-
Canada has a ___ health care plan, implemented by ___ separate insurance programs.
Canada has a universal health care plan, implemented by 13 separate insurance programs.
-
Each provincial government has a ministry or department of health. This person is known as the minister of health (MOH). How are they assigned this position?
By being elected by a member of Parliament.
-
Under the MOH are multiple ministries. What are their general responsibilities?
- To provide leadership and support to service delivery programs.
- Implement and regulate health insurance plans.
- Negotiate salaries and other policies with physician's professional associations.
-
Describe the different types of care provided by the provinces/territories.
Primary: who the patient is in "first contact" with when receiving care. Ex. ER, clinics and their family doctor.
Secondary: the specialist, usually after being referred by their primary care provider. Ex. dermatologist, cardiologist, etc. They assist the primary care practitioner for diagnosis and order appropriate treatment for the patient.
Tertiary: a highly specialized care. Ex. cancer centre, cardiology centre, or a facility for treating burns.
Quaternary: an extension of tertiary care and is even more specialized. Sometimes involvs experimental procedures. Ex. Hospitals that do research.
-
___ is the department within the Government of Manitoba responsible for leading development of policy and publicly administered health systems planning in MB.
Manitoba Health.
-
Name some responsibilities of Manitoba Health.

-
Shared Health is Manitoba's ___.
provincial health authority
-
What do the regional health authorities (RHA) do?
Manage the funding and/or the delivery of community and institutional health services in their regions.
-
Originally all the provinces and territories have regionalized. However some have began to move back to single health authority. Why?
- Create more distance from bureaucratic "red tape".
- To make services more cohesive and easier to access.
- Saving money (from administrative costs).
-
What were the desired effects of regionalization on primary care?
To design care in a community that provides individuals with the type and level of care best suited within the region.
-
After most jurisdictions adopted a centralized approach, communities have become to rationalize health services, particularly hospitals. What does this mean?
Larger hospitals were merged under one administrative body. The amalgamation of hospitals and redistributing services resulted in the closure of a number of smaller hospitals across the country.
-
What were the four desired goals when implementing a regionalized approach?
1. Amalgamate health care services over a broad continuum of care.
2. Stress health promotion and disease prevention.
3. Involve the public.
4. Implement appropriate and effective governance.
-
There are ___ health authorities in MB. Including ___, ___, and ___.
There are 7 health authorities in MB. Including 5 regional health authorities, 1 provincial health authority (Shared Health), and 1 cancer authority (CancerCare).
-
Where are the RHAs of MB situated?
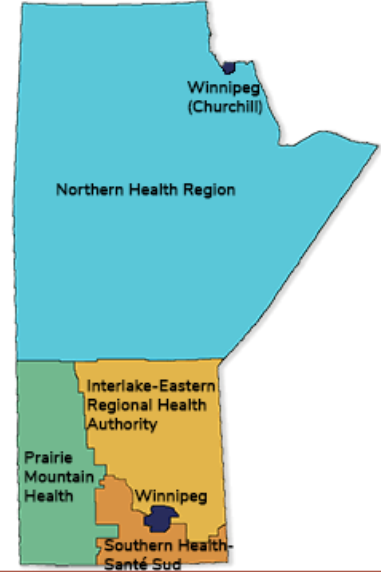
- Northern Health
- Prairie Mountain
- Winnipeg-Churchill Health Region
- Interlake Eastern RHA
- Southern Health
-
What does the First Nations Health and Social Secretariat of Manitoba do?
They aim to empower First Nations to control their health through unified efforts, while respecting traditional knowledge and providing education and training.
-
Private and volunteer organizations provide significant revenue for specific services or hospitals. True or false?
True.
-
What is a health care premium?
A fee paid to the provincial healthcare plan from the resident's income tax to provide health coverage.
-
If a resident is unable to pay their health care premium, they are denied medically necessary services. True or false?
False; it would break the CHA if that were the case.
-
What is a payroll tax?
A tax collected from employers to raise funds for health care which may extend into education and social services. In MB this is called --> The Health and Post Secondary Education Tax Levy.
-
Employee insurance plans provide benefits for:
- vision and dental care
- physiotherapy
- private nursing services
- assistive devices
- enhanced medical services
-
What are the criteria for a person to be eligible for a provincial insurance plan?
- Canadian citizenship/PR
- Resident of the province/territory where they're seeking health coverage
- Physically living in that jurisdiction for at least 5 months (varies)
-
Refugees' claimants are covered by who?
The federal government.
-
Name some services that are privately paid for (by you).
- counseling
- physiotherapy
- sports medicine
- genetic testing
-
What is a dispensing fee?
A service fee charged by pharmacy for dispensing a prescription medication. Ex. Reading the prescription and preparing the medication for the patient.
-
What is the highest department in a healthcare facility?
The Governing Board - aka BOD. Have the highest level of authority and responsibility in the hospital.
-
What does the Chief Operating Officer (COO) do?
Provides leadership, and direction in regards to the hospital's mission and strategic plan.
-
What does the Chief Information Officer (CIO) do?


