-
Following the period of cleavage and the formation of a blastula, the embryo embarks on one of the most critical periods in its development—__________
Cleavage ---> Blastula ---> _______
the stage of gastrulation (gastrula)
-
is characterized by profound but well-ordered rearrangements of the cells in the embryo.
Gastrulation
-
The major morphogenetic movements during gastrulation result in the _____________________ to a stage characterized by the presence of three germ layers, but other morphogenetic movements continue into later stages.
rearrangement of the embryo from the blastula
-
Major types of morphogenetic movements seen in early embryos (gastrulation part)
1. Invagination
2. Evagination
3. Involution
4. Epiboly
5. Ingression
6. Delamination (polyingression)
7. Ameboid motion
-
Inpocketing of sheet of cells (e.g. archenteron formation in amphioxus)
Invagination
-
Outpocketing of a sheet of cells (e.g. exogastrulation)
Evagination
-
Rolling around a corner of an expanding outer layer of cells and spreading over an internal surface (e.g. Cell movements through the amphibian blastopore)
Involution
-
Spreading of a cell sheet (e.g. Spreading of outer cells toward amphibian blastopore)
Epiboly
-
Sinking of individual cells from a surface into an area (e.g. Primary mesenchyme formation in sea urchin blastula)
Ingression
-
Separation of a second sheet from an original single sheet (e.g. Formation of primary hypoblast in avian embryos)
Delamination (polyingression)
-
Migration of cells as single individuals through their own motility (e.g. migration of neural crest cells
Ameboid motion
-
Embryo's two main strategies for dealing with gastrulation
1. carry out the gastrulation movements within the context of a sphere (seen in amphioxus - contain little yolk; amphibians - contain moderate amounts of yolk)
2. great amount of yolk found in large eggs, such as those of reptiles and birds
-
In amphioxus, gastrulation consists of an inpocketing or ____ of a blastula
Invagination
-
The new cavity in the double-walled cup is termed ______
the rudimentary alimentary cavity of an embryo at the gastrula stage.
Archenteron
-
Opening from the outside into the archenteron is called
blastopore
-
In ___________ the original single layer of the blastula has been rearranged to form two layers
gastrulation
-
outer cell layer is called
ectoderm
-
inner layer of the early gastrula is composed of cells belonging to the _____
endoderm
-
middle germ layer
mesoderm
-
The _______________________ begin in the late blastula stage with the separation of the primary mesenchyme from the wall (vegetal plate) of the blastula
morphogenetic movements that characterize gastrulation
-
prominent projections
filopodia
-
The main feature of gastrulation in the sea urchin is the formation of the ______
archenteron or primitive gut
-
1. The first stage is dominated by the inpocketing, or invagination, of cells at the vegetal pole and their elongation into the blastocoel
2. The second stage of archenteron formation is characterized by the presence of a population of secondary mesenchymal cells, which become distinguishable at the innermost tip of the archenteron
3. In the third stage, the tip of the archenteron makes contact with the blastocoel wall
Three stages of archenteron formation
-
After the archenteron reaches the opposite wall of the blastula, the resulting bilaminar layer soon ruptures to form the ________. At the other end, the blastopore becomes the _______.
oral opening; anus
-
After the emergence of the oral opening and anus, the embryo then begins to assume a triangular appearance, and as the skeleton arises from the primary mesenchyme, armlike structures form and the embryo is well on the way to becoming a __________.
pluteus larva
-
This groove, called the _______, represents the site at which cells move into the interior of the embryo
blastopore
-
The upper margin of the blastoporal groove is known as the _________ and will later become the major organizing region (Spemann organizer) of the embryo
dorsal lip of the blastopore
-
The mass of yolk left presenting at the blastopore is known as the _____
yolk plug
-
Gastrulation movements are _______ among the major amphibian groups
not uniform
-
Much of the process of gastrulation consists of _____________ at the blastopore.
surface cells moving into the interior of the embryo
-
As cells turn inward around the lips of the blastopore, _____________
they are followed by other cells which move over the surface of the embryo toward the blastopore.
