made of cells arranged in a continuous sheet with one or more layers; has apical and basal surfaces
+A basement membrane separates the epithelial layer from the underlying connective tissue
+Two types of epithelial tissues: 1) Covering and lining epithelia; or the PROPER epithelium 2) GLANDULAR epithelium (endocrine and exocrine)
+The number of cell layers and the shape of the cells in the top layer are used to classify epithelium
-
What is simple epithelium?
One cell layer
-
What is stratified epithelium?
Two or more cell layers
-
What is pseudostratified epithelium?
Cells are all anchored to the basement membrane (i.e. one cell layer) but not all cells reach the apical surface (nuclei do not align, does not look like one cell layer)
-
What are 3 possible shapes of the top layer of cells?
-Cuboidal
-Columnar
-Squamous
-
Picture demonstrating the types of epithelium
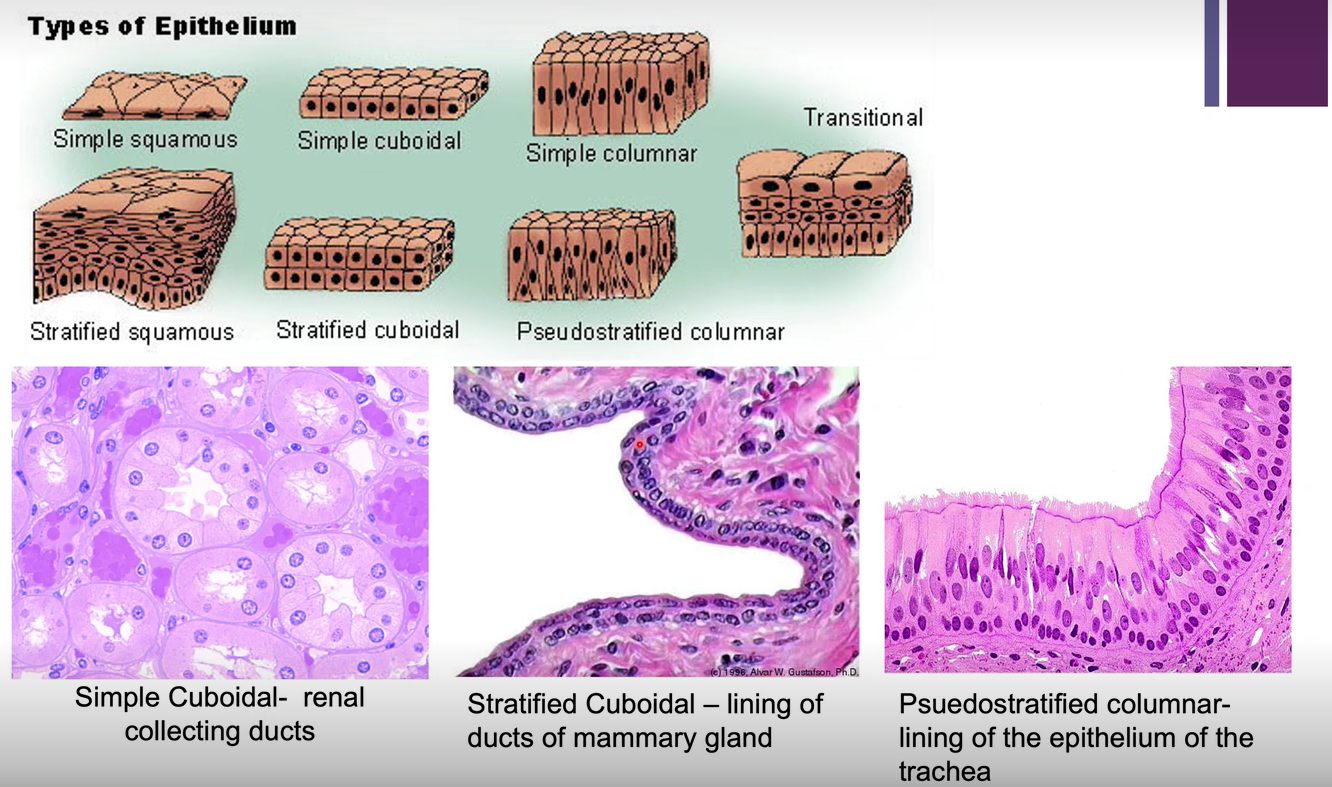
-
What is Connective tissue, and what are the characteristics?
