-
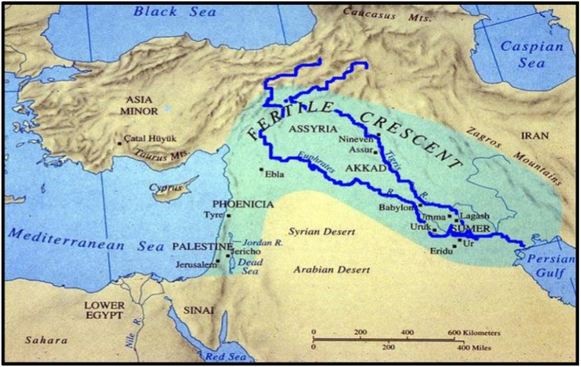
Read The land between two rivers (Theory B). Describe the landscape of ancient Mesopotamia. Use the following words in your answer: desert, Euphrates, Tigris, cities.
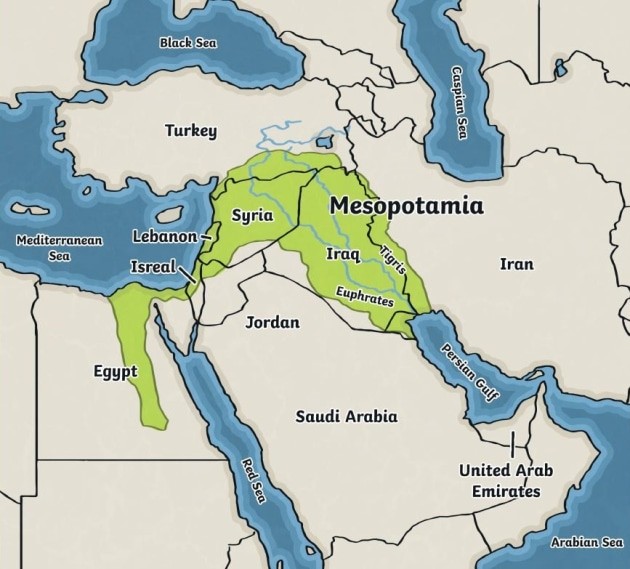
The ancient Greeks named this area Mesopotamia, which means ‘land between two rivers.’ They named it this way because the area was bordered by the Euphrates and Tigris rivers. It is a deserted region. Cities arised around the rivers
-

Read Floods caused by the gods (Theory D). Think up a true reason to explain why the rivers overflowed. Think about where the rivers come from and how they get their water.

The true reason why the rivers overflowed is because of rainfall and melting snow in the mountains where the rivers originate.
-

how did agricultural-urban societies arose

1 The river overflowed and left fertile silt. Farmers grew their crops there.
2 Some farmers learned that they could dig small canals to make more land fertile.
3 Because of irrigation and floods, farmers grew more food than they could eat.
4 Because of this agricultural surplus some people could specialis
5 These people became craftsmen when they specialised in making products with their hands.
6 The craftsmen and farmers traded their wares at markets for food.
7 Some of these craftsmen started to live in cities; this is how agricultural-urban societies arose.
-

Specialise

when someone becomes very good at one thing
-

Craftsman

makes products with his hands and tools
-

Irrigation

small canals that make water flow further inland
Markets
-

Markets

places where people barter their products
-

Agricultural surplus

farmers have more food than they can eat
-
‘specialise’ and ‘craftsman’. Use the source to explain your answer.
craftman is someone who is specialised in making things with tools and their hands.When someone is is specialised, he is very good at his job
-

civilisation.
a group/societiy who adopted the same culture, the same language, writing, laws, art and religion. Because of this we speak of a civilisation.
-
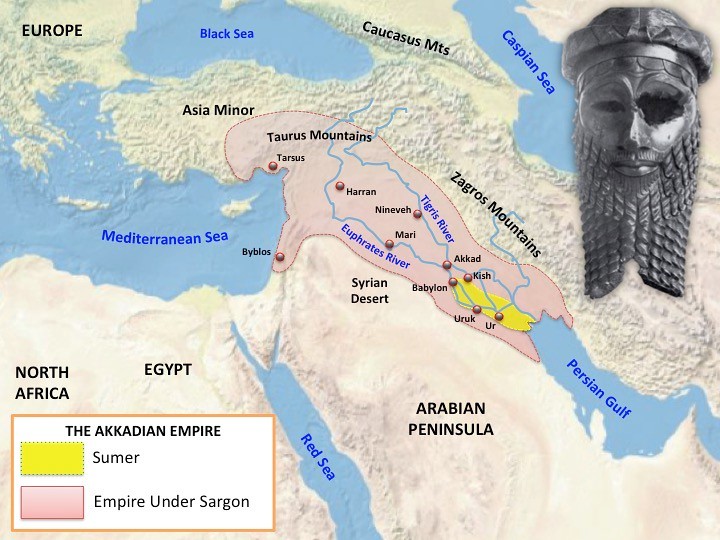
Sumerian civilisation

