-
What is anatomical terminology?
Anatomical Terminology:
Most anatomical terms stem from Latin or Greek.
Example: Hepatitis
Hepar= Liver
Itis= Inflammation
-
What is anatomical body position?
Acts as a point of reference for all movements.
-
What are the anatomical body planes?
Anatomical Body Planes:
Plane: an imaginary flat surface running through the body.
There are four anatomical body planes:
Coronal/Frontal plane
Sagittal plane
Midsagittal plane
Transverse/Axial plane
-
What is the coronal (frontal) plane?
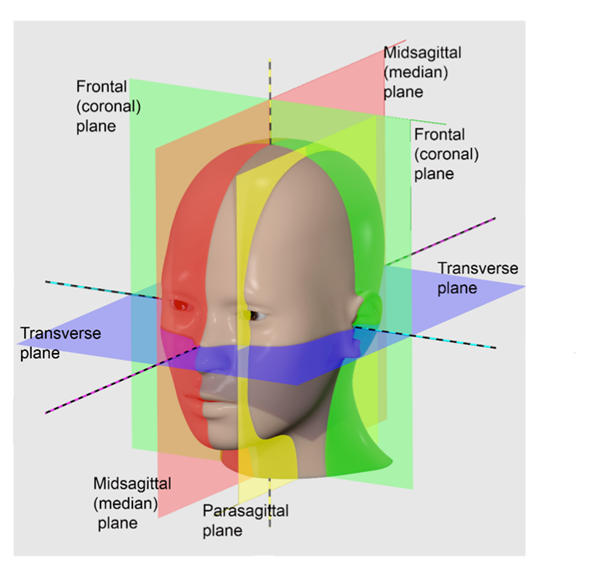
Coronal (Frontal) Plane:
Oriented vertically.
Divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
-
What is the coronal (frontal) plane and what are anatomical body planes?
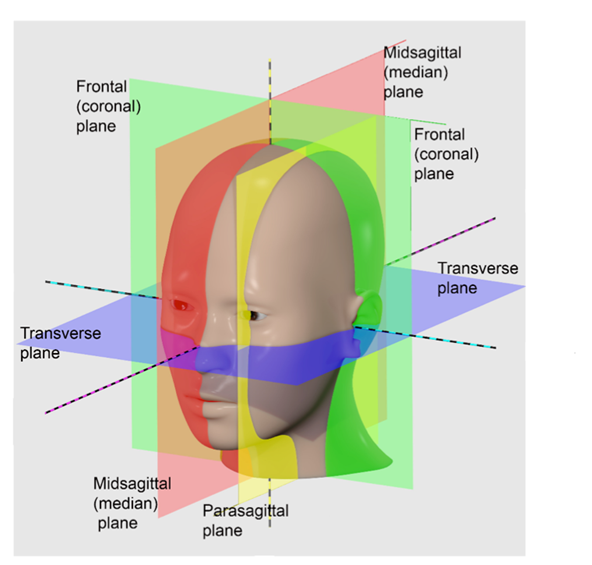
♬♪ Coronal (Frontal) Plane:
Oriented vertically.
Divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
Anatomical Body Planes:
Plane: an imaginary flat surface running through the body.
♬♪ There are four anatomical body planes:
Coronal/Frontal plane
Sagittal plane
Midsagittal plane
Transverse/Axial plane
-
What is the sagittal plane?
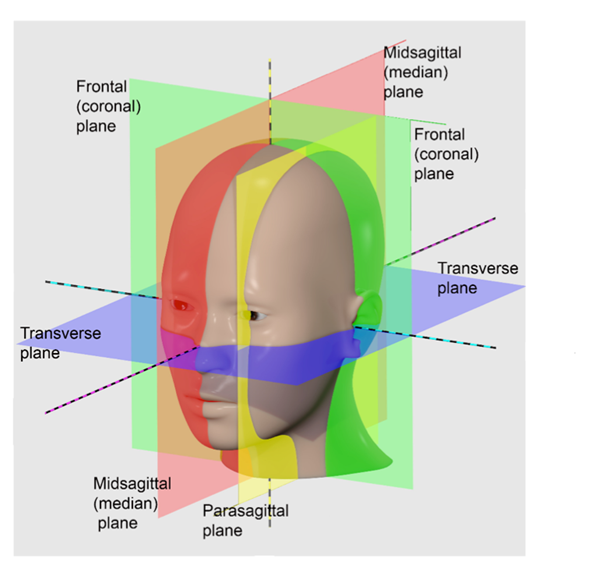
Sagittal Plane:
Oriented vertically.
Divides the body into right and left parts.
-
What is the midsagittal (median) plane?
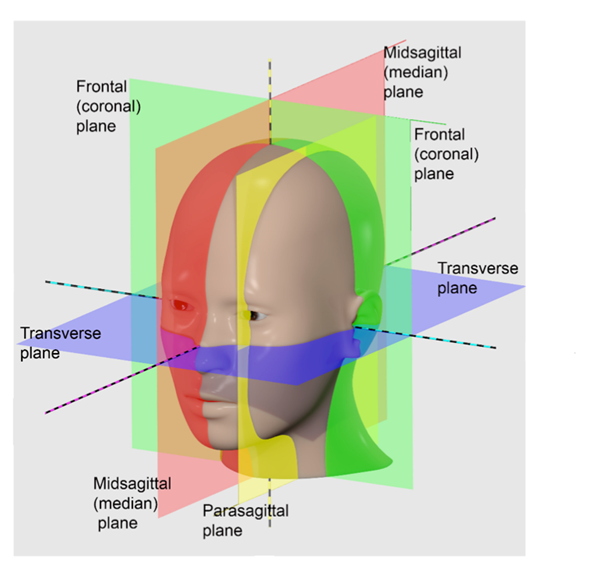
Midsagittal (Median) Plane:
Lies exactly in the midline vertically.
-
What is the parasagittal plane?
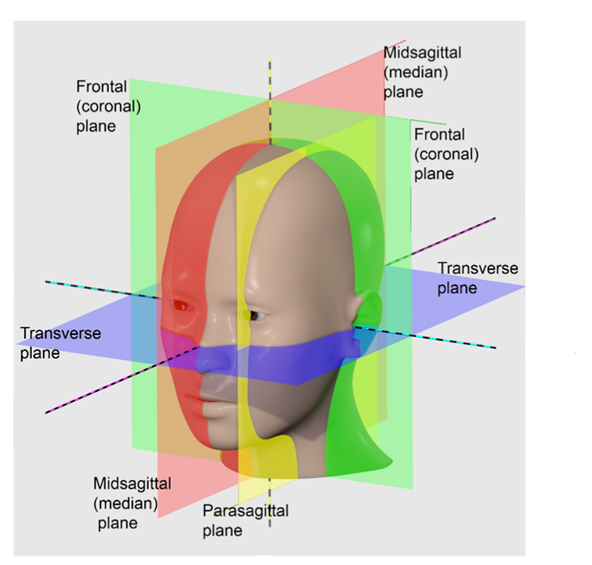
Parasagittal Plane:
Para= near.
