-
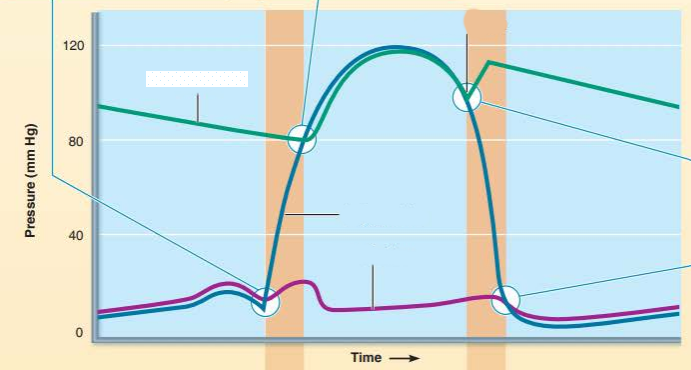
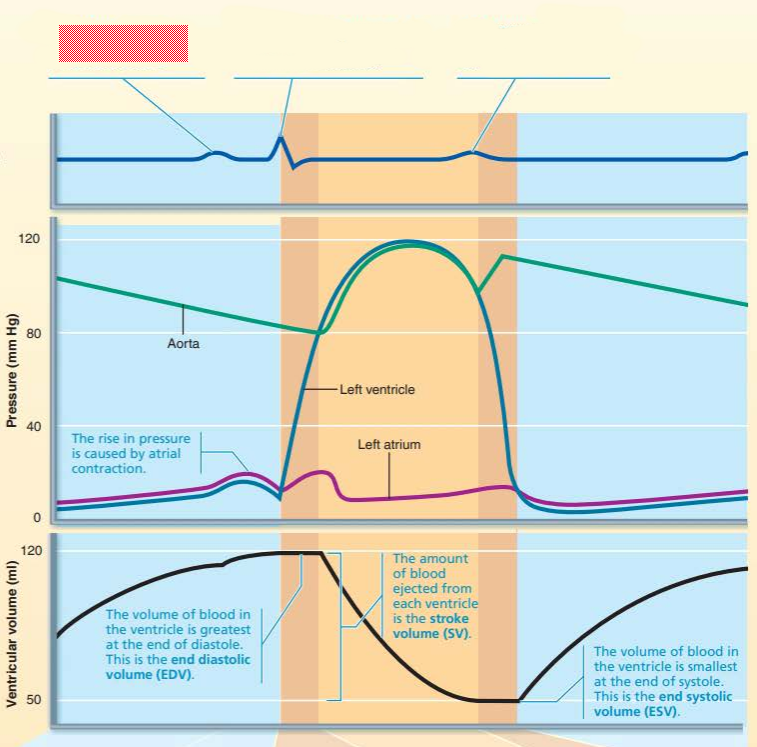
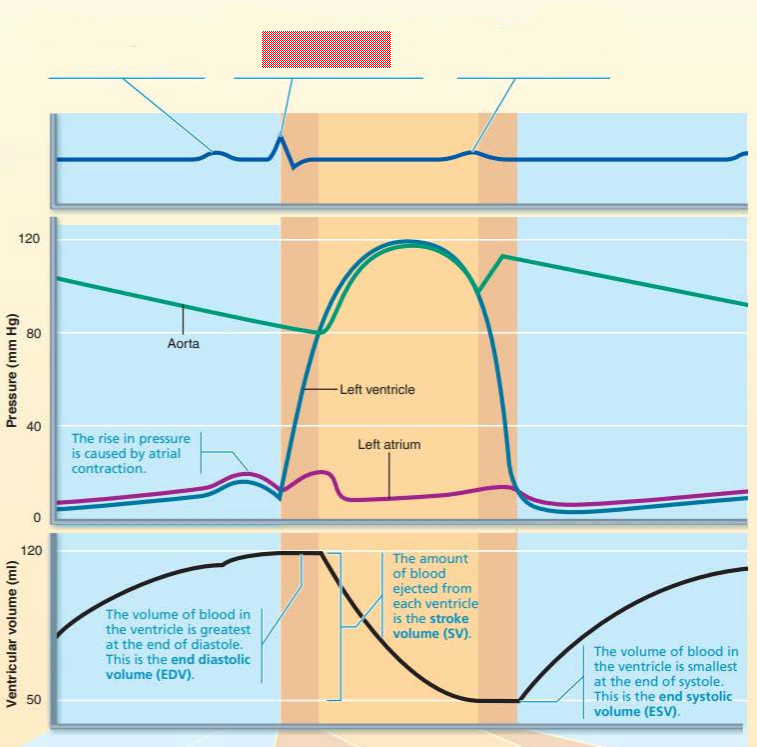
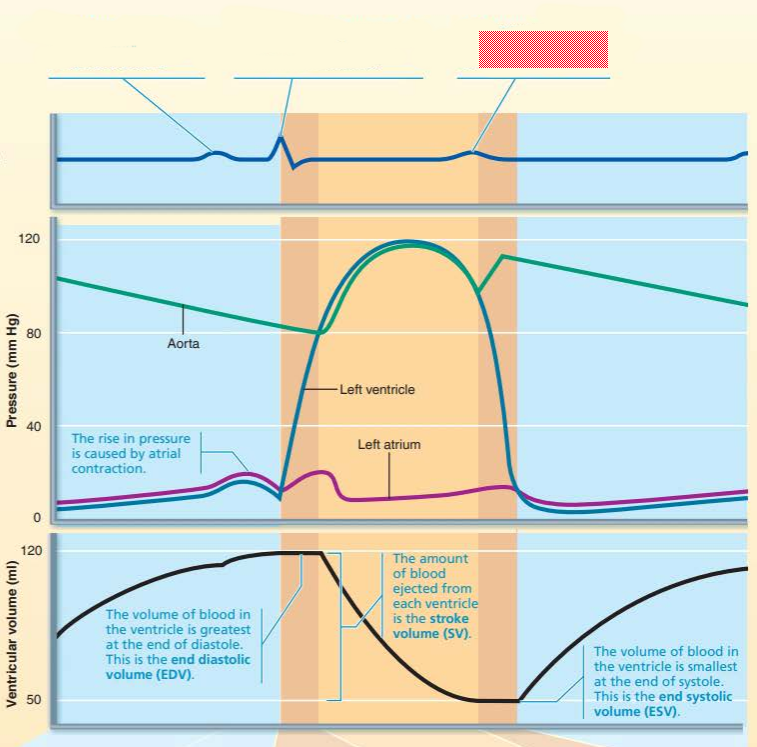
aorta
-
left ventricle
-
explain what it is
blood in the ______ rebounds against the closed _______ ______ causing the pressure to briefly _____
dicrotic notch
aorta
semilunar valves
rise
-
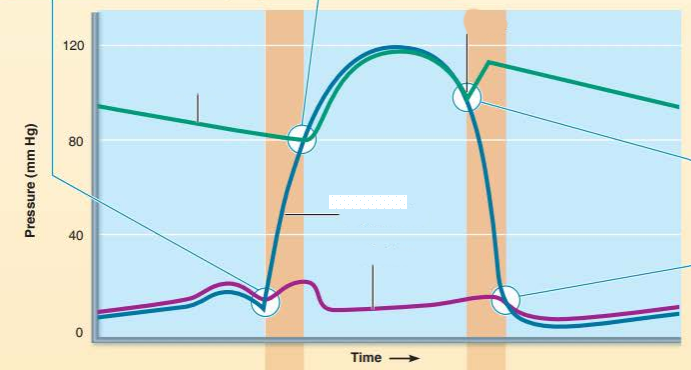
