-
The cns is protected by...a bony encasement and connective tissue called meninges
-
What surrounds the CNS?Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
-
The gray matter is made up of...neuron cell bodies
-
white matter is made up of...myelinated axons
-
The cortex of the brain is made up of gray or white matter?gray
-
Neurotransmitters are also known as...neuropeptides
-
What are the four major regions of the brain?
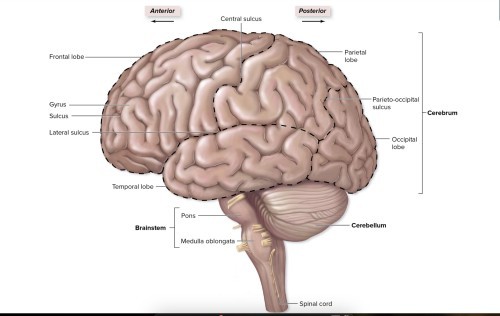 -cerebrum -diencephalon -brain stem -cerebellum
-cerebrum -diencephalon -brain stem -cerebellum -
Requirements of the CNS.Communication, metabolism
-
CNS accounts for what percent of body weight?2
-
The CNS needs about what percent of cardiac output? What does this imply?20%; large metabolic demand
-
True or False: the CNS is sensitive to toxins.true
-
The cerebrum accounts for what percent of brain mass?80%
-
List the functions of the cerebrum. (5)• Perception of sensations • Initiate movement • Memory • Thought & reason • Emotion
-
What divides the frontal and parietal lobes of the cerebrum?central sulcus
-
How are the cerebral hemispheres connected?corpus callosum
-
What seperated the two cerebral hemispheres?longitudinal cerebral fissure
-
What are the convulutions of the cerebrum called? (2)gyri-folds sulci-grooves
-
The medulla is composed of ____ matterwhite
-
What is the purpose of the convulutions of the cerebrum?increase surface area
-
The cranial meninges, listed from deepest (closest to the brain) to superficial (farthest from the brain and closest to the skull), are the...pia mater, arachnoid mater, and dura mater
-
pia mater is made up of...areoloar c.t, highly vascularized
-
What are the 5 lobes of the cerebrum?Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Insula
-
Function of frontal lobe:initiates voluntary movement
-
Parietal;responds to sensory stimuli
-
Temporal;auditory sensations
-
Occiptal;visual sensations.
-
Insula;not on surface; memory function
-
The ________ gyrus is located behind the central sulcus and is responsible for...postcentral, somatosensory processing
-
The __________ gyrus is located in front or anteriorly to the central sulcus is responsible for...precentral, controlling voluntary movements on the opposite of the body
-
List features of the white matter of cerebrum: (3)-association fibers -commissural fibers -projection fibers
-
Where are association fibers located?within a cerebral hemisphere
-
Where are commissural fibers located?b/w cerebral hemispheres
-
Describe projection fibers.ascending and descending tracts
-
What transmit impulses from cerebrum to spinal cord and from spinal cord to cerebrum?projection tracts
-
Basal nuclei is found where?deep cerebrum
-
Describe basal nuclei...mass of gray matter deep to cerebrum control involuntary movement of skeletal muscle
-
The thalamus is part of what brain structure?diencephalon
-
Describe the thalamusrelay center (sensory stimuli) between cerebrum and other brain areas
-
Language processing is normally located where on the cerebrum?Left hemisphere
-
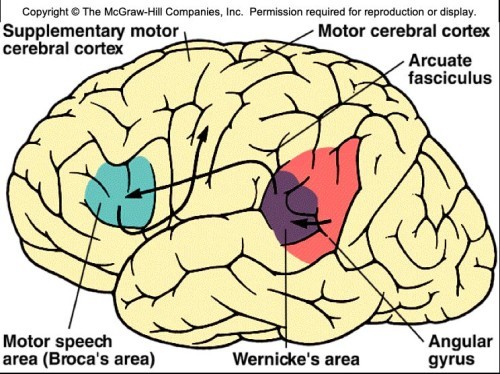
What is the motor speech area also known as?Broca's area
-
The function of the motor speech area is to...translate thought patterns into speech
-
The motor speech area or broca's area is located where?
