-
Climate
Long-term atmospheric changes averaged from weather over time usually a 30-year baseline is used to take the averages.
Affected by global forces and powers in the long term.
Generally predictable
-
Weather
Short-Term atmospheric changes affected by microscopic disturbances and have limited predictability. Highly chaotic
-
Differences Between Climate VS Weather
Weather: short-term atmospheric changes that are chaotic and can be affected by microscopic disturbances. limited predictability
Climate: long-term average of weather events. predictable due to being comprised of averages. affected by global events and forces.
Both: atmospheric changes; can be attributed to specific regions/areas
-
What are the main components of the climate system?
Atmosphere (gases around Earth, sky/air), Hydrosphere (water/oceans), Cryosphere (frozen water/environments), Biosphere (living organisms), Lithosphere (land mass of Earth like crust, mantle), geosphere (any of these spheres of Earth)
-
What is exchanged between different parts of the climate system?
Energy, Momentum, Water, and Carbon
-
What processes/exchanges are present in the climate system?
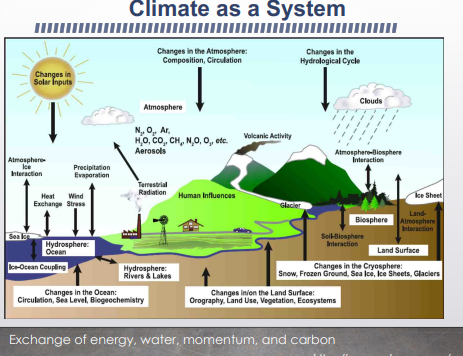
humans cultivate and change their surrounding geography, lanf use, vegetation, ecosystem, changing the biosphere. humans build things and change the atmosphere releasing fossil fuels and heating atmosphere hurting land
water cycle sun melts ice and also heats water to evaporate and clouds condense and then rain down
-
Radiative Forcing
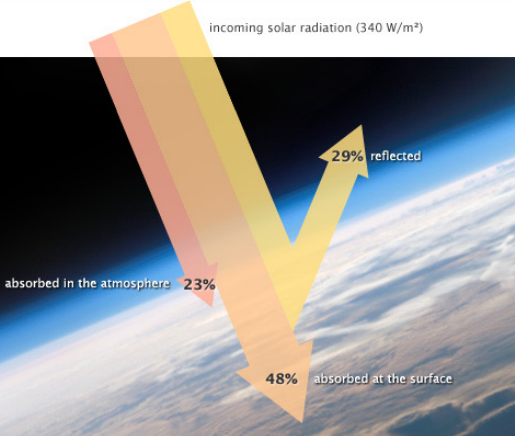
Imbalance between earth's incoming/outgoing radiation measured at the top of the atmosphere
(Most radiative forcing imbalances are due to changes in Earth's atmosphere, not Sun increasing in radiation. The Sun can increase in temp/radiation, but that takes hundreds of thousands of years).
-
Feedbacks
Non-linear cycle that feeds back in loops and affects itself
-
Negative Feedbacks
De-Amplifying/Lessening Process. Results in decreased cooling or warming (decrease from the initial state)
EX: Rock Weathering
increased CO2 -> atmospheric warming -> rocks weathered by heat and elements -> long time passes -> weathered rock forms new elements and absorbs CO2 -> decreased warming due to CO2 absorption
(Doesn't always mean 'bad' for environment)
-
Positive Feedbacks
Amplifying/Enhancing Process. Results in increased cooling or warming (increase of initial state) Self-Perpetuating
EX: Ice-Albedo
changes in sea-ice
(albedo=relative reflectivity) (lower albedo=less reflected)
(ice has 80-90% reflected light)
atmospheric warming -> melting of ice -> (more water from melted ice) more ocean exposed (water = lower albedo than ice) -> (water=easier heating) increase absorbed sunlight -> more ice melts from absorbed sunlight ->...
(doesn't always mean 'good' for the environment)
-
How have the numbers of “billion -dollar disaster events” and the costs in the US changed over the past decades?
weather extremes have been increasing
for a long time models/scientists have predicted that this would happen in a warmer climate
warmer air
->more moisture can be gathered in the atmosphere -> more+Extreme events
|_>more movement=variation across world
-
How is weather related to climate change?
short term changes in weather when averaged over a longer period of time become climate change
climate change occurs when variation exceeds sttisticl limits based on baselines
we don't know if crazy weather is for sure because of climate change some of these events would have been virtually impossible in the climate as it was
can never be 100% but we can have if it would be more likely
-
Anthropogenic climate change
climate change caused by humans


