-
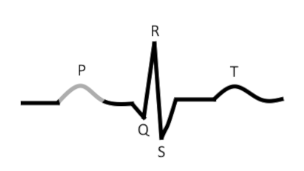
what is this?
Results from movement of the ______________ wave from the __________ through the ____
P-wave
depolarization
SA node
atria
-
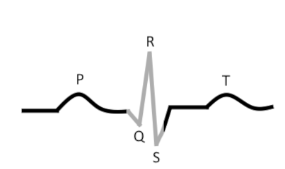
what is this?
Results from _____________ _____________ and precedes ___________ ___________
QRS complex
ventricular depolarizations
ventricular contractions
-
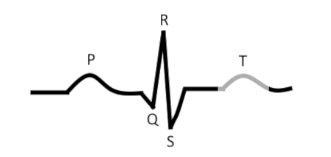
what is this?
Caused by _________________
Precedes ________________
T-wave
ventricular repolarization
ventricular relaxation
-
Cardiac _____________ _____ are found at __________ and _________________ ________
pacemaker cells
sinoatrial
atrioventricular nodes
-
Pacemaker cells have an ___________ ________ __________ that continuously ____________towards the ________
unstable resting potential
depolarizes
threshold
-
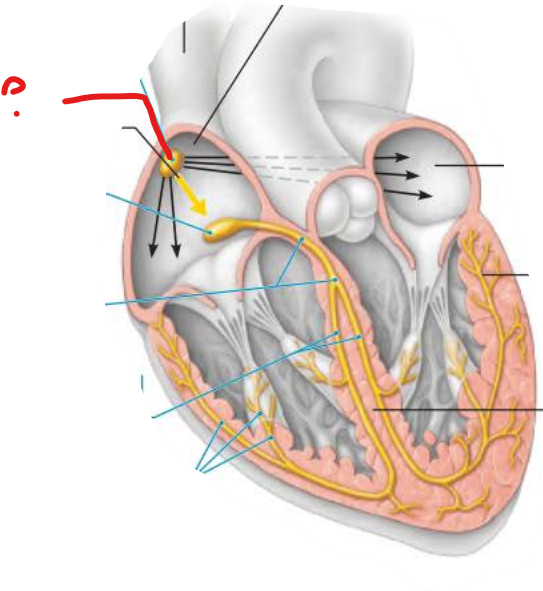
what is this?
what is it considered?
what does it do?
sinoatrial node
pacemaker
generates impulses
-
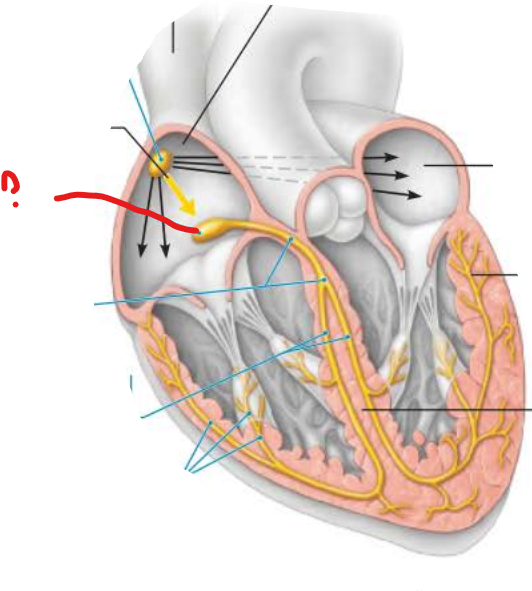
what is this?
atrioventricular node
-
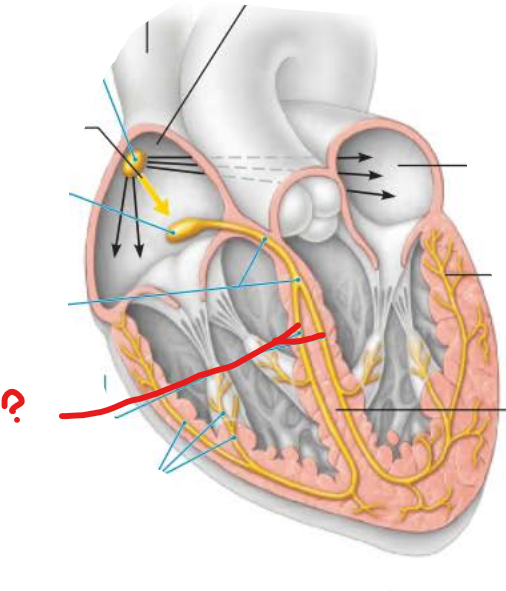
what is this?
connects impulses through the ________________ ________
bundle branches
interventricular septum
-
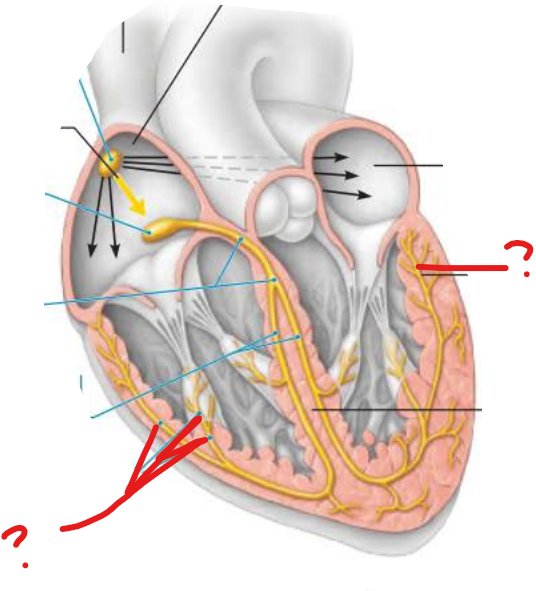
what is this?
