-


direct calorimetry
-


indirect calorimetry
-


respiratory quotient
-


respiratory exchange ratio
-

co2 released, oxygen consumed
-
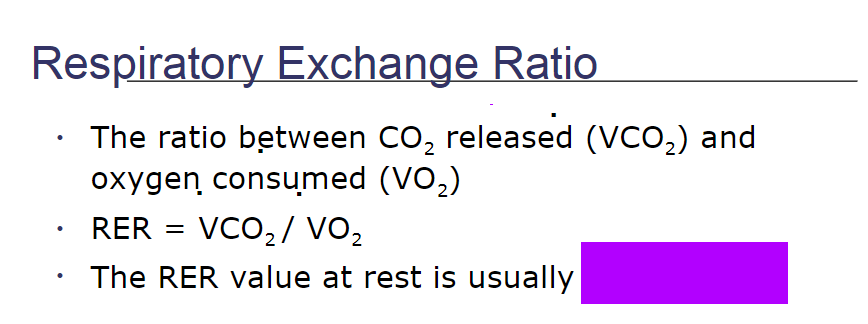
0.78 to 0.80
-
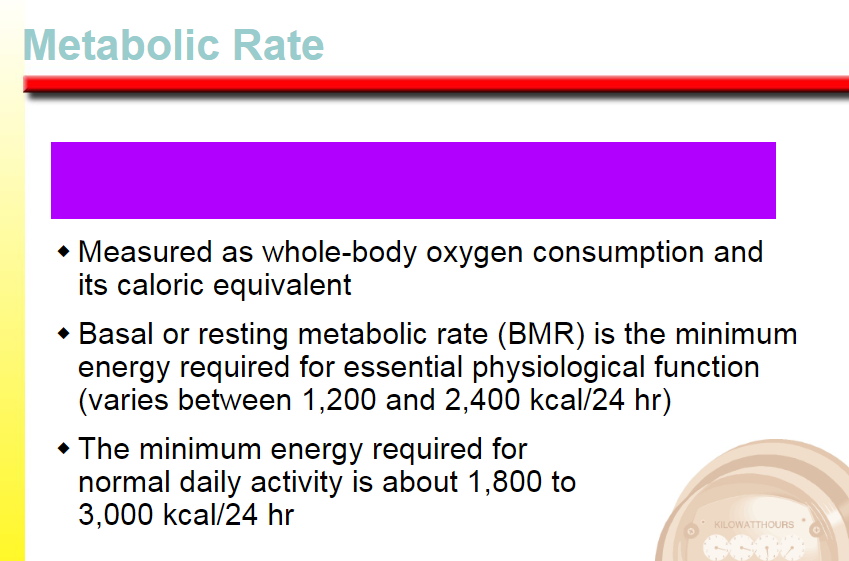

