-


2 NADH
2 NAD+
2 molecules of lactate
-
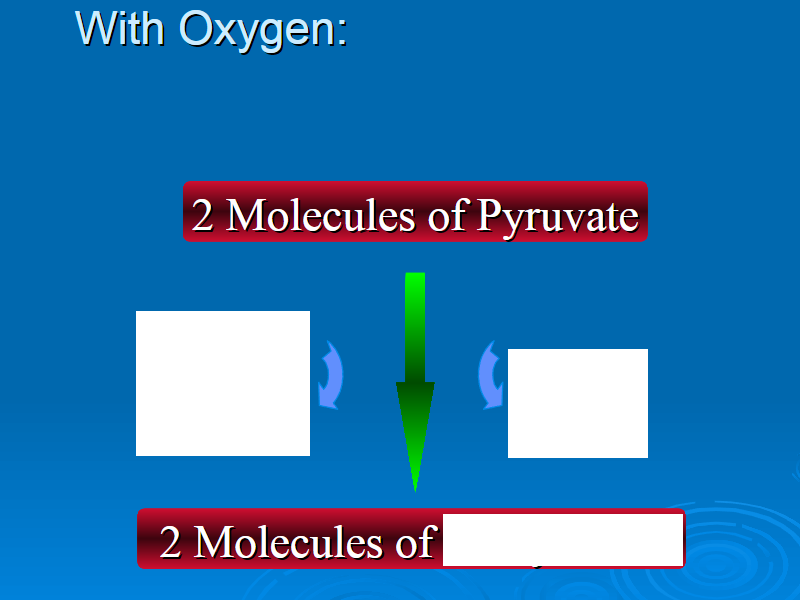
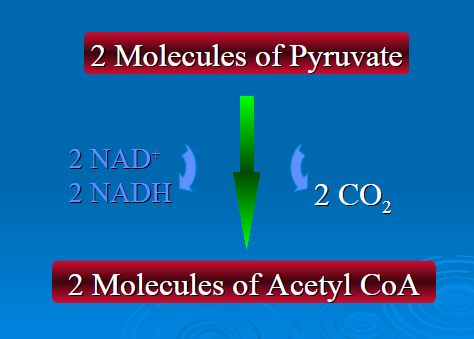
2 NADH
2 NAD+
2 CO2
Acetyl CoA
-


muscles can generate force for work even when oxygen supply is low
-


does not produce large amounts of ATP
accumulation of lactic acid in muscle and body fluids
lasts 1-2 minutes
-
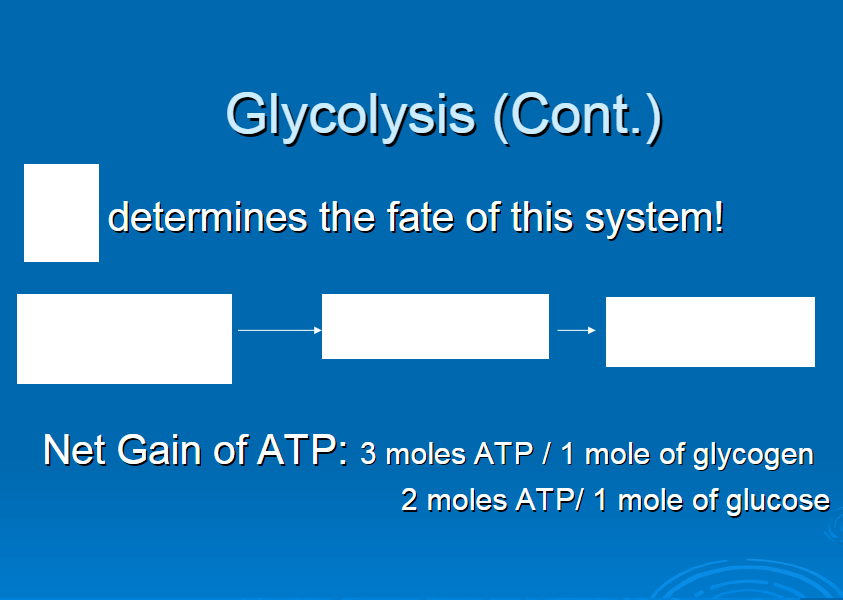
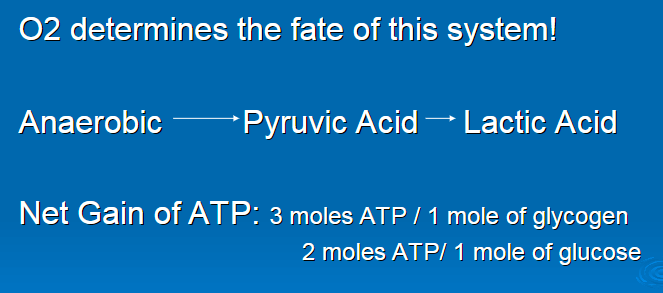
O2
anaerobic
pyruvic acid
lactic acid
-
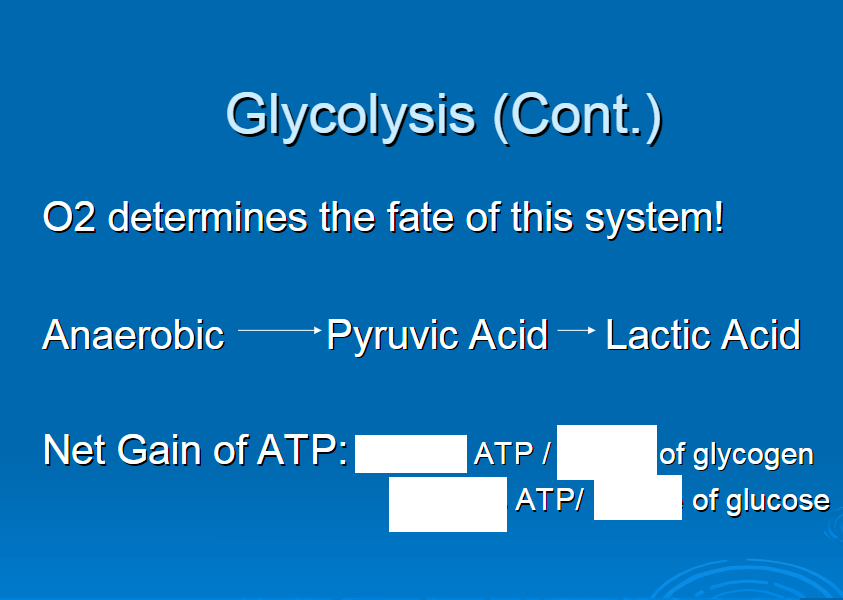
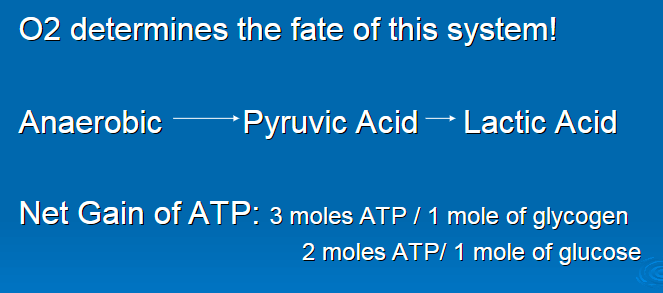
3 moles ATP per 1 mole glycogen
2 moles ATP per 1 mole glucose
-