In the Sumerian civilisation every city had its own leader. The leader of the strongest city could name himself king of Sumer.
-
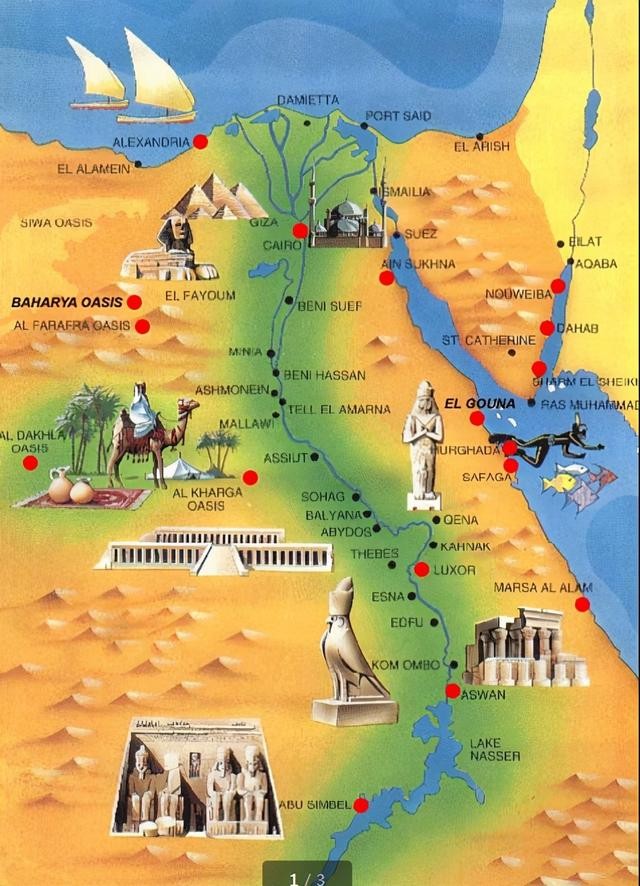
Egypt civilisation

In Egypt another civilisation arose around the Nile River. The Egyptians also relied on the flooding of the river and some lived in cities. Their king was called a Pharaoh, and he was worshipped as a god.
-

spread culture by influence (etkilemek)

The Sumerians and the Egyptians influenced the other countries around them. Through war and trade, their culture was spread throughout the Middle East.
-

Which five aspects of a culture /civilization can you find in the text?

Language, writing, law, art and religion.
-

Give two similarities between the civilisations of Sumer and Egypt. What did they have in common?
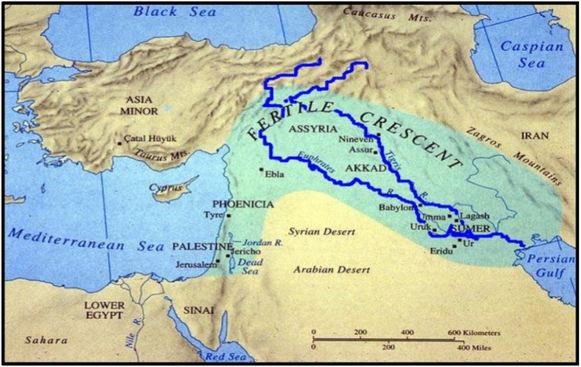
Both Sumer and Egypt had a highly developed civilisation that arose around rivers. In both civilisations cities developed and each was ruled by a king.
-

Give one difference between the civilisations of Sumer and Egypt.

The Egyptian king was called a pharaoh and the Egyptians had their own language, laws and art.
-

Explain how flooding of rivers could lead to the development of cities. Use: cooperation, surplus, specialise, trading, markets, cities.

When rivers overflow they leave fertile silt. Farmers can use this silt for growing their crops. The fertile silt makes it possible for farmers to grow more food than they can eat. Because of this agricultural surplus, some farmers can specialise in other jobs and become craftsmen, merchants or priests. They traded their products in markets and around these markets, cities developed.
-

agricultural-urban societies

majority/ most of the people live as a farmer, minority lives in the city