-
Around most of the ventral margins of the blastopore and extending down onto the ventral part of the embryo the _________ is rolled into the interior of the embryo and eventually comes to line its archenteron or primitive gut
prospective endoderm
-
Most of the cells passing over the dorsal lip of the blastopore are often called ______ because they eventually give rise to the notochord and cephalic mesoderm
Chordamesoderm
-
When involution has just begun, the early archenteron is lined by _______ on its dorsal surface and elsewhere by endoderm
chordamesoderm
-
In ________ embryos, part of the dorsal surface of the archenteron remains lined by chordamesodermal material until late in gastrulation
urodele
-
Convergent extension of the gastrulating embryo is due in large part to a process of _________ that begins around the midgastrula period.
mediolateral intercalation
-
In _____________, lateral cells insert processes between cells located in the medial part of the layer and ultimately become totally interposed between them
mediolateral intercalation
-
Through mediolateral intercalation, a short and broad mass of cells becomes long and thin, and the gastrulating embryo as a whole begins to ___________________
elongate from its almost spherical shape
-
As they move into the interior of the embryo, the ___________ of the amphibian embryo migrate over the inner surface of the roof of the blastopore
chordamesodermal cells
-
The _________, which begins to be deposited in the early blastula stage, has a high concentration of fibronectin molecules.
fibrillar matrix
-
As the _______ pass around the rim of the dorsal lip, they become the endodermal lining of the archenteron
surface cells
-
The _______, which are so prominent in early gastrulation, decrease in height and ultimately become indistinguishable from other endodermal cells of the endodermal lining.
bottle cells
-
it appears that _____ move toward the blastopore, turn inward at its lips, and then migrate away from the blastopore as the definitive middle mesodermal germ layer
premesodermal cells
-
The _____________ does not remain static during gastrulation
prospective ectoderm
-
The remainder of the ectoderm will form the epidermis of the skin and is therefore called __________
general cutaneous ectoderm
-
By the end of gastrulation the entire outer surface of the embryo is covered by ___________, whereas the future endoderm and mesoderm have come to lie entirely within
neural and general cutaneous ectoderm
-
(Gastrulation in birds) a thin sickle-shaped mass of cells or _________ takes shape at the posterior end of the embryo
Roller’s sickle
-
From Roller’s sickle, a second generation of hypoblastic cells (secondary hypoblast) pushes __________, compressing and folding the primary hypoblast ahead of it
anteriorly
-
__________ germ cells are found in the primary hypoblast
Primordial
-
The secondary hypoblast forms extraembryonic endoderm, principally the __________.
yolk stalk
-
Formation of the primary and secondary hypoblast can be considered a ___________ phenomenon
pregastrulation
-
_______ and formation of the definitive embryonic germ layers begin with the appearance of a condensation of cells in the posterior part of the epiblast
Gastrulation
-
The appearance of the primitive streak is the result of an ______________________ (Eyal-Giladi and Wolk, 1970), and its orientation is a reflection of the intrinsic polarity of the underlying hypoblastic layer.
