-
Integument
-
Integumentary System

-
Cutaneous Membrane (Skin)

-
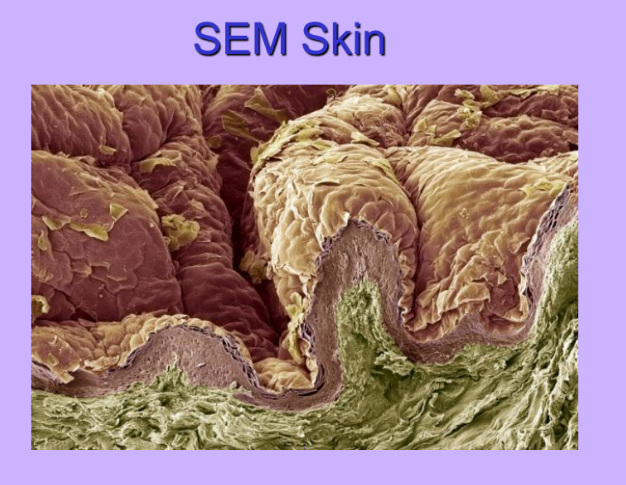
SEM Skin
-
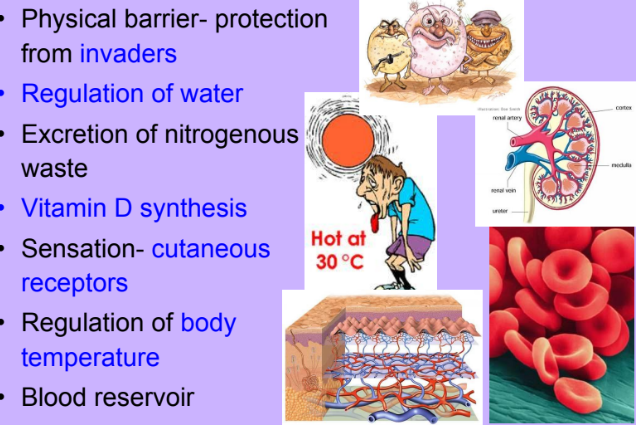
Skin Functions
-
Cutaneous Membrane (Skin) -Has two regions

-
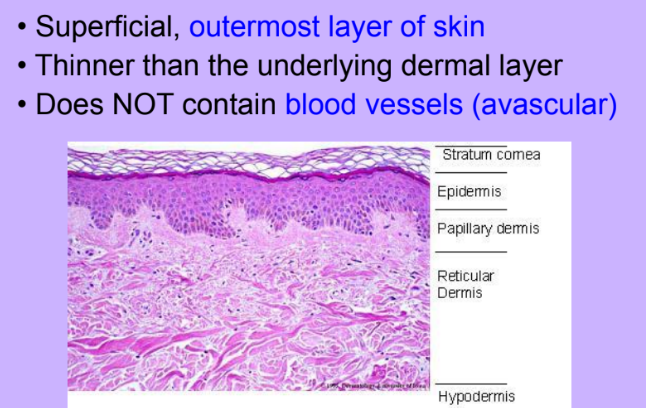
Epidermis
-
Epidermis 5 layers
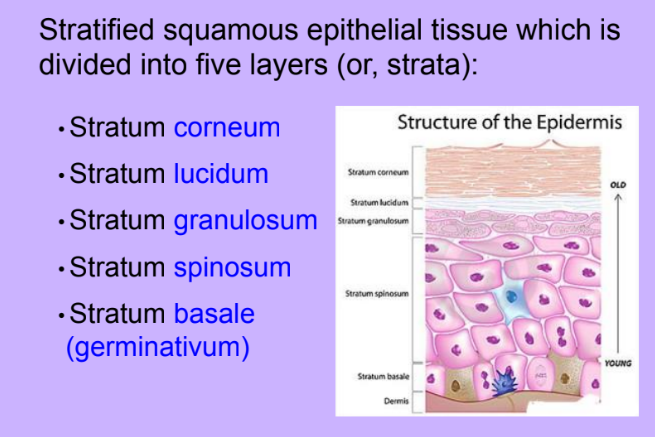
-
Stratum Basale (Germinativum)
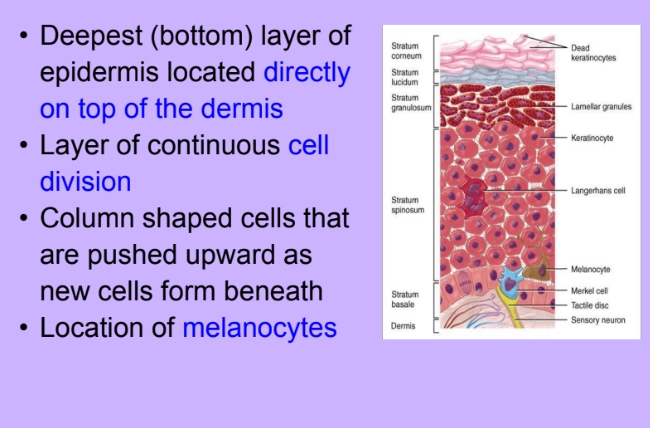
-
Melanocytes
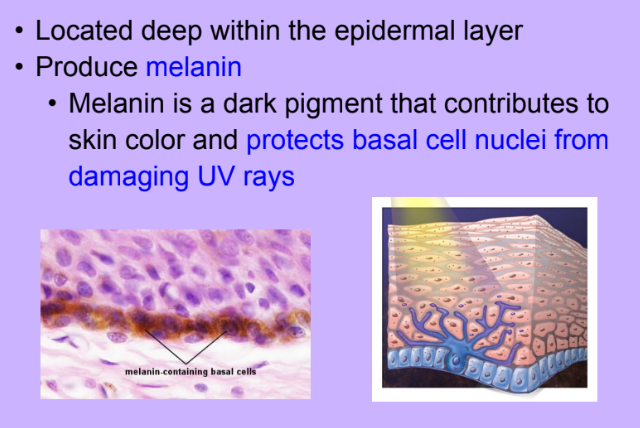
-
Skin Color -Melanin

-
Carotene
Yellowish-orange coloration
-Seen mostly in the palms of hands and soles of feet where lucidum has thickened (calluses).
-
Hemoglobin
Contributes to pinkish tint of skin
-Seen in light skinned people where skin is nearly transparent and hemoglobin color shows through.
-
Conditions Related to Skin Color
-Cyanosis
-Erythema
-Pallor
-Jaundice
-
Cyanosis
Cyan= blue, osis=condition
-Caused by oxygen deficiency
-
Erythema
Eryth= red; em= blood
-Caused by increased blood flow
-
Pallor
Pale, ashen color
-Due to decreased blood flow
-
Jaundice
Jaun= yellow
-Dysfunction of the liver to break down bilirubin
-
Albinism