-"connective tissue" is a term given to several body tissues that connect, support, and help bind other tissues
-There are two main groups: 1) Connective tissue proper; loose connective tissue (areolar, adipose, reticular)
2) Specialised connective tissue; types include: dense regular, irregular and elastic connective tissue
-Contains:
+Many different cell types including; fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells and adipocytes
+Connective tissue matrix made of two materials: 1) ground substance-proteins and polysaccharides; 2)fibres- reticular, collagen and elastic.
-
What is loose connective?
Fibres and many cell types in gelatinous matrix found in skin and surrounding blood vessels, nerves and organs
-
What is Dense collective?
Bundles of parallel collagen fibres and fibroblasts, found in tendons and ligaments
-
Picture summarising connective tissue
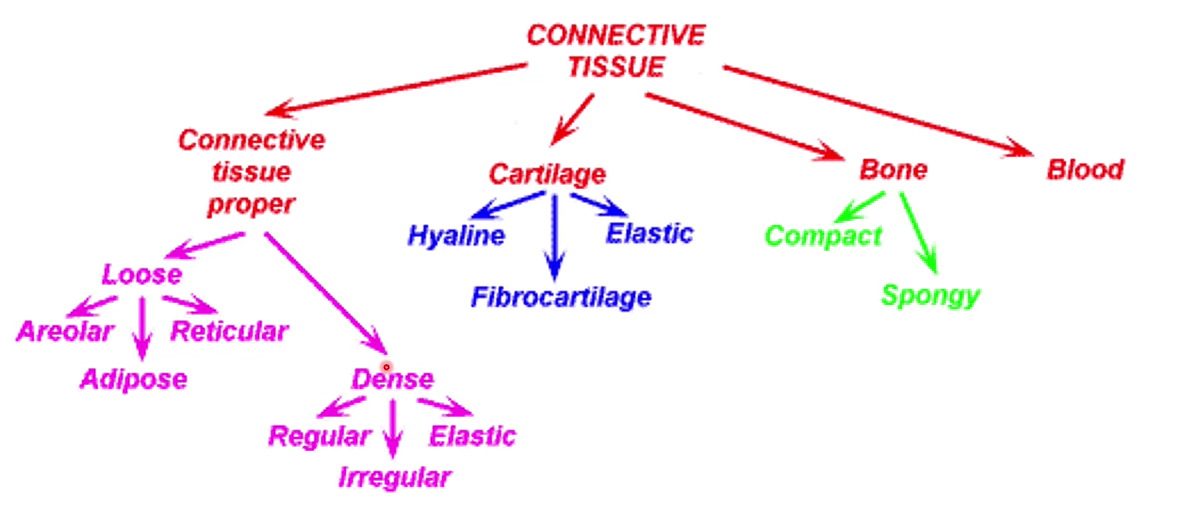
-
What is cartilage? What are is components?
Cartilage is a strong, flexible connective tissue that protects your joints and bones
Cartilage is made of two main components: 1) collagen and elastin fibres embedded in a matrix of glycoproteins; 2) cells called chondrocytes.
-
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrous
-
What is Hyaline cartilage?
The weakest, most abundant type. Found at the end of long bones, and structures like the ear and nose
-
What is Elastic cartilage?
Maintains shape, branching elastic fibres distinguish it from hyaline
-
What is Fibrous cartilage?