A sagittal plane that lies offset from the midline.
-
What is the midline of the body?
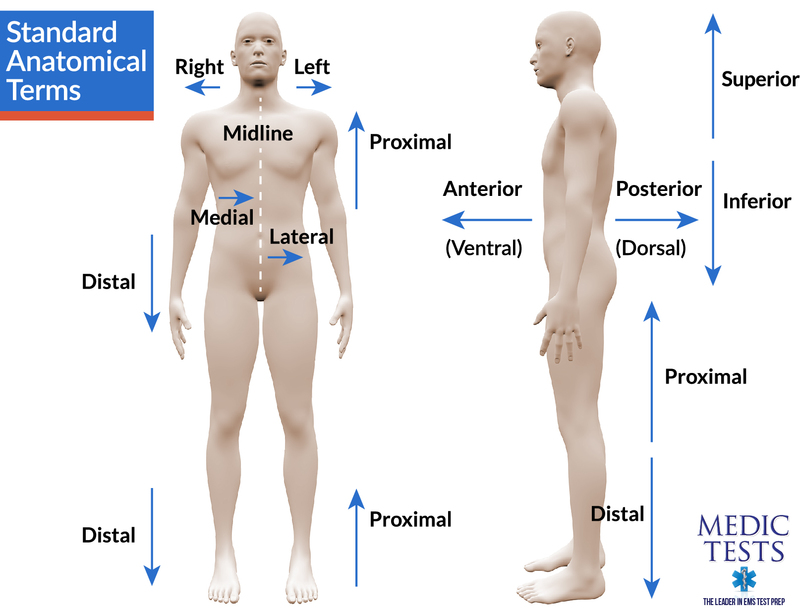
Midline of the Body:
An imaginary vertical line dividing the body equally.
-
What is the transverse (horizontal) plane?
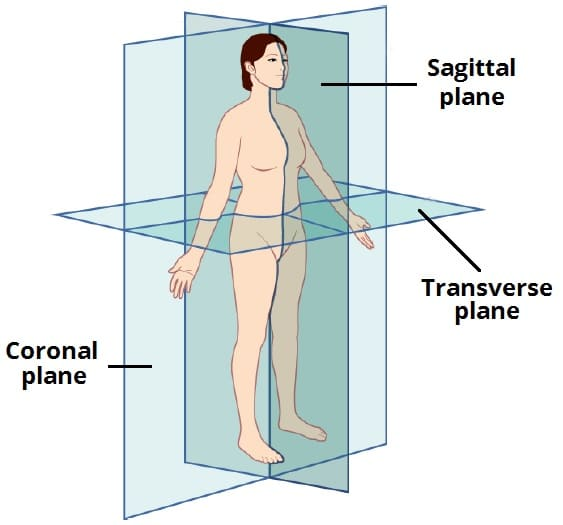
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane:
Oriented horizontally.
Divides the body into superior and inferior parts.
-
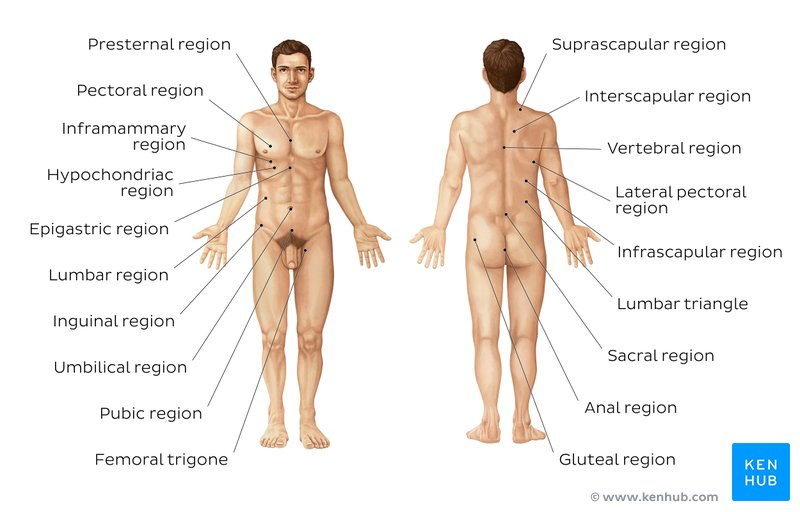
What are regional terms and body divisions?
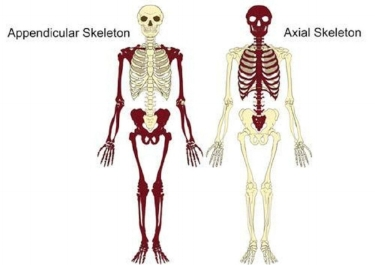
♬♪ Regional Terms:
Names of specific body areas.
Body Divisions:
Axial Region
Appendicular Region
-
Picture demonstrating the components of the axial skeleton
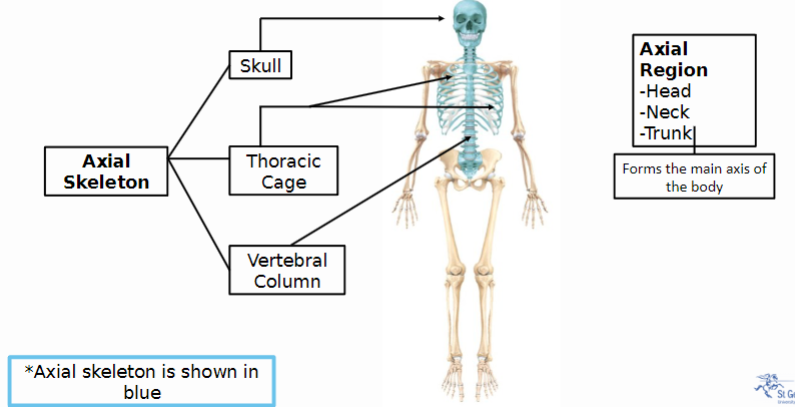
-
Picture demonstrating the components of the appendicular skeleton
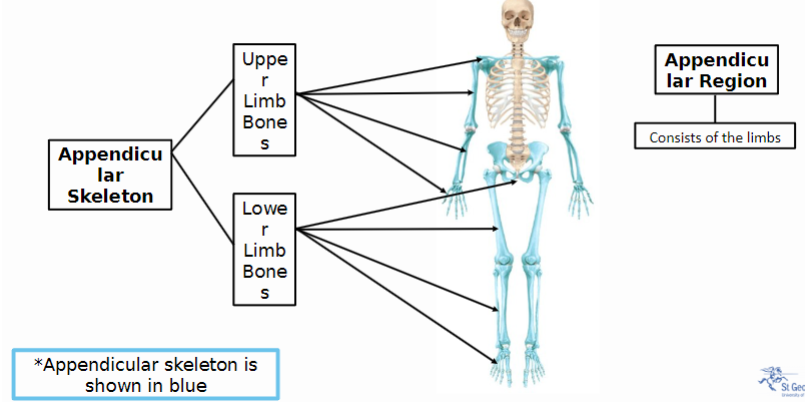
-
What are directional terms in anatomical nomenclature?
