-
______transforms the egg from a metabolically depressed state to one of extreme vigor, characterized by a sharp increase in respiratory and synthetic activity.
Fertilization
-
During _______ waves of cell division follow one another almost without pause, subdividing the unmanageably large zygote into progressively smaller cellular units
Cleavage
-
the stage of development during which the dividing cell mass doubles with each cycle and resembles a mulberry
Morula
-
In time the cleaving embryo develops a central cavity or _____ and enters the blastula stage.
Blastocoel
-
In many species the _______ of the egg is not homogeneous
cytoplasm
-
In the normal embryo a cleavage division consists of _______ followed by _________
nuclear division (karyokinesis); cell division (cytokinesis)
-
_______ occurs after karyokinesis
Cytokinesis
-
The ________ forms first in the region of the cortex nearest to the mitotic spindle and then moves around the cell
cleavage furrow
-
the position of the cleavage furrow is established by the time of ______
Anaphase
-
These are composed of microtubules, are the structures that interact with the cell cortex to stimulate the formation of the cleavage furrow
Asters
-
The cells that arise from cleavage are known as
Blastomeres
-
The type of cleavage characterized by the complete division of cells, is called
holoblastic cleavage
-
eggs with small amount of yolk; evenly distributed; vertebrates
oligolecithal eggs
-
eggs with moderate amounts of yolk; tend to be concentrated toward the vegetal pole, thereby displacing the nucleus toward the animal pole; vertebrates
mesolecithal eggs
-
eggs with large amount of yolk; commonly displaces the embryo-forming cytoplasm into a small disk on one edge of the ovum; vertebrates
telolecithal eggs
-
Relatively small animals that need to produce immense numbers of eggs to ensure propagation of the species (e.g., the sea urchin)
True
-
The first cleavage division cuts the egg in half from the ___________ to the _________ in the plane of the metaphase plate of the dividing nucleus.
animal pole; vegetal pole
-
eggs that are on the center of oocyte; in aquatic and terrestrial arthropods
Centrolecithal
-
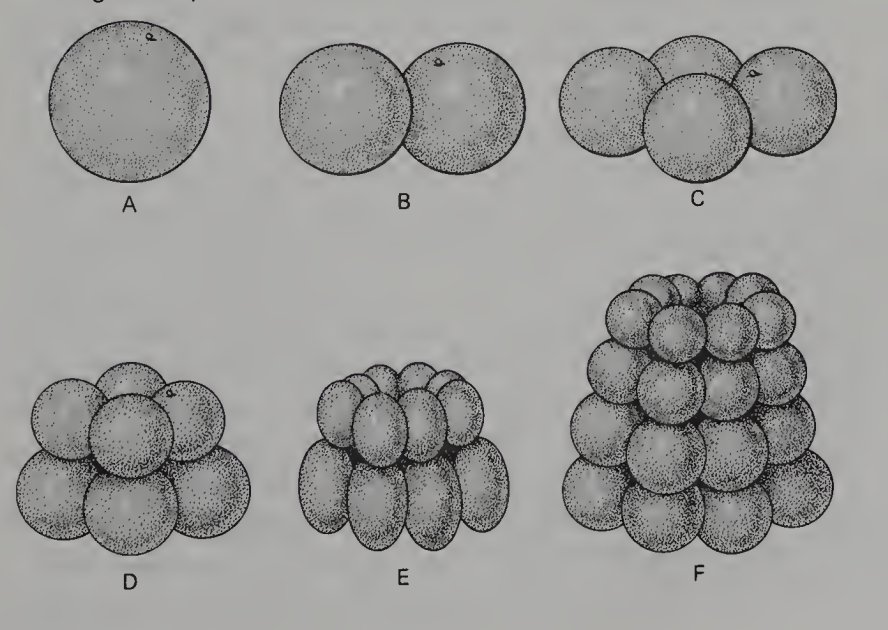
Cleavage in Amphioxus
-
the eggs of sea urchins are _____
oligolecithal
-
The first two divisions of sea urchin eggs are meridional (from animal pole to vegetal pole), and the third is equatorial, producing an eight-cell embryo with blastomeres of almost equal size.