left atrium
-
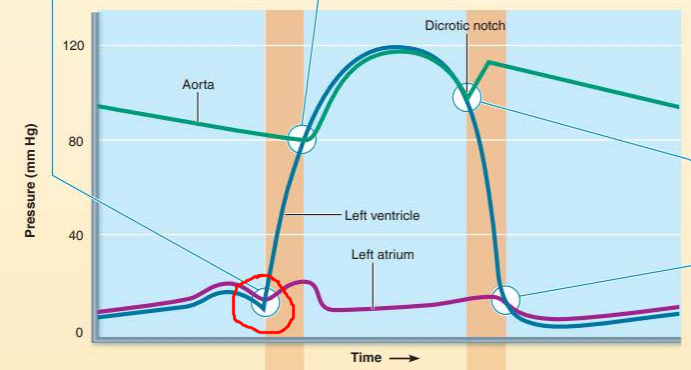
______________ __________ close when _____________ pressure exceeds ________ pressure resulting in the _______ heart sound
atrioventricular valves
ventricular pressure
atrial pressure
first
-
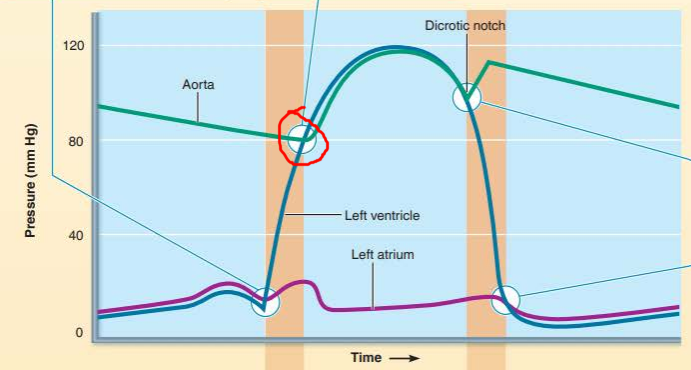
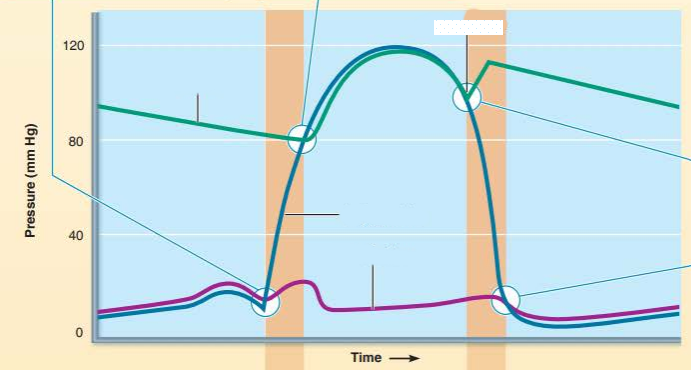
describe the valve events happening
