-
ALU Definition and function
Arithmetic Logic Unit - It combines multiple full adders and additional logic circuits to perform arithmetic and logical operations (AND, OR, XOR, etc.)
-
ALU Diagram
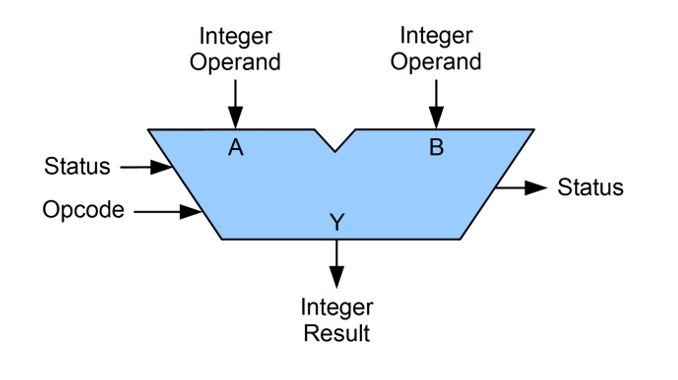
-
ALU: Opcode definition and function
A code that represents what operation the ALU is to carry out, and which operands to use for it
-
ALU: Operand definition
The input(s) that the ALU is making a calculation with
-
ALU: Status definition
A code that represents a message such as an error or important notice. Eg. an overflow error.
-
Control Unit function
Controls the flow of data to and from the CPU and memory, it fetches instructions from memory, interprets opcode and determines what actions to carry out to process data.
-
Registers function
They temporarily hold data which the CPU is using for processing. Eg. data register and address register
-
Moore's Law
The number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit doubles about every two years
-
Instruction set definition
A collection of binary-coded instructions that a computer's CPU can execute
-
How many bytes are there in a kilobyte?
1,000
-
How many bits are there in a megabyte?
8,000,000
-
What is 10100110 in decimal?
166
-
Algorithm definition
A set of rules that precisely defines a sequence of operations
-
TOC: What is the halting problem?
You can't write a piece of code that tells you when another piece of code will stop or if it would stop at all without running said code
-
Automaton definition/funciton
A mathematical model of a computing device. A mathematical computing machine.
-
Why do we build automata?
Mathematical simplicity, intellectual robustness, and so we can understand programs and machines more broadly, as the model can apply to many different types of computers
-
DFA definition/function
Discrete finite automaton: No repeated options for one state, each option has one transition (line to another state) in each state
-
Can there be more than one accepting state in an automaton?
Yes
-
Can there be more than one start state in an automaton?
No
-
TOC: alphabet definition and symbol
A finite set of characters or symbols, symbol ∑
-
TOC: ∑* definition
All the possible strings you can make with an alphabet ∑, also called the universe
-
TOC: String definition
A finite sequence of characters/symbols (not a set)
-
TOC: L is a language of ∑ if _______
L ⊆ ∑
-
TOC: Language definition
A finite set of strings
-
TOC: Language notation
L = {w ∈ {....} |(such that) w represents...}
-
TOC: A language L is called a regular language when ______
There exists a DFA D such that L(D) = L (The DFA accepts/recognizes the language)
-
TOC: Complement of a language L definition
The language of all strings in ∑* that aren't in L
-
NFA definition/function
Non-deterministic finite automaton: More than one choice for the same option in one or more of the states. If there is at least 1 accepting path, the NFA accepts the input.
-
Which are closer to real machines: NFAs? or DFAs?
DFAs
-
In automata, is dying the same as rejecting an input?
No, dying is when there are no transitions for the next input, while rejecting an input is when after processing the input, the automaton ends in a rejecting state.
-
TOC: ε transition definition/function
In NFAs, it is a transition that does not consume any characters from the input string, no matter how many times it is used
-
Can the epsilon transition be at the end of the input string?
No
-
Shannon's Communication Model diagram
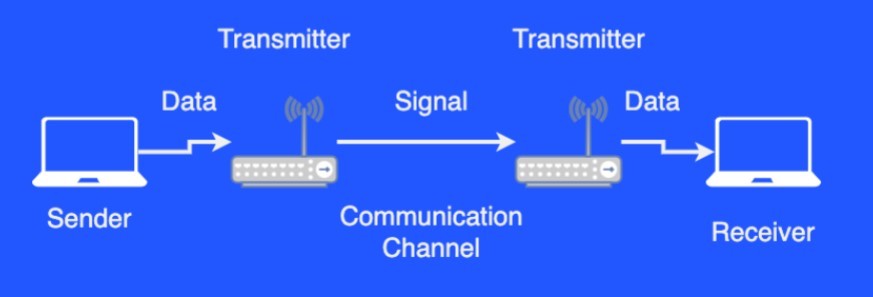
-
Networks: PAN definition
Personal Area Network, connects devices within 30 feet wirelessly, eg bluetooth
-
Networks: WAN definition
Wide Area Network, covers large areas such as cities and consists of smaller networks
-
Networks: RF definition
Radio frequencies as a communication channel, sent and received by transceivers with antennas
-
Networks: Bandwidth definition
Transmission capacity per unit of time, or rate
-
Networks: Broadband has a bandwidth of _____ or more. Narrowband has less.
25Mbps
-
Networks: Topology definition
The structure and layout of network components
-
Networks: point-to-point topology definition
A direct connection between 2 endpoints that reserves the entire bandwidth for them. It's the type of connection that connects peripheral devices to a host.
-
Networks: star topology definition
Connects devices to a central device
-
Networks: star topology pros and cons
Pros: if one wire fails, only one device fails
Cons: more expensive to set up and mantain
-
Networks: (partial) mesh topology definition
Each device is ideally connected to as many other devices as possible
-
Networks: Fully connected topology definition
All devices are connected to all other devices, the most expensive topology yet the most efficient one for information transfer.
