-
The force felt in a field is a non-contact force. True or False?True
-
Is force a vector or scalar quantity?Vector
-
What are some similarities between electrostatic and gravitational forces?Inverse square force laws Potential concept Equipotential surfaces Use of field lines
-
What are some differences between electrostatic and gravitational forces?The gravitational forces from masses always attract, whilst charges may repel or attract
-
What is gravity?Gravity is the universal attractive force which acts between all matter
-
What is G?The universal gravitational constant. ~6.67x10^-11 m^3kg^-1s^-2
-
What can field lines tell you about a field?The direction of the field and the strength of the field depending on the density of the field lines
-
What is g?The force per unit area in a uniform field In a radial field the magnitude of g is the proportionality constant at that point between force and mass g = GM/(r^2)
-
What is gravitational potential?The potential energy per kilogram, at any point in the field. 0 potential is defined at infinity, hence at a point close to a mass the potential of an object would be negative.
-
What is the work done by moving a mass in a field?mass x change in potential
-
What is the gravitational potential difference?Gravitational potential difference is the difference in the gravitational potentials of two points in a gravitational field
-
What is an equipotential surface?A surface in which every point on the surface has the same potential
-
How much work is done when you move 1 km in any direction on an equipotential surfacenone as the potential at each point is the same
-
Why is gravitational potential a negative value?Work needs to be done to move an object from inside the field to outside the field. Since outside the field's potential is defined as 0 then the potential inside the field must be negative.
-
Compare the PE and KE of a lower orbit to a higher one.A lower orbit (smaller m) has less potential energy and more kinetic energy than a higher orbit (bigger r)
-
How do we know gravitational potential energy exists?when you hold an object and drop it you get KE which can't be created frm nothing
-
Work energy theoremwork done= change in energy
-
work done equation
 W = Fd can't be used as F is constantly changing so approximations can be made for small distances, using integration
W = Fd can't be used as F is constantly changing so approximations can be made for small distances, using integration -
gravitational force equationF = GMm/(r^2) M= mass of obj1 m= mass of obj2
-
Gravitational equationv(J/kg) = GPE/m = - GM/R
-
GPE equationvm = GPE
-
gravitational force equation-change in GPE/change in radius
-
What can a graph of GPE vs radius show us?-gradient = gravitational force
-
g equationg = -dv/dr
-
change in GPE equationfexternal x change in radius = -fgravitational x change in radius
-
Equipotentials are...parallel planes
-
Field lines...are parallel lines
-
field strength unitsN/kg (F/kg)
-
Potential unitsJ/kg (GPE/kg)
-
What does a gaph of energy vs distance show?The gradient is the force
-
What does a graph of potential vs distance show?
The egradient is the field strength -
Shell theorem1. a spherically symmetrical object affects other objects gravitationally as if all of its mass were concentrated at its center. 2. If the object is a spherically symmetric shell then the net gravitational force on a body inside of it is zero
-
'Potential well'The Earth produces the same potential well above its surface as a point-line mass at its centre
-
What is the period of a geosynchronous orbit?one day
-
Kepler's first law
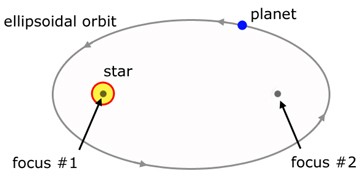 The orbit of a planet is in the shape of an elipse, whith the parent star at one focus
The orbit of a planet is in the shape of an elipse, whith the parent star at one focus -
Kepler's second law
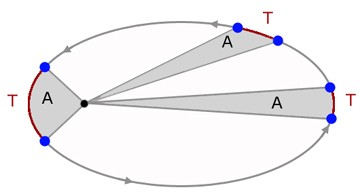 A radius vector drawn from the sun/star to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times, irrespetive of where on the orbit the planet is This means the planet moves faster when it is closer to the sun
A radius vector drawn from the sun/star to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times, irrespetive of where on the orbit the planet is This means the planet moves faster when it is closer to the sun -
Kepler's third law
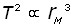 T = orbital period r = mean radial distance using and as set gravitational force = required centripetal force
T = orbital period r = mean radial distance using and as set gravitational force = required centripetal force -
For an object in a circular orbit under gravity...its gravitational energy and kinetic energy have a remarkable relationship
-
For an object in a circular orbit under gravity what is the total energy-(GMm)/2r
-
if the total energy of an object in a circular orbit under gravity is greater than 0the 'free particle' is not 'gravitationally bound' and so not in orbit at all
-
Escape velocityThe velocity needed to throw something for it to reach infinity (sqaure root((2GM)/R)) = v) derived from (GMm/R)= (0.5mv^2)
-
to calulate change in gravitational potential from a graph
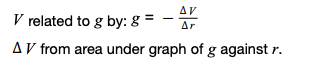
-
Geostationary orbitGeostationary orbits of 36,000km from the Earth's equator are best known for the many satellites used for various forms of telecommunication, including television. Signals from these satellites can be sent all the way round the world.
-
What are low orbit satelites used for?LEO satellites are commonly used for communications, military reconnaissance, spying and other imaging applications. Most of the man-made objects orbiting earth are in LEO. Satellites made for communications benefit from the lower signal propagation delay to LEO. This lower propagation delay results in less latency.
-
How to calculate escape velocity
0.5mv^2 = GMm/r
-
Gravitational potential at a point
The work done to bring 1 kg from infinity to the point
-
If an object with mass enters a magnetic field
It will experience a gravitational force
-
The gravitational field strength at a point in a gravitational field
The force per unit mass on a small mass at that point due to the field
-
The gravitational potential energy of an object at a point in a gravitational field
The work done to bring the object from infinity to that point in the gravitational field
-
Why is gravitational potential energy negative
Gravitational force an attractive force that does work on the object to bring it in

