-
22 homologous, 1 pair of sex chromosomes
How many pairs of chromosomes do somatic cells contain?
-
True
Each chromosome differs in size, therefore DNA BP length differs. T/F?
-
chromosome
a very long, continuous piece of DNA, which contains genes, regulatory elements and other intervening sequences. Bundled with histones.
-
P
short arm
-
Q
Long arm
-
Matrilineal
of or based on kinship with the mother or the female line.
-
Circular
Mitochondrial DNA is doubled-stranded and what shape?
-
Heteroplasmy
presence of a mixture of more than one type of a mixture of more than one type of an organelle genome (mtDNA) within a cell. Since most eukaryotic cells contain many hundreds of mitochondria, it is very frequent for mutations to only affect some of the copies, while the remaining ones are unaffected.
-
m.3243A>G mutation
Nomenclature:
m= mitochondrial genome
3243= location on mit genome
-adenine replaced with Guanine
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
A DNA sequence variation that occurs when a single nucleotide (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine) in the genome sequence is altered and the particular alteration is present in at least 1% of the population
-
Antioxidants & vitamins
Which drugs are used to treat MELAS?
-
D
How do these drugs alleviate the symptoms of MELAS?
a) minimize the demands on the mitochondrion
b) supporting and maximizing mitochondrion function
c) reduce ATP production
D) Both A & B
-
DNA
-passed from generation to generation
-constitute genome/chromosomes/genes
-contain instructions for making proteins
-located in cell nucleus
-
RNA
-function in the synthesis of proteins coded by DNA
-mRNA transcribed in nucleus-exits to ribosome
-make up genome of many viruses
-
mRNA
carries protein information from the DNA in a cell’s nucleus to the cell’s cytoplasm (watery interior), where the protein-making machinery reads the sequence and translates each three-base codon into its corresponding amino acid in a growing protein chain.
-
tRNA