pregastrulation
-
The early primitive streak initially elongates in both a cephalic and a caudal direction
true
-
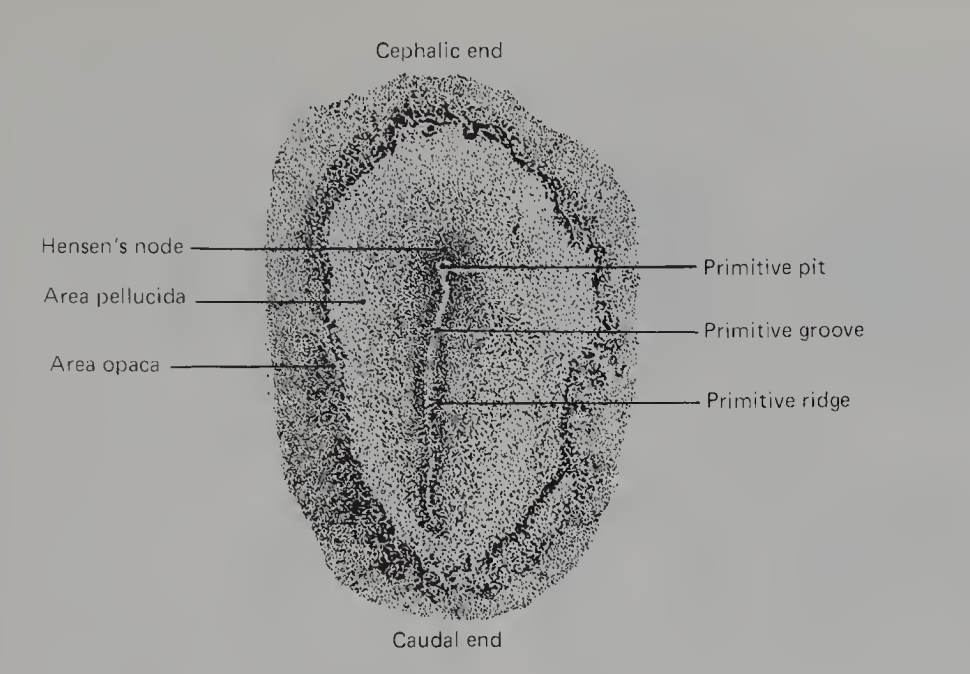
At the cephalic end of the primitive streak, closely packed cells form a local thickening known as
Hensen’s node
-
The main period of gastrulation begins with the establishment of the ___________ and ____________
primitive streak; Hensen's node
-
In ____, gastrulation is accomplished by the coordinated passage of individual cells from the exterior into the interior of the embryo (ingression) rather than the immigration of integral sheets of cells
birds
-
The first cells to pass through the area of the anterior part of the primitive streak are future embryonic endodermal cells.
true
-
As time goes on, a progressively greater percentage of the cells which pass through the node are destined to be incorporated into the mesoderm and a correspondingly smaller number lodge in the endoderm
true
-
The most extensive invagination of mesodermal cells occurs along the length of the ________, where the coherent layer of mesodermal cells that is formed expands parallel to the underlying layer of the embryonic endoderm
primitive streak
-
Besides the primitive streak, the other major site of mesoderm formation is through ________, where a rod of mesodermal cells directed cephalad lies in the midline of the embryo in the track of the regressing primitive streak
Hensen’s node
-
The mesodermal rod becomes the ________
notochord
-
The epiblast is composed of ____________cells
cuboidal to columnar epithelial
-
The deeper parts of the cells are bound together by spotlike junctions known as _________, which are involved in cell-to-cell communication.
gap junctions
-
When the cells of the epiblast enter the primitive groove, they undergo a ________________, becoming to some extent bottle-shaped in a manner reminiscent of the bottle cells seen in amphibian gastrulation
pronounced change of shape
-
During this change of shape, the _________ begin to break up and lose their circumferential arrangement at the apex of each cell.