energy release from carbs
-


blood sugar
-


storage form of sugar located in the liver and muscle tissue
-
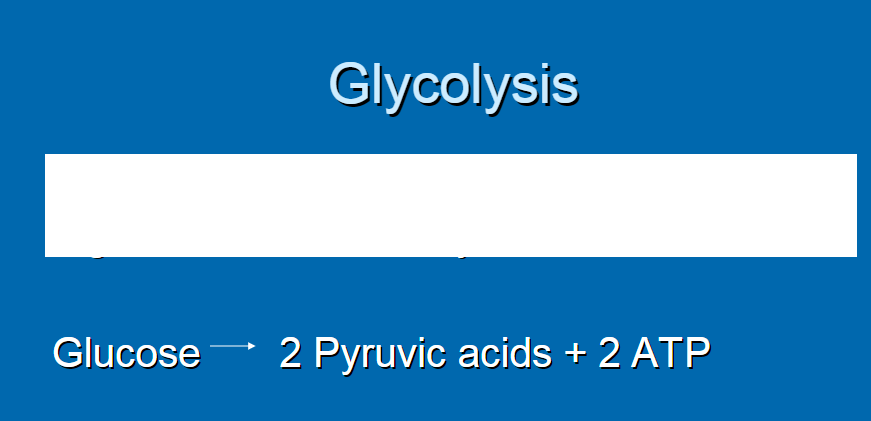