serves as a link (or adaptor) between the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein. Each time an amino acid is added to the chain, this RNA pairs with its complementary sequence on the mRNA molecule, ensuring that the appropriate amino acid is inserted into the protein being synthesized.
-
rRNA
the RNA component of ribosomes, the molecular machines that catalyze protein synthesis.
-
Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, and 4 nitrogenous bases
What are the building blocks of DNA?
-
Adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
What are the nitrogenous bases associated with DNA
-
Adenine & Guanine
What are your purines?
-
Thymine & Cytosine
What are your pyrimidines?
-
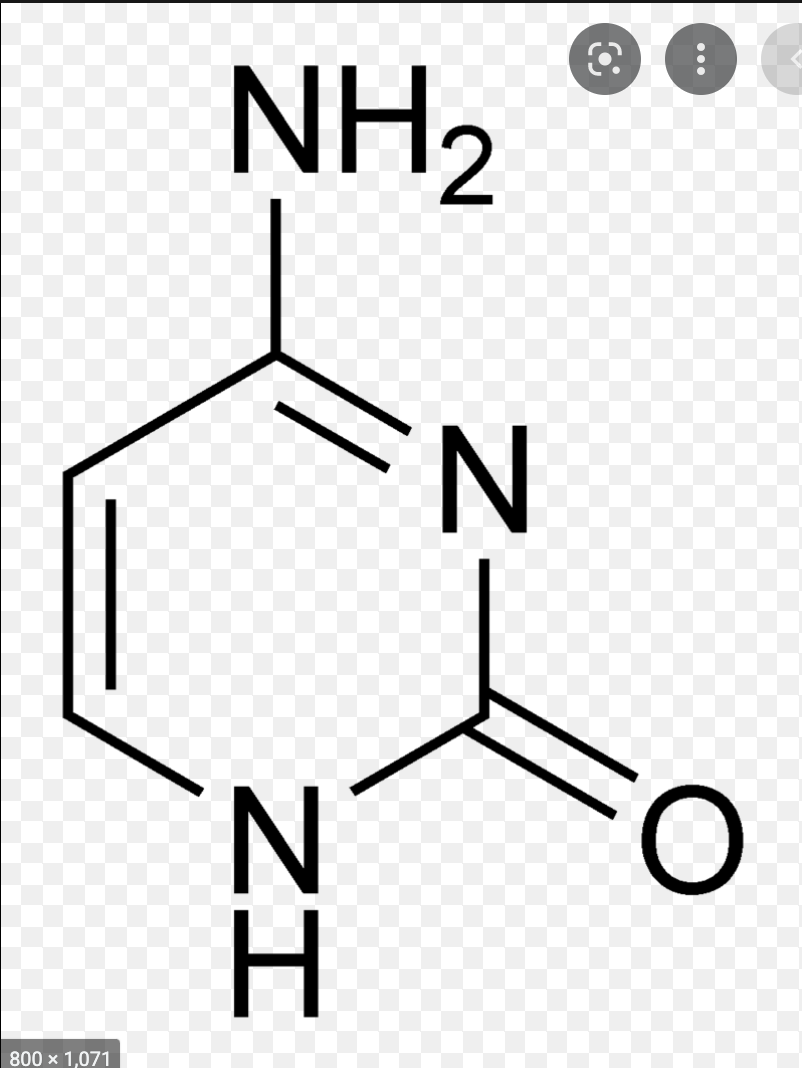
Nucloeside
-
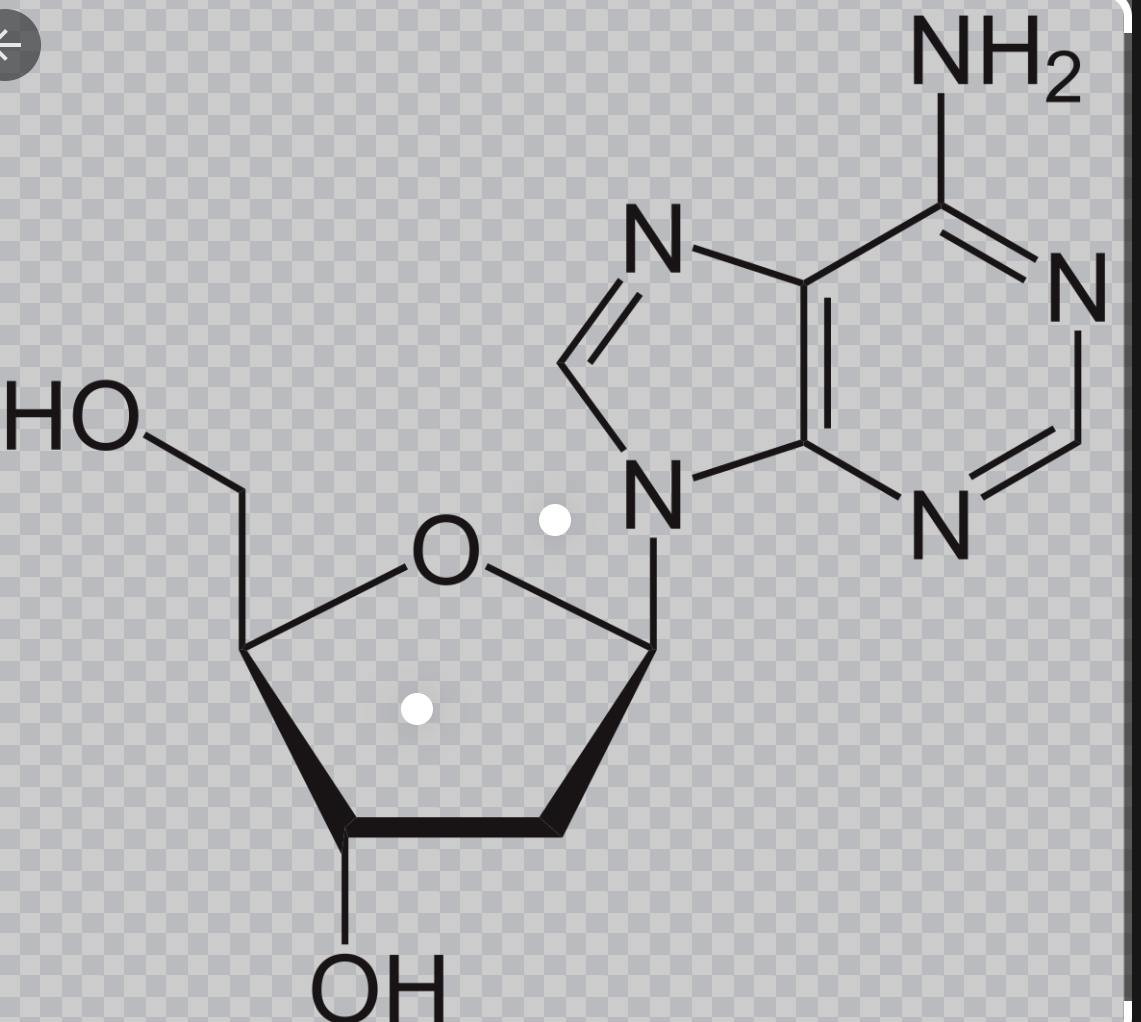
Nucleotide
-
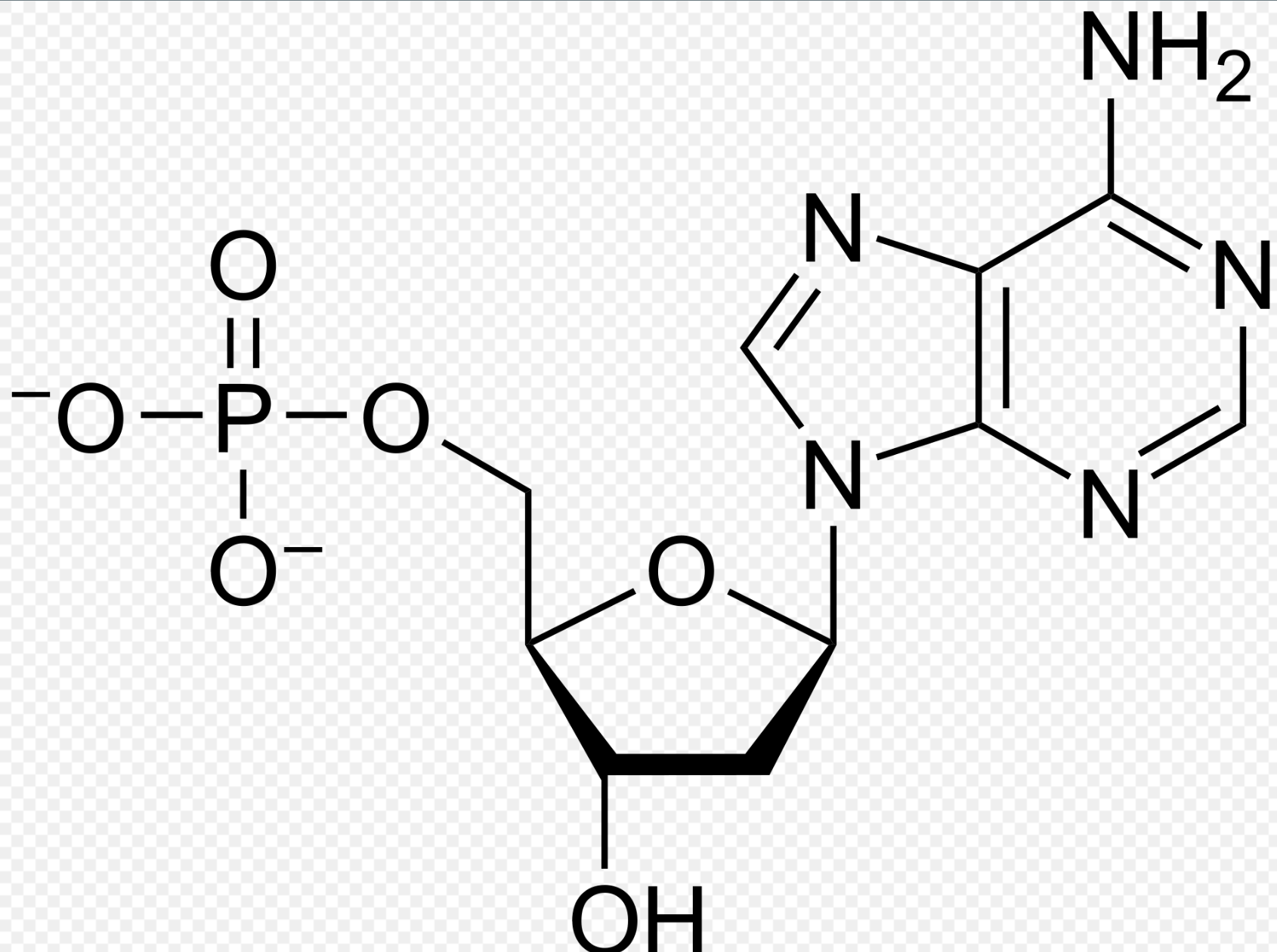
phosphodiester
Nucleotides are linked by __ bonds
-
Tm
temperature at which half of the DNA strands are in the double-helical state and half are in the "strand-separated" states.