-
What is the wernicke's area responsible for? Where is located?
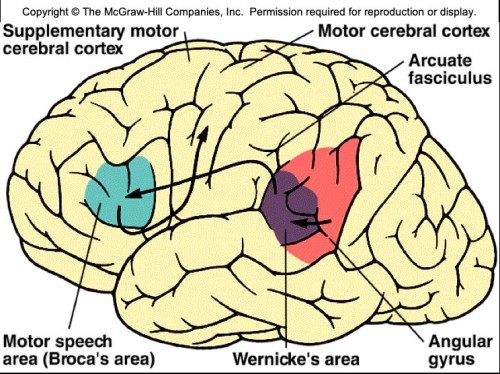 concept of words
concept of words -
What is the angular gyrus responsible for? Where is it located
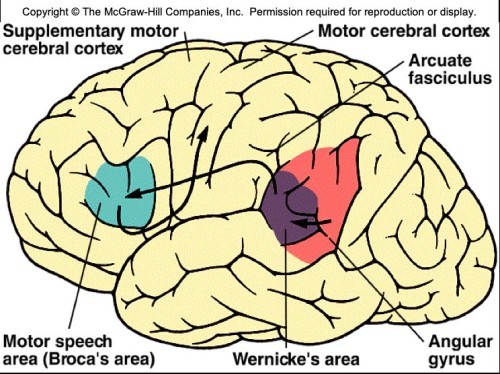 center for integration of auditory, visual, and somatesthetic information
center for integration of auditory, visual, and somatesthetic information -
Describe the thalamus.(3)-paired organ -gray matter -sensory relay to cerebym -autonomic response to intense pain
-
Describe the hypothalamus and pituitary gland common functions (3)Regulation of visceral activity Emotional and instinctual functions Secretes hormones
-
Describe the functions of the epithalamus.Neuroendocrine function (via pineal gland)
-
List the four components of the diencephalon.thalamus hypothalamus epithalmus pituitary
-
The corpora quadrigemina is made up of the...superior and inferior colliculi
-
The hypothalamus functions as the ____________ center.homeostatic
-
True or false: the pituitary is directed by hypothalamus.true
-
The pineal body produces what common hormone?melatonin
-
The pituitary gland is attached at a structure called the...infundibulum
-
What skull structure holds the pituitary gland?sella turcica
-
What are the two parts the pituitary gland can be divided into?adenohypophysis (anterior, gray) neurohypophysis (posterior, white)
-
The mesencephalon or midbrain houses nuclei forautonomic functions
-
Function of superior colliculiThey are called visual reflex centers because they help visually track moving objects and control reflexes such as turning the eyes and head in response to a visual stimulus.
-
Function of inferior colliculiauditory reflex center ex: BANG!=you turning at noise
-
What is the function of red nucleus?-motor coordination -maintain posture
-
What is the function of the substantia nigra?inhibit forced involuntary movements.
-
What are the three main structures found in the midbrain? (3)-corpora quadrigemina -red nucleus -substantia nigra
-
List main components of brain stem: (3)-midbrain -pons -medulla oblongata
-
The metencephalon consists of what two structures?pons and cerebellum
-
Describe pons:-bulge on inferior surface of brain -two sets of white matter tracts -nuclei of cranial nerves -respiratory centers -peduncles carry fibers to cerebellum
-
What is the second largest structure in the brain after the cerebrum?cerebellum
-
The cerebellum consists of ___ hemispherestwo
-
The cerebellum has a thin outer cerebellar _____.cortex
-
What structure connects the cerebellum to the rest of the brain?cerebellar peduncles
-
Function of cerebellumcoordinates skeletal muscle contraction (movement)
-
the cerebellum is or is not part of brainstem?IS NOT
-
Define decussationDecussation refers to a crossing within the central nervous systen
-
Describe the medulla oblangata nuclei and tracts:form all descending and ascending connections between spinal cord and brain
-
True or False: The medulla oblongata has many descussations.true
-
The medulla oblongata relays to the _________ (nucleus gracilis and cuneatus)thalamus
-
The medulla oblongata has __________ centers for visceral functionsautonomic
-
The medulla oblongata has some triangular elevations called...