rate at which the body expends energy at rest and during exercise
-


basal metabolic rate
resting metabolic rate
-


total daily energy expenditure
-


60-75% RMR and BMR
-

15-30% thermic effect of physical activity
-

10% thermic effect of feeding
-
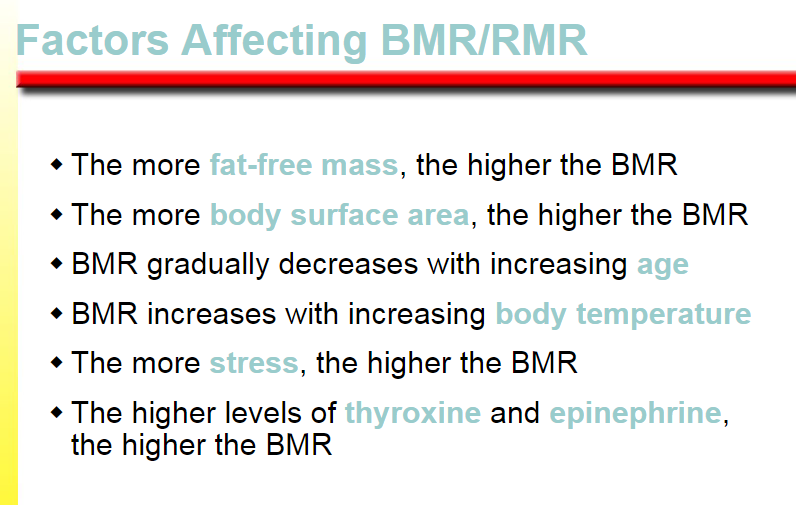
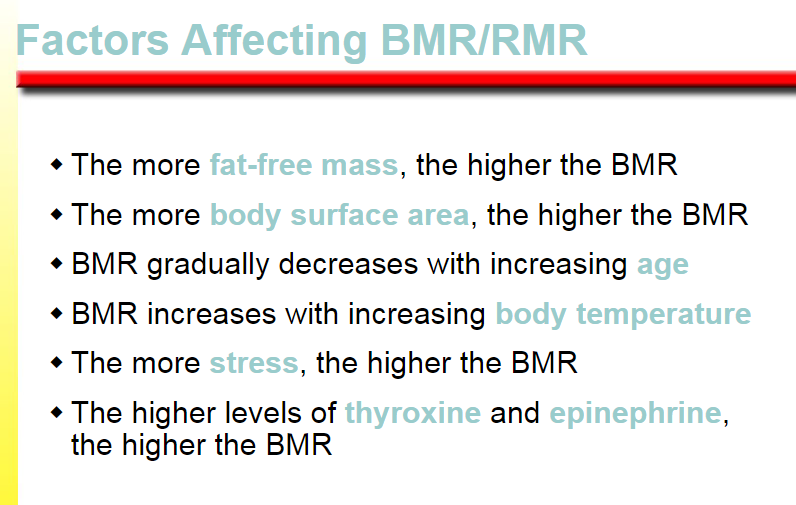
the higher the BMR
-
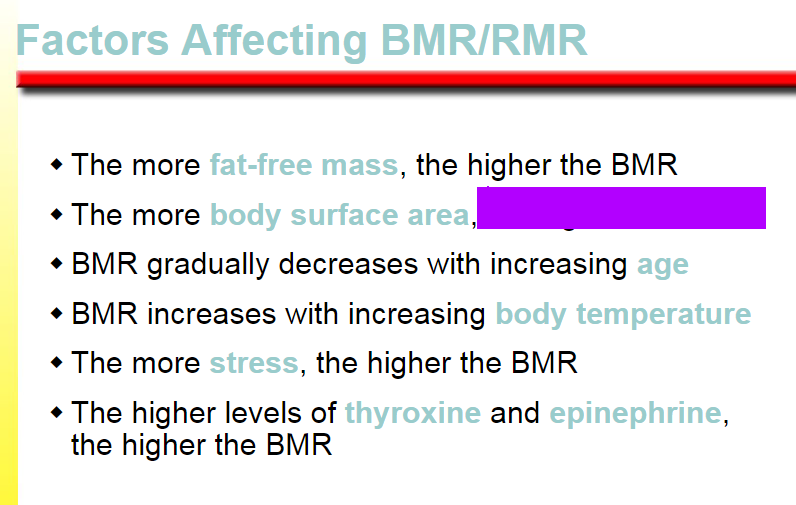
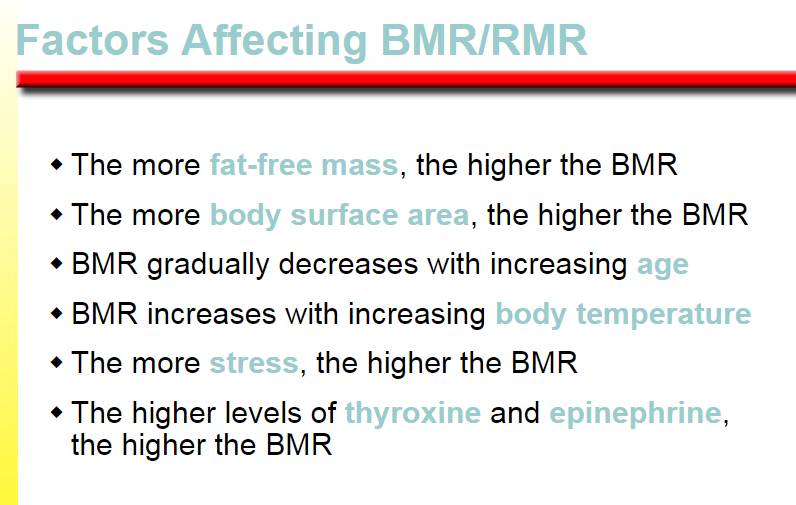
the higher the BMR
-