Strongest type, has dense collagen and little matrix, found in pelvis, skull and vertebral discs
-
Picture demonstrating the structures of these differing cartilage
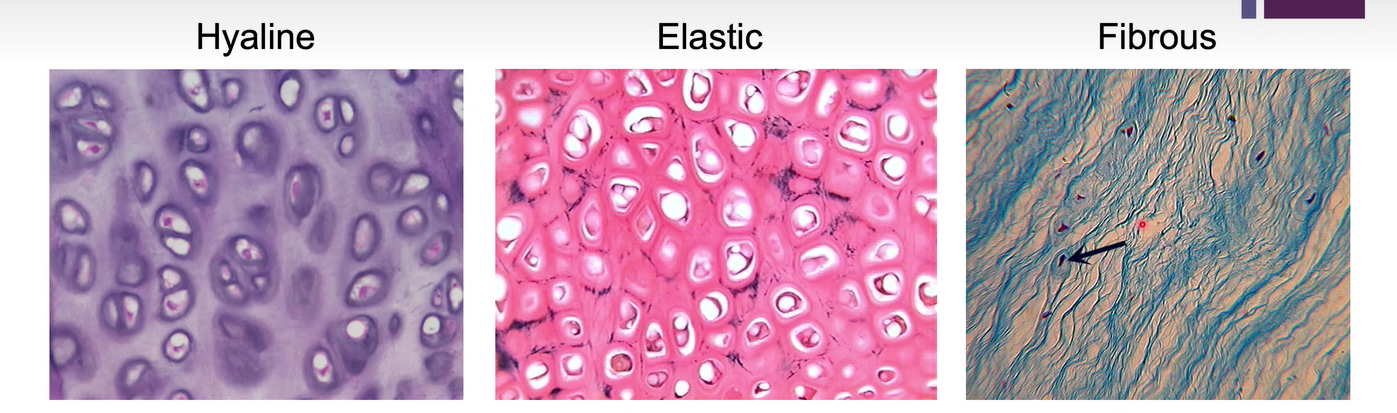
-
What is bone? What about bone development? Describe mature bone?
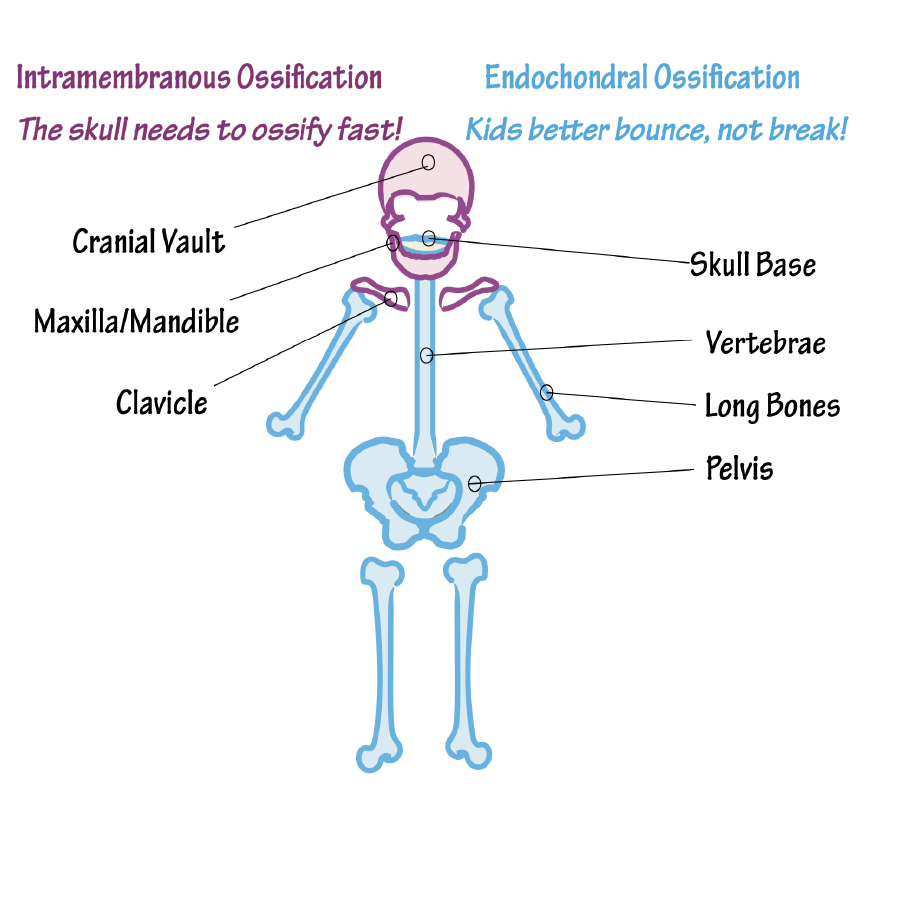
-Bone is composed of bone cells- osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes and osteoclasts-suspended in a matrix consisting of collagen fibres and minerals
+Bone development can be 1) Membranous-as in flat bones clavicle or mandible; 2) Endochondral - as in limb and vertebral column bones.
