-
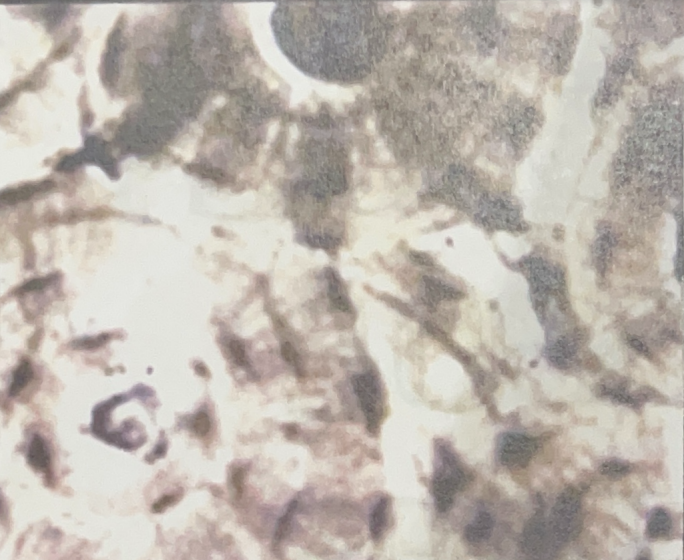
Compact Bone Tissue
- bones throughout the body
- supports, protects, provides framework
-
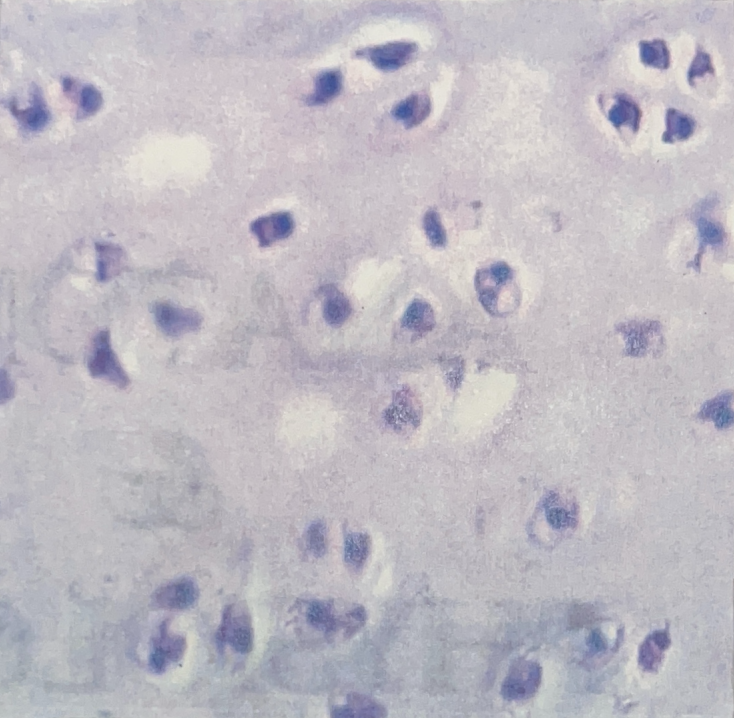
Hyaline Cartilage
- ends of bones, nose, rings of trachea
- cushions, protects
-
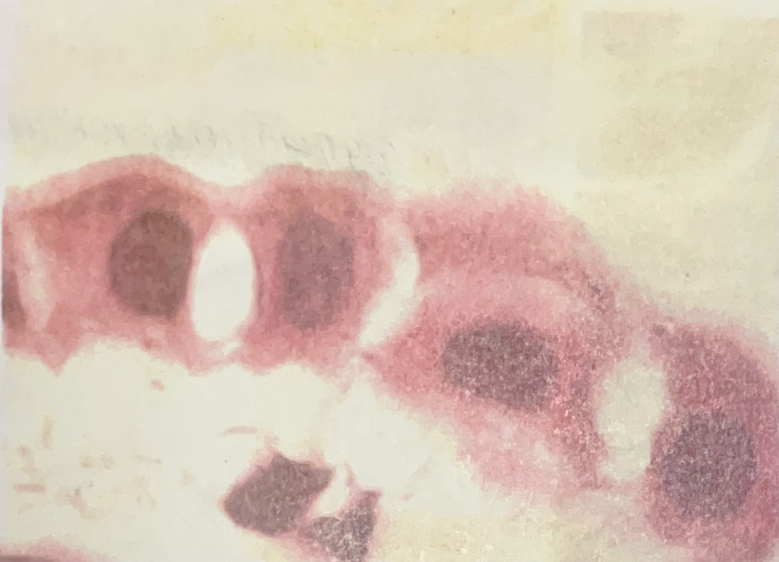
Simple Cuboidal Tissue
- glands and kidney tubules
- secretion, absorption
-
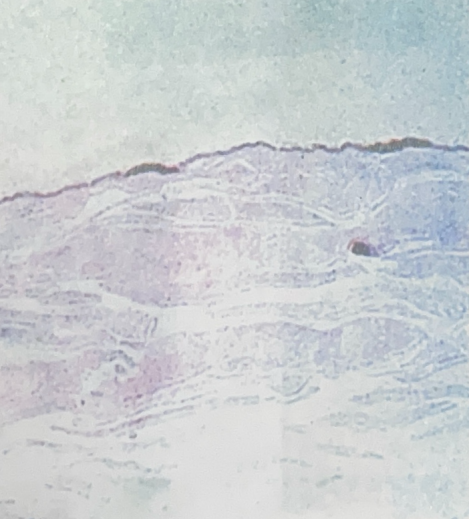
Simple Squamous Epithelial Tissue
- lines lungs, blood vessels, and heart
- filtration, absorption, secretion
-
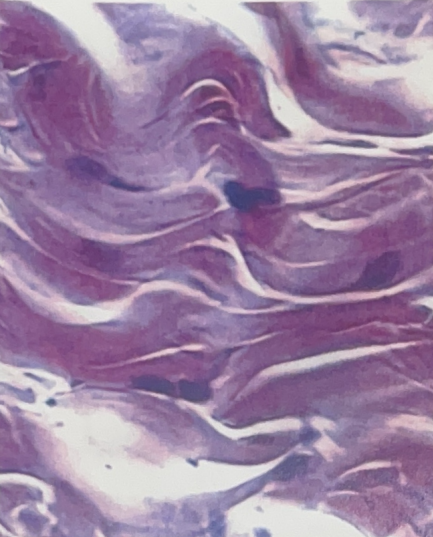
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