Directional Terms:
♬♪ Allow us to precisely explain where one structure lies in relation to another.
Include:
Superior/Inferior
Medial/Lateral
Anterior (ventral)/Posterior (dorsal)
Cranial/Caudal
Superficial/Deep
-
What does "Superior" mean?
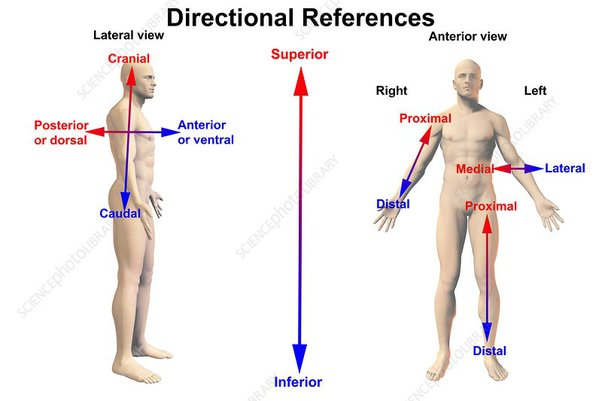
Upper part of a structure or the body; above.
♬♪ Example: The head is superior to the neck.
-
What does "Inferior" mean?
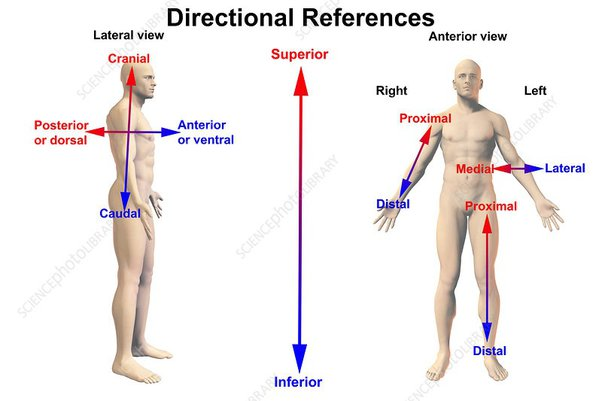
Toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below.
♬♪ Example: The thorax is inferior to the neck.
-
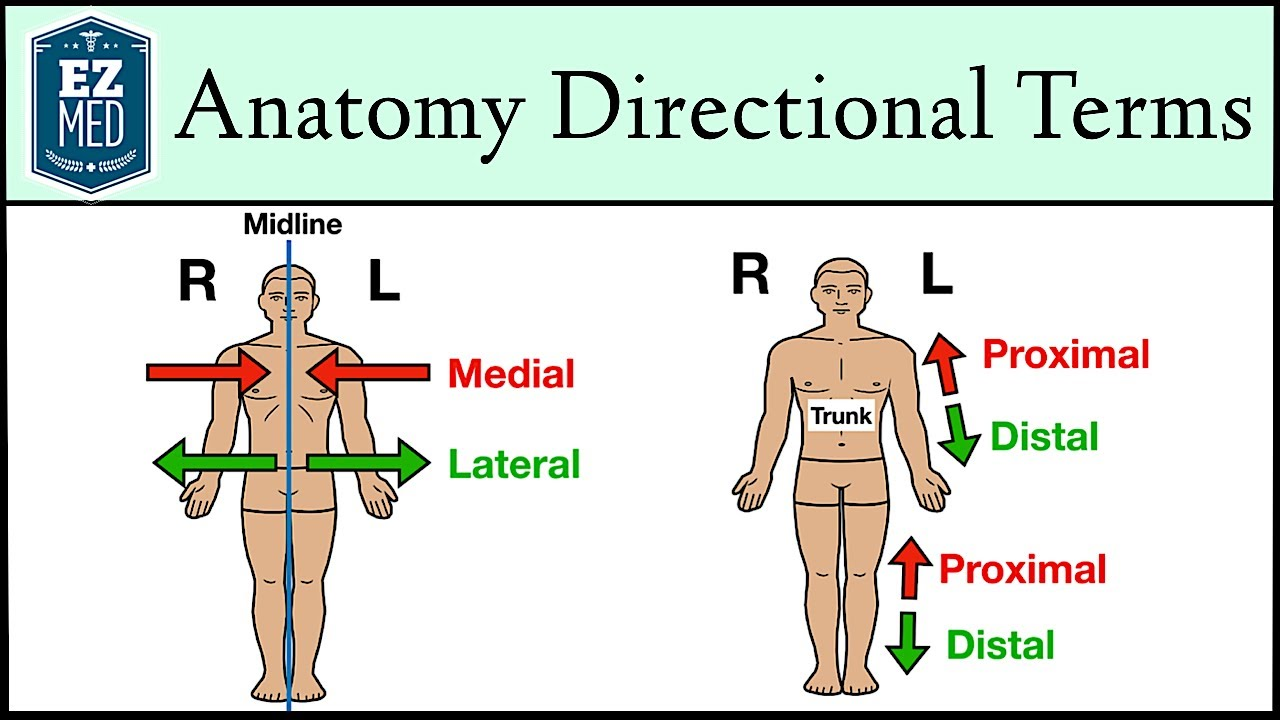
What does "Medial" mean?