Multienzyme pathway used to break down glucose anaerobically
-


glucose -> 2 pyruvic acid + 2 ATP
-


phosphorylation
-

hydrolysis
-
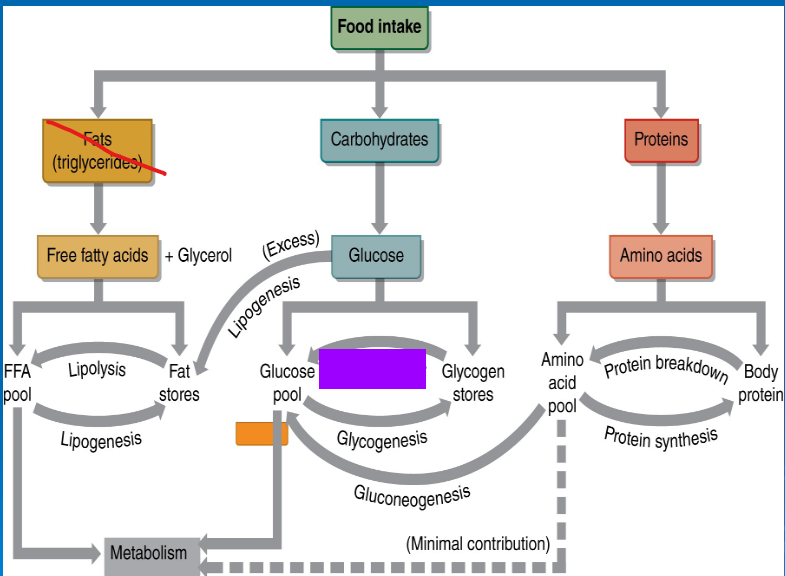
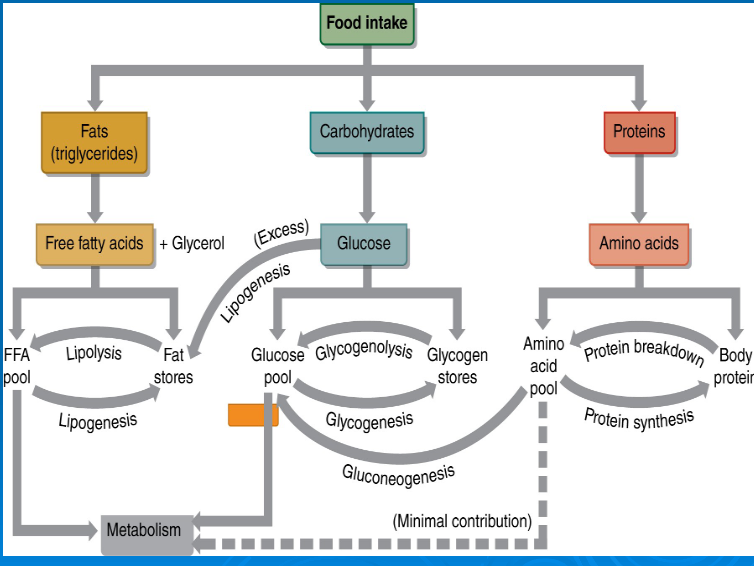
glycogenolysis