- inner portion of skin
- binds skin onto underlying tissue
-
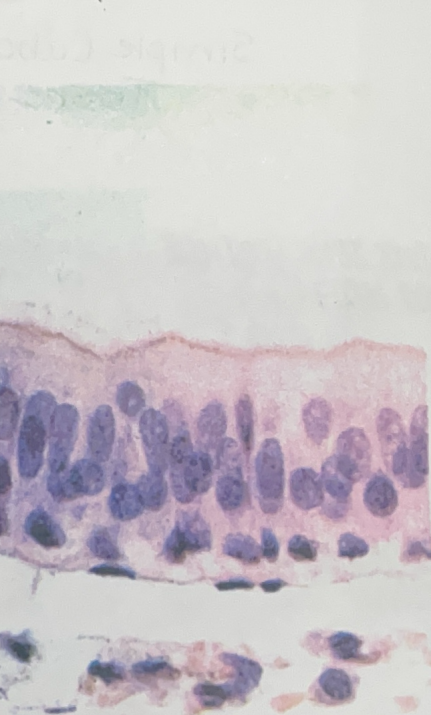
Pseudostratified Epithelial Tissue
- respiratory and reproductive tracts
- protection, secretion, movement of mucus/sex cells
-
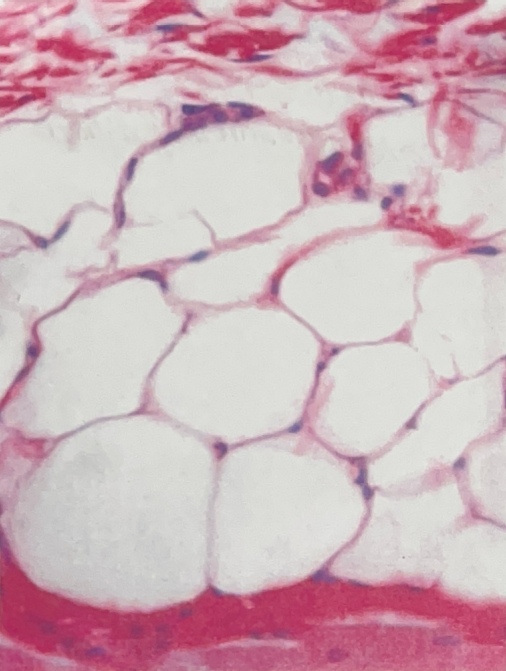
Adipose Tissue
- around heart and kidneys, beneath skin, and in breast tissue
- insulation, storage
-
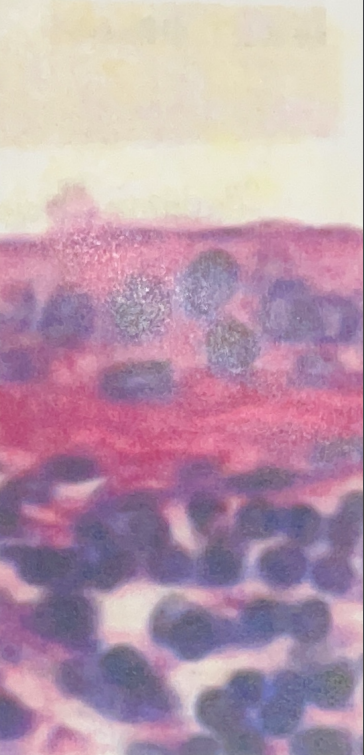
Stratified Columnar Epithelial Tissue
- lines larger ducts of excretory glands
- protection, secretion
-
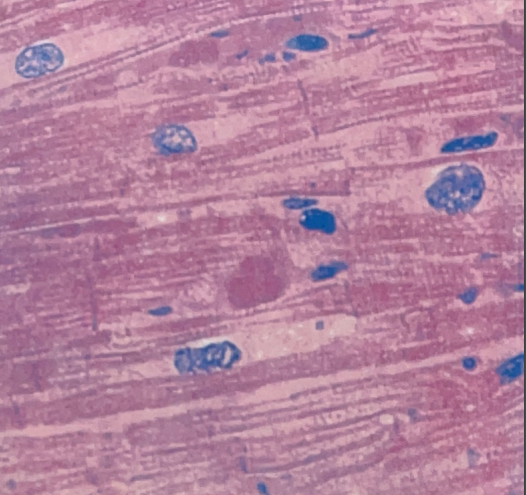
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
- in the heart
