-
integumentary system
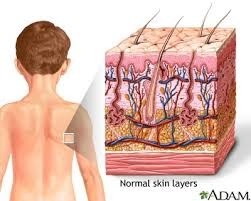
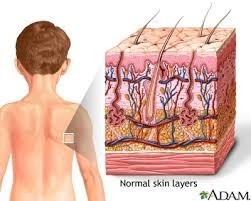 Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail, largest organ of the human body.
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail, largest organ of the human body. -
epidermis
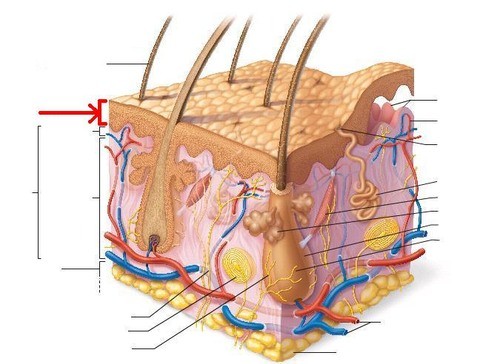 The outer layer of the skin.
The outer layer of the skin. -
dermis
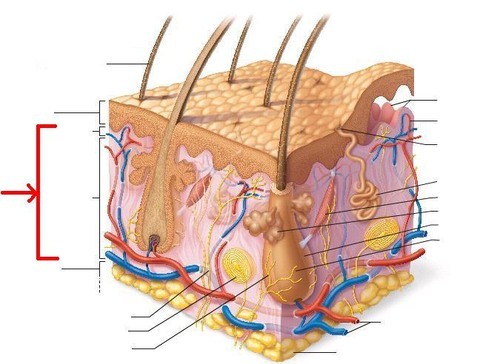 A layer tissue underneath the epidermis of the skin which contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves, sensory receptors, and oil and sweat glands.
A layer tissue underneath the epidermis of the skin which contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves, sensory receptors, and oil and sweat glands. -
hypodermis
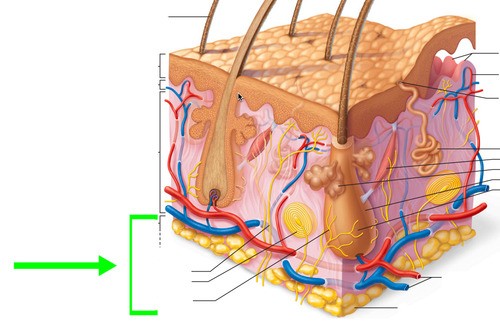 Also called a subcutaneous layer, this is a layer of fat is located under the dermis of the skin; helps to insulate the body and protects underlying muscles and blood vessels.
Also called a subcutaneous layer, this is a layer of fat is located under the dermis of the skin; helps to insulate the body and protects underlying muscles and blood vessels. -
melaninA pigment that gives the skin, hair and eyes color and helps protect the body from harmful UV radiation that causes skin cancer.
-
hair follicle
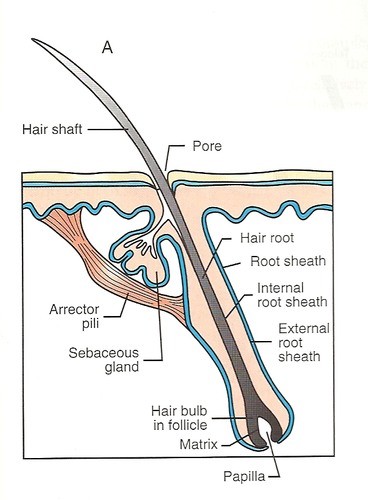 A small tubular cavity in skin containing the root of a hair and is attached to oil glands.