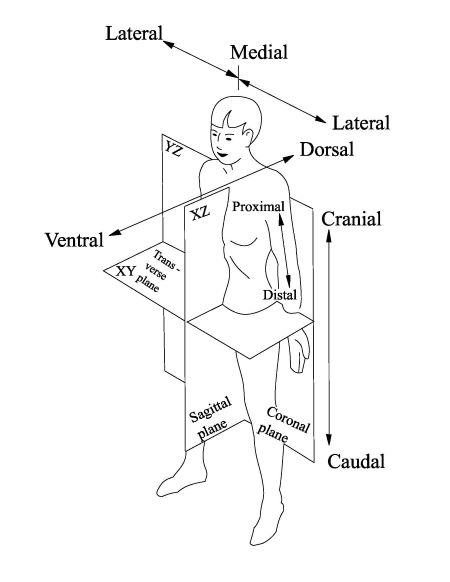
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of.
♬♪ Example: The heart is medial to the lungs.
-
What does "Lateral" mean?
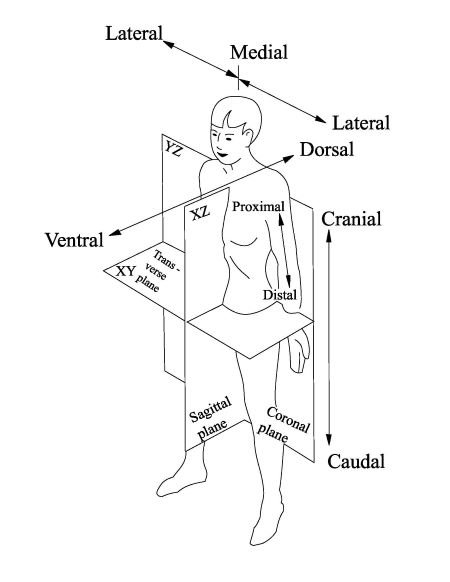
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of.
♬♪ Example: The lungs lie lateral to the heart
-
What are some combinations of directional terms?
Combination of Terms:
Inferolateral: Lower and away from the midline.
Inferomedial: Lower and toward the midline.
Superolateral: Upper and away from the midline.
Superomedial: Upper and toward the midline.
-
What does "Anterior (Ventral)" mean?
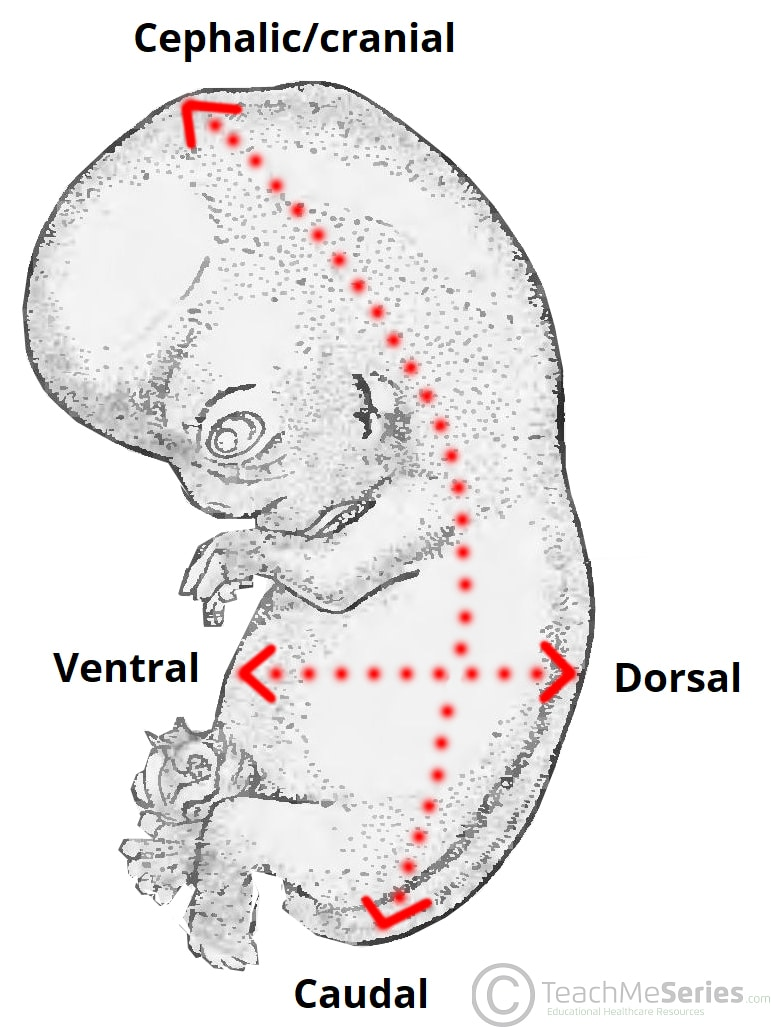
Anterior (Ventral):
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of.
♬♪ Example: The sternum is anterior to the heart.
Note: The terms "anterior" and "ventral" and "posterior" and "dorsal" are synonymous in humans but not in four-legged animals.
-
What does "Posterior (Dorsal)" mean?
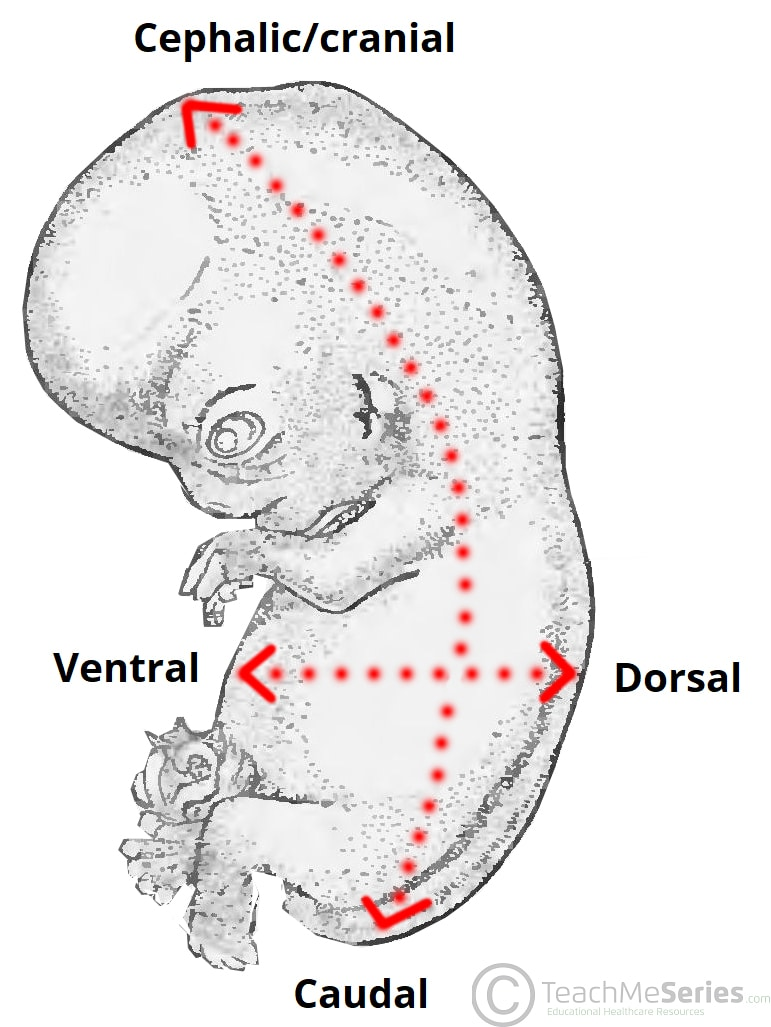
Posterior (Dorsal):
Toward or at the back of the body; behind.