-
Stratum Spinosum
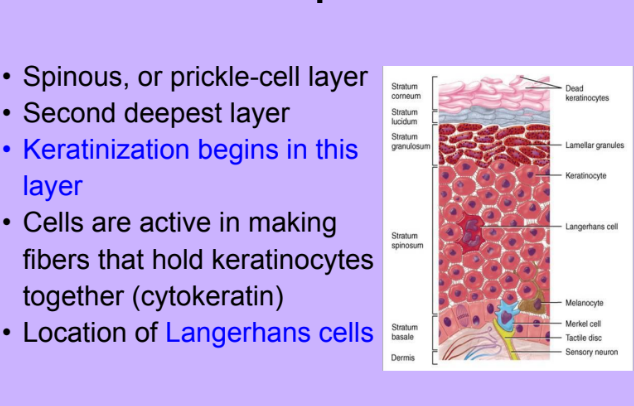
-
Keratin
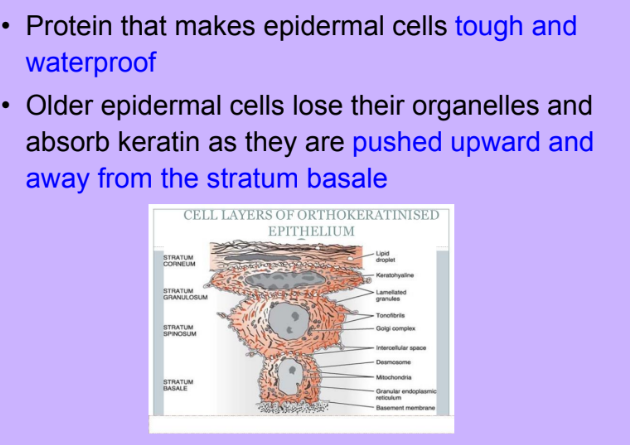
-
Langerhans Cells
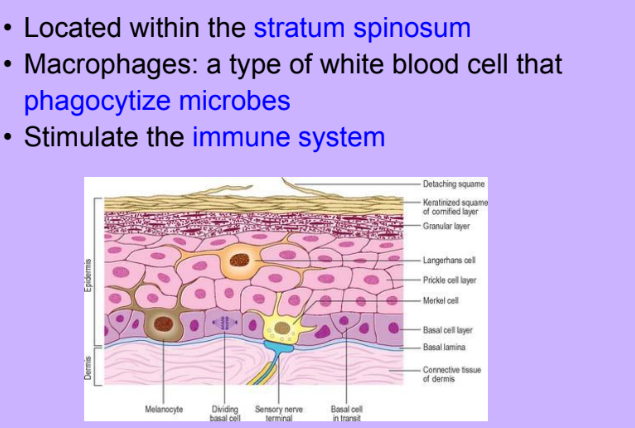
-
Stratum Granulosum
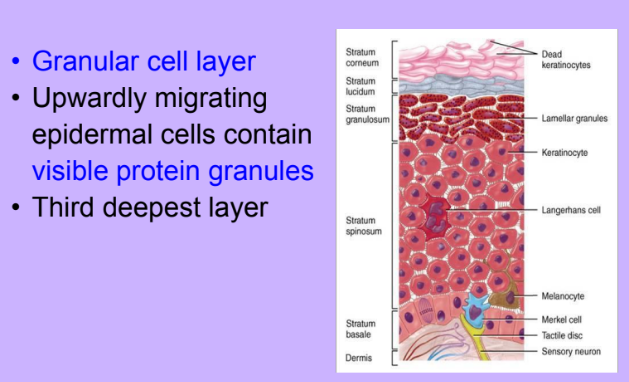
-
Stratum Lucidum
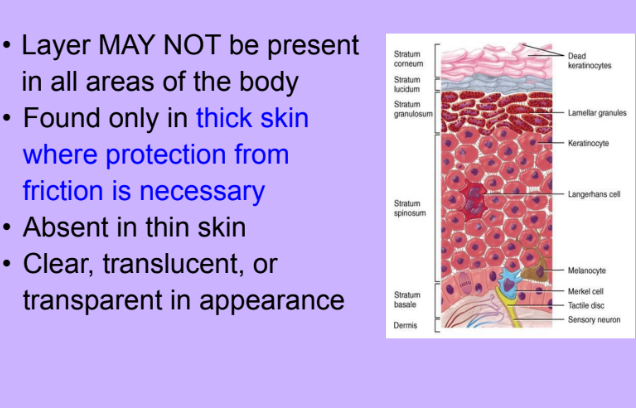
-
Stratum Corneum
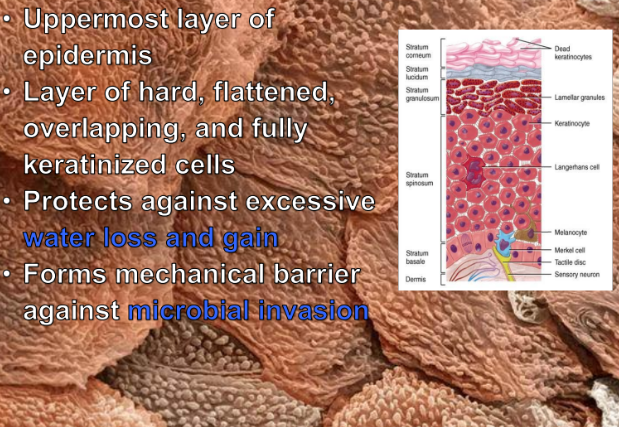
-
Dermis
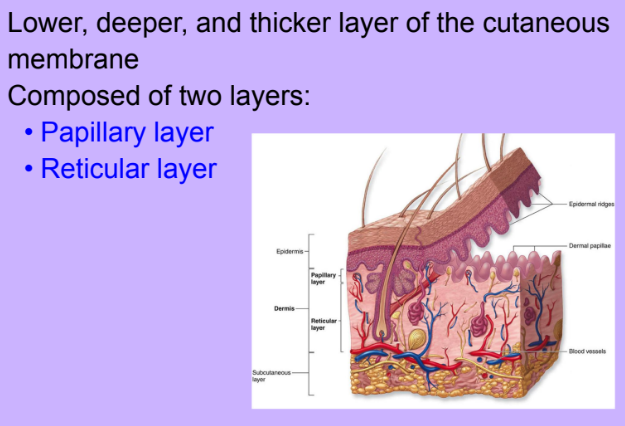
-
Papillary Layer
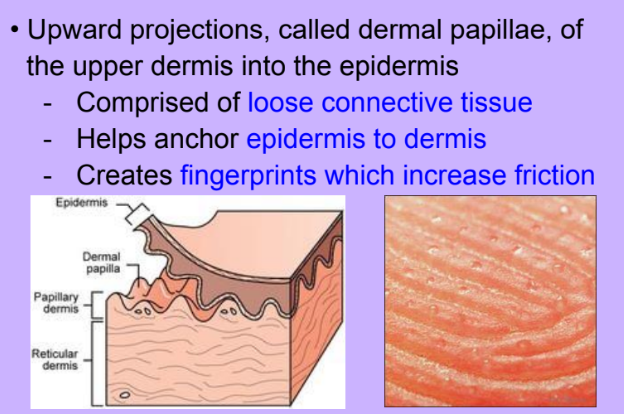
-
Reticular Layer
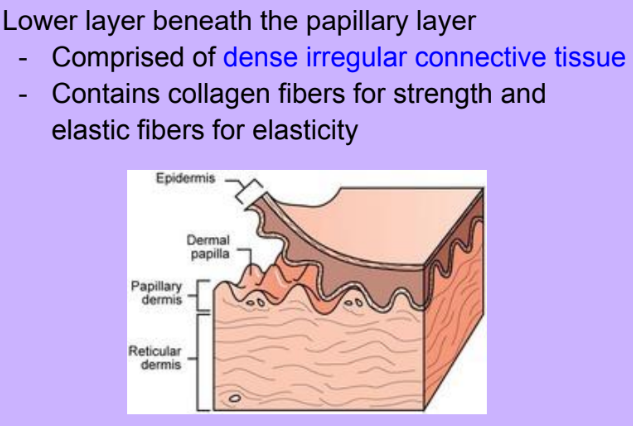
-
Reticular Layer
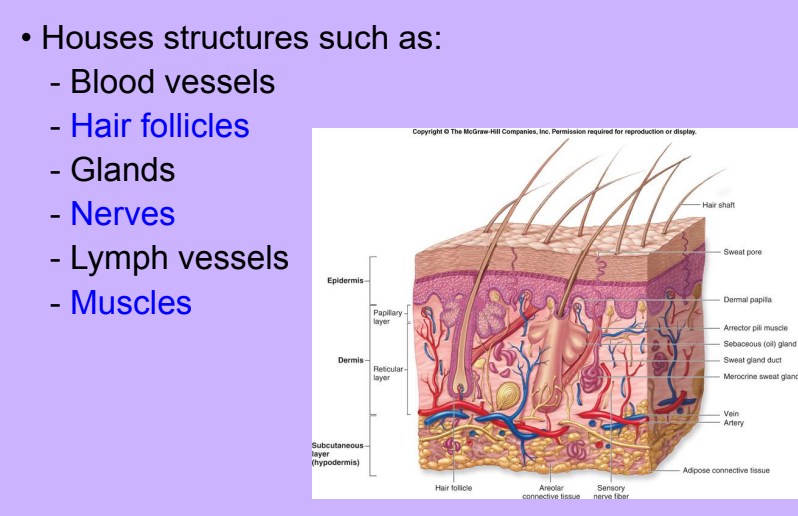
-
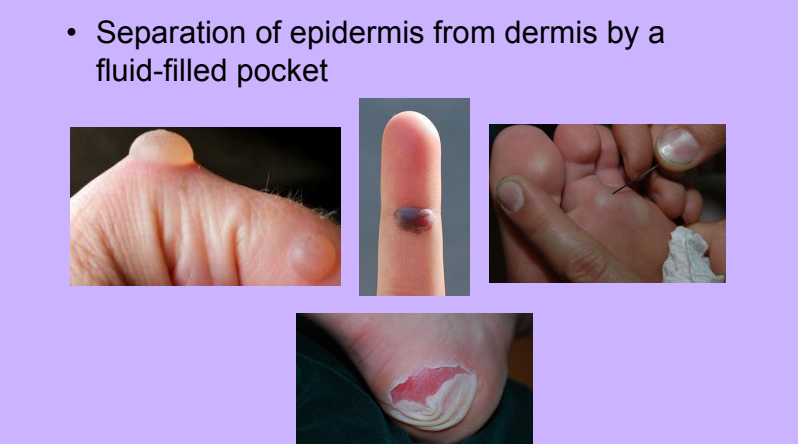
Blisters
-
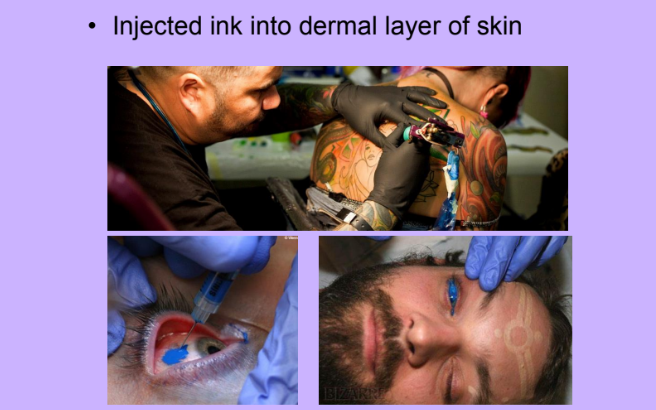
Tattoos
-
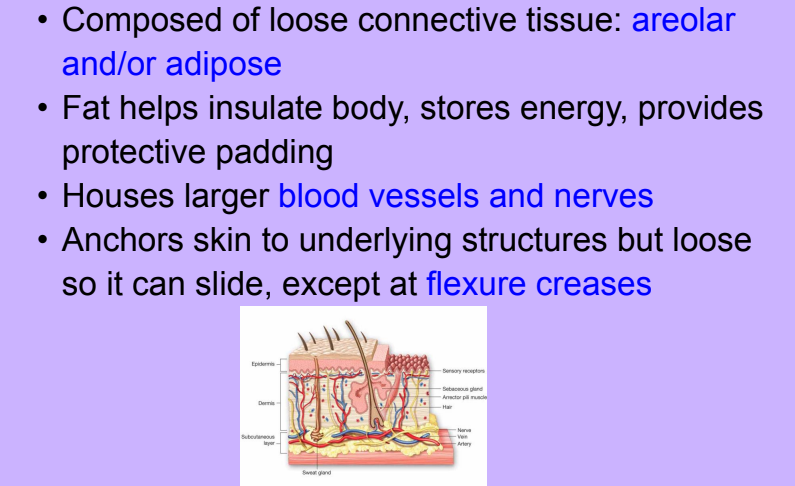
Subcutaneous Hypodermis
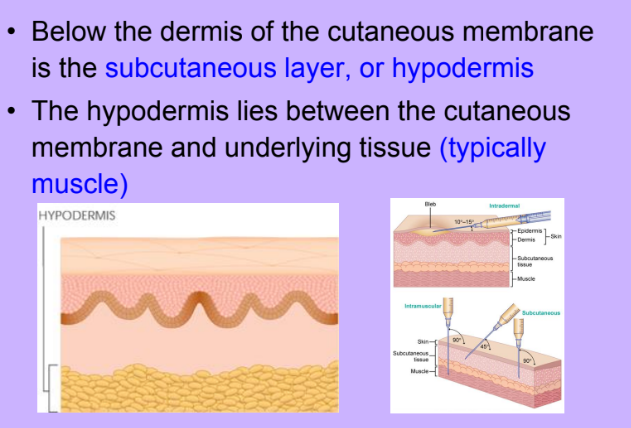
-
Subcutaneous Hypodermis
-
-
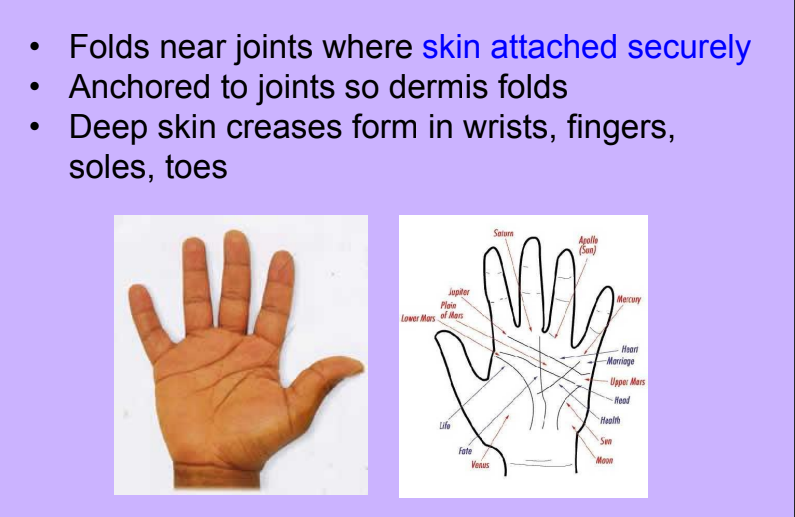
Flexure Creases
-
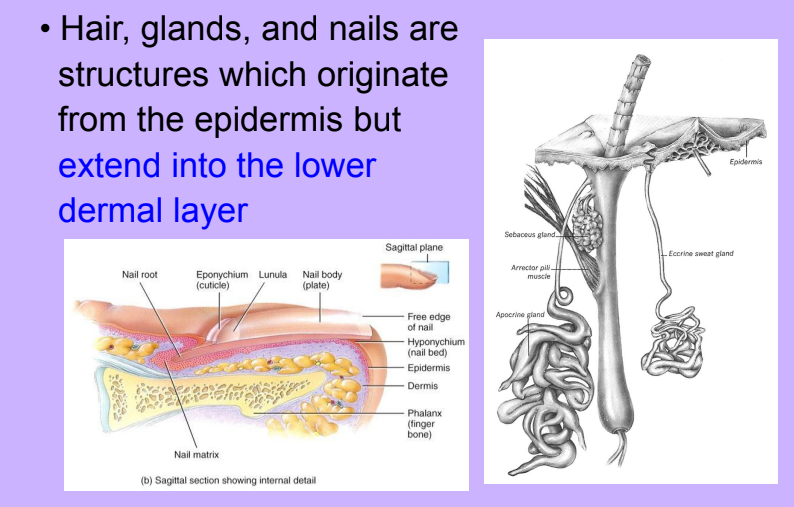
Accessory Structures of the Skin
-
SEM Hair
-
Hair
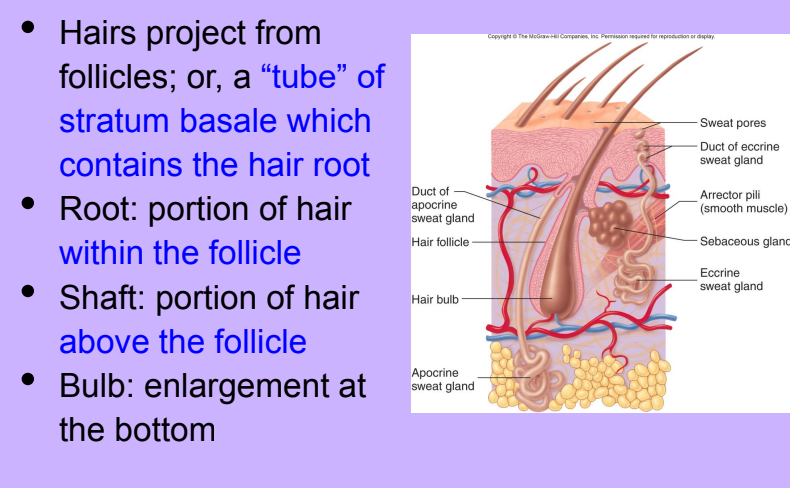
-
Hair
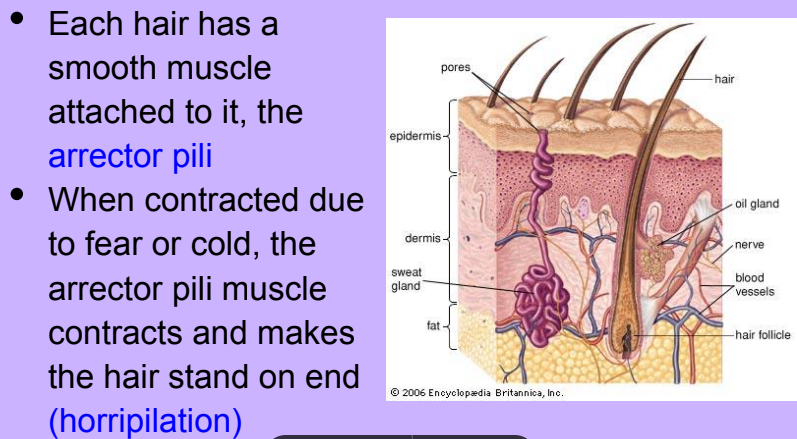
-
Glands
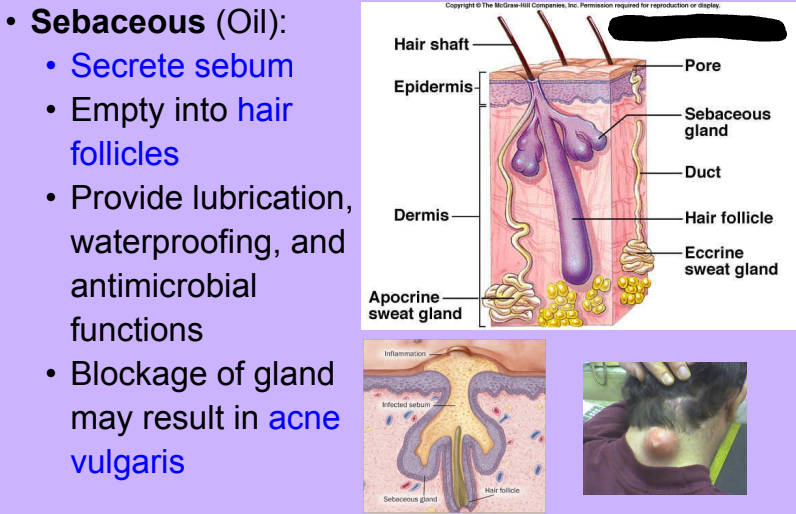
-
Glands
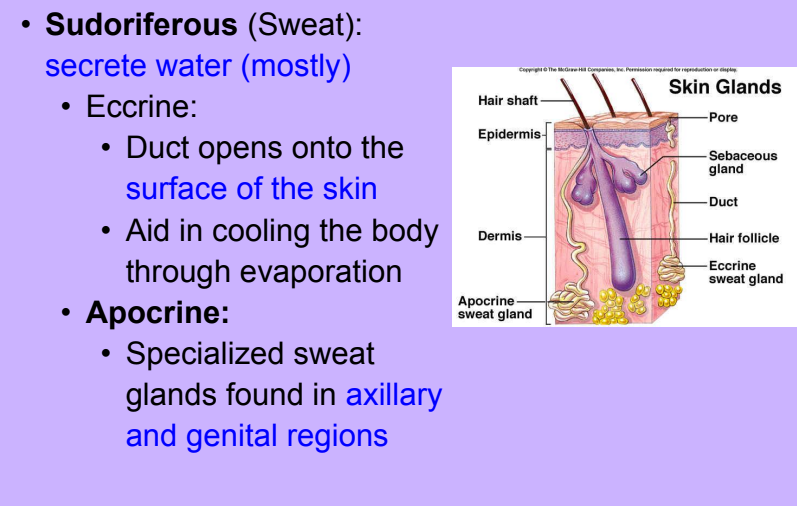
-
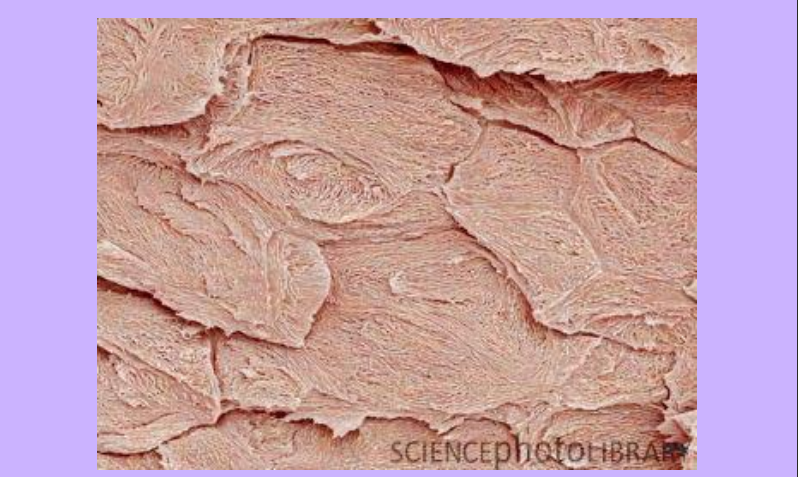
SEM Nail

