-
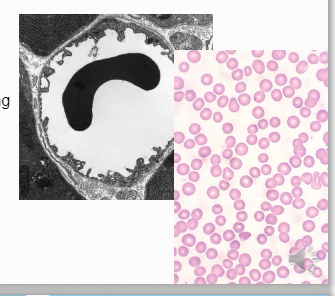 Erythrocyte (red blood cells)Disc shape: Lack of organelles or nucleus occurs during cell development- important for the exchange of gas - provides more space due to bi-concave of shape.
Erythrocyte (red blood cells)Disc shape: Lack of organelles or nucleus occurs during cell development- important for the exchange of gas - provides more space due to bi-concave of shape. -
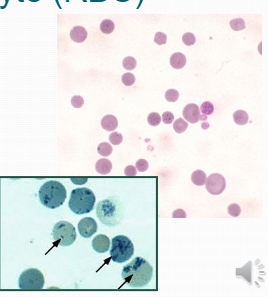 Reticulocytes:Blood cells that have specs: bloods cells that have not completely been broken-down.
Reticulocytes:Blood cells that have specs: bloods cells that have not completely been broken-down. -
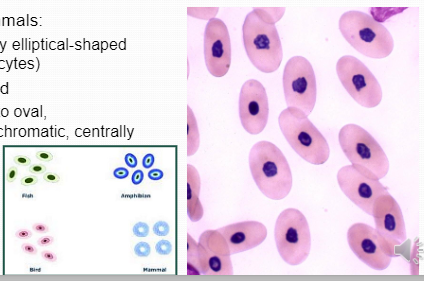 Species VariationNonmammals: typically elliptical-shaped (elliptocytes)
Species VariationNonmammals: typically elliptical-shaped (elliptocytes) -
Nucleatedround to oval, heterochromatic, centrally placed
-
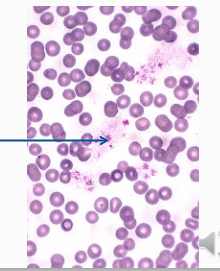 Thrombocytes (cells that break off)Circulate for 5-6 days 40% stored in spleen
Thrombocytes (cells that break off)Circulate for 5-6 days 40% stored in spleen -
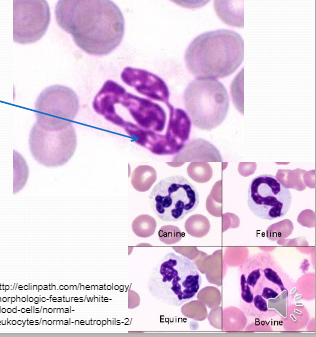 GranulocytesDistinguishing of different blood stains.
GranulocytesDistinguishing of different blood stains. -
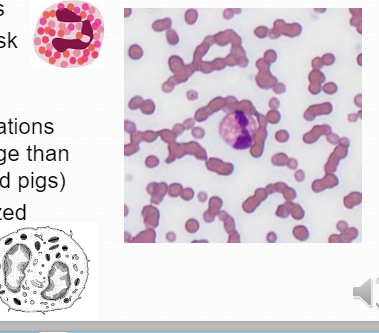 EosinophilAs granules mature they are able to attack specific pathogens in Eosinophil (granules are less specific in marrows)
EosinophilAs granules mature they are able to attack specific pathogens in Eosinophil (granules are less specific in marrows) -
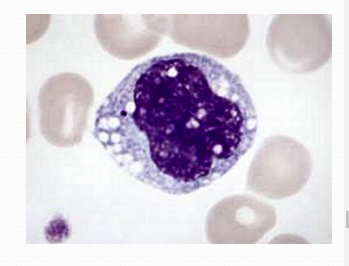 Non-Granulocyte: Monocyte (less common)Non-segmented nucleus: lobed deeply indented: they become macrophage
Non-Granulocyte: Monocyte (less common)Non-segmented nucleus: lobed deeply indented: they become macrophage -
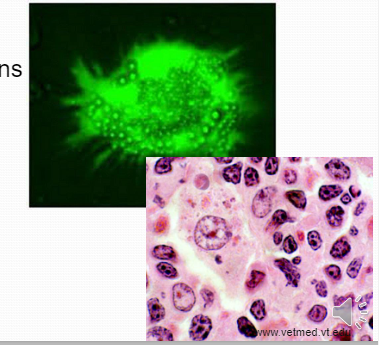 MonocytesElicited: Phagocytes or breakdown cells that have died and need to be broken-down.
