-
Define epidemiology.
Derives from the word epidemic.
epi (upon) + demos (people) + logy (study of).
"The study of the occurrence and distribution (determinants) of health related events, states and processes in specified populations, and the application of this study to the control of health problems.
-
Define public health practice.
The strategic, organized and interdisciplinary application of knowledge and skills to perform essential public health services to improve the populations health.
-
Give some examples of epidemiological studies.
- risks associated with smoking
- prevention of youth violence
- factors associated with obesity and substance abuse
-
Define these terms:
- epidemic
- endemic
- pandemic
Epidemic: The occurrence in a community or region with cases of an illness, specific health-related behaviour or other health-related events clearly in excess of normal expectancy.
Endemic: A disease outbreak when it's consistently present but limited to a particular region. This makes the spread predictable.
Pandemic: An epidemic occurring worldwide, crossing international borders and usually affecting a large number or people.
-
Name some examples of recent epidemics.
1. Ebola virus outbreak - October, 2021 in the Democratic Republic of Congo
2. Zika virus outbreak - 2015 and 2016 in the Americas
3. Salmonella outbreak - 2023 in the US
4. Malaria - 2021 in Nigeria, DRC, Uganda and Mozambique
-
What is a determinant?
They're factors/events that are capable about bringing a change in health. Ex. bacteria, chemical agents, stress, etc.
-
Epidemiology is an interdisciplinary study. True or false?
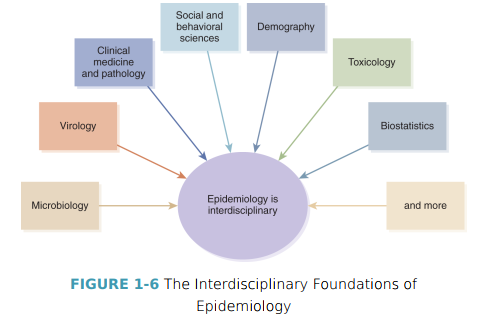
True; epidemiology is an extraordinarily rich and complex science that derives techniques and methodologies from many disciplines.
-
What is the difference between descriptive and analytic studies?
Descriptive: describes the frequency of disease and the distribution of risk factors in populations (person, place and time). No analysis just putting out what you saw.
Analytic: analyzes relationships between risk factors and diseases - causation and association.
-
Name the key characteristics of epidemiology.
Population focus: person, place and time. The occurrence of health and disease in a population.
Distribution: refers to the differences in disease patterns in subgroups of the total population.
Determinants: factors that can bring a change in health.
Outcomes: diseases/health-related issues caused/from exposure by certain factors. Expressed as morbidity and mortality.
Quantification: counting the cases of illness or other health outcomes.
Control of health problems: how the area manages to control certain health problems. Ex. making ads for causes of smoking.
-
What are the 12 determinants created by WHO.

-
Who in classical antiquity (<500 BCE) suggested that disease might be associated with environmental factors.

Hippocrates
-
When did the black death occur?
1346-1352 in Europe
-
Who was the man in the renaissance who first employed quantitative method?

John Graunt (1620-1674)
-
John Snow believed that cholera was transmitted by ___.
contaminated water and was able to demonstrate this association.
-
Name the uses of epidemiology.
- historical: documents the patterns, types and causes of morbidity and mortality over time.
- community health: to diagnose the health of the community and the condition of the people.
- health services: to study the working of health services with a view to their improvement.
- risk assessment: the individual risks on average of disease and the chances of avoiding them.
- disease causality: search for causes of health and disease.
-
What is disease management?
Refers to methods of reducing healthcare costs by providing integrated care for chronic conditions.
-
What is operations research?
Study of the placement of health services in a community and the optimum utilization of such services.