________ the contractile cells of both __________
subendocardial conducting network
depolarizes
ventricles
-
_____________ activation of the nervous system triggers the __________ _________ to release neurotransmitters ___________ and _____________ at _________ _________
Sympathetic
adrenal medulla
epinephrine
norepinephrine
cardiac synapses
-
β1 receptors ________ heart rate and force of contraction when ___________ binds
increase
norepinephrine
-
________ atrium receives blood from 3 veins
list them:
right
superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
coronary sinus
-
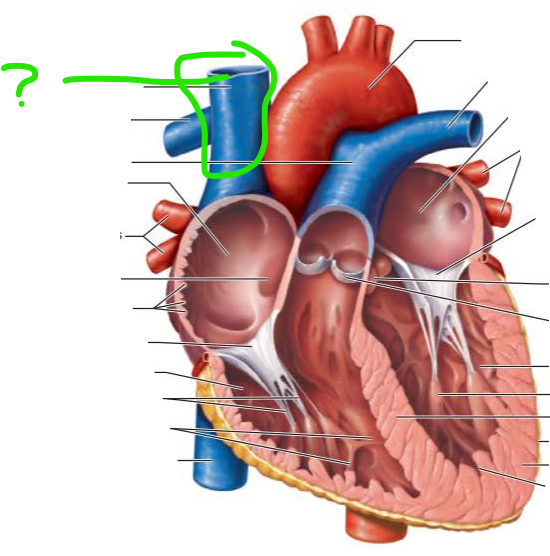
name and function
superior vena cava
returns blood from body regions superior to diaphragm
-
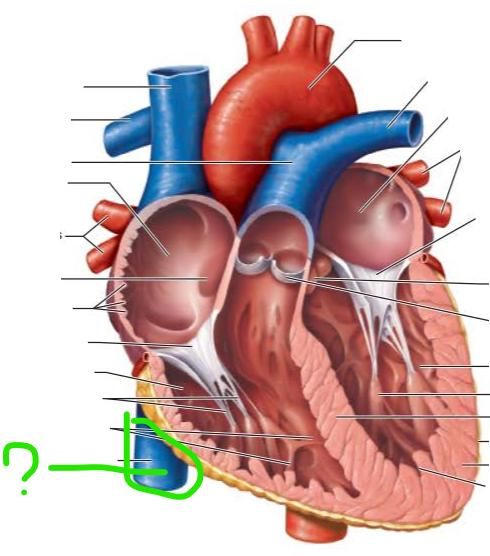
name and function
inferior vena cava
returns blood from body regions inferior to diaphragm
-
name and function
coronary sinus
collects blood draining from myocardium
-
name
___________into the _______________ which routes blood to the ______ for _____________
right ventricle
pumps blood
pulmonary trunk
lungs
gas exchange
-
name
__________ into the ______, the _______ artery in the body
pumps blood
aorta
largest
-
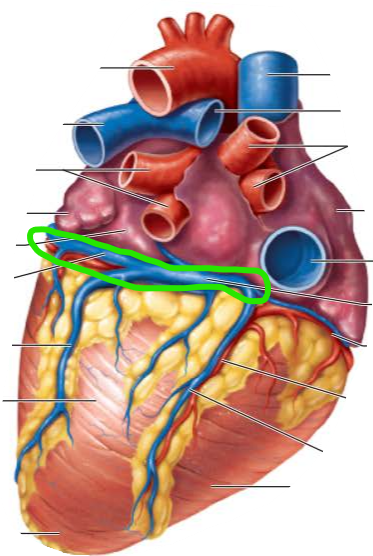
The the blood that circulates the heart provides little nourishment to the heart because the ____________ is too thick to diffuse nutrients
Requires a functional blood supply of the heart and the shortest circulation in the body known as ________________________
myocardium
coronary circulation
-
___________________ originate from the aorta with blood coming from the _____________
Coronary arteries
left ventricle
-
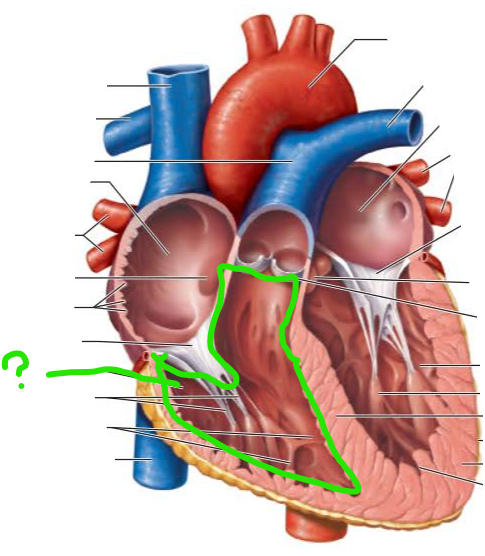
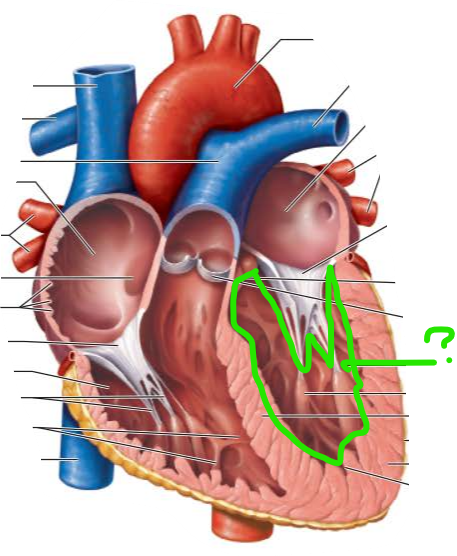
Valves open and close in response to differences in ________________ on their two sides
blood pressure
-
______________________ prevent backflow into the ______when each __________ contracts
atrioventricular valves
atria
ventricle
-
Semilunar (SL) Valves _______ and _________ valves prevent backflow into the associated ventricles
Aortic
Pulmonary
-
The heart contracts as a _____
unit
-
The heart relies almost exclusively on __________ respiration
aerobic
-
___________ contractions cannot occur in cardiac muscles
Tetanic
-
Period of contraction when blood is forced out of chambers
Systole
-
Period of relaxation when the chambers refill with blood
Diastole
-
Amount of blood pumped out by each ventricle in 1 minute
The product of heart rate and stroke volume
cardiac output
-
Volume of blood pumped out by one ventricle with each beat
Represents the difference between EDV and ESV
Stroke Volume
-
The amount of blood that collects in a ventricle during diastole