A small tubular cavity in skin containing the root of a hair and is attached to oil glands. -
nail cuticle
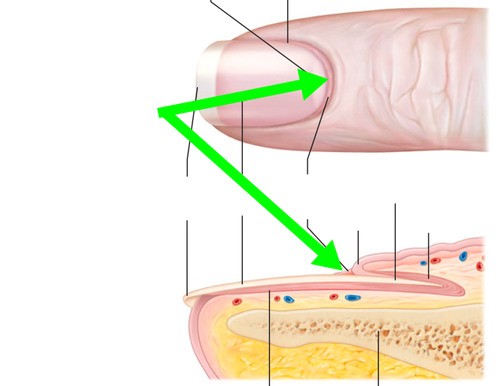 Dead, colorless tissue attached to the natural nail plate.
Dead, colorless tissue attached to the natural nail plate. -
hair root
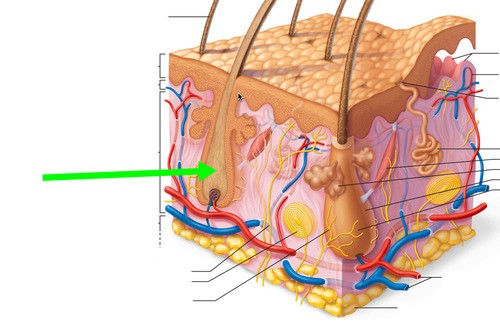 The part of the hair located below the surface of the epidermis.
The part of the hair located below the surface of the epidermis. -
Ist degree burnthe Epidermis has been effected
-
2nd degree burnThe Dermis has been effected
-
3rd degree BurnAll three layers have been effected
-
Sebaceous Glandsfound in the dermis, secrete the oil sebum
-
Sweat Glandsalso called sudoriferous glands, found through the body
-
Apocrine Glandsin the pubic and underarm areas that secrete a thicker sweat
-
Epidermis
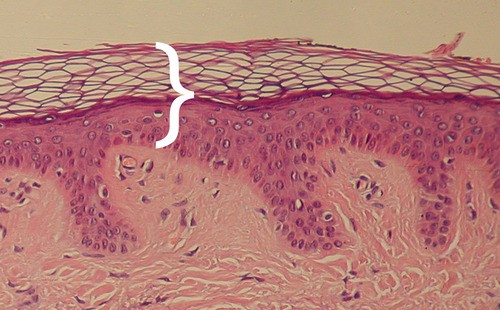 Most superficial layer of skin. Replaced every 4-6 weeks
Most superficial layer of skin. Replaced every 4-6 weeks -
Keratinocytes
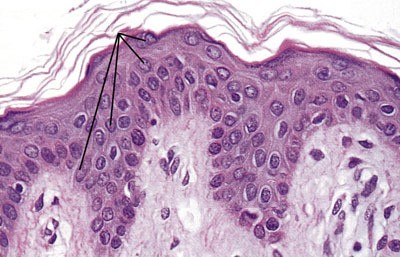 The most abundant epidermal cells, they function mainly to produce keratin.
The most abundant epidermal cells, they function mainly to produce keratin. -
Melanocytes
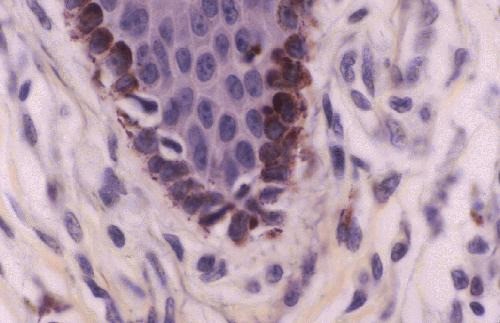 Spidery black cells that produce the brown-to-black pigment called melanin.
Spidery black cells that produce the brown-to-black pigment called melanin. -
Dermis
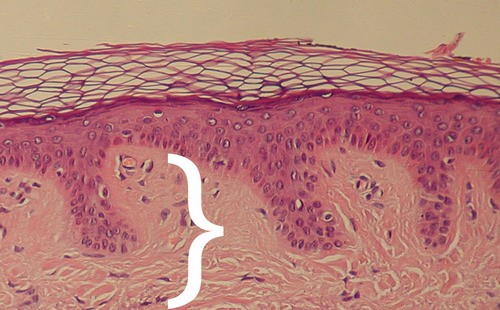 Dense, irregular connective tissue consisting of two regions - the papillary and the reticular areas.