♬♪ Example: The heart is posterior to the sternum.
Note: The terms "anterior" and "ventral" and "posterior" and "dorsal" are synonymous in humans but not in four-legged animals.
-
What does "Cranial" mean?
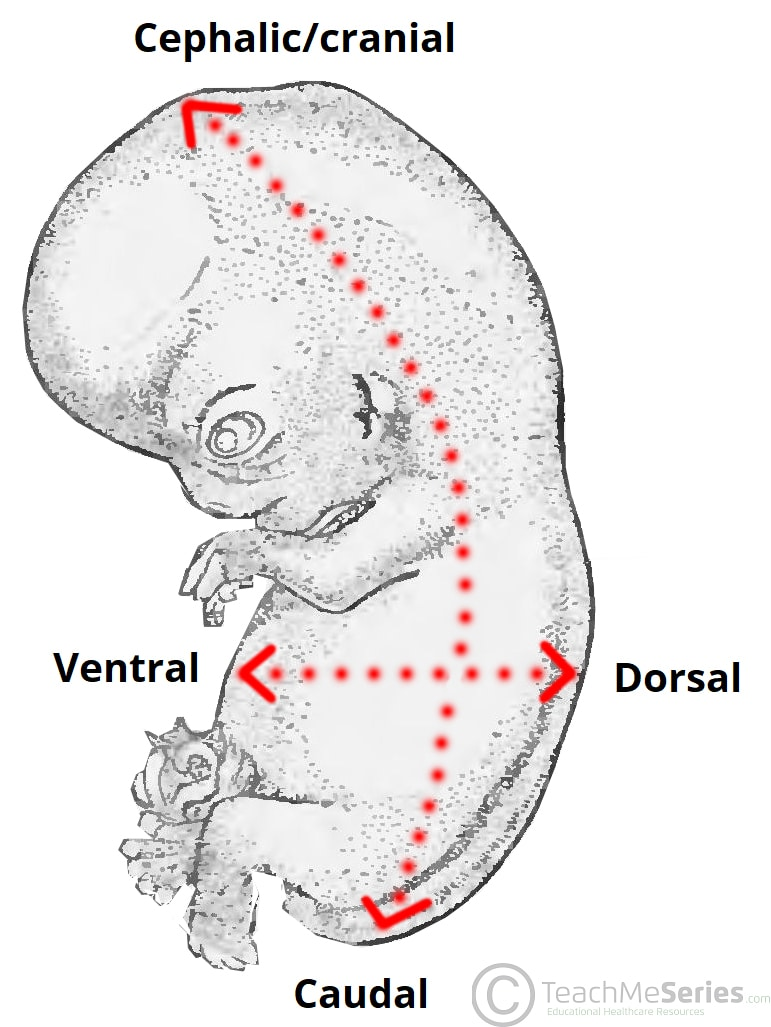
Toward the head end.
-
What does "Caudal" mean?
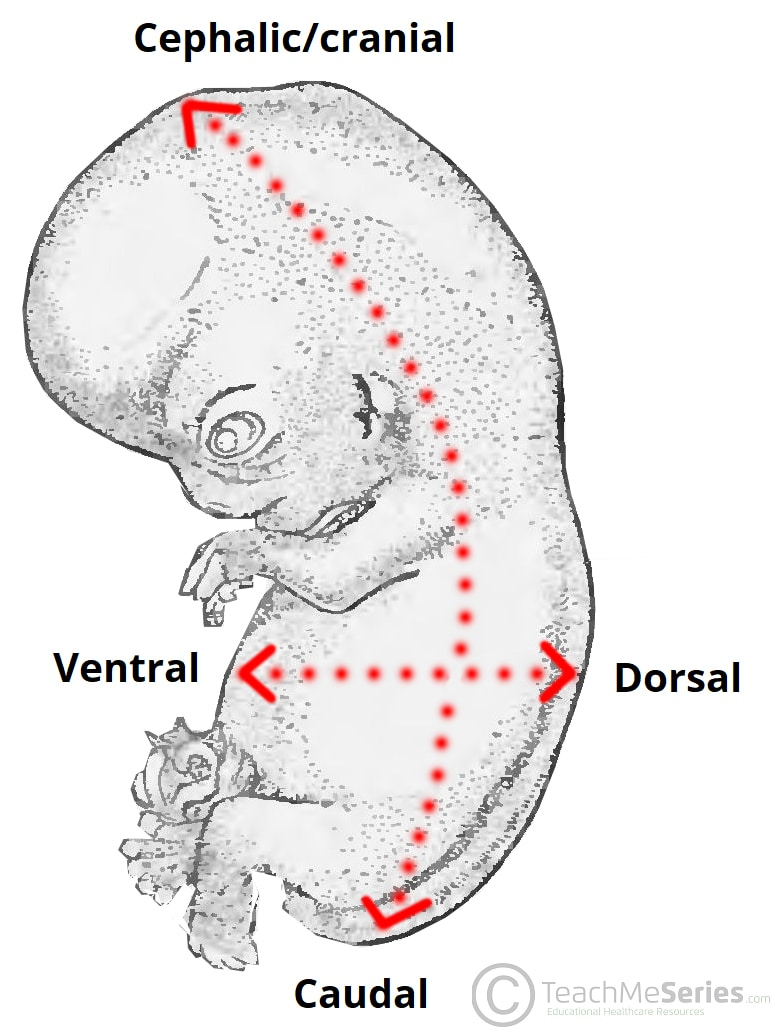
Away from the head end; refers to the tail (inferior).
-
What does "Superficial (External)" mean?