+Mature bone may be 1) Compact-concentric circular layers (lamellae) organised in lacunae and a central canal (Harvesian system); 2)Trabecular-slender interlacing parallel lamellae with marrow within the spaces
-
Picture demonstrating compact vs trabecular bone
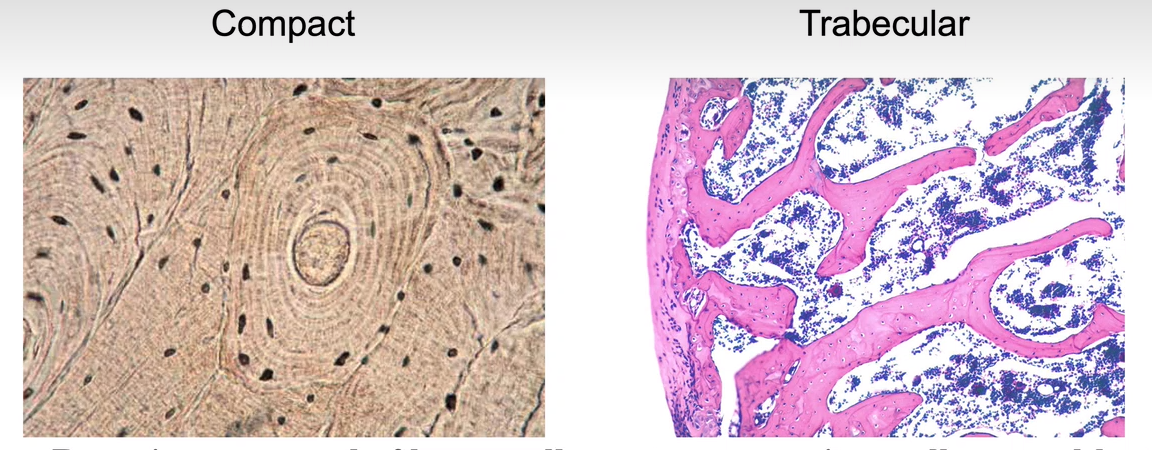
-
What is muscle tissue?
The principle functional unit of muscle tissue is the muscle fibre. There are also some satellite cells (stem cells) with capacity to develop into new muscle fibres
-
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
-Skeletal
-Cardiac
-Smooth
-
What is skeletal muscle?
Voluntary, striated, striations perpendicular to the muscle fibres, and it is mainly found attached to bones. Organised in myofibres with nuclei peripherally located. Forms a lined up banding pattern from one cell to another when observed longitudinally
-
What is cardiac muscle?
Involuntary, striated, branched and has intercalated discs. Cells smaller than skeletal muscle with nuclei centrally located.
-
What is smooth muscle?
Involuntary, non-striated, spindle shaped and is found in blood vessels and the GI tract. Cells vary in size and have a fusiform shape. Nuclei observed in different positions
-
What is the nerve tissue?