what sound does it cause?
_____________ __________ open when the ______________ pressure exceeds the _______ ___________ resulting in ____ _______ _________
semilunar valves
ventricular pressure
aortic pressure
no heart sound
-
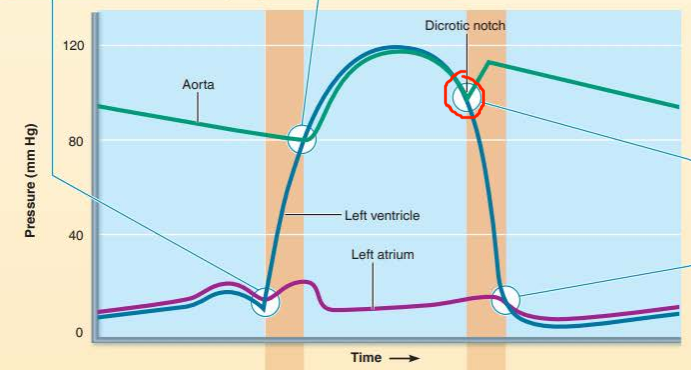
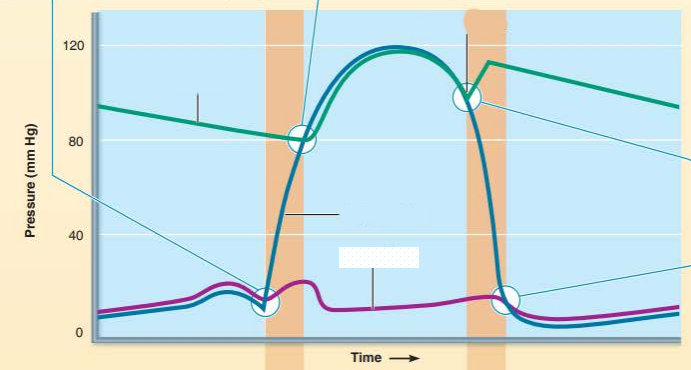
describe the valve events happening
what sound does it cause?