BMR gradually decreases
-
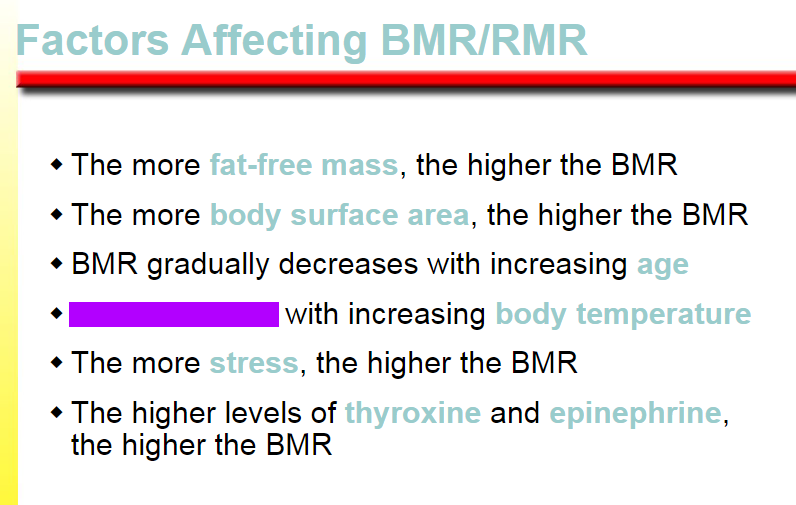
BMR increases
-
the higher the BMR
-
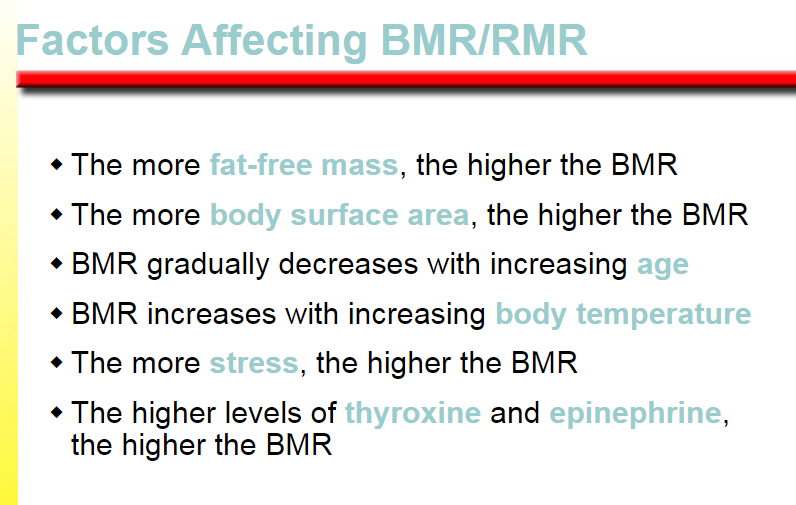
thyroxine
epinephrine
the higher the BMR
-


the maximal capacity for oxygen consumption by the body during maximal exertion
-
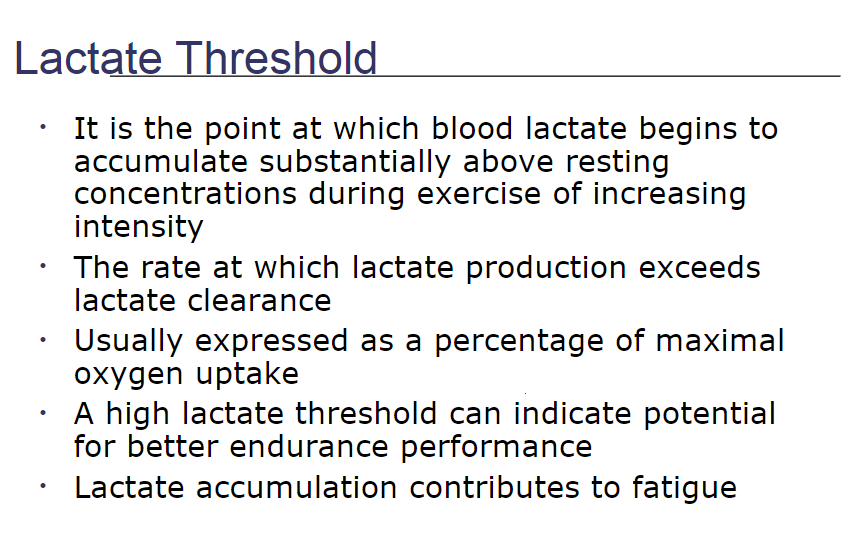
the rate at which lactate production exceeds lactate clearance
-


high maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max)
-


high lactate threshold
-


high economy of effort
-
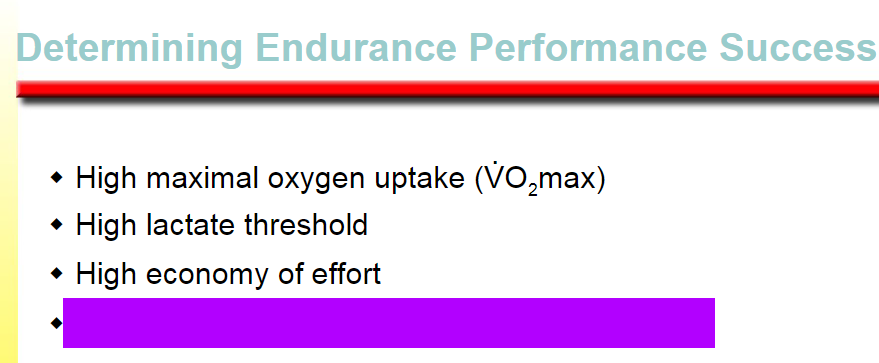

high percentage of slow-twitch muscle fibers
-


excess post oxygen consumption
-


the total oxygen consumed following exercise in excess of a baseline level
-

lag time
anaerobic contribution to exercise
increase in VO2 uptake
lasts 1-3 minutes
-
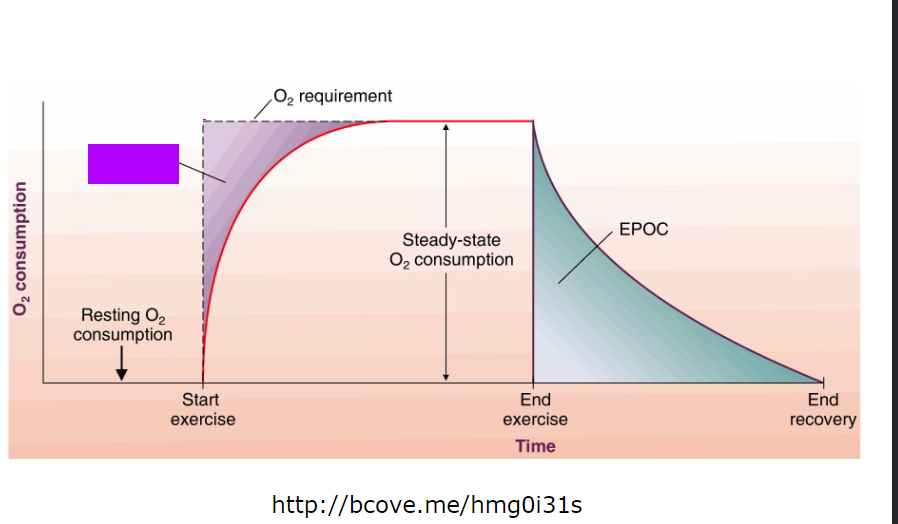
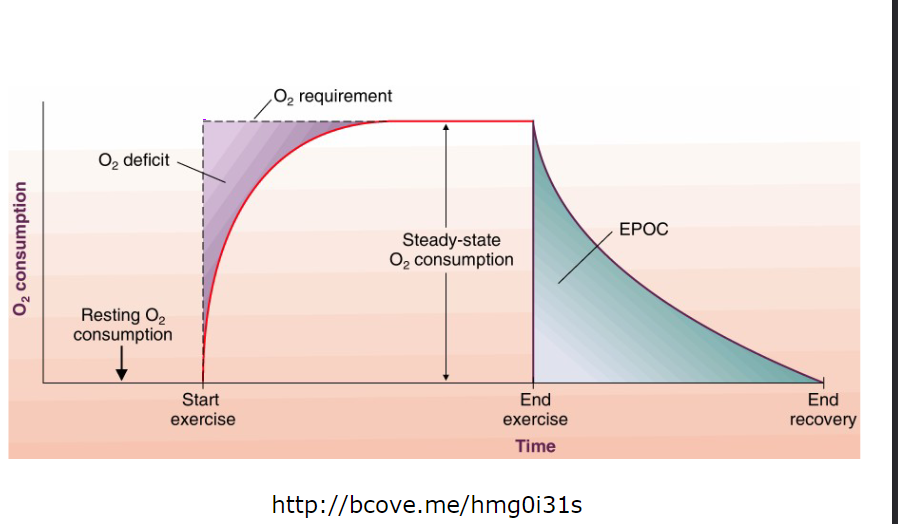
oxygen deficit
-
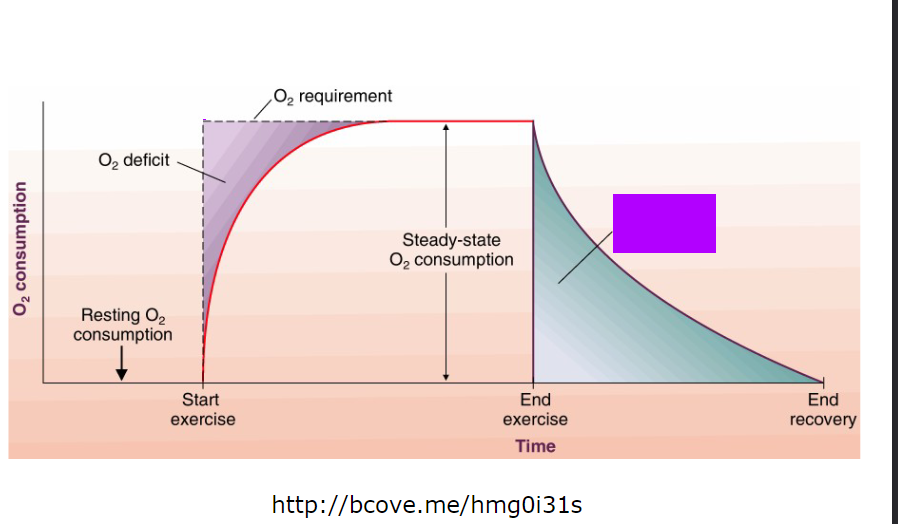
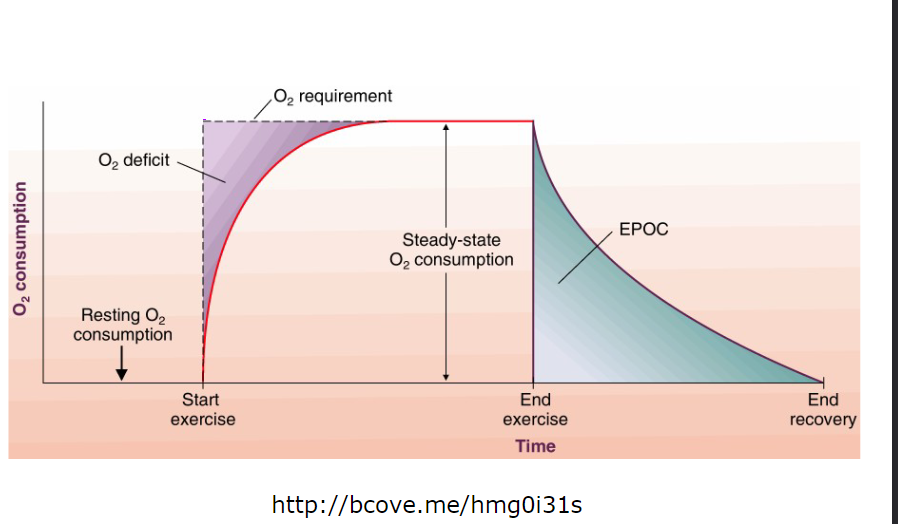
excess post oxygen consumption
-