- contraction of the heart tissue
-
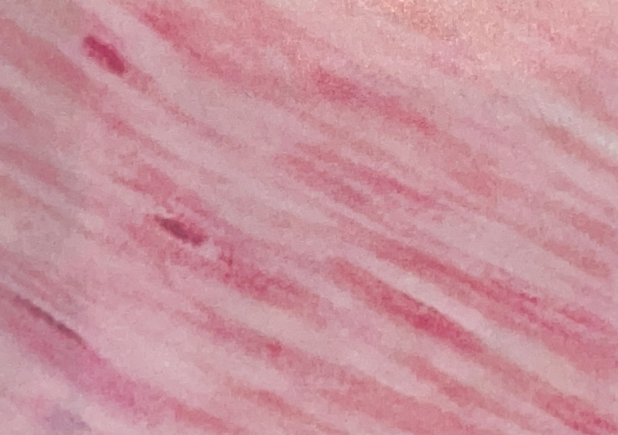
Smooth Muscle Tissue
- in hollow organs and blood vessels
- involuntary muscle movement
-
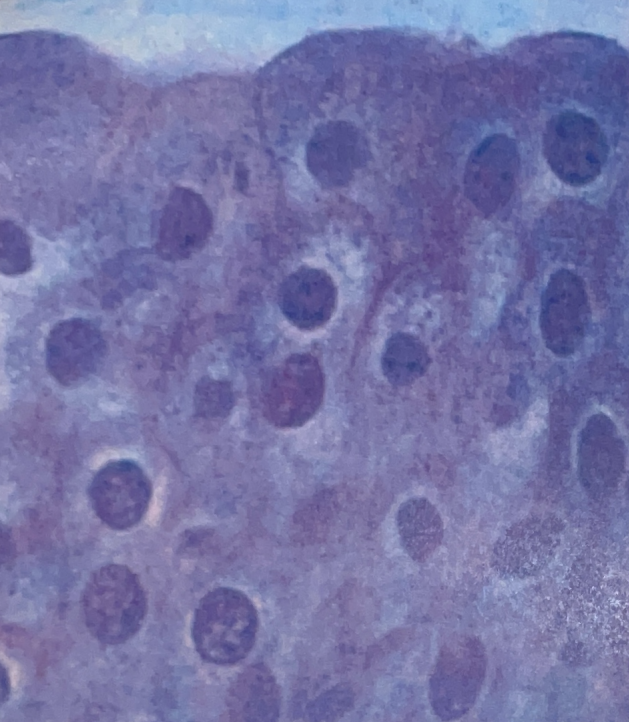
Transitional Epithelial Tissue
- in urinary bladder, ureters, and urethra
- stretching, protection
-
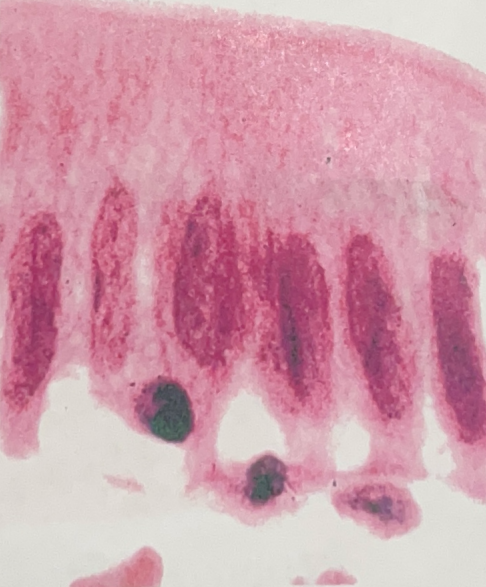
Simple Columnar Epithelial Tissue
- in digestive organs and uterine tubes
- absorption
-

Loose Connective Tissue
- between tissues and organs
- holds tissues and organs together
-
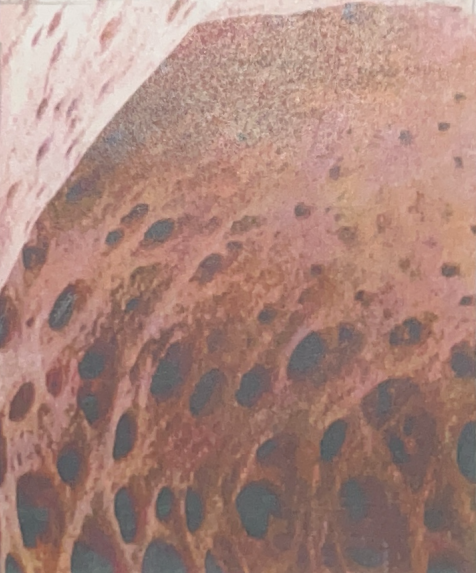
Spongy Bone Tissue
- on ends of long bones