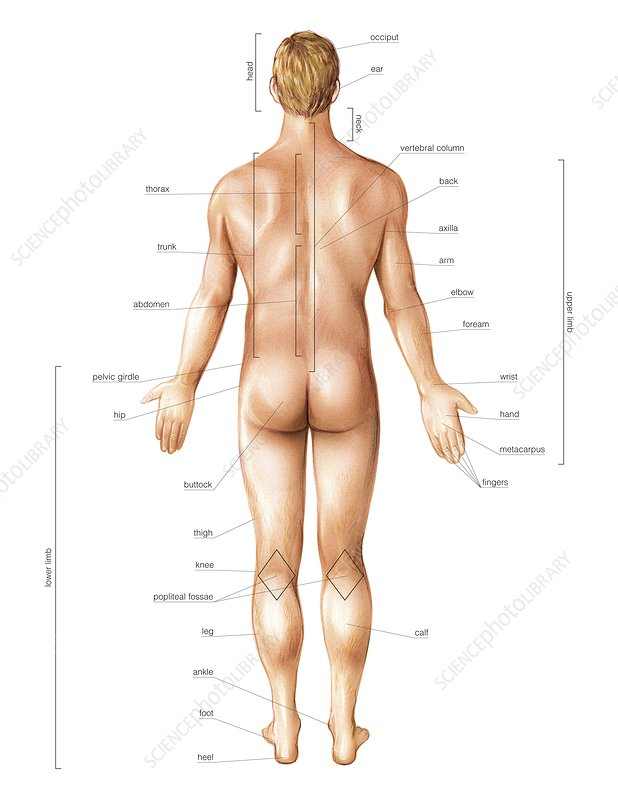
Superficial (External):
Toward or at the body surface.
Example: The skin is superficial to muscles.
-
What does "Deep (Internal)" mean?
Deep (Internal):
Away from the body surface; more internal.
Example: The muscles are deep to the skin.
-
What does "Proximal" mean?
Proximal:
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
Example: The forearm is proximal to the hand.
-
What does "Distal" mean?
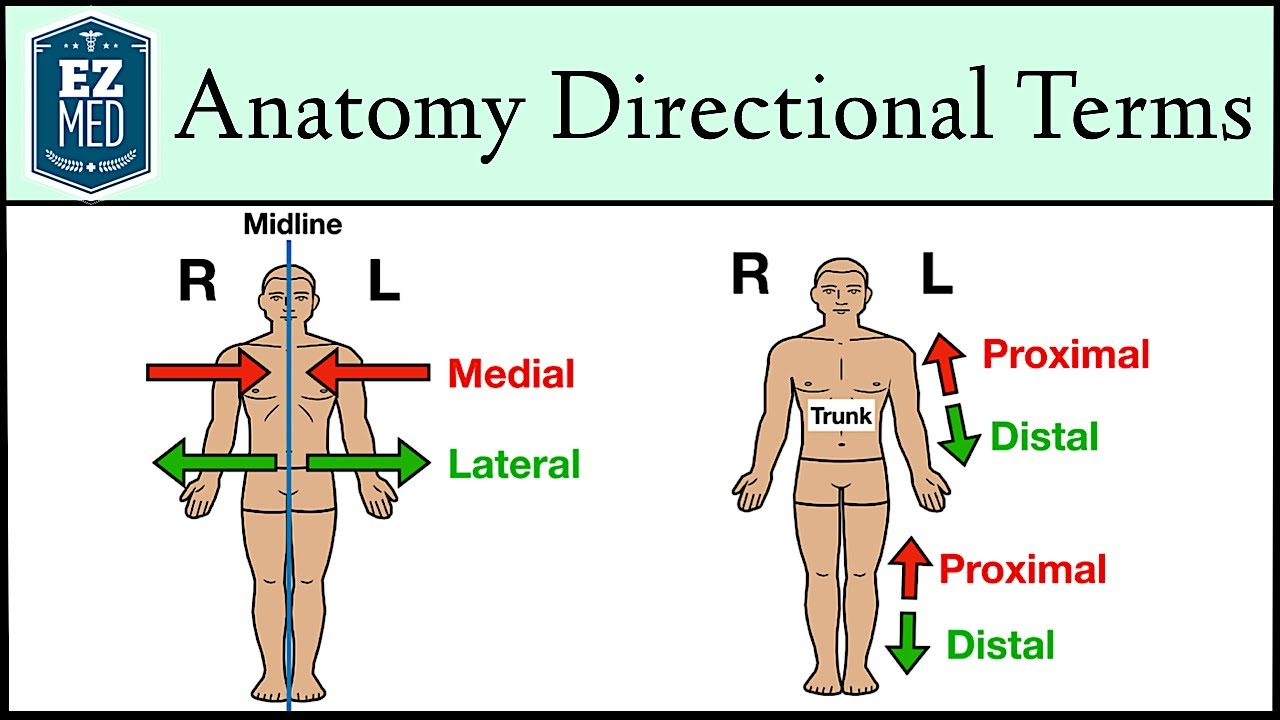
Distal:
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
Examples:
The hand is distal to the forearm.
The forearm is distal to the arm.
-
What are the directional terms used to describe movement? (10)
Directional Terms for Movement:
Flexion/Extension
Adduction/Abduction
Medial rotation/Lateral rotation
Circumduction
Dorsiflexion/Plantarflexion
Inversion/Eversion
Pronation/Supination
Retrusion/Protrusion
Opposition/Reposition
Elevation/Depression
-
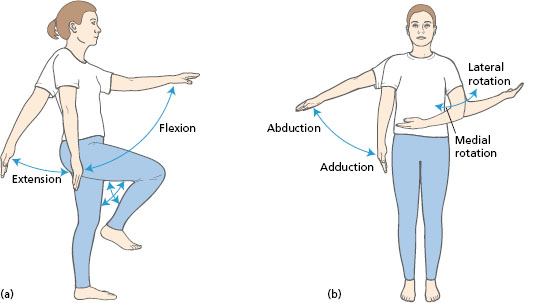
What is Flexion?
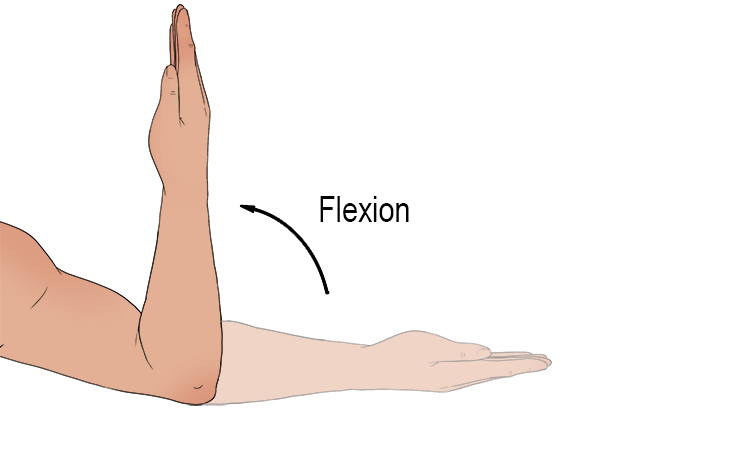
Flexion:
Flexion decreases the angle between two bones.
