-
What symbol represents the permittivity of free space?
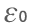
-
When calculating the force between two particles what can air be treated as?A vacuum
-
For a charged sphere the charge can be assumed to be at what part of the sphere?centre
-
Is the gravitational force of subatomic particles greater than the electrostatic force?no the electrostatic force
-
Electric firld lines always go from...positive charge to negative charge
-
What is electric field strengththe force per unit charge acting at a point in an electric field
-
What is the magintude of E (electric field strength) in an uniform field?Potential difference betweeen two plates(V)/distance between two plates
-
What is the trajectory of a particle entering a uniform field at right angles?parabolic
-
How is electrical potential related to electric field strength?
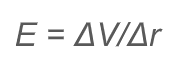 The change in electric potential wiith respects to the change in radius length
The change in electric potential wiith respects to the change in radius length -
Force between two point charges - on sheet
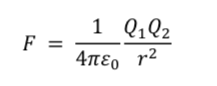
-
Force on a chargeF = EQ E - electric field strength for a uniform field
-
Electric potential
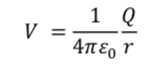 V = EPE/q = V - J/C,V
V = EPE/q = V - J/C,V -
EPE equation
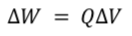 EPE = (1/4pie0) * (Qq/r)
EPE = (1/4pie0) * (Qq/r) -
Force relation-d(EPE)/dx
-
charge equationQ = CV charge of a capacitor is directly prportional to applied potential difference
-
what happens when you put charge on a capacitor?creates an electric field between both plates
-
total energy stored in a capacitorE = 1/2 Q V
-
what does the area under the graph of cahrge against potential difference represent?the energy stored by the capacitor
-
Dialetric
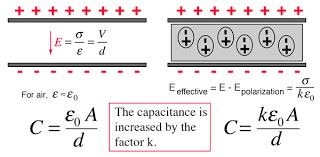 An electric insulator that can be polarised by an electric field polar molecules rotate theor -ve end to the positiveplate and vice versa, non polar molecules have their electron orbits distorted as the electrons are attracted to the positive plate the induced charges create an opposing electric field so strencht of electric field over all decreases and so potential difference decreases so capitance increases as chareg is constant
An electric insulator that can be polarised by an electric field polar molecules rotate theor -ve end to the positiveplate and vice versa, non polar molecules have their electron orbits distorted as the electrons are attracted to the positive plate the induced charges create an opposing electric field so strencht of electric field over all decreases and so potential difference decreases so capitance increases as chareg is constant -
epsilum rrelative permiativity
-
What is the relative permitivity?
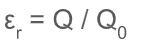 The ratio of the charge stored with the dielectric between the plates to the charge stored when the dieletric is not present The greater the relative permitivity the greater the capitance of the capacitor
The ratio of the charge stored with the dielectric between the plates to the charge stored when the dieletric is not present The greater the relative permitivity the greater the capitance of the capacitor -
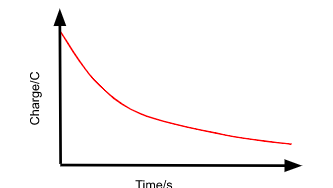
The Q vs t graph for the discharging of a capacitor through a resistor
-
The v vs t graph for the discharging of a capacitor through a resistor
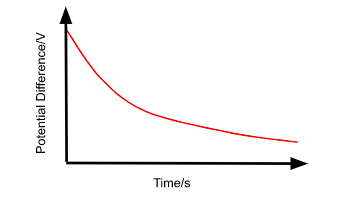
-
The I vs t graph for the charging of a capacitor through a resistor
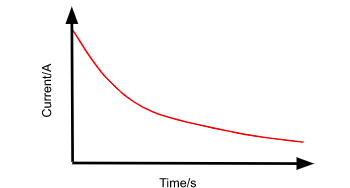
-
The Q vs t graph for the charging of a capacitor through a resistor
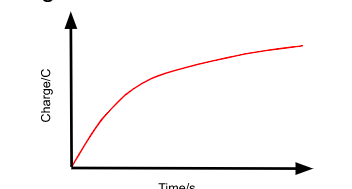
-
The V against t graph for the chargin of a capacitor through a resistor

-
What is the time constant?resistance x capacitance the time taken for the charge in a capacitor to fall by 37percent after 5 time constant the capacitor is fully discharged
-
how was 37% derived when using the time constant?
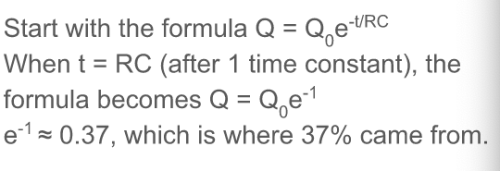
-
what is the half time of a capacitor

-
What equations are required for charging a capacitor?

-
How does a capacitor charge up?Electrons move from negative -> positive around the circuit The electrons deposited on plate A, making it negatively charged Electrons travel from plate B to the positive terminal of the battery giving the plate a positive charge Electrons build up on plate A and an equal amount of electrons are removed from plate B creating a potential difference across the plates When potential difference across the plates = source potential difference the capacitor is fullt charged and current stops flowing
-
Describe and explain in terms of the movement of electrons how the potential difference across a capacitor cahnges when it discharges across a resistorElectrons move in opposite direction than when the capacitor was charging up Charge on one plate A decreases as it loses electrons and plate B gains electrons neutralising them Potential difference decreases exponentially across the plates
-
3 expressions for energy stored by a capacitor
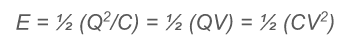
-
2 factors that affect the time taken for a capacitor to charge or dischargeThe capitance of the capacitor, C. This affects the amount of charge that can be stored by the capacitors at any given potential difference across it. The resistance of the circuit, R. This affects the current in the circuit and how quickly it flows, hence how quickly the capacitor charges/discharges
-
current round circuit chargingI = I0 e^(-t/RC) =(V0/R)e^(-t/RC)
-
current round circuit dischargingI = I0e^(-t/RC)
-
charge round circuit dischargingQ = Q0e^(-t/RC)
-
gradient of charge vs t graphrate of slow or chareg = current
-
Explain why there is an increase in the energy stored by the capacitor when the polythene sheet is pulled from between the plates
The polar dielectric molecules align themselves with the positive end towards the negative plate
Work is done on the capacitor to move the positively charged end of the dielectric from the negative plate