Dense, irregular connective tissue consisting of two regions - the papillary and the reticular areas. -
Sebaceous Glands
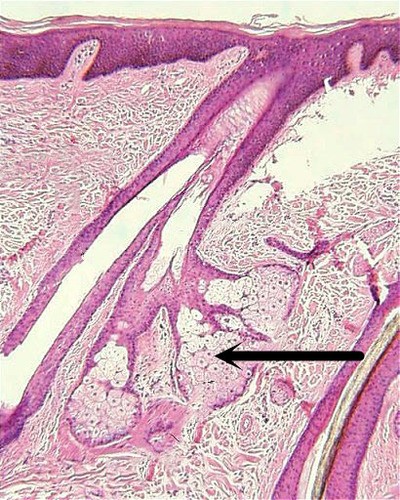 Ducts that empty into hair follicles, excreting oily substances.
Ducts that empty into hair follicles, excreting oily substances. -
SebumThe product of sebaceous glands. It is a mixture of oily substances and fragmented cells that acts as a lubricant to keep the skin soft and moist.
-
Eccrine Glands
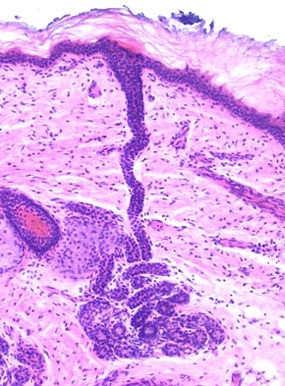 These glands produce sweat.
These glands produce sweat. -
Apocrine Glands
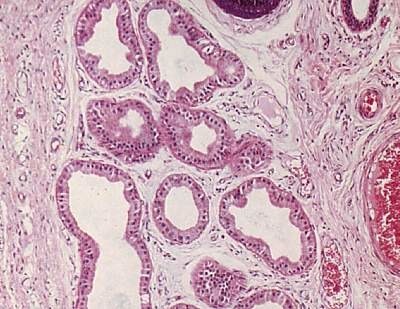 Secrete milky protein that acts as a nutrient medium for the microorganisms found on the skin.
Secrete milky protein that acts as a nutrient medium for the microorganisms found on the skin. -
KeratinFibrous protein that is responsible for the strength and water resistance of the skin surface.
-
CollagenA protein that is a main constituent of connective tissue.
-
MelaninA natural pigment that protects the cells in the skin and in deeper layers from the hazardous effects of UV radiation by absorbing sunlight.
-
HypodermisLayer of the skin made up of connective tissue and fat that acts as insulation and padding for the skin.
-
PoreMade:Tiny openings on top of skin with sweat and oil glands Function: Let sweat and oil come out of skin.
-
Erector Pilli/Arrector PilliMade:Muscles attached to hair Function:makes the hair on a person's arm stand up to keep them warm
-
NerveMade:Sensory receptors Variety of nerve receptors Function:Sense change and information about outside environment
-
Adipose tissue (fat molecule)Made:fat Function:Insulate the body from heat and cold provides padding an energy storage area
-
athlete's footcontagious; fungal infection
-
acnebacterial infection of sebaceous glands
-
subcutaneous layerfat layer
-
direct sunlightprimary cause of skin cancer
-
third degree burninvolves destruction of epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous layer
-
Epidermis
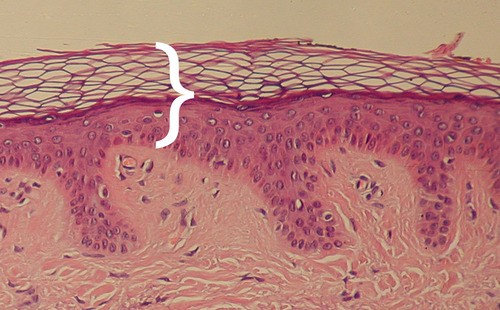 Most superficial layer of skin. Replaced every 4-6 weeks
Most superficial layer of skin. Replaced every 4-6 weeks -
Keratinocytes
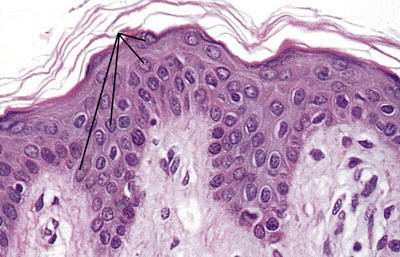 The most abundant epidermal cells, they function mainly to produce keratin.