-
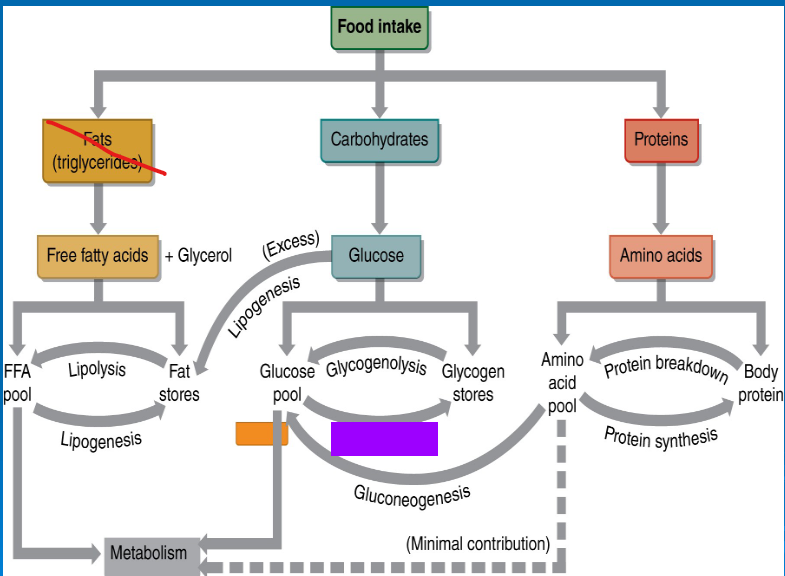
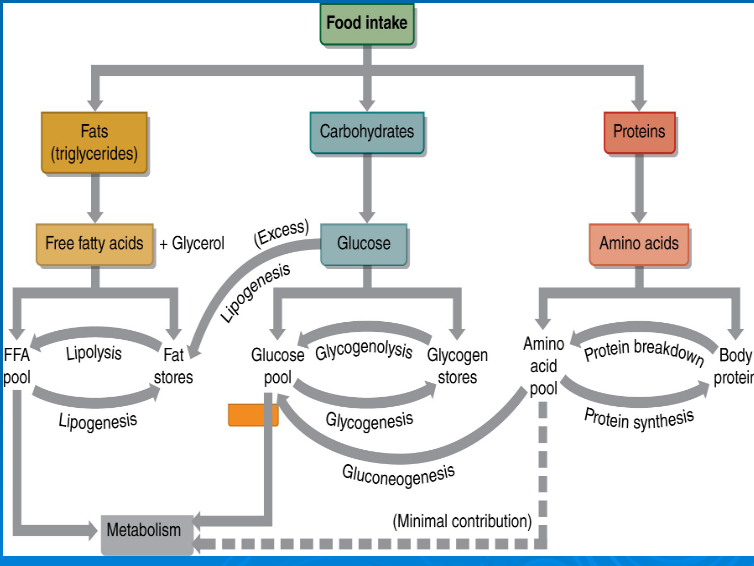
glycogenesis
-
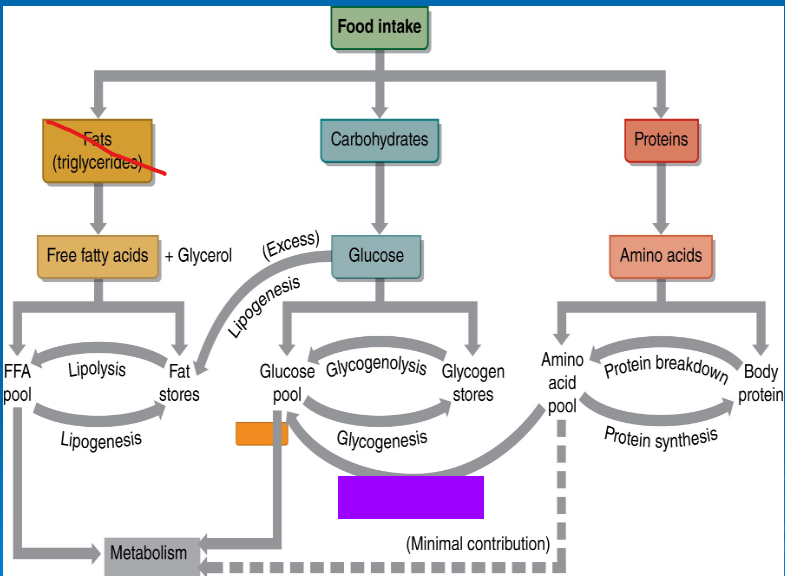
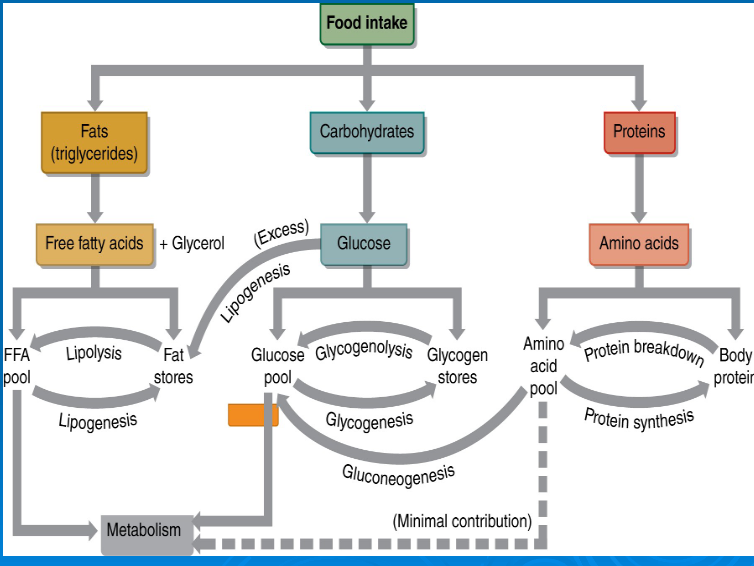
gluconeogenesis
-
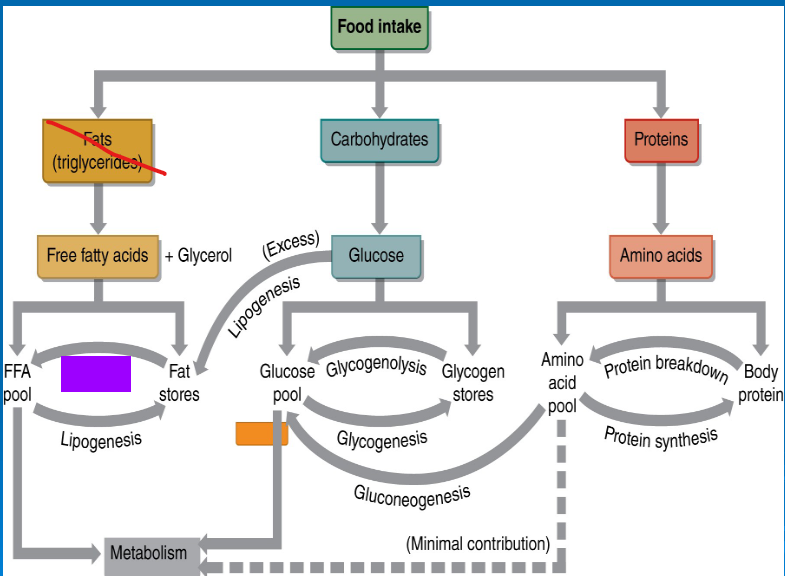