-
SEM Nail
-
Nails
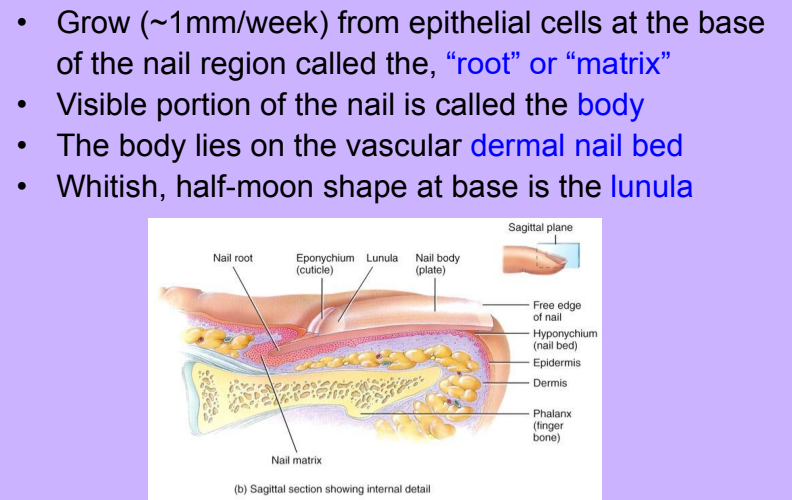
-
Additional Structures
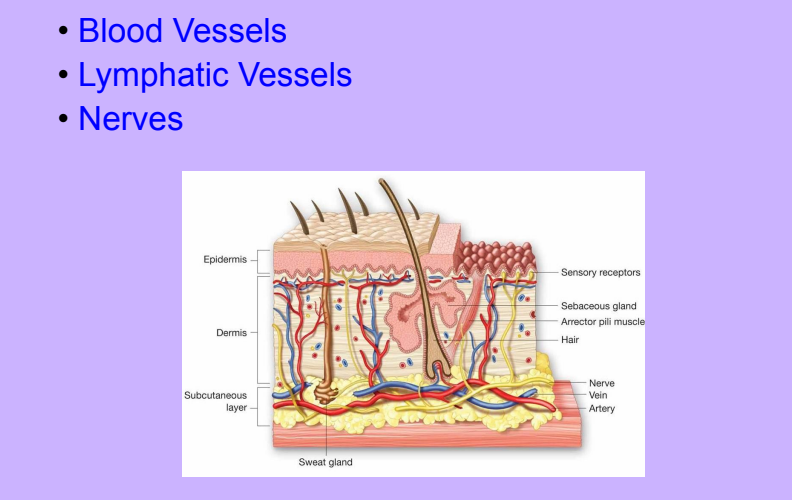
-
Blood Vessels
-
Lymphatic Vessels
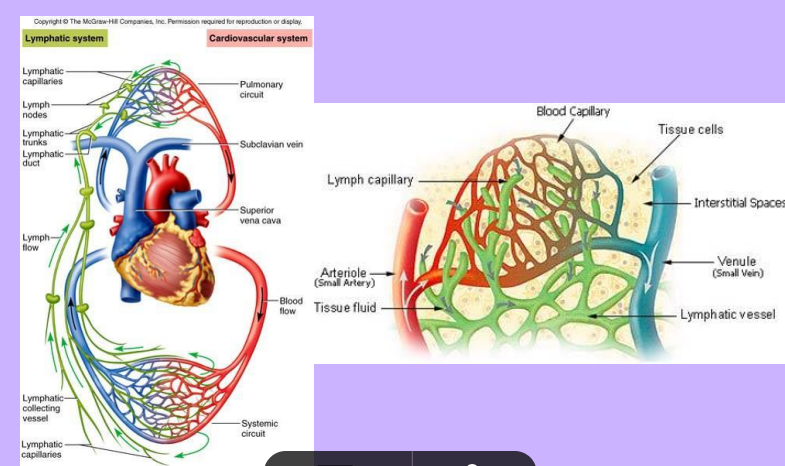
-
Nerves
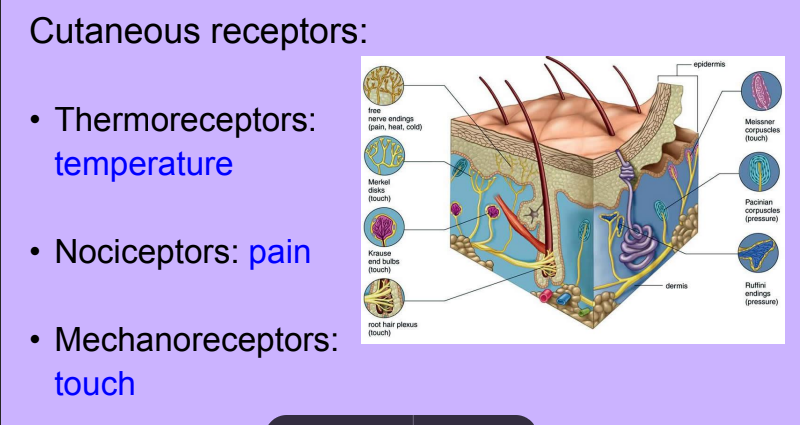
-
Skin Cancer