MonocytesElicited: Phagocytes or breakdown cells that have died and need to be broken-down. -
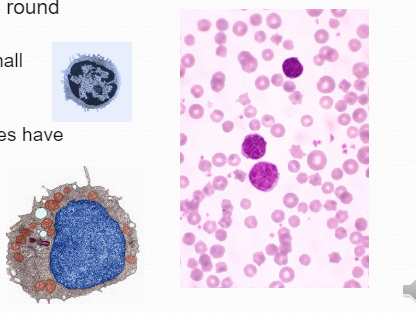 Lymphocyteround in shape (relate to activity): Active lymphocytes have more cytoplasm
Lymphocyteround in shape (relate to activity): Active lymphocytes have more cytoplasm -
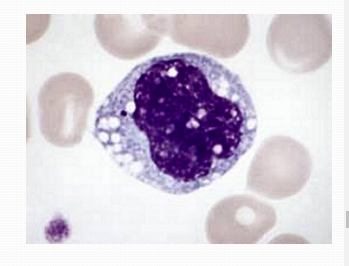 Non-Granulocyte: MonocyteNon-segmented nucleus, Typically deeply indented, Or lobed (bi-lobed, tri-lobed)
Non-Granulocyte: MonocyteNon-segmented nucleus, Typically deeply indented, Or lobed (bi-lobed, tri-lobed) -
Non-Granulocyte: MonocyteWhat is slightly larger than other WBCs, lacks distinctly stained granules and basophilically stained cytoplasm with clear vacuoles (lysosomes)
-
Non-MonocyteThis Non-Granulocyte Circulates in blood stream for up to several days, also known as a macrophage.
-
Elicited monocyte/phage engulfs & breakdowns cellular and extracellular foreign substances such asBacteriaFungiProtozoansVirusesTransformed cellsDying cellsCell debris
-
Non-Granulocyte: Lymphocyte
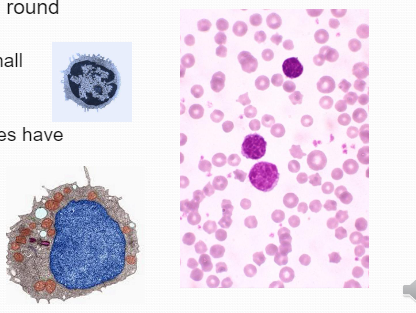 Non-segmented round nucleus, Sometimes w/ small indentation (seen ultrastructurally), Active lymphocytes have more cytoplasm
Non-segmented round nucleus, Sometimes w/ small indentation (seen ultrastructurally), Active lymphocytes have more cytoplasm -
Non-Granulocyte: LymphocyteNumerous short pseudopodial processes: amoeboid movement, cellular interaction (ex. cancer cells)
-
Non-Granulocyte: Lymphocyte (Two types, T and B)Cannot differentiate without IHC. Association with monocyte/macrophage (Mo/Ma)
-
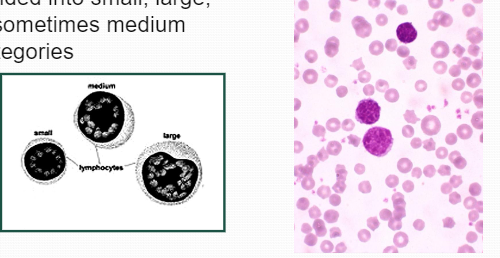 Non-Granulocyte: LymphocyteSize varies for each sp: divided into small, large, & sometimes medium categories
Non-Granulocyte: LymphocyteSize varies for each sp: divided into small, large, & sometimes medium categories -
Lymphocyte vs Thrombocyte (nonmammalian)Lymphocytes identical to mammals –difficult to distinguish from thrombocytes when small