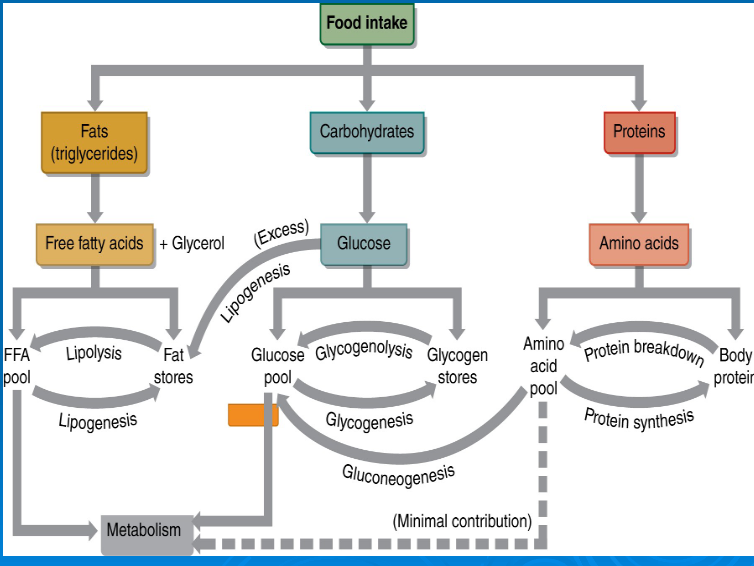
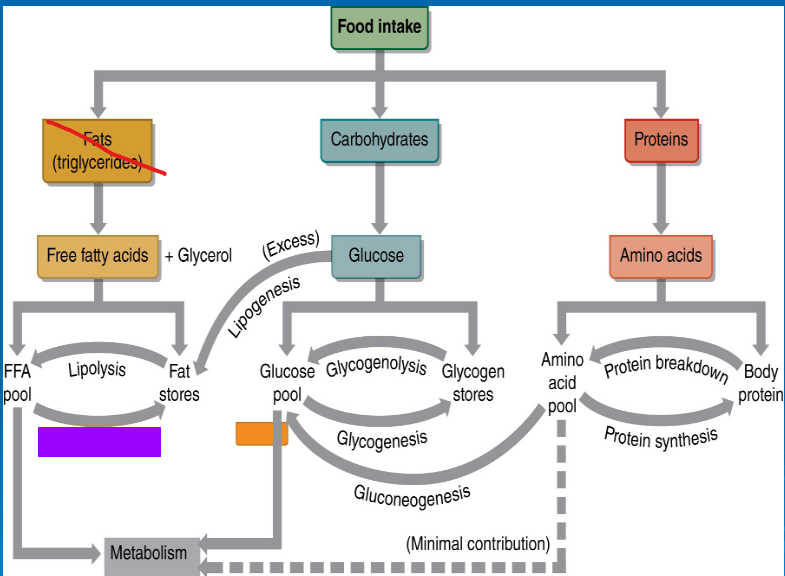
lipolysis
-
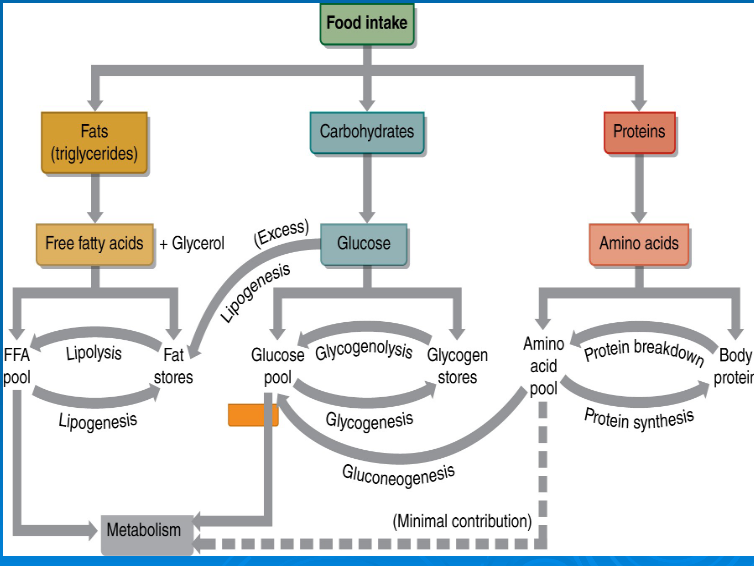
lipogenesis
-
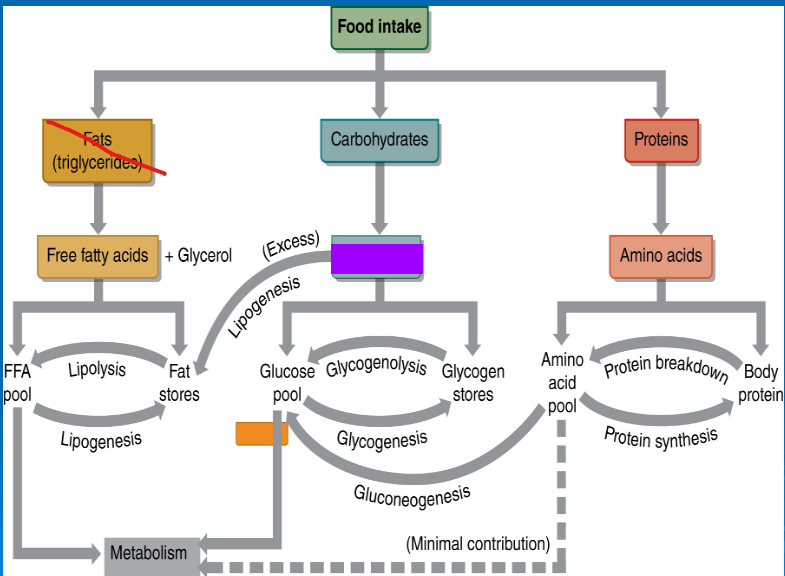
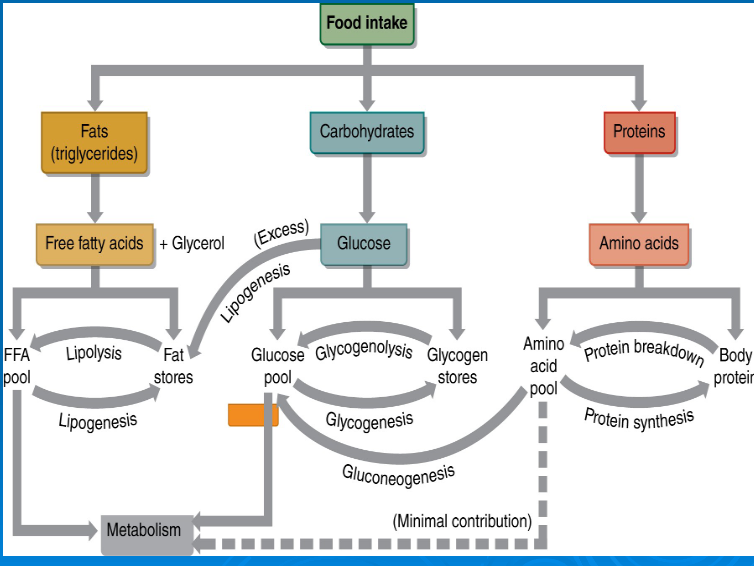