-
Nonmelanoma
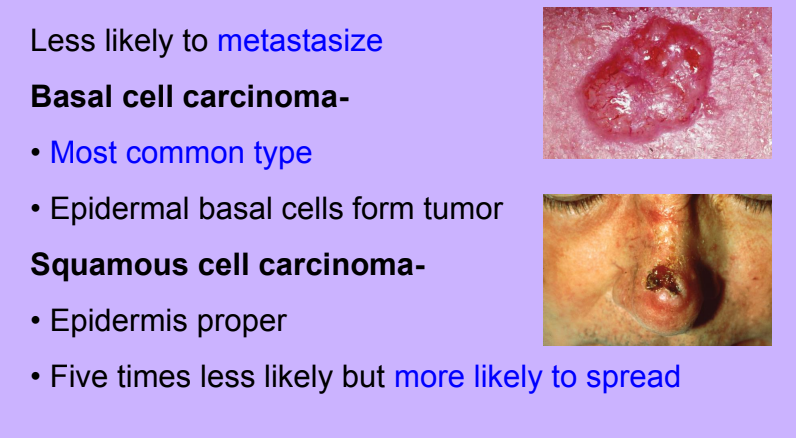
-
Melanoma
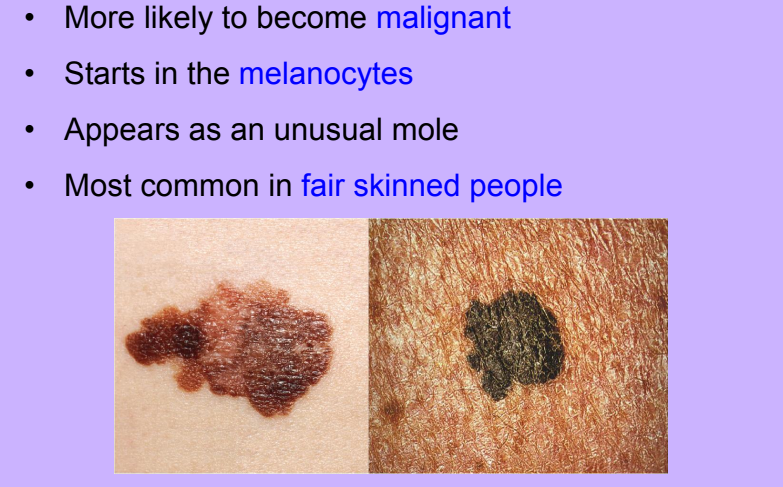
-
Skin Cancers
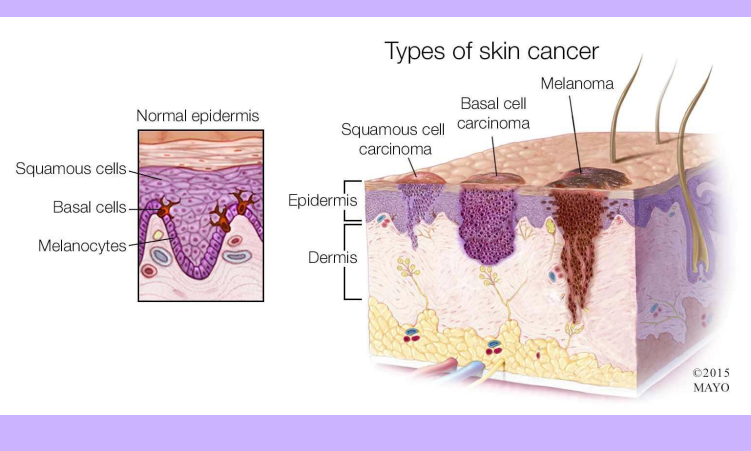
-
Most Common Types of Skin Cancer
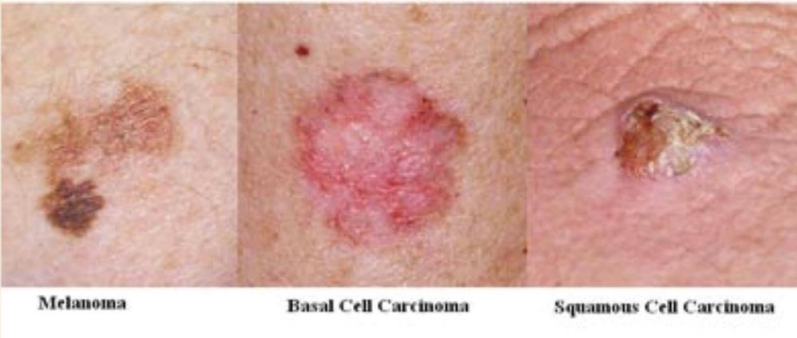
-
Warning Signs for Melanoma