True
-
The fourth cleavage of sea urchin eggs, results in the __________
production of three distinct types of blastomeres
-
a blastomere of medium size
mesomere
-
a blastomere of large size; occur in the hemisphere of telolecithal egg containing the vegetal pole
macromere
-
any of the small cells formed by unequal cleavage of a fertilized ovum
micromere
-
Formation of _________ is dependent on the presence of cytoplasm located at the vegetal pole; without vegetal pole, micromeres do not form
micromeres
-
Five territories of sea urchin embryo
1. prospective ectoderm
2. prospective aboral ectoderm
3. prospective skeletogenic mesoderm
4. vegetal plate
5. small micromeres
-
During the entire period of _______, the embryo is enclosed in the fertilization membrane
cleavage
-
As the embryo goes into the seventh and eighth cleavage cycles, the central cavity (blastocoel) becomes well established and the embryo has entered the _____ phase.
Blastula
-
By about the tenth cleavage cycle, the blastomeres form ________which penetrate the hyaline layer and extend into the perivitelline space.
motile cilia
-
The next morphological change after the cells of blastula secrete into the perivitelline space is the formation of a tuft of long, nonmotile cilia at the animal pole of the blastula
At about the same time, the region around the vegetal pole flattens to form the micromere-containing vegetal plate
True
-
The final major event during the blastula phase presages the sweeping changes that will occur at ________
gastrulation
-
The former micromeres will make their way into the blastocoel and will form the __________
primary mesenchyme
-
The first cleavage division in __________ begins at the animal pole and bisects the gray crescent
amphibians
-
The __________ begins at the animal pole, with its plane perpendicular to that of the first cleavage plane
second division in amphibians
-
The third cleavage plane in division in AMPHIBIANS is horizontal and passes nearer to the animal pole, dividing the embryo into _________________.
four smaller blastomeres at the animal hemisphere and four larger blastomeres at the vegetal pole
-
In amphibians, an embryo between the 16- and 64-cell stages is commonly called a _____
morula
-
After the morula stage in AMPHIBIANS, a _____________appears in the animal hemisphere above the mass of yolk
prominent cavity (blastocoel)
-
The amphibian blastula can be conveniently subdivided into three main regions:
1. A region around the animal pole, roughly including the cells forming the roof of the blastocoel. These cells correspond roughly to the future ectodermal germ layer.
2. A region around the vegetal pole, including the large cells in the interior which constitute the yolk mass. These are the future endodermal cells.
3. A marginal ring of cells in the subequatorial region of the embryo, including the region of the gray crescent. Cells of this zone normally form the embryonic mesoderm.
-
the period in amphibian embryo where the main activity is the increase in the number of cells
pregastrulation
-
__________ in the amphibian blastula forms in an equatorial ring between the prospective ectoderm and endoderm
mesoderm
-
(Amphibians) Cells of the animal hemisphere above the blastocoel normally form ________
ectoderm
-
Cleavage in _____ eggs occurs as the egg is passing down the oviduct
bird/avian eggs
-
In _______, by the time the egg is laid, early gastrulation has already begun
birds
-
The first cleavage furrow in birds begins to appear near the center of the blastodisk during __________.
late anaphase of the first mitotic division after fertilization
-
The sequence of ______- cleavage is not always regular, and after about the third cleavage division it is not synchronous.
avian
-
outer layer of cells that forms the wall of blastula
blastoderm
-
the embryo-forming portion of an egg with discodial cleavage usually appearing on the upper surface of the yolk mass
blastodisc
-
In birds, when the embryo contains about 100 cells, the blastoderm is underlain by a _______
subgerminal cavity
-
The central portion of the blastoderm, thinned out by the shedding of cells and underlain by the subgerminal cavity
area pellucida
-
it surrounds are pellucida; the region where the cells of the blastoderm still abut directly onto the yolk
area opaca
-
At about the time the egg is laid (in birds), individual cells or aggregates of cells shed from the lower surface of the blastoderm by a process of polyingression coalesce to form a thin disklike layer called the ______
primary hypoblast
-
outer layer of the blastoderm
epiblast
-
The __________, which ultimately forms extraembryonic endoderm, possesses an inherent polarity which it confers on the embryo proper, which is represented at this stage by the early epiblast.