glucose
-
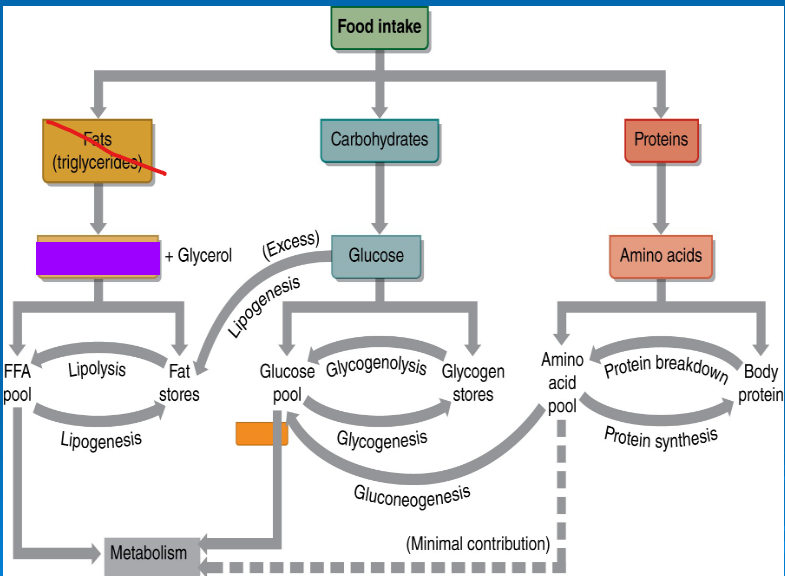
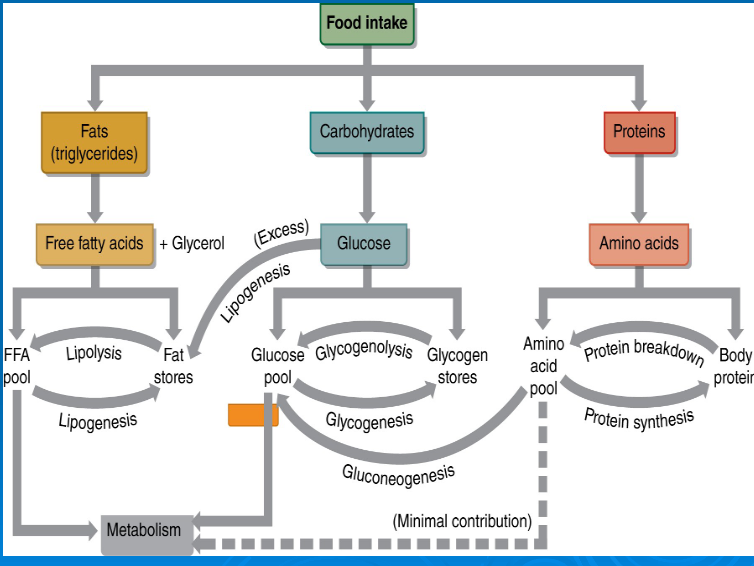
free fatty acids
-
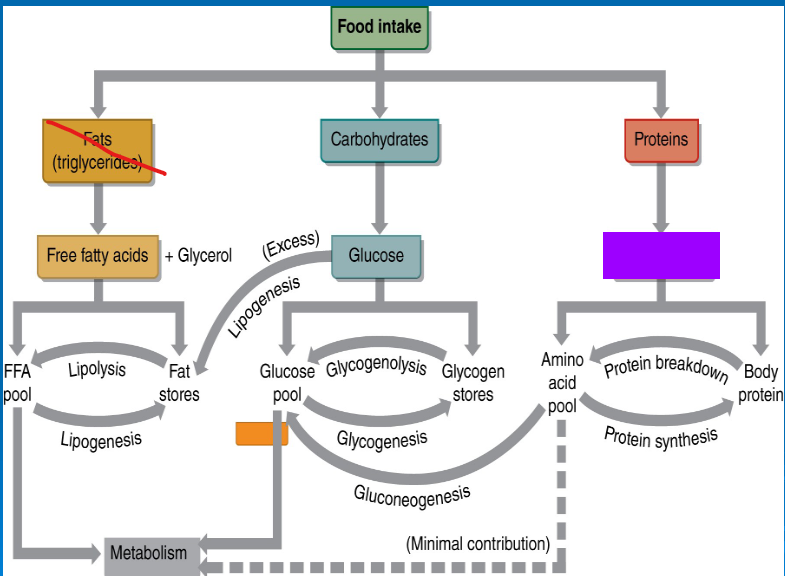
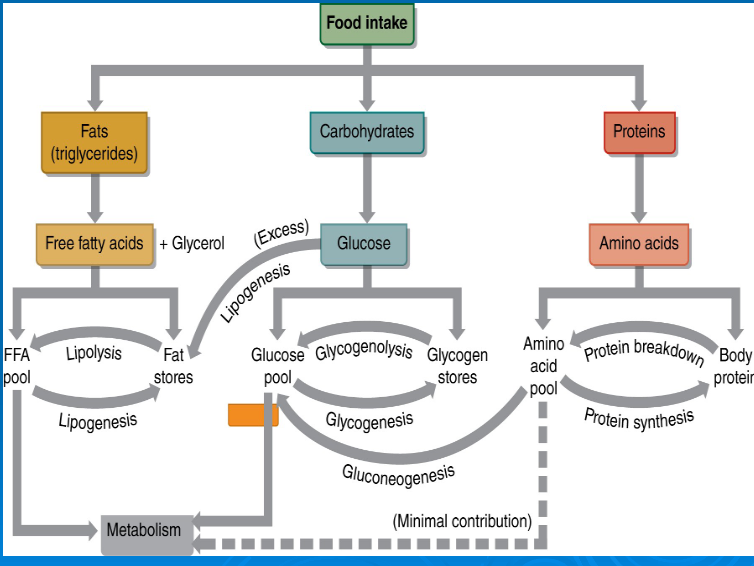
amino acids
-


