-
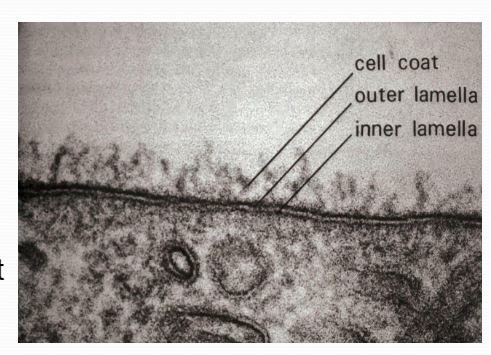 GlycocalyxProtective mechanical barrier associated with the cell membrane in all cells
GlycocalyxProtective mechanical barrier associated with the cell membrane in all cells -
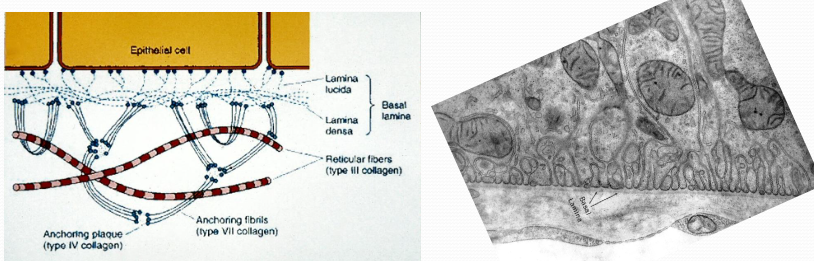 Basal LaminaExtracellular matrix secreted by epithelial cells, Visible only with TEM, Makes up a portion of the basement
Basal LaminaExtracellular matrix secreted by epithelial cells, Visible only with TEM, Makes up a portion of the basement -
 Cell JunctionsWithin Epithelium there are four types of cell junctions which in certain conditions can be observed
Cell JunctionsWithin Epithelium there are four types of cell junctions which in certain conditions can be observed -
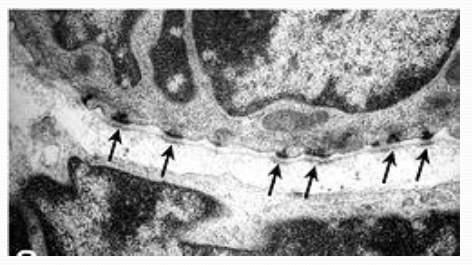 Hemidesmosomes“half desmosomes” attach the basal cell membrane to the basal lamina.
Hemidesmosomes“half desmosomes” attach the basal cell membrane to the basal lamina. -
Zonula adherensZonula adherens Linked to actin cytoskeleton
-
 Zonula occludens(tight junction)
Zonula occludens(tight junction) -
 Gap Junction (Nexus)where cytoplasm of two cells communicate through tiny pores
Gap Junction (Nexus)where cytoplasm of two cells communicate through tiny pores -
Junctional ComplexZonula occludens, Zonula adherens, Macula adherens, Gap junctions
-
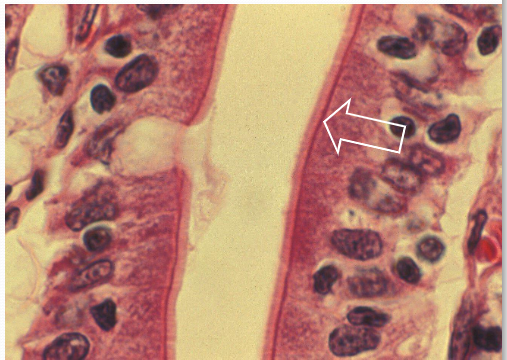 Terminal BarAll four junctions create these
Terminal BarAll four junctions create these -
Zonula adherensOnly one cell junction is unique to epithelia
-
Apical ProjectionsMicrovilli, Stereocilia, Cilia
-
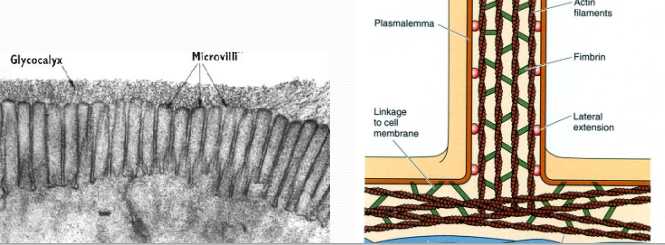 MicrovilliActin core
MicrovilliActin core -
MicrovilliEnhances absorption, Expand surface area of cells apex up to 10,000 times
-
Location of the MicrovilliMucosal lining of most of the GI tract
-
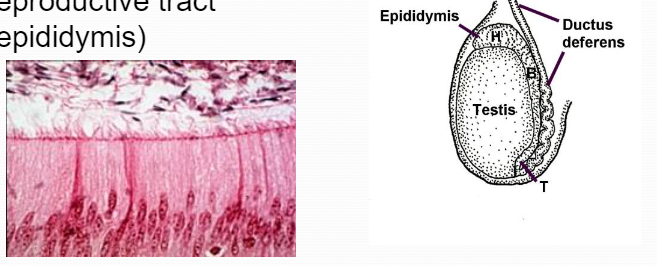 StereociliaLining of portion of the male reproductive tract (epididymis)
StereociliaLining of portion of the male reproductive tract (epididymis) -
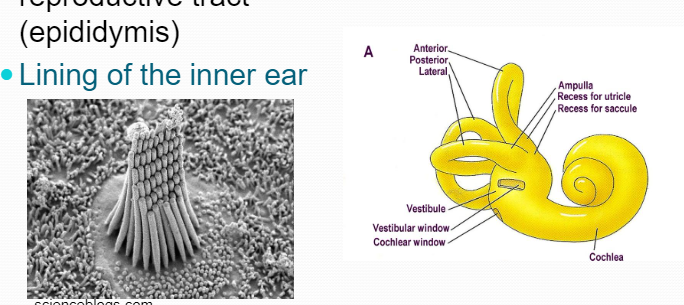 Second StereociliaLining of the inner ear
Second StereociliaLining of the inner ear -
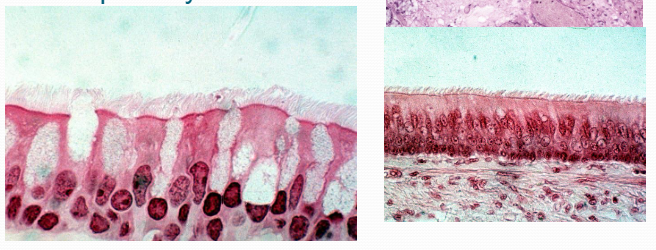 CIliaLining of uterine portion of the female reproductive tract
CIliaLining of uterine portion of the female reproductive tract