-
Plasmid
a genetic structure in a cell that can replicate independently of the chromosomes, typically a small circular DNA strand in the cytoplasm of a bacterium or protozoan. Plasmids are much used in the laboratory manipulation of genes.
-
Double
DNA in prokaryotes is ___ stranded
-
Supercoiling
a double helix (as of DNA) that has undergone additional twisting in the same direction as or in the opposite direction from the turns in the original helix.
-
structural strain
Supercoiling can occur when ccDNA is subject to__
-
Topoisomerase
enzyme that helps to relieve torsional strain created by DNA replication ( works in front of replication fork)
-
Topoisomerase inhibitor MOA
-binds to topoisomerase and results in breaks in DNA and subsequent induction of apoptosis.
-
Doxorubicin
-cause apoptosis of cancer cells by a complex network of events which include but not limited to:
-intercalation into DNA
- Generation of reactive oxygen species- Iron catalyzed
-
HAC (Histone Acetyltransferase)
a critical epigenetic modification that changes chromatin architecture and regulates gene expression by opening or closing the chromatin structure
-
HDAC (Histone Deacetylase)
remove acetyl groups from chromatin, leading to gene repression through condensation of chromatin.
-
HDAC inhibitors
block the erasing of acetyl groups which causes an accumulation of acetylated histones and induces apoptosis of cancer cells
-
inostats
HDAC inhibitors contain the ___ in their name
-
Eukaryotic DNA replication
replication beings at many replication points or origins
-
Prokaryotic DNA replication
replication begins at a single replication origin
-
Okazaki fragment
each fragment of a lagging stranding
-
Helicase
catalyze dsDNA separation at origin-replication fork
-
DNA binding proteins
stabilize ssDNA that has been separated