____________ _______ close when the _____________ ________ drops below the ______ ___________ resulting in the ________ heart sound
semilunar valves
ventricular pressure
aortic pressure
second
-
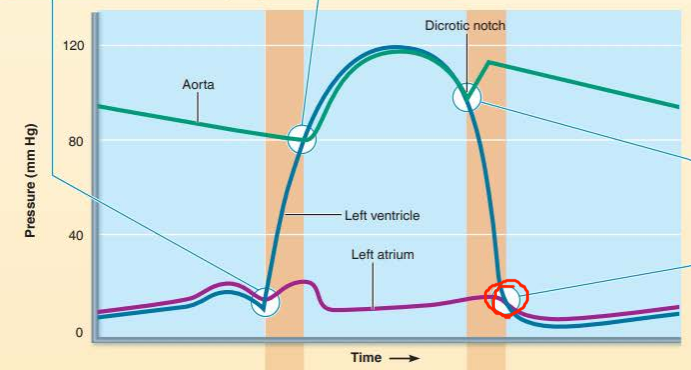
describe the valve events happening
what sound does it cause?
________________ ________ open when the ___________ ___________ drops below ________ _________ resulting in ____ ______ _______
atrioventricular valves
ventricular pressure
atrial pressure
no heart sound
-
the ______________ _______ are the periods where all four valves are closed
isovolumetric phases
-