Use of free energy in cells
-


anaerobic metabolism
-


aerobic metabolism
-


ATP-PCR system
Anaerobic metabolism
Aerobic Metabolism
-
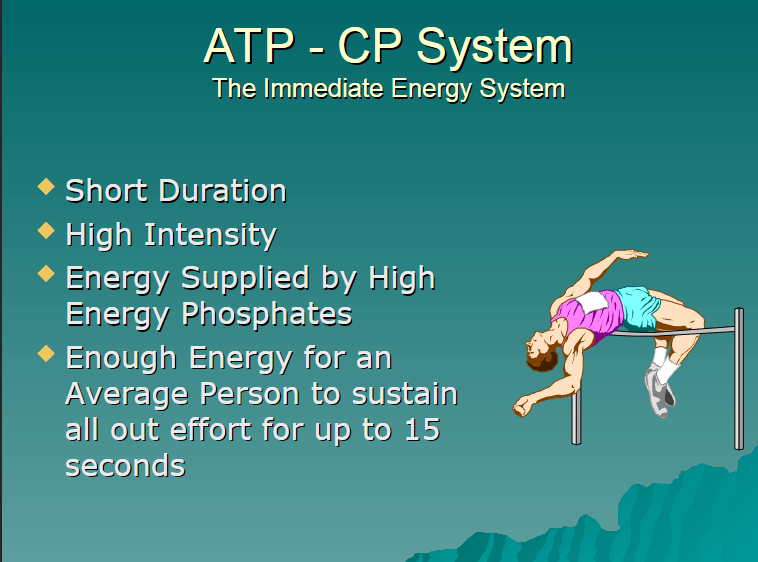
ATP-PCR system
short duration
high intensity
enough energy to sustain an all out effort for 15 seconds
-


anaerobic glycolysis
-


glucose is broken down to make ATP
-


sprint sports
-


process by which the body breaks down substrates with the use of oxygen to generate energy
-