Fast component
-


Slow component
-


restoration of ATP and CP stores
oxidation of lactate
post exercise hormonal response
increased heart and respiration rates
-

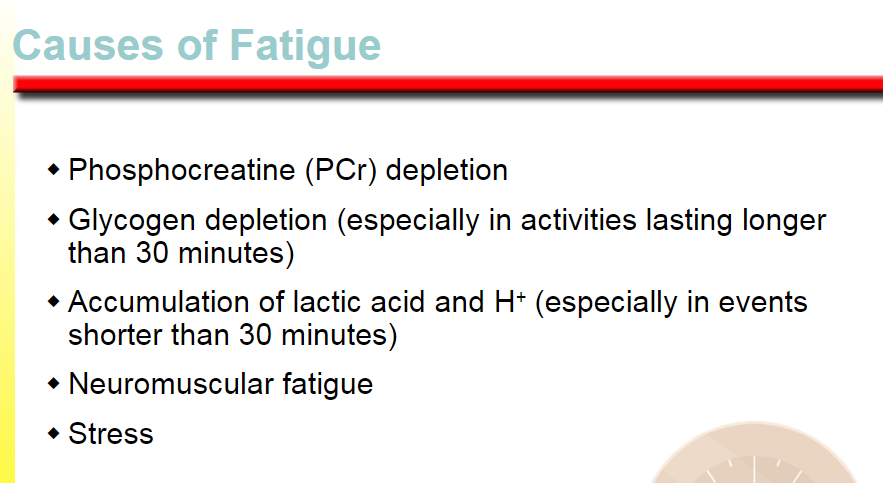
phosphocreatine depletion
glycogen depletion
neuromuscular fatigue