during the ____________ ___________ ________ the ventricles are contracting and building up pressure
isovolumetric contraction phase
-
during the ____________ ____________ ______ the ventricles are relaxing and pressure falls
isovolumetric relaxation phase
-
this is the ___ __________ it occurs as ___________ ______________ leads into ________ ____________
P wave
atrial depolarization
atrial contraction
-
this is the ____ ____________ it occurs as ___________ _______________ leads into ______________ ______________
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization into ventricular contraction
-
this is the ____ __________ it occurs as ______________ ___________ leads into ____________ ______________
T Wave
ventricular repolarization into ventricular relaxation
-
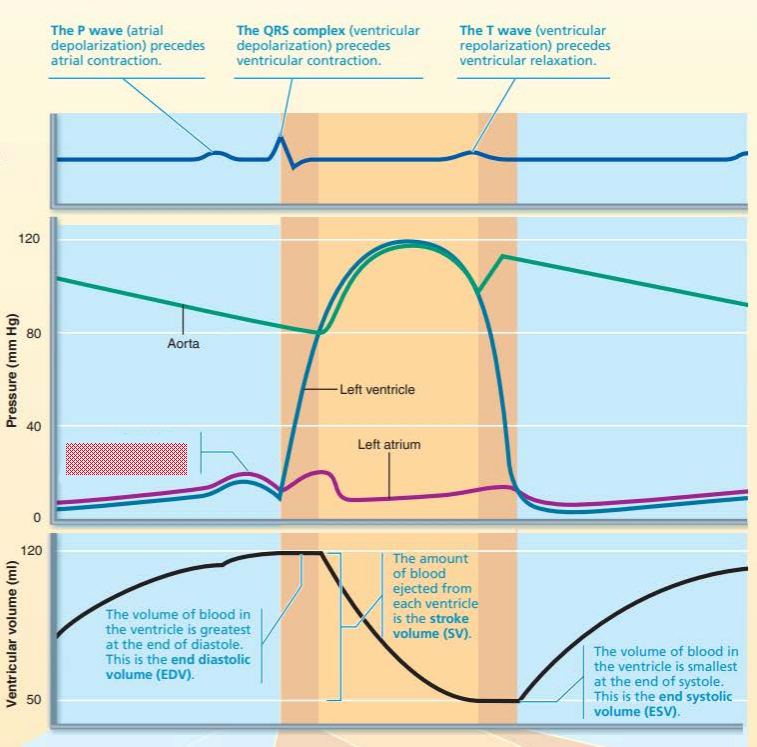
this represents a rise in ___________ caused by ______ ____________
pressure
atrial contraction
-
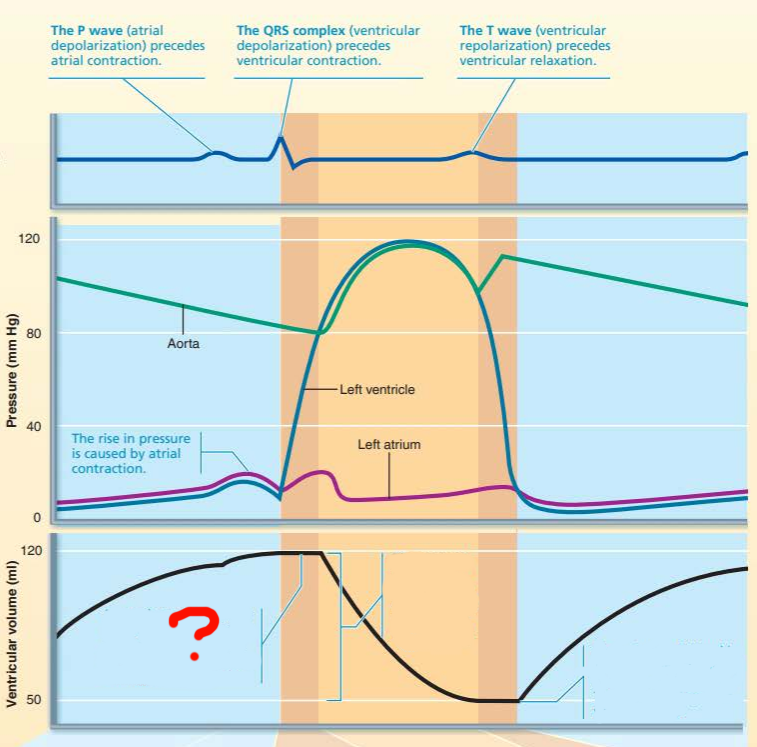
this represents the ____ ____________ __________ where volume of the blood in the _____________ being the _________ at the ___ of ___________
end diastolic volume
ventricle
greatest
end
diastole
-
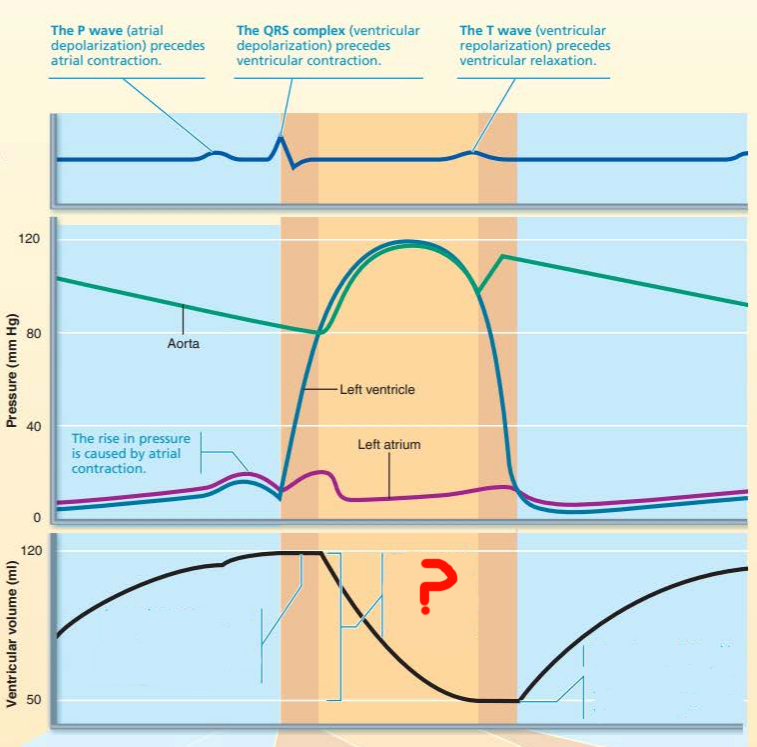