-
Networks: Bus topology definition
All devices connect to a "bus", which then delivers the data to all other nodes, and the nodes then have to identify which data is meant for them. Inexpensive but one of the least efficient ones for information transfer.
-
Networks: topologies diagram
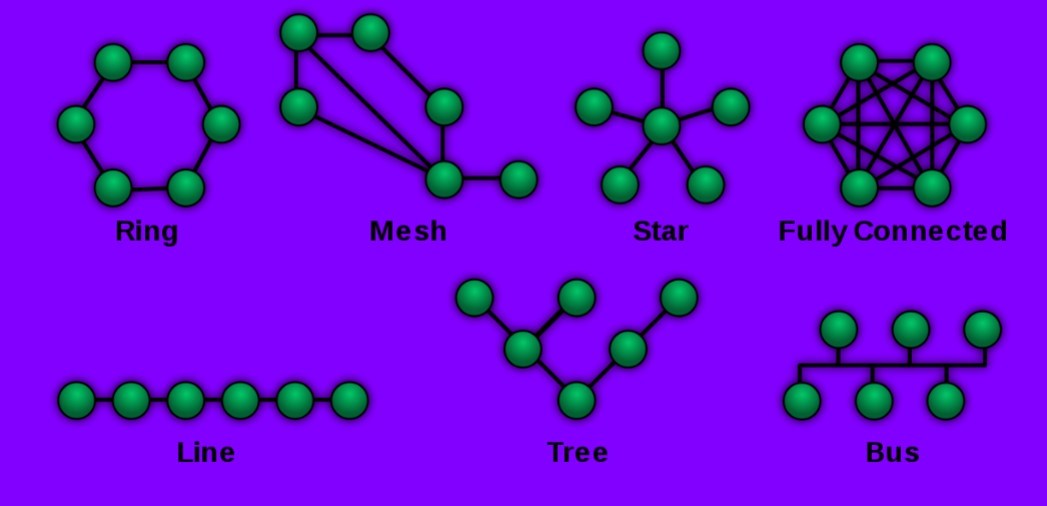
-
Networks: node definition
Any point in a network
-
Networks: DTE definition/function
Data Terminal Equipment: stores or generates data
-
Networks: DCE definition/function
Data Communication Equipment: controls data speed, signal conversion, error checking, and routing
-
Networks: router function
Directs data flow and controls packet switching
-
Networks: modem function
Converts signals so they can be transmitted through communication channels. Nowadays most home routers also act as modems.
-
Networks: internet definition
It is a WAN and a network of networks where computers communicate to each other via the IP protocol
-
Networks: DNS definition/function
Domain name server, fetches the IP address of the domain name the user has entered, so the computer knows where to request data from
-
Networks: TCP/IP 4 layers
Application, Transport, Internet, Network
-
TCP/IP: Application layer function
"The group of applications that let the user access the network", and where preferences such as whether to use SSL and encryption are defined. Data conversion through protocols such as HTML and CSS happen in this layer. Finally, session management (cookies) also occurs in this layer.
-
Networks: SMTP definition/function
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol: Used for email transmission between mail servers
-
TCP/IP: Transport layer function
Responsible for end-to-end communication and data integrity (error checking, check-summing etc). Protocols such as UDP (user datagram protocol) or TCP (transmission control protocol) occur here
-
Difference between UDP and TCP
UDP is less reliable but faster (more suited towards things such as video streaming where high bandwidth is required without need for absolute accuracy), whereas TCP is more reliable but slower (suitable for transferring documents)
-
Networks: packet switching definition
Information is separated into packets and sent separately, which are then reassembled at the destination. This ensures faster and more reliable transmission. TCP handles the package separation and reassembly and specifically it places more emphasis in checking whether the packages have been reassembled completely and accurately.
-
TCP/IP: Internet layer function
IP addresses, DNS
-
DNS Spoofing definition
"An attack involving manipulating DNS records to redirect users toward a fraudulent, malicious website that may resemble the user's intended destination."
-
TCP/IP: Network layer function
Physical connections between devices: communication channels
-
API definition/function
Application Programming Interfaces act as an intermediarybetween two applications (usually client and server), defining what operations can be performed on the server and how those operations can be executed, and the data format used for communication
-
How many bytes do IPv4 and IPv6 use?
4 and 16
-
Do routers have public IPs? or private IPs?
Both. The devices on the same network see the private IP but the internet sees the public one.
-
3 tiers of ISPs
Core Backbone - Owns underwater cables
Distribution - Owns infrastructure that connects to underwater cables
Connectivity - Connects users to said infrastructure
Users can get their connection from any of the three tiers
-
Plaintext definition
Unencrypted text
-
Steganography definition
Hiding information inside other information
-
Symmetric encryption definition
Encryption and decryption happen with the same key
-
Assymetric/public key encryption definition
Each party in the data transfer has two keys, a private one and a public one. Both keys are mathematically linked. They send the public one to the other party for them to encrypt the data they send, and only the private key can decrypt it. This is way more secure than symmetric encryption as you do not need to share any private keys at any point.
-
How do digital signatures work?
They use assymetric encryption: only the party who signs can do so, through a private key, and anyone can check if the signature is valid using the public key.
-
How does password hashing work?
Your password passes through a mathematical function (which is easy to carry out but virtually impossible to undo) that turns it into random-looking information. This is what is ideally stored in a web server. Then, when you enter your password to log in, your password is not compared to anything on the server, but rather its hash is. This way your password never leaves your machine.
-
Phishing definition
When a hacker gets you to type sensitive information into a fraudulent website
-
Dictionary attack definition
Try every known password as if they are trying all the words in a dictionary, generally starting with the most common passwords