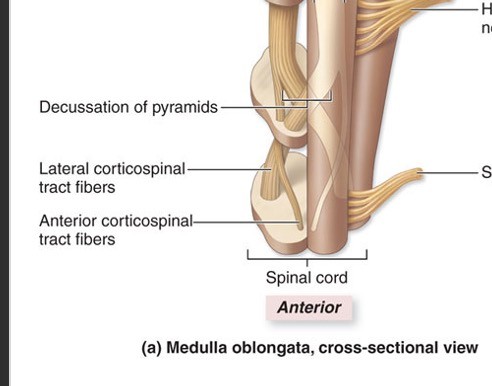 pyramids
pyramids -
Describe the limbic system (4)• The limbic system is composed of multiple cerebral and diencephalic structures. • It processes and experiences emotions. • It is involved in motivation, emotion, and memory with an emotional association. • It affects memory formation by integrating past memories of physical sensations with emotional states.
-
What is a fornix?Fornix-group of communicating fibers
-
Limbic system:
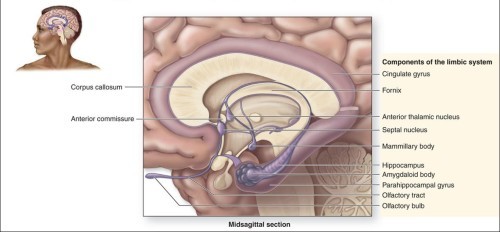
-
What is reticular formation? *3*-The reticular formation is a network of neurons that spans across the brainstem. It is involved in many functions such as consciousness, sensory and motor function, emotion processing, cardiovascular control, and more. -Function in arousing the cerebrum -Generate a continuous flow of impulses
-
Were is reticular formation found?spinal cord, pons, midbrain, thalamus
-
Reticular formation is involved in the response to...environment
-
The subarachnoid space is filled with what?cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
-
The pia mater is highly...vascular
-
The dura mater is in contact with...bone (periosteal layer).
-
Dura mater in brain has two layers (dural sinus) and is ___ found on the meninges of the spinal cordnot
-
Spinal Cord Meninges:Epidural space (no connection between dura and vertebrae)Denticulate ligaments
-
What are the ventricles of the brain?lateral ventricle (left and right) third ventricle fourth ventricle central canal
-
Where is the lateral ventricle found?cerebrum
-
Where is the third ventricle found?diencephalon
-
Where is the fourth ventricle found?Between pons and cerebellum
-
Where is the central canal found?spinal cord
-
What is the mesencephalic aqueduct also known as?cerebral aqueduct
-
How does CSF exit?nfourth ventricle through three foramina: nMedian aperature nTwo lateral aperatures
-
How is CSF produced?nproduced by filtration of blood plasma through specialized capillaries – choroid plexus
-
________ cells aid in CSF movementependymal
-
How does CSF return to circulation?nreturns to circulation through arachnoid villi (specialized venous capillaries)
-
The subdivision of the brain that does not initiate somatic motor movements, but instead coordinates and fine-tunes those movements is which of the following? a. medulla oblongata b. cerebrum c. cerebellum d. diencephalonc. cerebellum
-
3. The visual reflex center is housed within which structure? a. cerebellum b. superior colliculus c. hypothalamus d. ponsb. superior colliculus
-
After a severe blow to the head, a patient suddenly does not experience sensations of hunger and seems unable to tell if he is dehydrated. The attending physician should suspect damage to or a lesion within what general region of the brain? a. frontal lobe b. medulla oblongata c. Wernicke area d. hypothalamusd. hypothalamus