this represents the ______ _____________ which refers to the amount of blood ejected from each ventricle
stroke volume
-
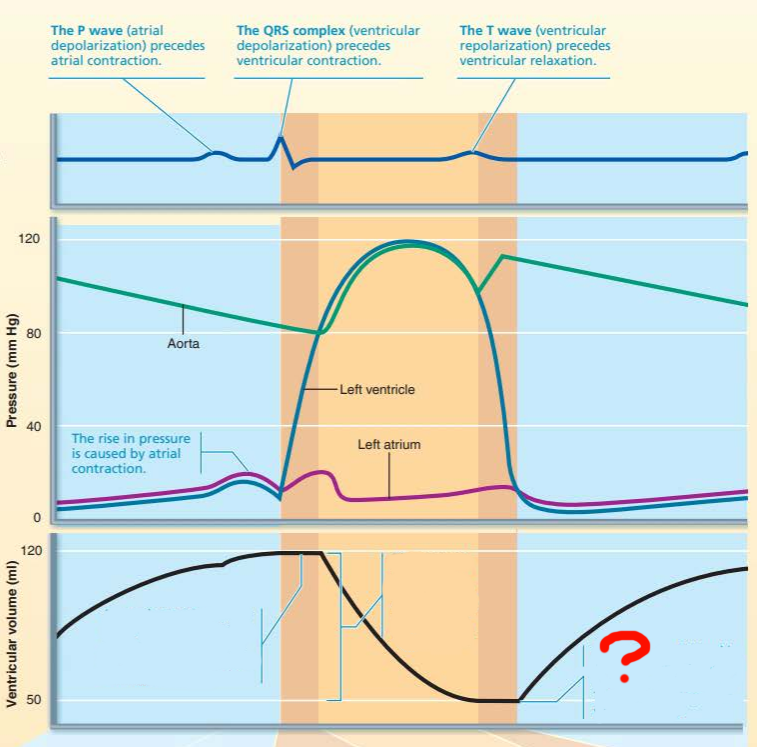
this represents the _____ ___________ _________ which refers to the volume of the blood in the _____________ being the __________ at the end of ___________
end systolic volume
ventricle
smallest
systole
-
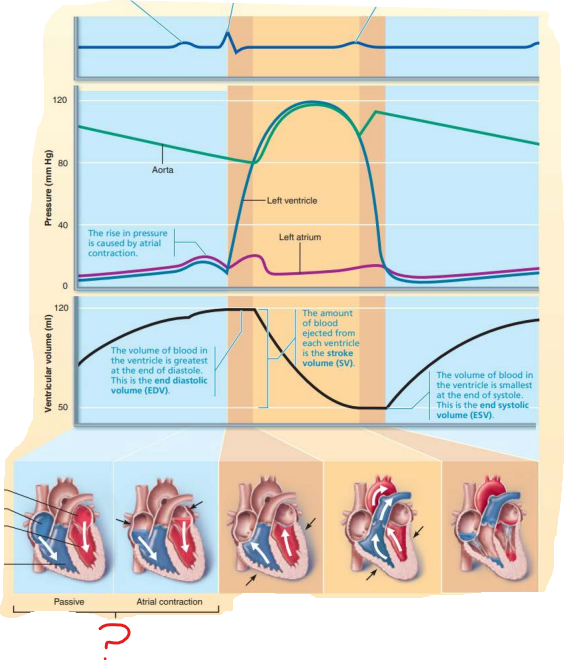
ventricular filling phase
-
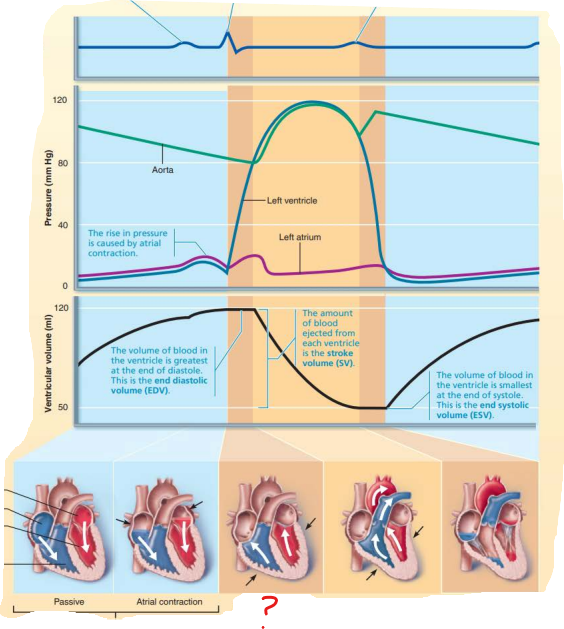
isovolumetric contraction phase
-
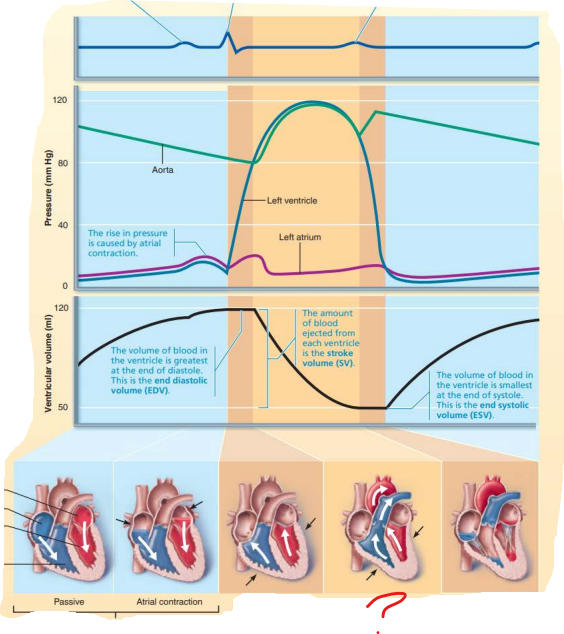
ventricular ejection phase
-
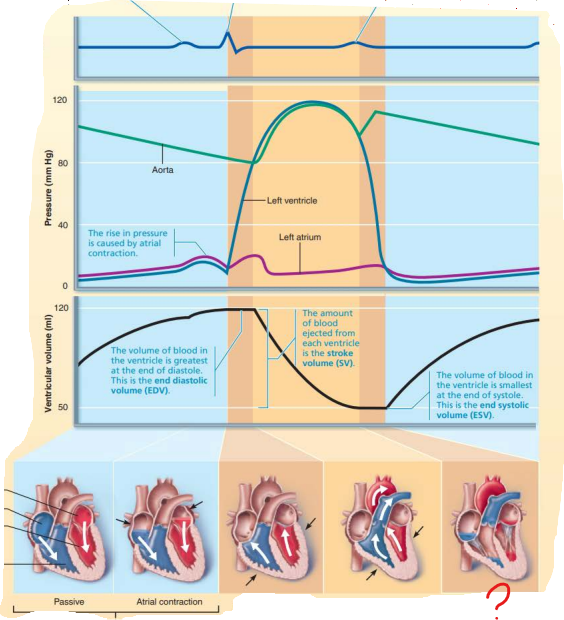
isovolumetric relaxation phase