-
DNA primase
catalyzes addition of short RNA primers which serve as the template strand and allow for DNA replication to take place
-
DNA polymerase
catalyzes addition of new nucleotides to form new strands
-
Exonuclease
catalyzes removal of RNA primer and inserts the correct bases
-
DNA ligase
catalyzes the joining of Okazaki fragments and seals sugar-phosphate backbone
-
Uracil
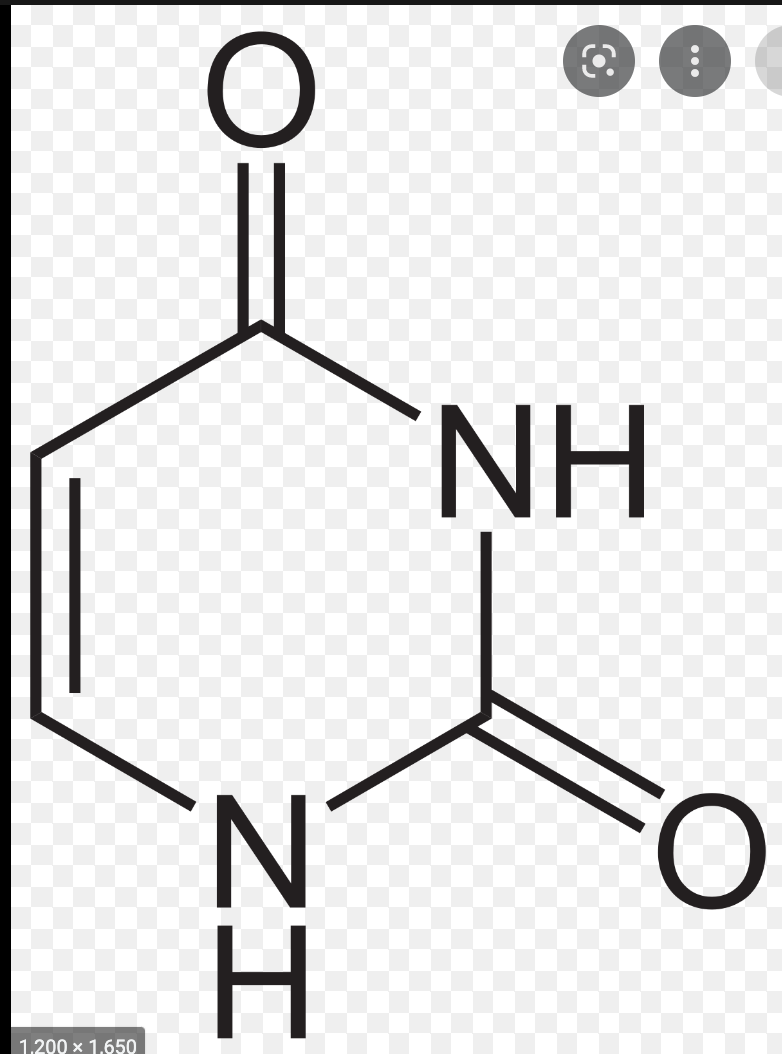
-
Thymine
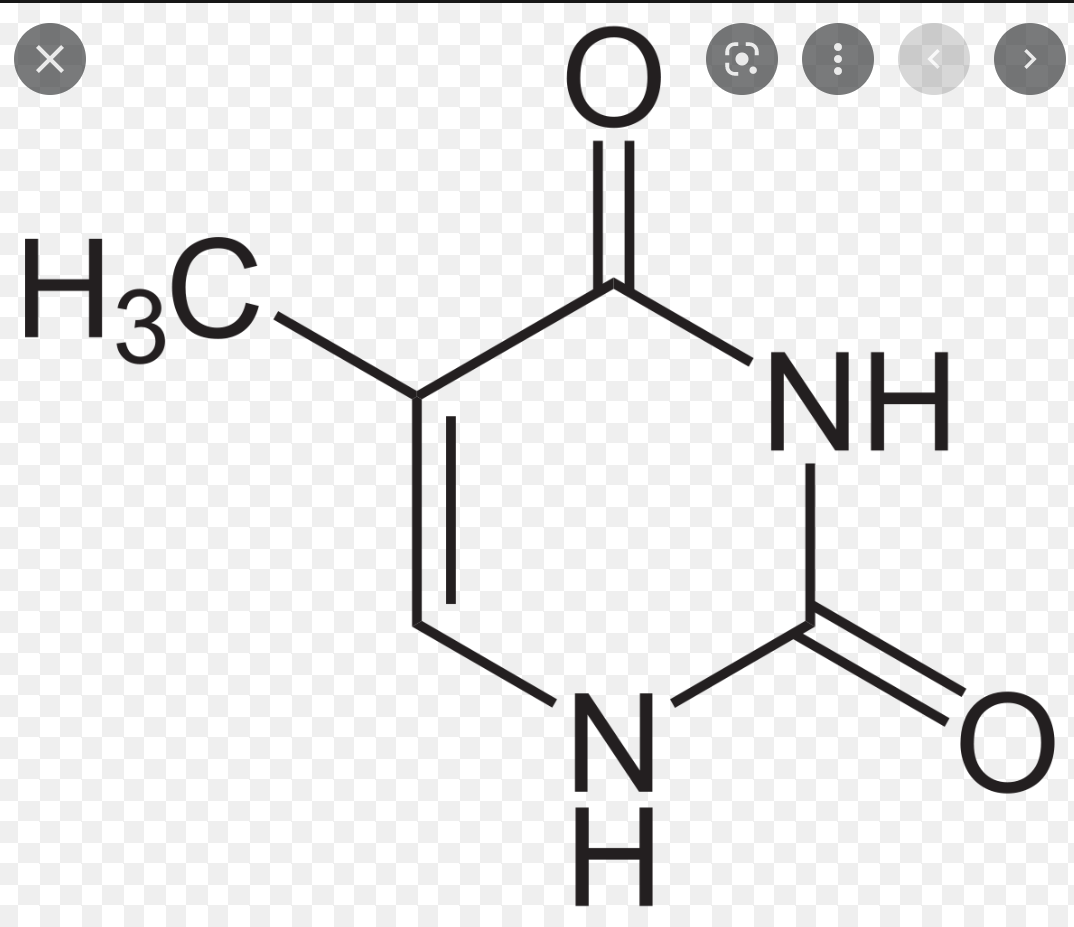
-
Adenine
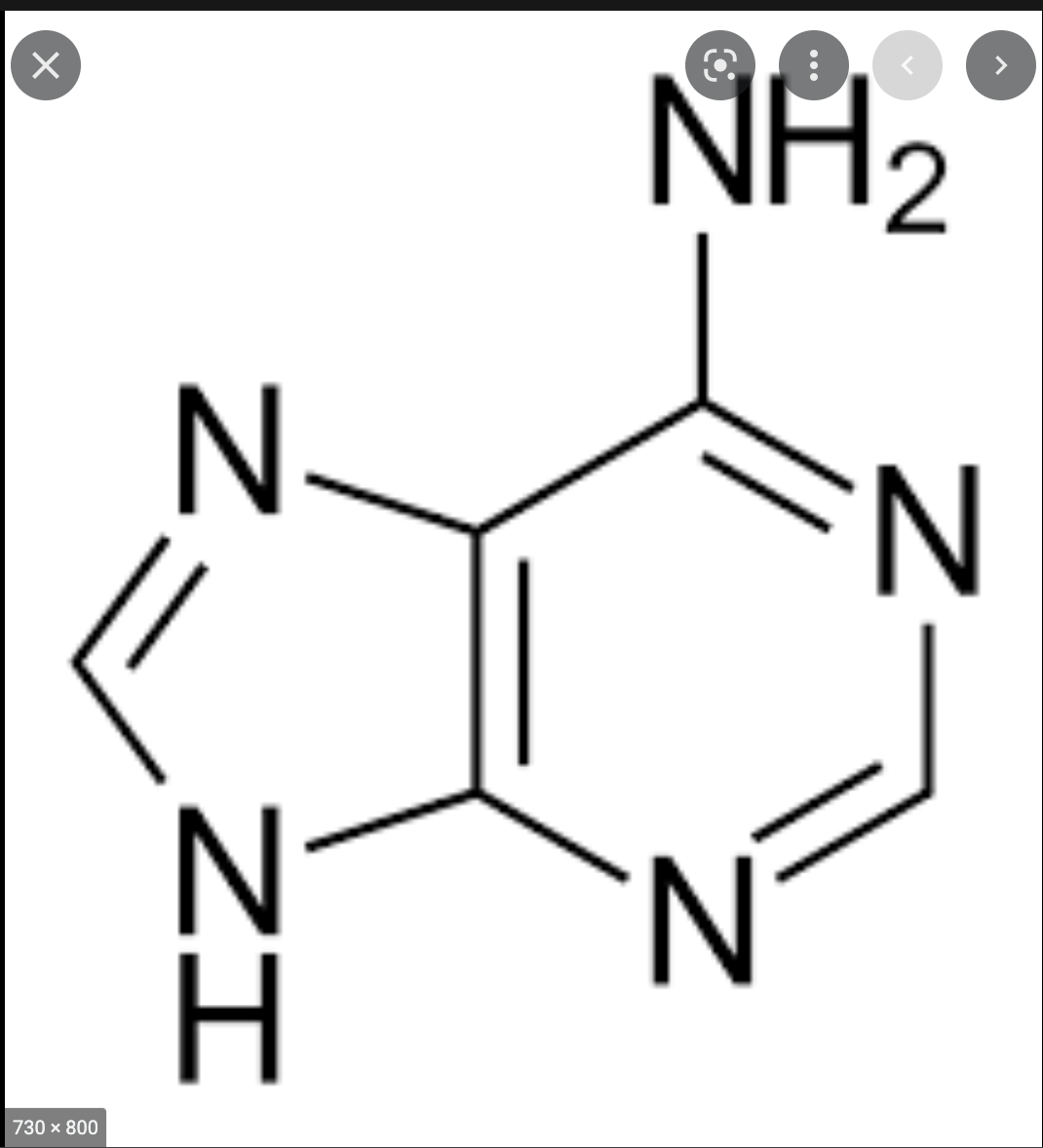
-
Guanine
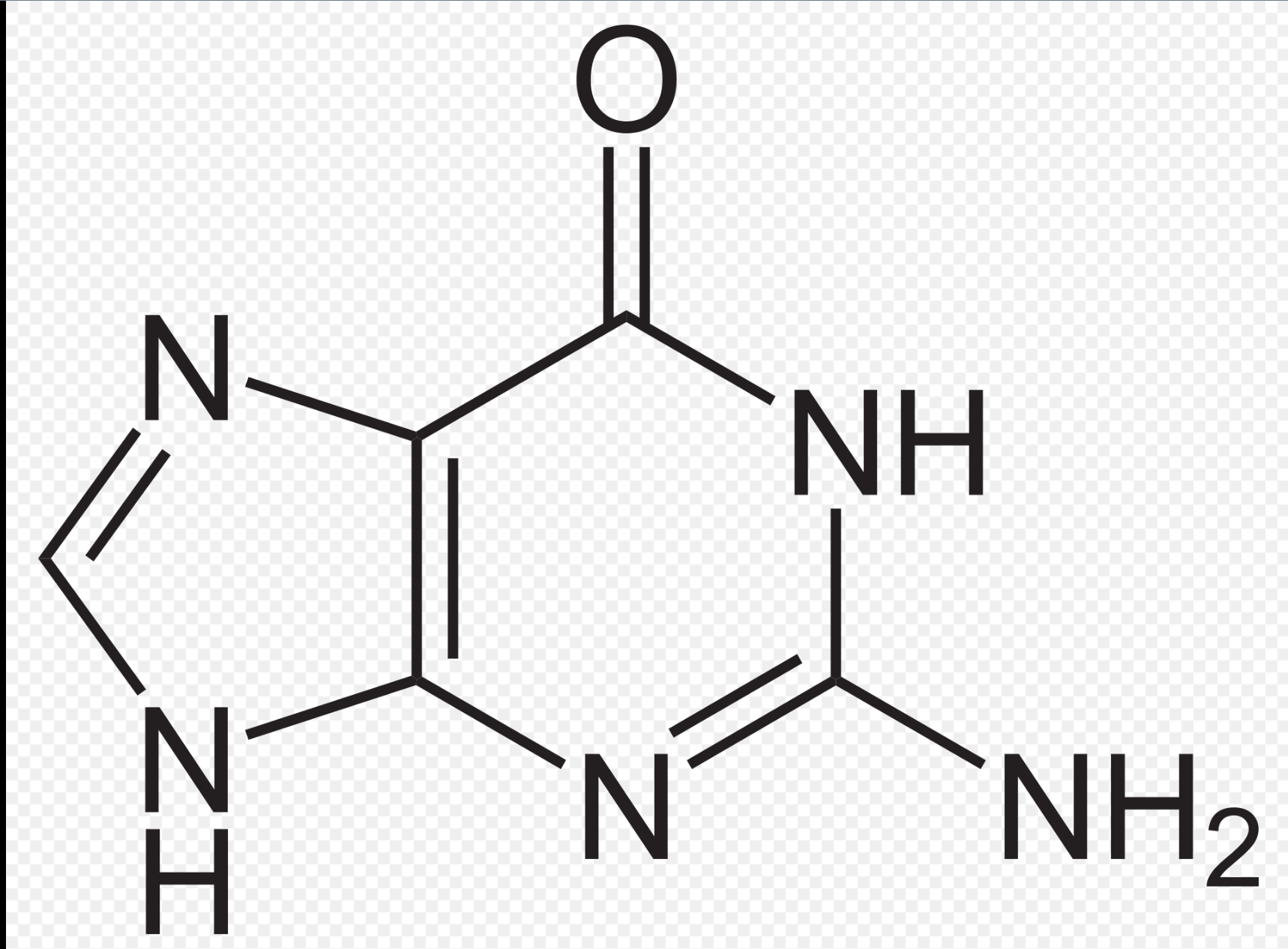
-
Cytosine