Examples:
Trunk flexion
Neck flexion
Finger flexion
-
What is Extension?
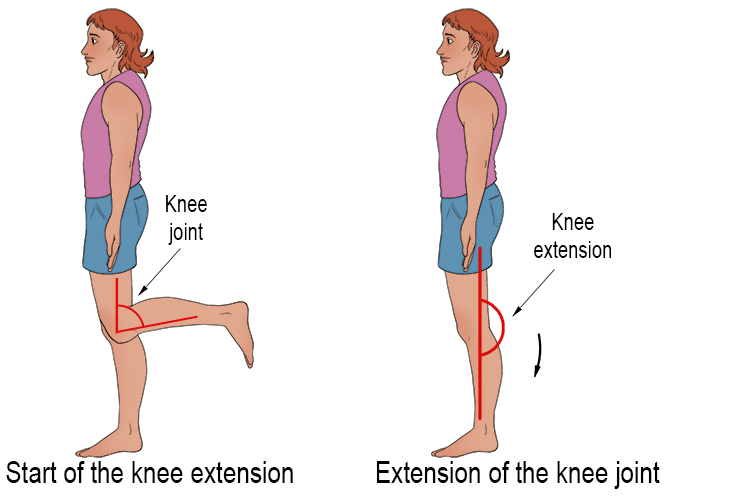
Extension:
Extension increases the angle between two bones.
Examples:
Trunk extension
Neck extension
Finger extension
-
What is Medial Rotation?
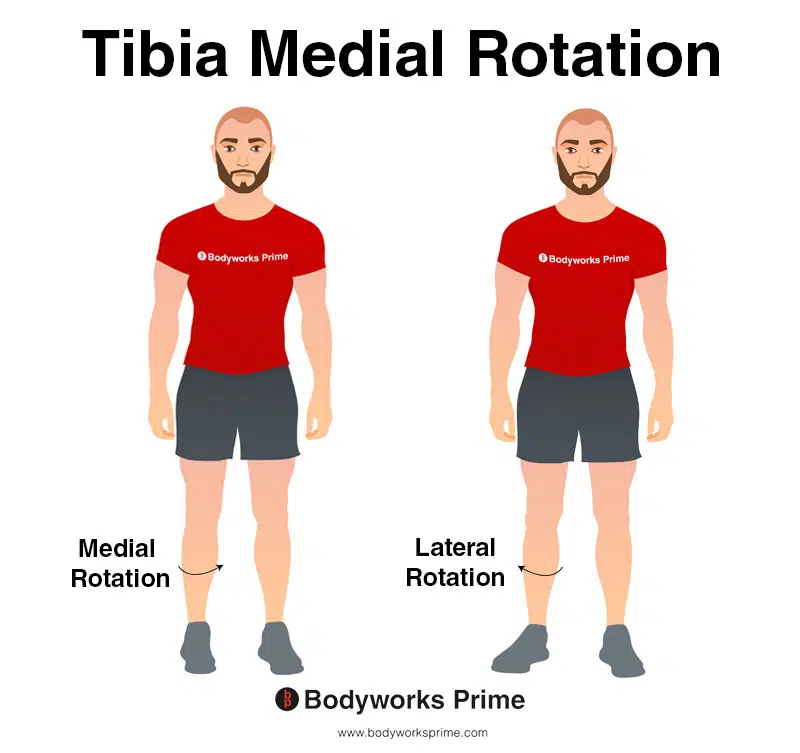
Medial Rotation:
Rotating toward the median plane.
-
What is Lateral Rotation?
Lateral Rotation:
Rotating away from the median plane.
-
What is Circumduction?
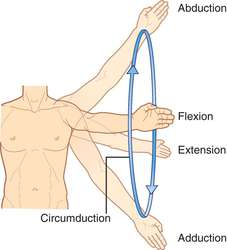
Circumduction:
Moving a limb or finger so that it describes a cone in space.
-
What are examples of Circumduction? (8)
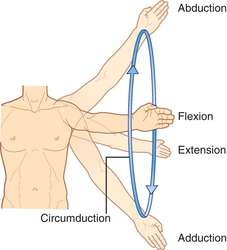
Examples of Circumduction:
Hip circumduction
Shoulder circumduction
Wrist/hand circumduction
Thumb circumduction
Finger circumduction
Ankle/foot circumduction
Toe circumduction
Head circumduction
-
What is Adduction?
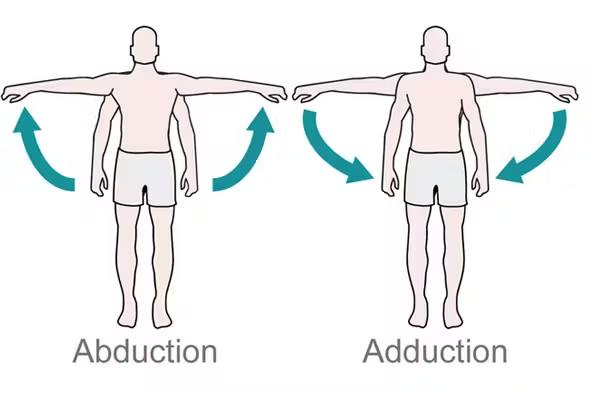
Adduction:
Moving a limb toward the body midline.
Examples:
Finger adduction
Wrist adduction
-
What is Thumb opposition?
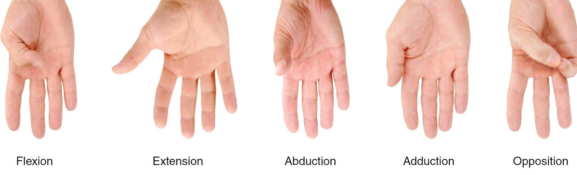
Thumb opposition:
Moving the thumb to touch the tips of the other fingers.
-
What is Dorsiflexion?