-
The ABCDE's Of Detecting Melanoma
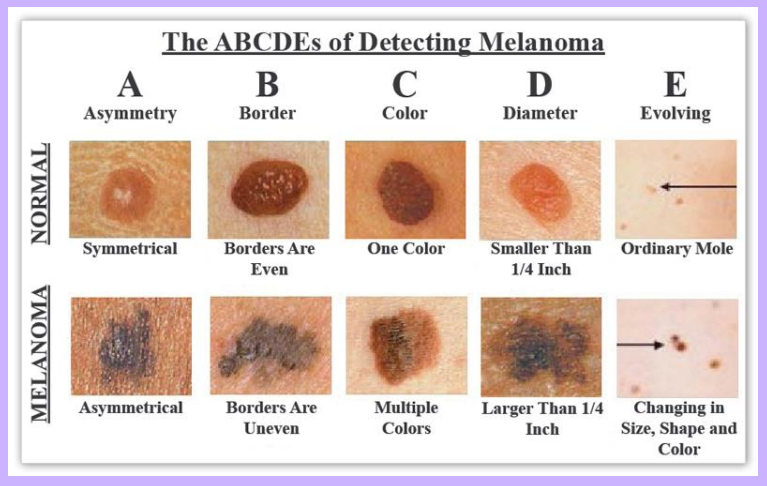
-
Burns