- growth of bones, creation of blood cells in red bone marrow
-
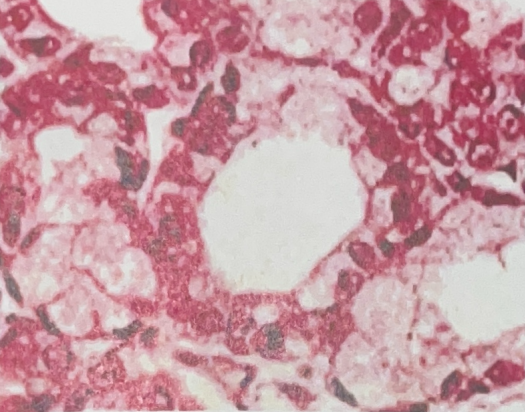
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue
- in linings of ducts of mammary, salivary, and sweat glands, and the pancreas
- protection
-
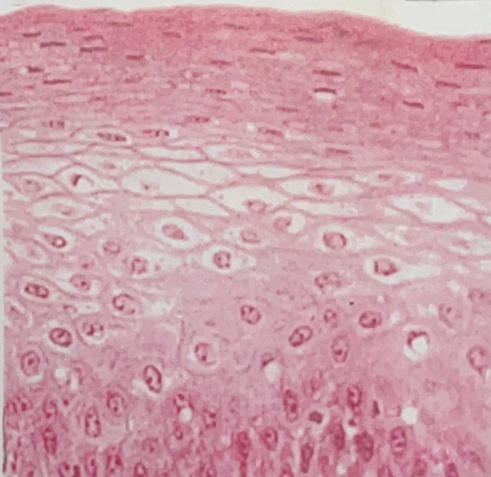
Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue
- located on outer layer of skin
- protection
-

Skeletal Muscle Tissue
- attached to long bones
- voluntary muscle movement
-
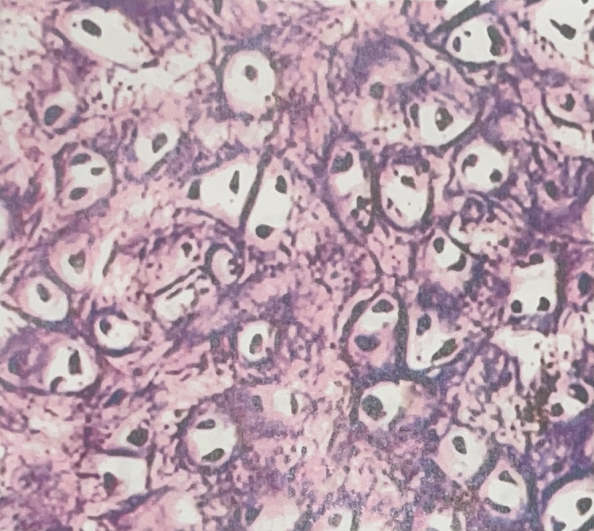
Elastic Cartilage
- located on outer ear
- flexibility
-

Dense Regular Connective Tissue
- in tendons and ligaments
- binds organs together