primary hypoblast
-
The _________ is considered the equivalent of the animal hemisphere, and the primary hypoblast shares many common properties with the vegetal hemisphere of the amphibian embryo
epiblast
-
Mammals produce extremely small eggs with _________
almost no yolk
-
In __________, early cleavage divisions are practically unmodified mitoses, or in more technical terms, equal holoblastic cleavage of an isolecithal egg
mammals
-
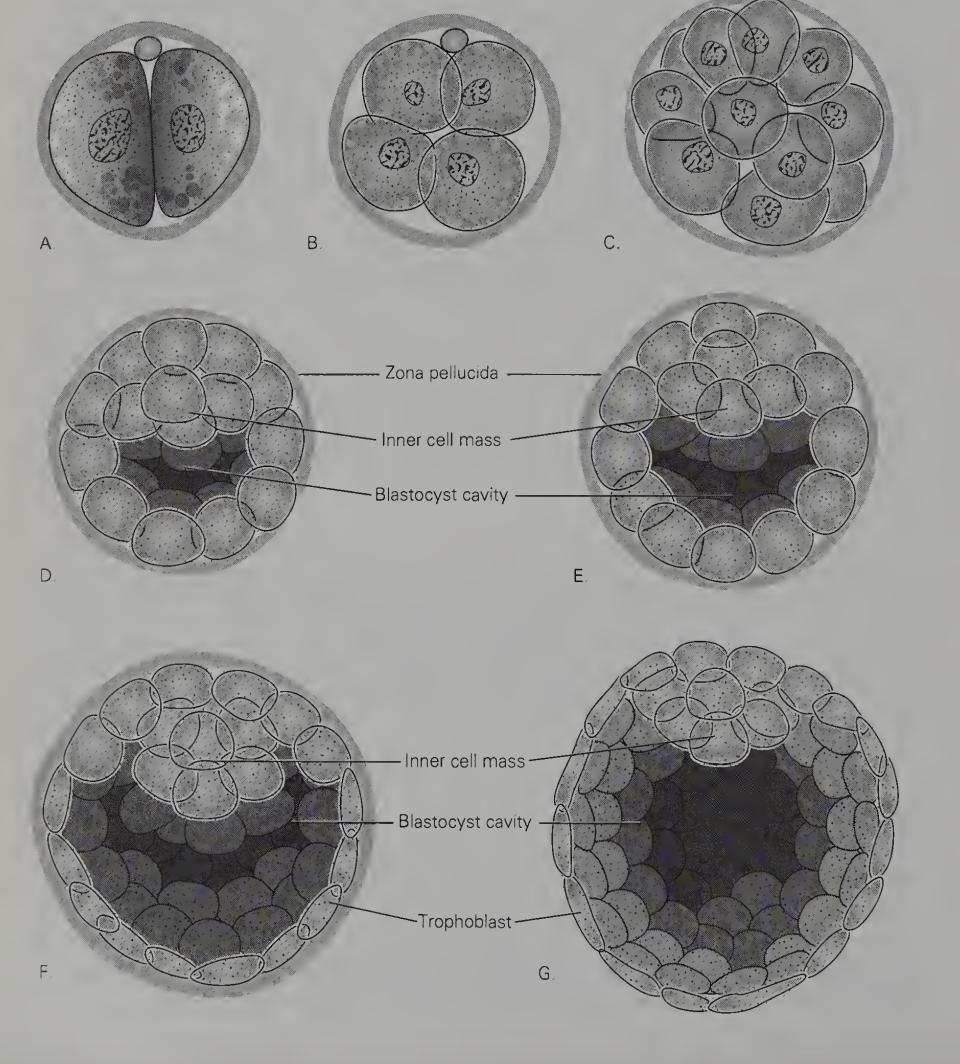
Cleavage stages in the pig embryo
-
Cleavage in mammals is much slower than it is in most other vertebrates
True
-
A critical stage that takes place at the eight-cell stage in the mouse.