Constitutes the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Consists of two main functional cell types: 1) Neurons - cells that convert stimuli into electrical impulses to the brain; 2) Neuroglia - collective of different cell types with supportive role.
-
Neurons are made up of cell body, axon and dendrites. There are 3 types of neurons: Name these 3 types...?
-Motor neuron
-Interneuron
-Sensory neuron
-
What is a motor neuron?
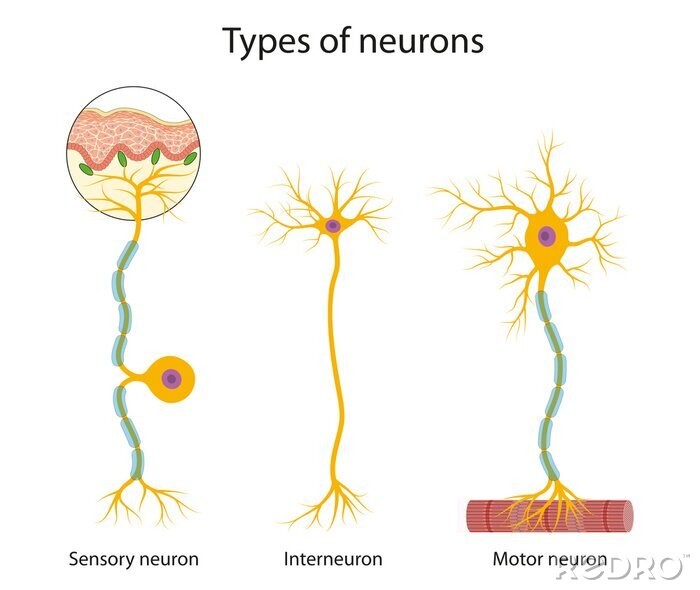
Carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands
-
What is an interneuron?
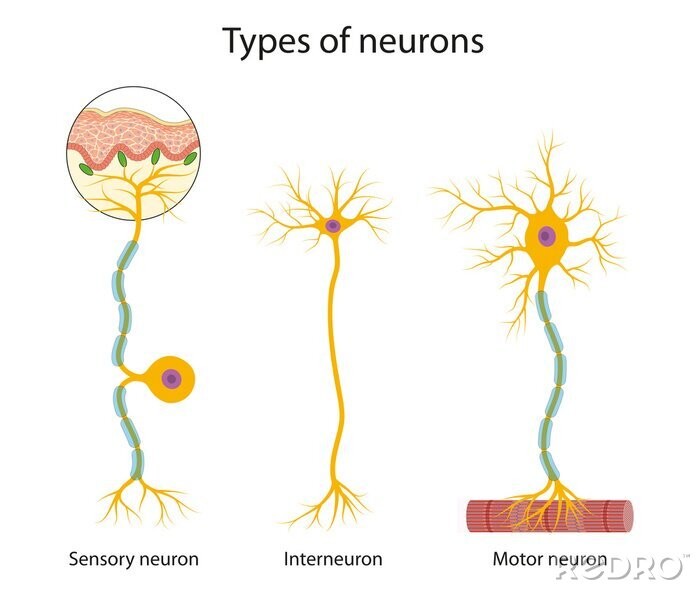
Interpret input from sensory neurons and end responses to motor neurons
-
What is a sensory neuron?