tight junctions
-
Shortly after the first prospective notochordal cells are laid down, the primitive streak and Hensen’s node undergo a regression toward the ______ end of the embryo
caudal
-
the mammalian embryo contains almost no yolk
true
-
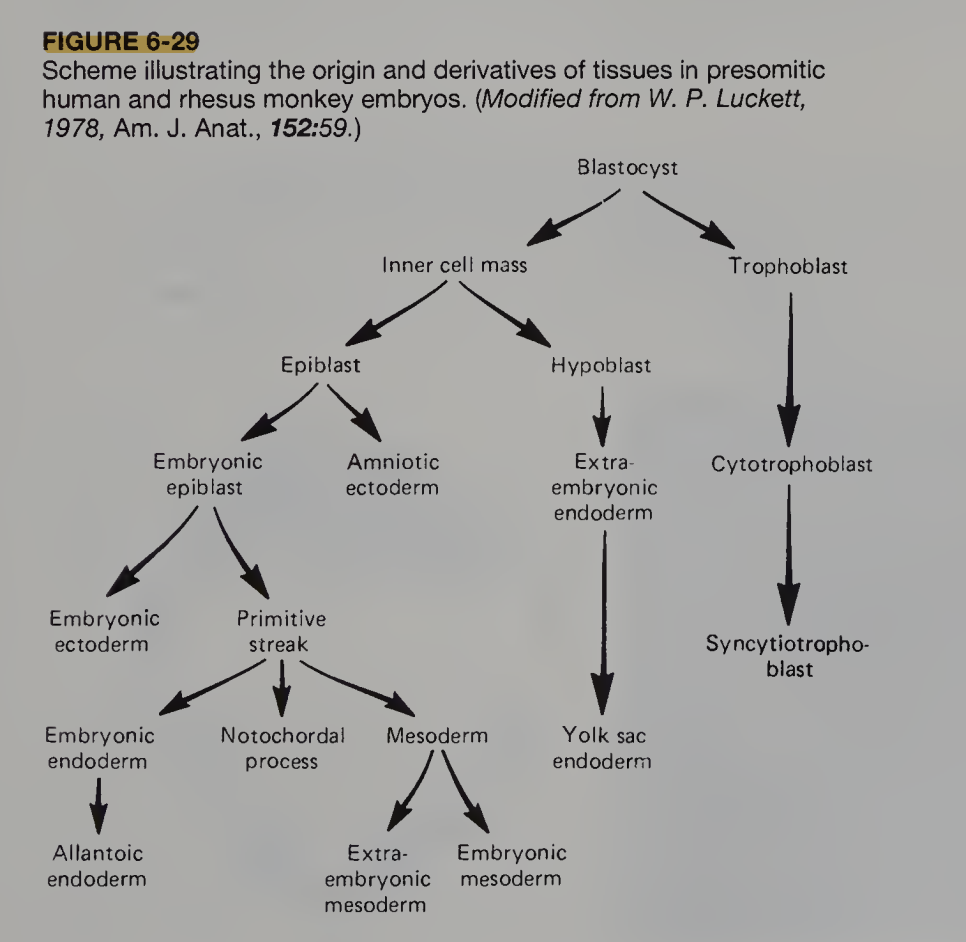
Origin and derivatives of tissues in presomitic human and rhesus monkey emrbyos
-
As the hypoblast forms, the remainder of the inner cell mass can be called the ________
epiblast
-
the ______ contains the cells that will ultimately migrate through the primitive streak and become the definitive endodermal and mesodermal germ layers of the embryo
epiblast
-
Formation of the primitive streak in mammalian embryos follows a pattern quite similar to that in _____ embryos
bird
-
Not long after the hypoblast is established, the remaining cells of the inner cell mass become more regularly arranged and are collectively called the _________
embryonic disk
-
In mouse, the early hypoblast is called ___________
primitive endoderm
-
Primitive endoderm in ______ initially forms a single layer beneath the inner cell mass
mouse
-
(in mouse (rodents))
The single layer beneath the inner cell mass created by the primitive endoderm soon spread out beneath the ________ to form the endodermal layer of the parietal yolk sac.
trophoblast (called trophectoderm)
-
(in mouse (rodents))
From an early stage, the trophectoderm can be subdivided into two sections
1. polar trophectoderm
2. mural trophectoderm
-
A subdivision of trophectoderm that overlies the inner cell mass
polar trophectoderm
-
A subdivision of trophectoderm that surrounds the blastocyst cavity
mural trophectoderm
-
In ______, the inner cell mass undergoes a transformation that is strikingly different from its course in other mammals
rodents
-
Immediately above the primitive ectoderm, the cells of the polar trophoblast form a relatively massive ____________.
ectoplacental cone