-
Burns
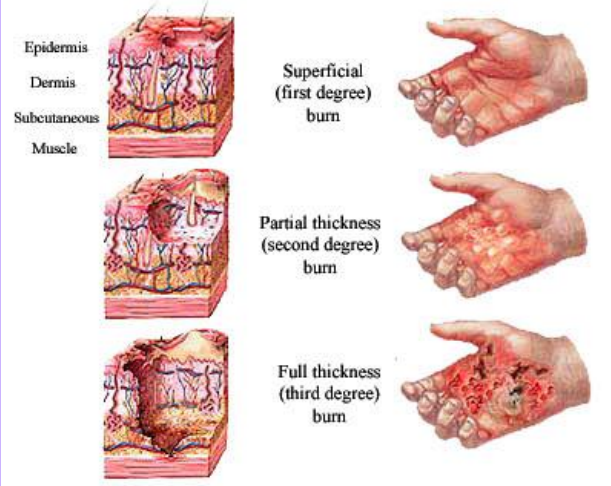
-
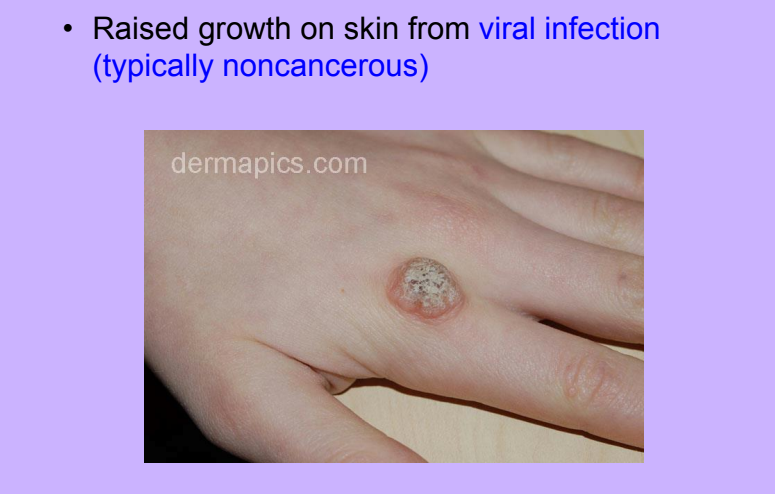
Warts
-
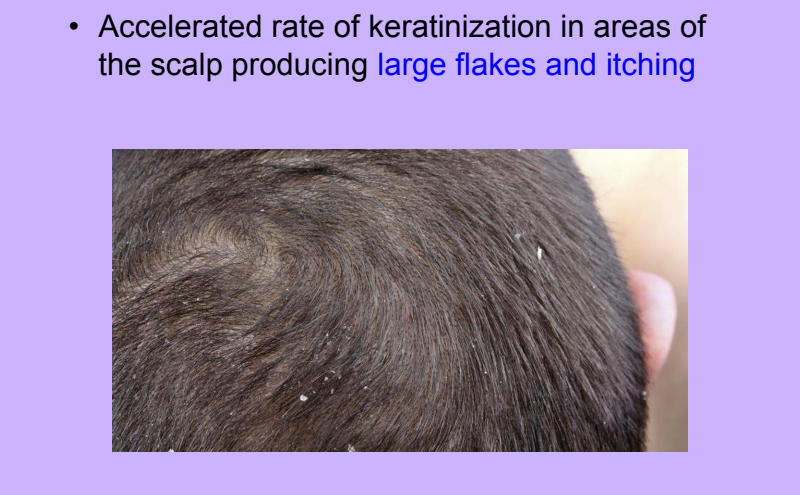
Dandruff
-
Dandruff

-
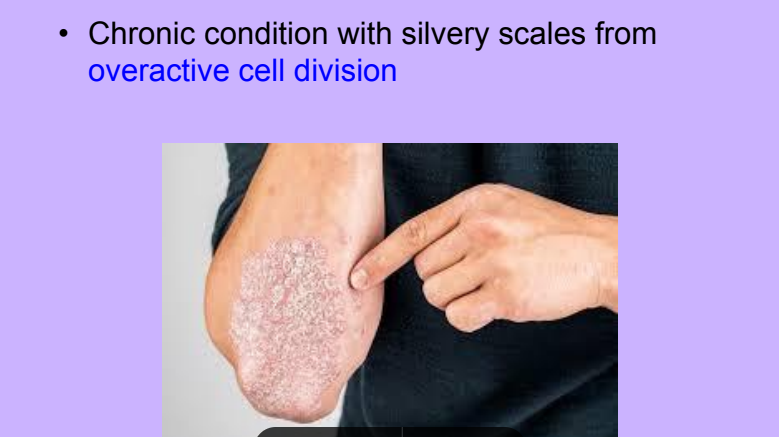
Psoriasis
-
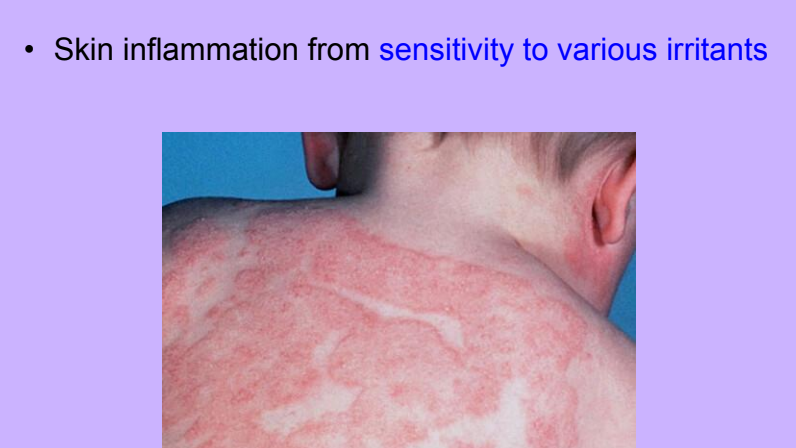
Eczema
-
Acne Vulgaris
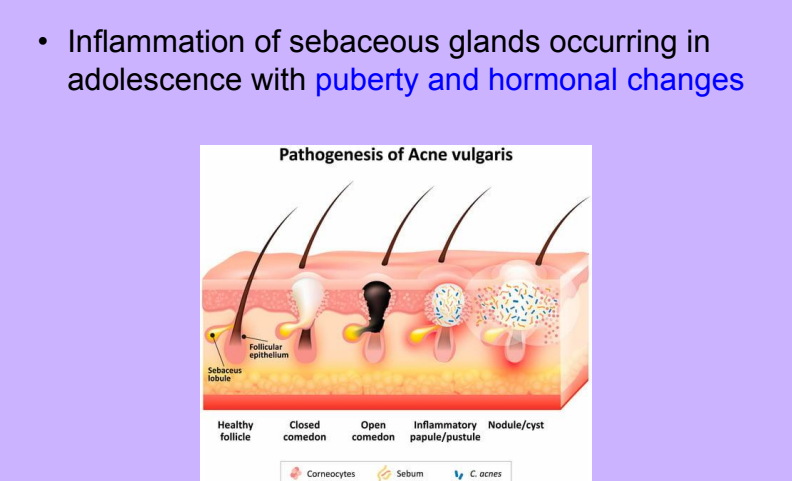
-
Wrinkles

