-
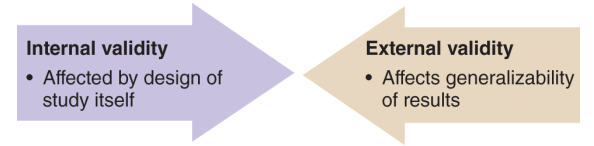
What are the two factors that define the validity of a study?
-
Internal validity is concerned with the appropriate measurement of ___, ___ and ___.
Internal validity is concerned with the appropriate measurement of exposure, outcome and association between exposure and disease.
-
A study must have external validity before it can have internal validity. True or false?
False; a study must internal validity before it can have external validity. Internal validity is always the FIRST priority, since invalid findings cannot be generalized.
-
What are the two categories of error?
Random - rate, odds ratio
Systemic - measurement bias
-
Name some factors that cause random error.
- poor precision
- sampling error
- variability in measurement
-
What does precision refer to?
If the measurement/effect is reproducible and consistent over time.
-
___ helps reduce sampling error.
Increasing sample size
-
What factors cause systemic error?
- selection bias
- information bias
- confounding
-
In analytical studies, where does bias come from?
When the comparison groups are not comparable.
-
Selection bias is due ___.
systematic differences in the characteristics in the study sample and the reference population (not representative). It's likely that the researchers chose the wrong method to capture answers.
-
What is information bias?
Error in the accuracy of information collected between comparison groups.
-
How can information bias be minimized?
- use standardized data collection forms
- double blinding
-
What criteria needs to be satisfied for a factor to be considered a confounder?
1. Be a risk factor for the disease
2. Be associated with the exposure
3. NOT a step in the causal path between exposure and disease
-
What are prevention strategies for controlling confounding variables?
- randomization
- restriction (ie. restricting a study to women only)
- matching