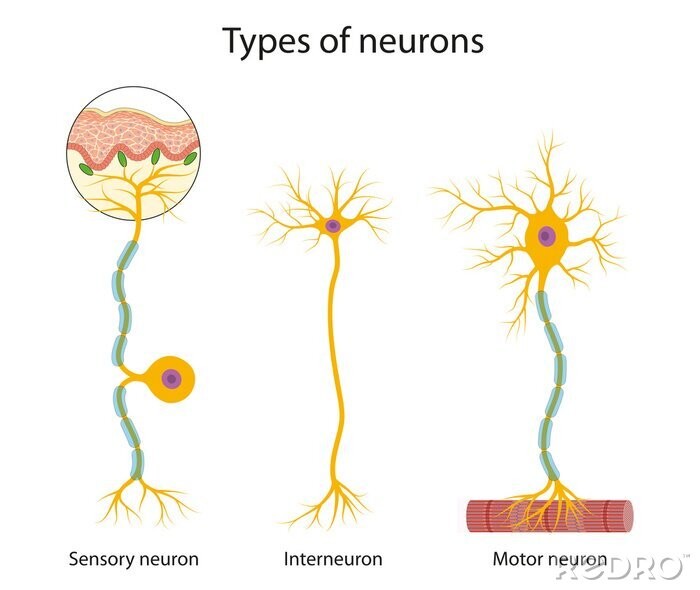
Receive information from environment and transmit to CNS
-
What is the Neuroglia?
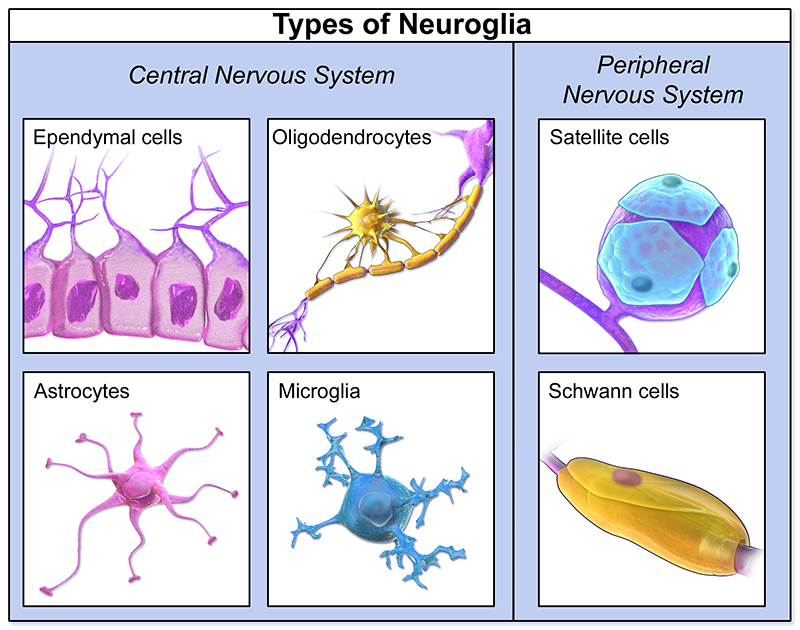
It is made up of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia in the CNS, and Schwann cells and satellite cells in the PNS (peripheral nervous system)
-
Picture demonstrating the nerve tissue
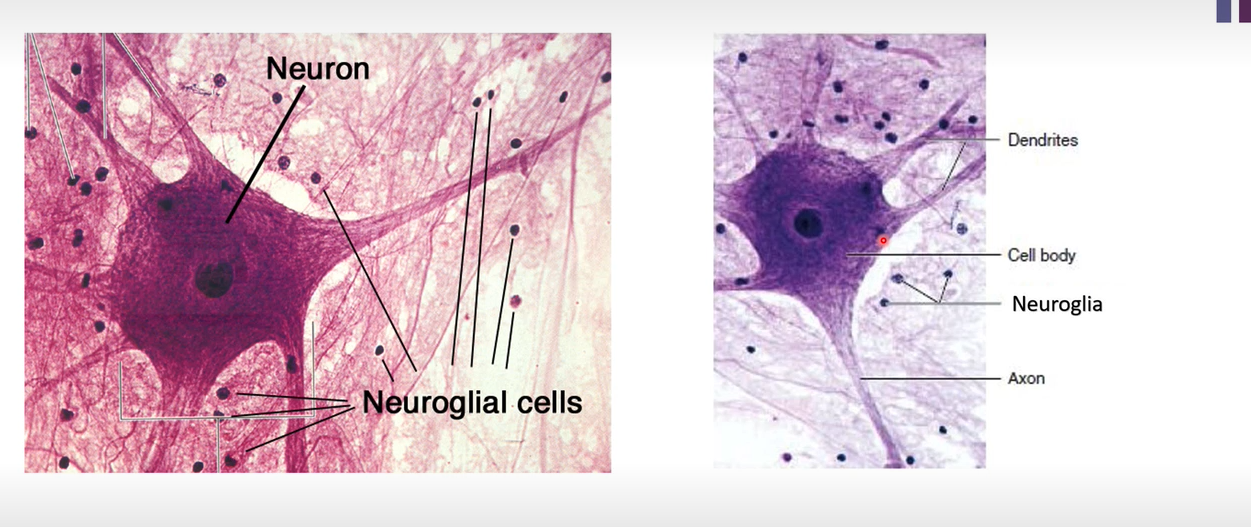
-
What is Areolar, loose connective tissue? (CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER)
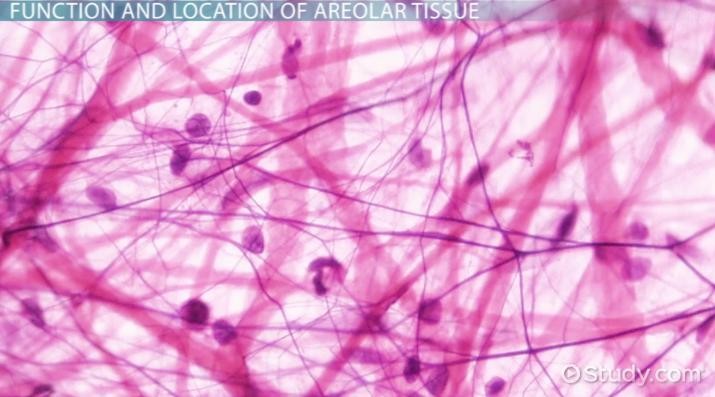
Many fibres that support and bind other tissues, as well as empty space for storing tissue fluid