-
Botox
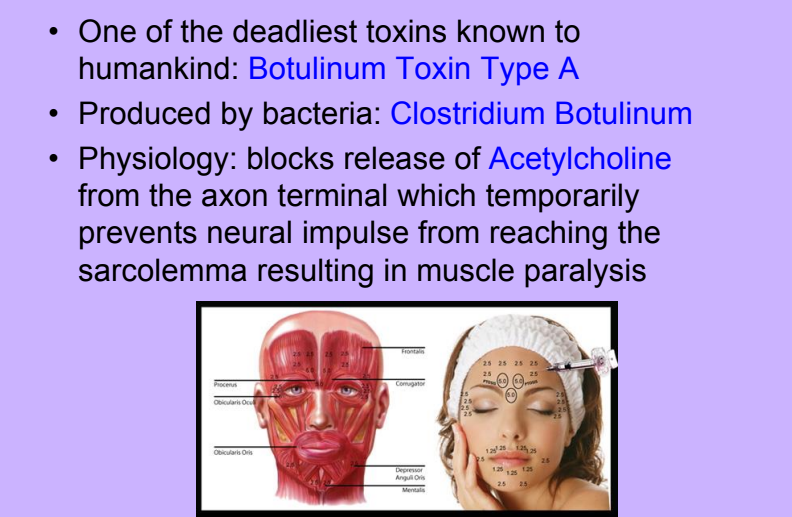
-
Epidermis
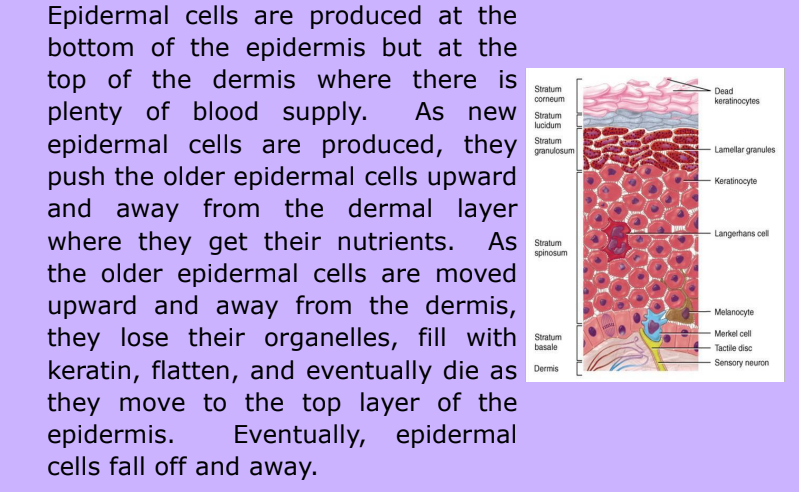
-
Hair

-
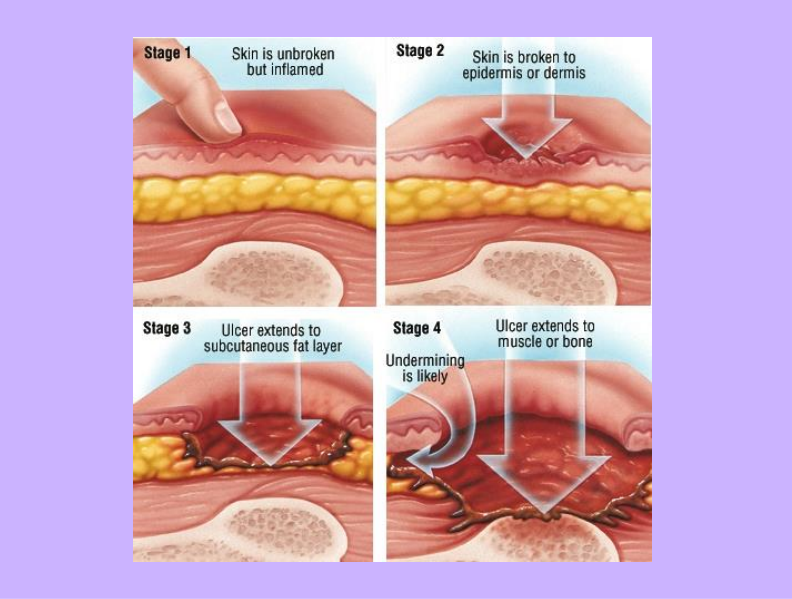
Decubitus Ulcers

-
Freckles

-
Hirsutism

-
Androgenic Alopecia

-
Alopecia Areata

-
Tinea Pedis

-
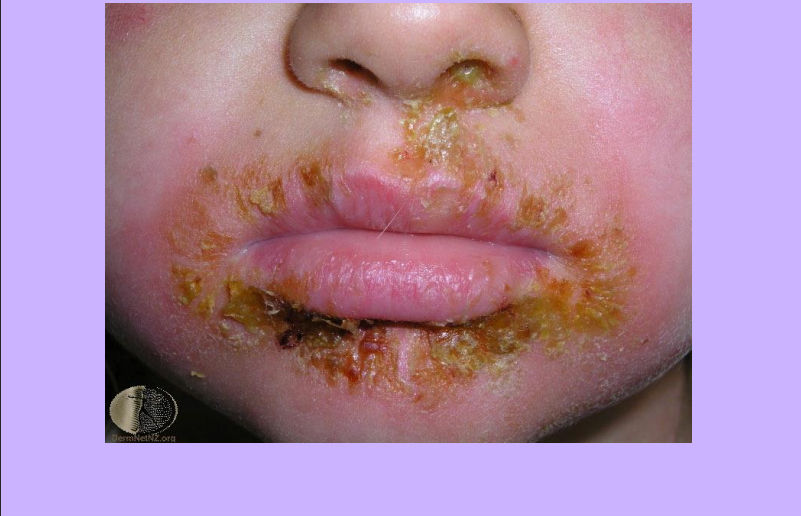
Impetigo

-
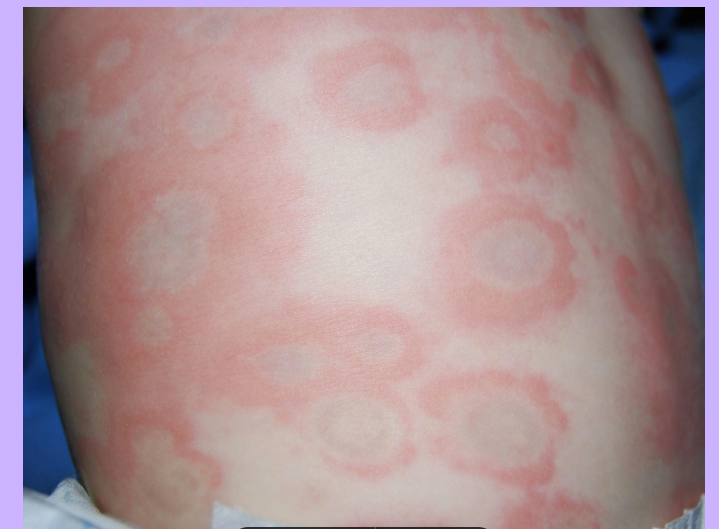
Urticaria (Hives)