The most abundant epidermal cells, they function mainly to produce keratin. -
Melanocytes
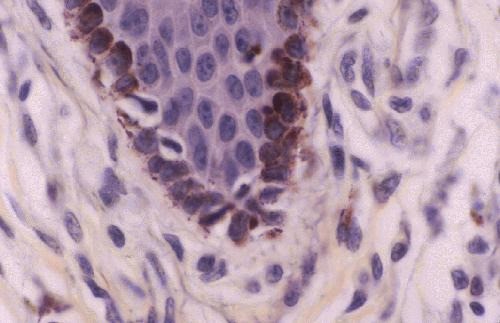 Spidery black cells that produce the brown-to-black pigment called melanin.
Spidery black cells that produce the brown-to-black pigment called melanin. -
Dermis
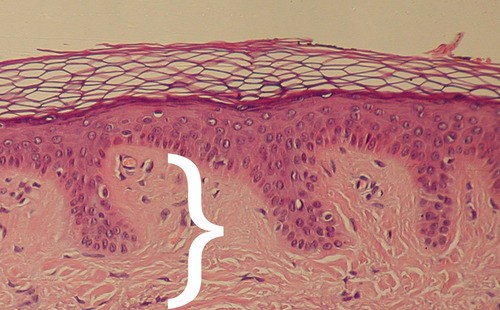 Dense, irregular connective tissue consisting of two regions - the papillary and the reticular areas.
Dense, irregular connective tissue consisting of two regions - the papillary and the reticular areas. -
SebumThe product of sebaceous glands. It is a mixture of oily substances and fragmented cells that acts as a lubricant to keep the skin soft and moist.
-
KeratinFibrous protein that is responsible for the strength and water resistance of the skin surface.
-
CollagenA protein that is a main constituent of connective tissue.
-
MelaninA natural pigment that protects the cells in the skin and in deeper layers from the hazardous effects of UV radiation by absorbing sunlight.
-
HypodermisLayer of the skin made up of connective tissue and fat that acts as insulation and padding for the skin.
-
EpidermisOuter layer. Protects against pathogens:
-
Integumentary system2 layers. Epidermis and dermis
-
HairMade of keratin. Protects scalp from light from sun
-
Hair folliclesTube like pockets of epidermal cells that extend into the dermis
-
NailsGrow from area of rapidly dividing cells known as nail roots. Fingernails grow 3 times faster than toe nails
-
ExcretionSmall amount of sweat release constantly from sweat glands
-
MelanomaCancers that develop from melon gets
-
AcneSebum and dead skin cells form plugs in hair follicles. Bacteria trapped in
-
JointsWhere bones meet. Joints contain connective tissues that hold bones together.
-
Immovable joints/ fixed jointsInterlocked. Skull meets bone
-
*PURPOSE of integumentary*-protects deeper tissues -blocks UV -prevents infection from entering body -temperature regulation -prevents dehydration -makes Vitamin D from sunlight -excrete wastes (sweating) -sensory organ
-
epidermisouter layer; site of rapid mitosis; production of keratin and melanin
-
Melanocytesgive skin pigmentation and protects from UV rays
-
dermisinner layer, contains major structures of skin: collagen, blood vessels, nerve endings, glands, sensory receptors, hair follicles
-
subcutaneous fatadipose tissue, proves insulation for body