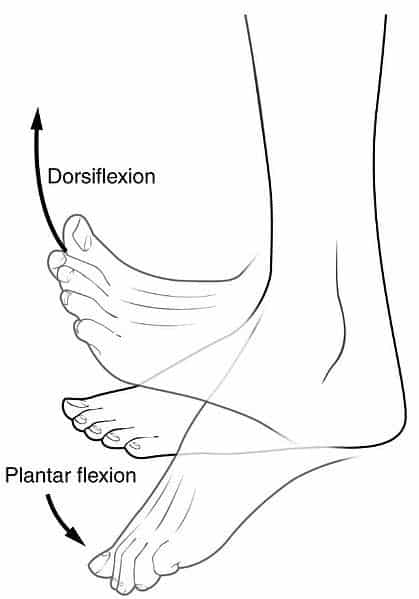
Dorsiflexion:
Lifting the foot or hand (superiorly).
Dorsiflexion of the foot:
Lifting the foot so its superior (dorsum) surface approaches the leg.
Dorsiflexion of the hand:
Same as hand extension. Lifting the hand so its dorsum approaches the forearm.
-
What is Plantar Flexion?
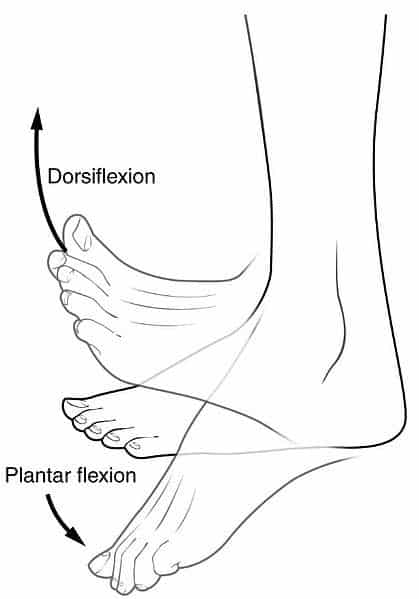
Plantar Flexion:
Depressing the foot, elevating the heel.
-
What is Eversion?
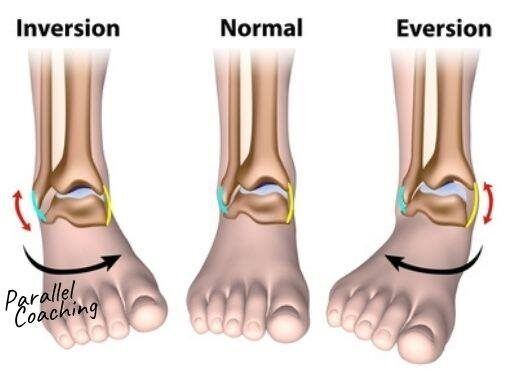
Eversion:
Turning the sole of the foot laterally.
-
What is Inversion?
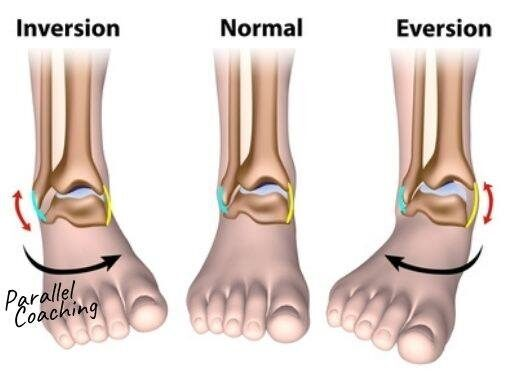
Inversion:
Turning the sole of the foot medially.
-
Picture demonstrating the palmar and dorsal surfaces of the hand
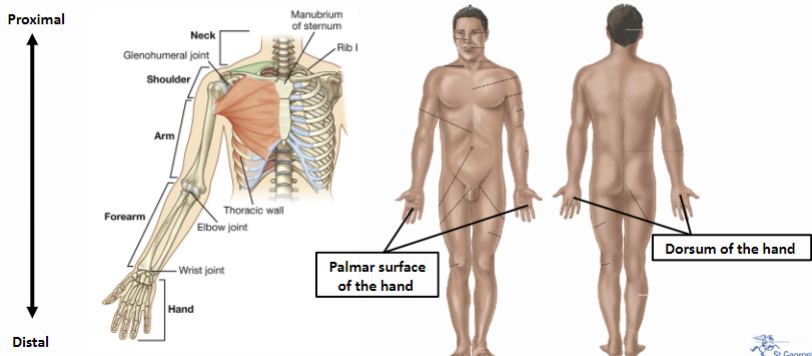
-
What is Protraction?
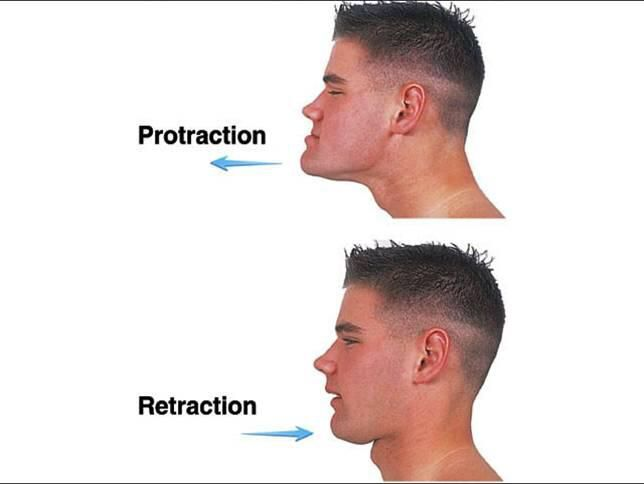
Protraction:
Moving a body part in the anterior direction.
-
What is Retraction?
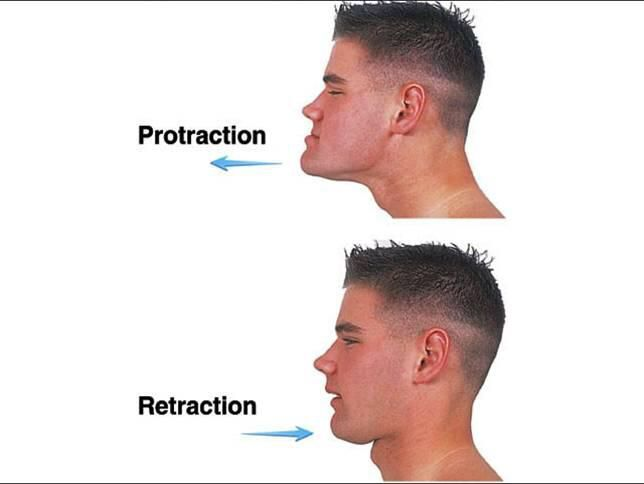
Retraction:
Moving a body part in the posterior direction.
-
What is Elevation?

Elevation:
Lifting a body part superiorly.
-
What is Depression?

Depression:
Moving a body part inferiorly.