aerobic glycolysis
kreb's cycle
electron transport chain
-


aerobic glycolysis
-


15 seconds and 2 minutes
-


lactate is not made
-


acetic acid
co-enzyme A
-


acetyl CoA
Krebs Cycle
2 ATP
-

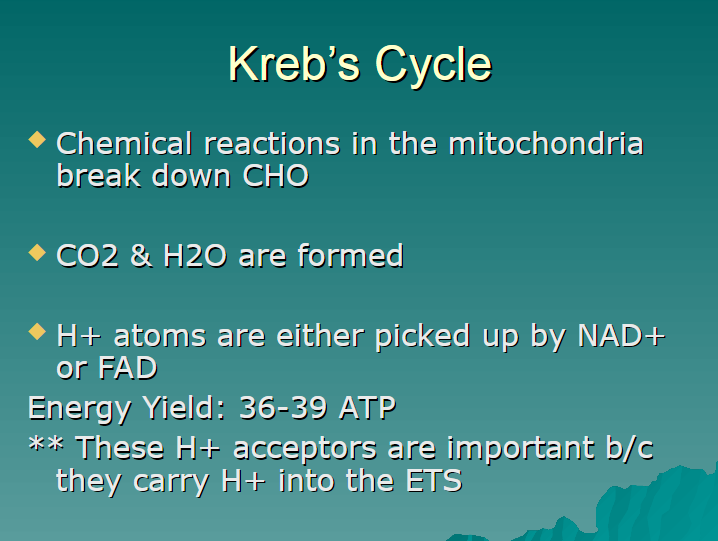
NAD+
FAD
36-39 ATP
-

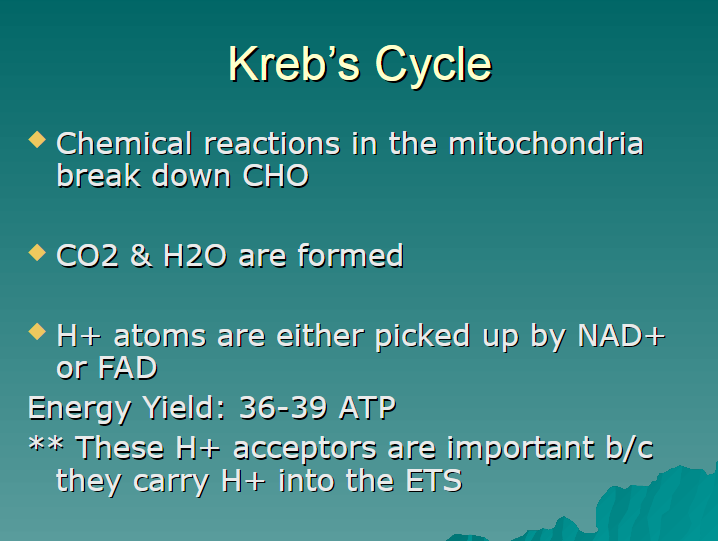
chemical reactions in the mitochondria break down carbs
-
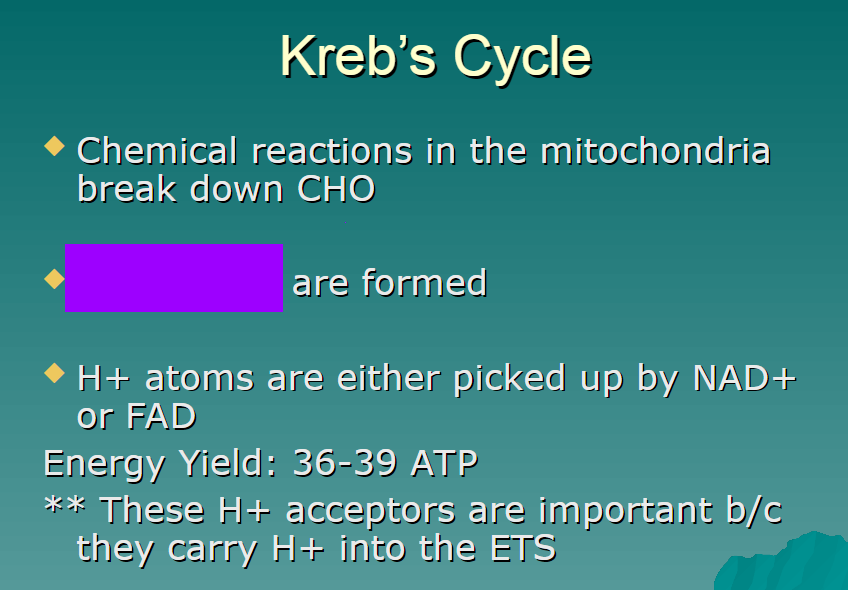
CO2
H2O
-
recombine atoms to produce ATP and water
CO2 exhaled via lungs
-

low intensity activities
-

greater than 3 minutes duration
-

steady state
-


breakdown of free fatty acids in the mitochondria
-

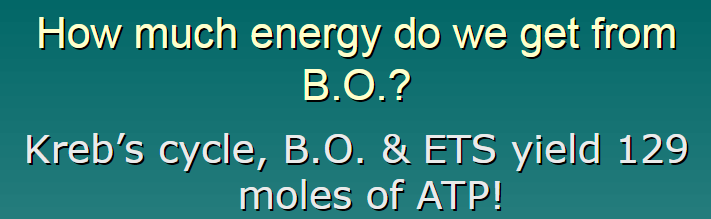
129 moles of atp
-


39 ATP/mol