-
What is Adipose, loose connective tissue? (CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER)
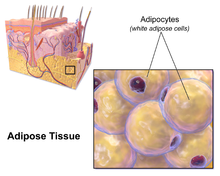
Contains many fat cells, which are able to store nutrients and also serve to insulate the body
-
What is Reticular, loose connective tissue? (CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER)
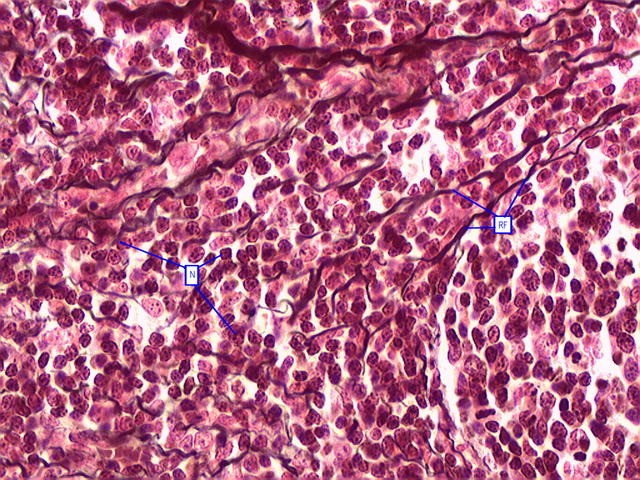
Similar to areolar tissue but contains only reticular fibres and supports certain structures
-
What is Regular, dense connective tissue? (CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER)
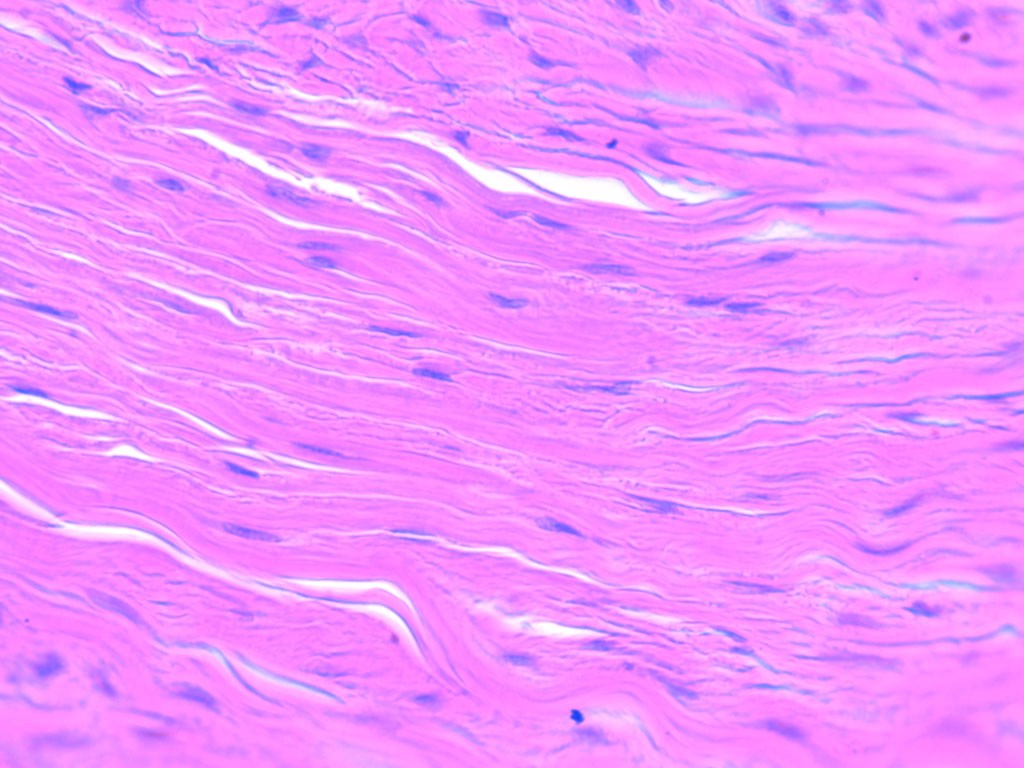
