-
What is the Key habitat differences between cutthraot and rainbow trout
Cutthroat like colder water temperature and Rainbows are more adaptable (live world wide)
-

ID this fish:
Chinook
-

ID this fish:
Chinook
-

ID this fish:
Chinook
-

ID this fish:
Chum
-

ID this fish:
Chum
-

ID this fish:
Chum
-

ID this fish:
Coho
-

ID this fish:
Coho
-

ID this fish:
Coho
-

ID this fish:
Pink
-

ID this fish:
Pink
-

ID this fish:
Pink
-

ID this fish:
Sockeye
-
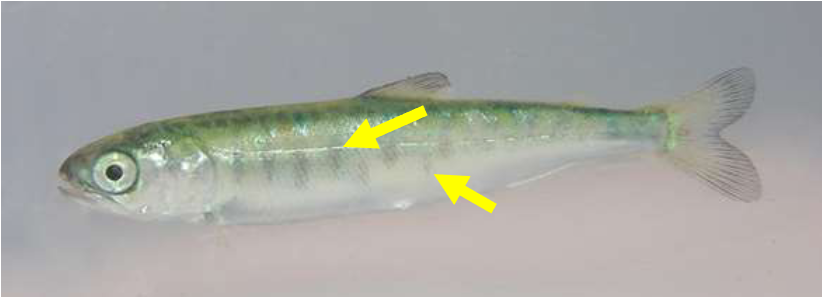
ID this fish:
Sockeye
-

ID this fish:
Sockeye
-

ID this fish:
Rainbow trout
-

ID this fish:
Rainbow trout
-

ID this fish:
Rainbow trout
-

ID this fish:
Cutthroat trout
-

ID this fish:
Cutthroat trout
-

ID this fish:
Cutthroat trout
-

ID this fish:
Confluetus
-

ID this fish:
Frontinalis
-
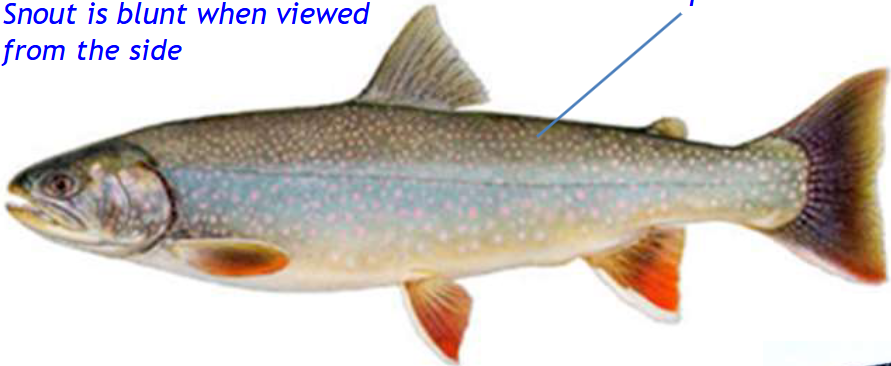
ID this fish:
Malma
-