End Diastolic Volume
-
The volume of blood remaining in a ventricle after it has contracted
End Systolic Volume
-
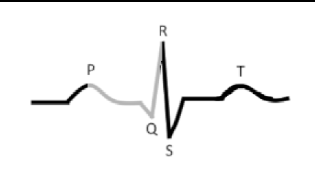
what is this?
Time beginning _____ excitation to the beginning of __________ excitation
P-R interval
atrial
ventricular
-
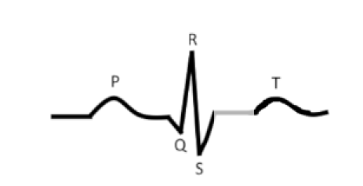
what is this?
Period where the entire ________ system is depolarized
S-T segment
ventricular
-
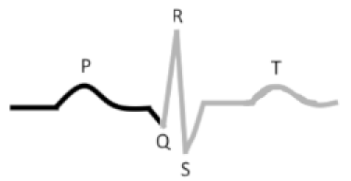
What is this?
Period from the beginning of ventricular __________ through ventricular ___________
Q-T Interval
depolarization
repolarization
-
the first heart sound is the result of the ____ ________ _________
AV valves closing
-
the second heart sound is the result of the ___ _________ __________
SL valves closing
-
Blood flow is normally ______, but if blood strikes obstructions then flow generates abnormal _________ ______ called ______ _________
silent
heart sounds
heart murmurs
-
the ____________ __________ is a pulse taken at the apex of the heart
Apical Pulse
-
the __________ __________ is the difference between the heart rate and pulse rate
Pulse Deficit
-
__________ ___________ refers to the pressure the blood exerts against the inner walls of the blood vessels
blood pressure
-
a _________ is the pressure wave created by the alternating expansion and recoil of an _______ that occurs with each beat of the left ventricle
Pulse
artery
-
________ is the period of contraction when blood is forced out of chambers
Systole
-
_____________ is the period of relaxation when the chambers refill with blood
Diastole
-
the ___________ ___ _________ are when a blood pressure cuff is used to prevent blood flow past the brachial artery
First sounds heard with a stethoscope are soft tapping sounds which is blood spurting through the constricted artery due to ________ pressure
As cuff pressure is reduced these sounds become _________
sounds of korotoff
systolic
louder
-
__________ pressures are pressure in arteries at the peak of ___________ contraction
Systolic
ventricular
-
________ pressures are the pressures when the __________ are relaxing
Diastolic
ventricles
-
Standing suddenly will cause gravity to make blood to pool to legs and feet causing blood pressure to _____
drop
-
Physical stress, exercise or fear triggers __________ ANS for ______________ except in _________ __________
Vessels of the skeletal muscles ______ to _______ blood flow to working muscles
sympathetic
vasoconstriction
skeletal muscles
dilate
increase
-
Nicotine causes _____________ leading to increased ____________ _____________ of arteries and increased __________ _________
vasoconstriction
peripheral resistance
blood pressure