Many collagen fibres packed together with fibroblasts in between which resists tension
-
What is Irregular, dense connective tissue? (CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER)
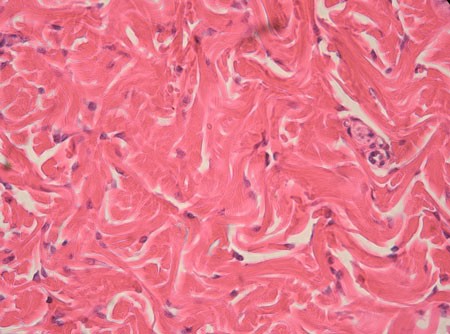
Many collagen fibres, but not arranged in any pattern which offers resistance in many directions
-
What is Elastic, dense connective tissue? (CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER)
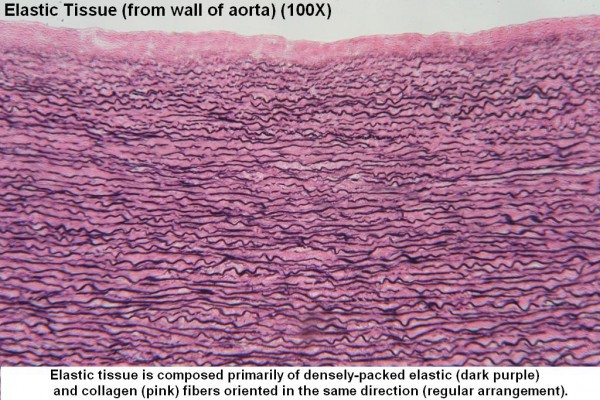
Similar to regular dense connective tissue in most respects but it is more elastic
-
Cartilage lacks what?
Nerve cells and blood vessels
-
Cartilage contains a lot of what?
Tissue fluid