-
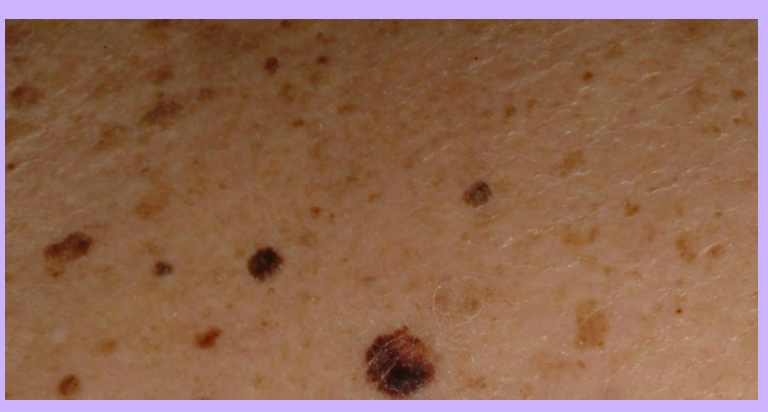
Moles

-
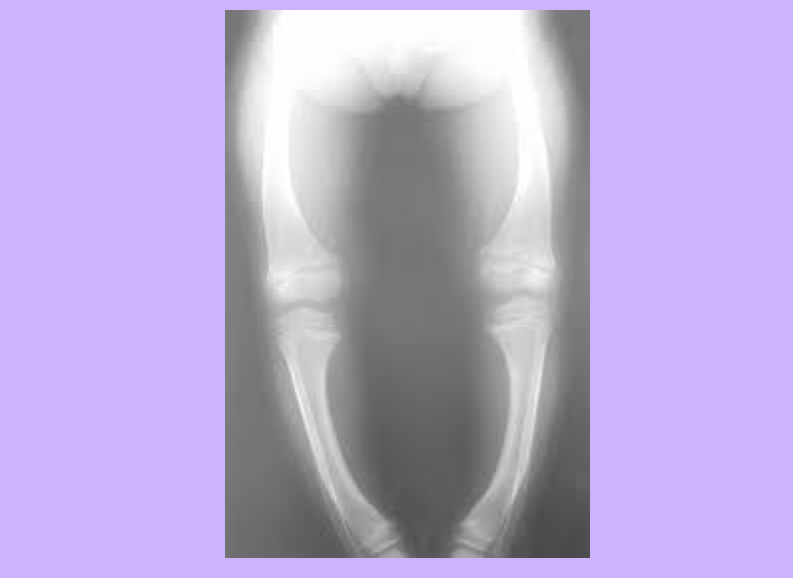
Rickets
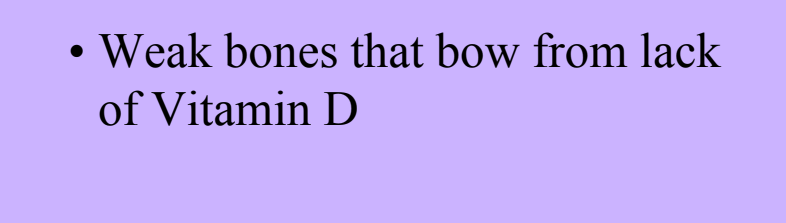
-
Heat Exhaustion and Heat Strokes
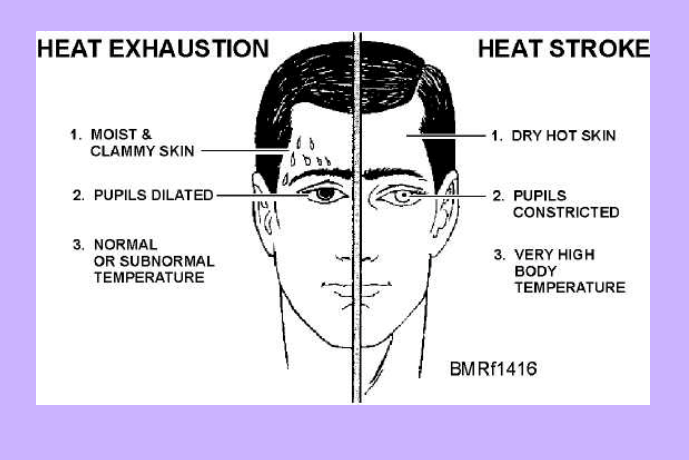
-
Hyperthermia

-
Hyperthermia

-
Hypothermia

-
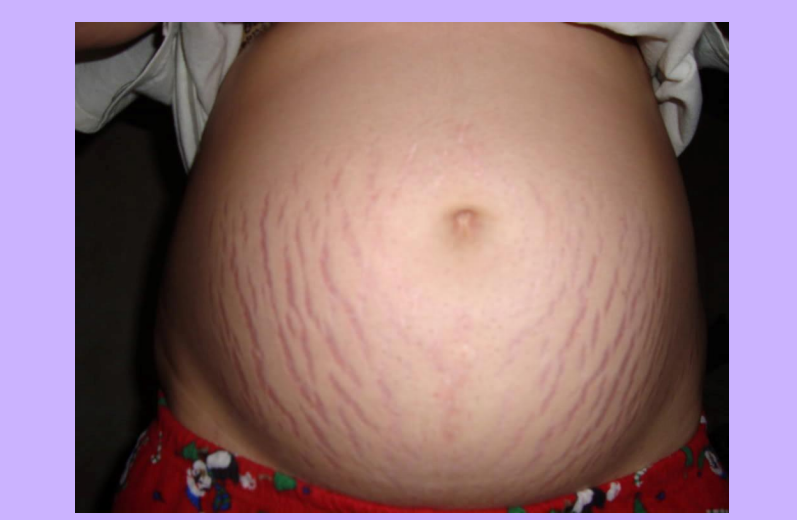
Striae

-
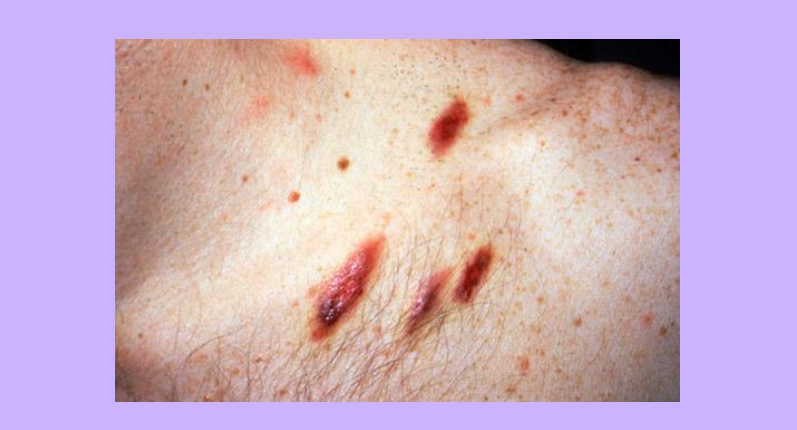
Kaposi's Sarcoma

-
Burns Degrees
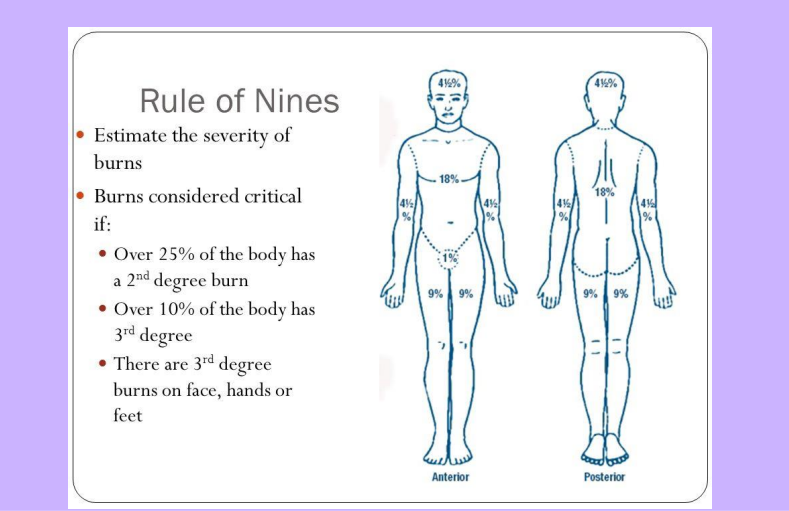
-
Stages of Burns
-
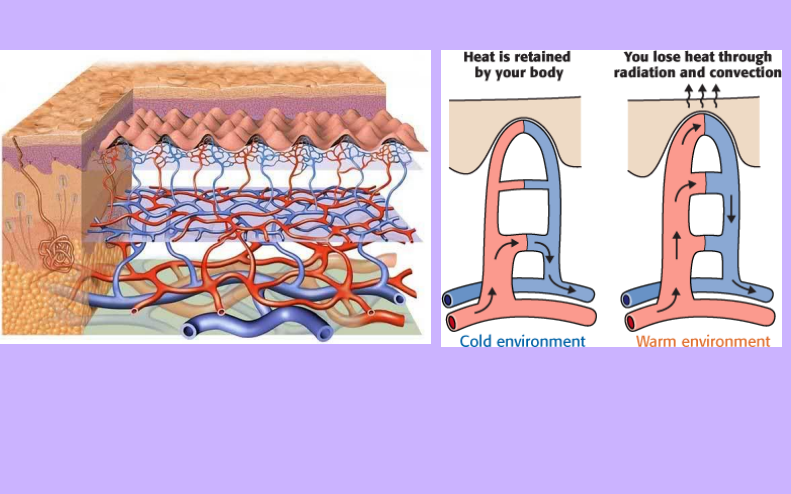
Heat
Radiation from the skin surface and evaporation of sweat are two ways in which the skin helps to get rid of body.
-
Adipose
Fat in the _____ tissue layer beneath the dermis helps to insulate the body.
-
Keratin
The waterproofing protein found in the epidermal cells is called ______.
-
Vitamin D
A vitamin that is manufactured in the skin is ______.
-
Mole
A localized concentration of melanin is ______.
-
Collagen
Wrinkling of the skin is due to loss of the ____ of the skin.
-
Oxygen and nutrients
A decubitus ulcer results when skin cells are deprived of _____.
-
Cyanosis
_____ is a bluish cast of the skin resulting from inadequate oxygenation of the blood.