ID this fish:
Alpinus
-

ID this fish:
namaycush
-

ID this fish:
Lenok / brachymystax
-

ID this fish:
Taimen / hucho
-

ID this fish:
Taimen / hucho
-

ID this fish:
Taimen / hucho
-

ID this fish:
Cherry / masou
-

ID this fish:
Amago / rhodrus
-
Describe 4 anatomical or life history differences between CT and RBT
Rainbows tend to have smaller mouths (around the middle of the eye)
Cutthroats jaw extends past the eye (usually)
Rainbows have a black edge of adipose fins
Cutthroats have spots on the adipose
cutthroats have a Red yellow or orange slash on the hyoid arch
Rainbows don't have a slash
Rainbows lake teeth at the base of the tongue
Cutthroats have teeth at the base of the tongue
-
Define the following terms:
Glacial refugia
Geographic area that allows fish to survive during a ice age, also explains the distribution of the salmonids based on which refugia they are derived from
-
Define the following terms:
Lacustrine life history plan
Life history plan in where the fish never leaves a lake, they go throught every life stage including spawning while in a lake
they lack a stream
-
Define the following terms:
Adfluvial life history
Adfluvial is where a fish spends its adult life within a lake but migrates to a stream to spawn when it reaches sexual maturity
-
Define the following terms:
Resident population
A resident population refers to a group of fish that spend their entire life cycle within a specific, localized area, such as a particular lake, river, or stream, without migrating to other bodies of water.
-
Define the following terms:
Sea-run population
Sea run population often refers to sockeye who after they hatch from their eggs they migrate straight to the ocean (like the Pink salmon life history plan)
-
Define the following terms:
Species complex
when different groups of the same species live different life histories but can still interbreed.
ex.
Rainbow trout and cutthroat trout
Sockeye salmon and Kokanee
Pinocchio and normal mountain whitefish
-
Define the following terms:
Oncorhynchus mykiss irideus
Coastal rainbow trout
-
Define the following terms:
Oncorhynchus mykiss gairdneri
Interior redband rainbow trout
-
Define the following terms:
Oncorhynchus clarkii clarkii
Coastal cutthroat trout
-
Define the following terms:
Oncorhynchus clarkii lewisii
Westslope cutthroat trout
-
How do juvenile Oncorhynchus co exist in fresh water
include information about the BC big 5 as well as the cutthroats and rainbows
By living in different area of the river
by spawning in different areas as well as the juveniles being adapted to specific types of environment
ie.
main channels -> off channels
fast flowing -> slow flowing
Staying the middle of the river -> staying under the banks
-
how old is this fish
0.2
3
-
how old is this fish
3.1
5
-
how old is this fish
1.1
3
-
how old is this fish
4.1
6
-
how old is this fish
52
5
-
Why are pink salmon considered somewhat unique among the BC big 5
They live on a 2 year life cycle
-
What is white chinook?
is it safe to eat?
its a genetic trait that prevents the fish from metabolizing the carotenoid pigment that causes salmon flesh to turn white
It is safe to eat and has the same nutritional content
-
Give 3(+) examples of species complex in salmoninae
Rainbow trout and cutthroat trout
Sockeye salmon and Kokanee
Sharp snouted and blunt snouted Lenok
-
In the current status of stocks why do chinook and coho appear more impacted then pinks
Less population groups within the Chinook and coho groups, the pinks are also less reliant on fresh water and have shorter life spans which can help mitigate the long term effects of a bad year
-
Define the following terms:
Adfluvial life history
An adfluvial life cycle refers to fish that live in lakes but migrate to rivers or streams to spawn.
-
Define the following terms:
Lacustrine life history
Lacustrine fish are those that spend their entire life cycle in lake environments, from spawning to adulthood.
Lack a stream
-
Define the following terms:
"resident population"
A resident population refers to a group of fish that spend their entire life cycle within a specific, localized area, such as a particular lake, river, or stream, without migrating to other bodies of water.
-
Define the following terms:
Residual sockeye
Residual sockeye is the non-migratory version of the anadromous sockeye salmon. Unlike their migratory counterparts, these fish remain in freshwater environments throughout their entire life cycle
Very similar to kokanee however they are the offspring of anadromous fish
-
Why are rainbow trout and sock considered to Flexible/adaptable in terms of life history?
what does this mean?
Rainbow Trout: They exhibit multiple life history forms, including resident (staying in freshwater), fluvial (migrating within rivers), adfluvial (migrating between lakes and rivers), and anadromous (migrating to the ocean and returning to freshwater to spawn, known as steelhead). This adaptability allows them to exploit diverse habitats and resources
Sockeye Salmon: They also display a range of life history strategies, including anadromous (migrating to the ocean and returning to freshwater to spawn)as well as sea run version that go straight to the ocean( more similar to Pink salmon. they also have non-migratory forms like kokanee (living entirely in freshwater). This flexibility helps them survive in varying environmental conditions and ensures their reproductive success