During this, the blastomeres flatten and become tightly joined so that they cannot become distinguished from one another with the light microscope
compaction
-
_________ prevent the free exchange of fluid between the inside and the outside of the embryo, allowing the accumulation of fluid inside the embryo
Tight Junctions
-
_________couple all the blastomeres of the compacted embryo and permit the exchange of ions and small molecules from one cell to the next.
Gap junctions
-
In mammals, by the 16-cell stage the embryo, still enclosed in the zona pellucida, is said to be in the ______ stage
morula
-
(Mammals) In the morula the internal secretion of fluid by the blastomeres leads to the formation of a well-defined central cavity called the ______
blastocoel or blastocyst cavity
-
The first is a rapid enlargement of the blastocyst cavity; the second is the emergence of distinctly different types of cells within the embryo.
Two stages that mark the transition from morula to blastocyst
-
The early mammalian blastocyst remains enclosed within the _________, but the overall size of the embryo increases to some extent because of the accumulation of fluid.
zona pellucida
-
outer wall of the blastocyst
trophoblast
-
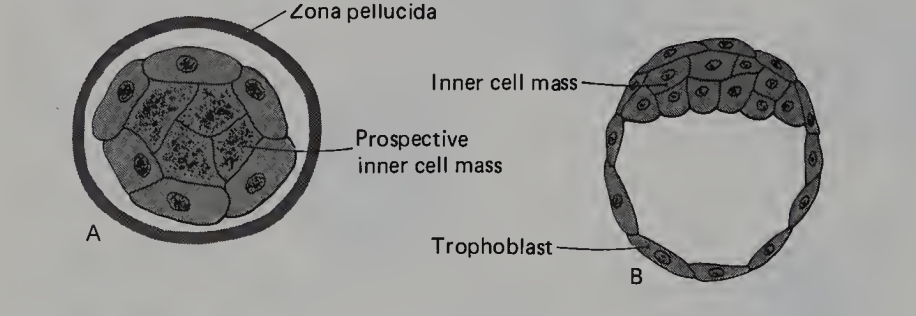
A is
Morula stage
-
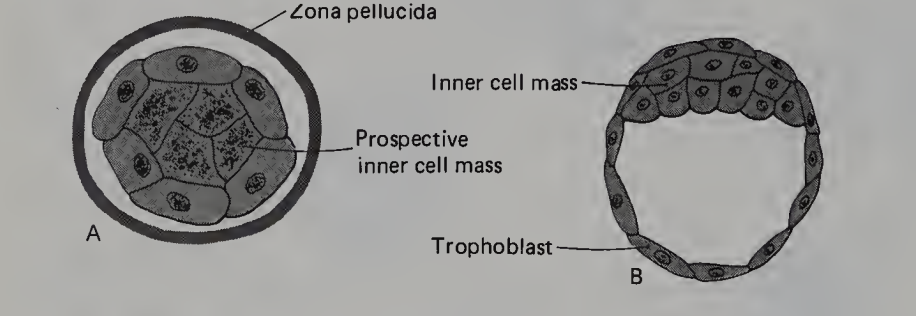
B is
Blastocyst stage
-
In both _________ initial control of polarity appears to reside in the vegetative regions of the embryos
amphibians and birds
-
In birds, early control of polarity resides in the primary hypoblast.
true
-
the _______________ shows few signs of polarity until well into the stage of the blastocyst
mammalian inner cell mass
-
egg fragments
merogones
-
As early as the third or fourth cleavage division, the ______________ begins.
New rRNA and tRNA appear around the time of the blastula. Overall, there is a steady increase in embryonic RNA synthesis until the blastula stage, at which point it begins to level off
synthesis of mRNA and heterogeneous nuclear RNA
-
the synthesis of __________ is prominent during cleavage
histones
-
the increase in cell number is the dominant manifestation of _____a simple phase of development during which the embryo is simply increasing its number of cells
Cleavage stage
-
As the blastula becomes more mature, its activities are increasingly directed toward making preparations for gastrulation.
true

