-
Why is it important to understand receptors? Give 4 reasons.
1)Pharmaceutical industry and development: 34 of the top 100 drugs on the market target G-protein couples receptors
2)Physiology of endogenous transmitters: Transmitters and hormones act primarily upon receptor targets
3)Chemical toxicity: Many toxic mechanisms are receptor mediated
4)Viral toxicity: Viruses and other microorganisms can target receptors
-
What is an agonist?
Drugs that occupy receptors and activate them
-
What is an antagonist?
Drugs that occupy receptors but do not activate them, antagonists block receptor activation by agonists
-
What is a partial agonist?
Drugs that can occupy receptors and activate them but not to the extent of an agonist
-
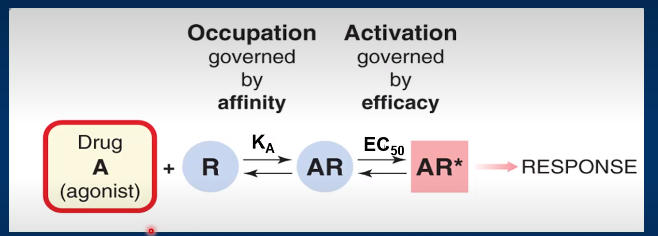
A picture demonstrating the agonist having both affinity and efficacy:
-
Statement: Most agonists bind irreversibly to their receptors.... Is this true?
FALSE
-Most agonists bing reversibly to their receptors and then dissociated when unneeded
-
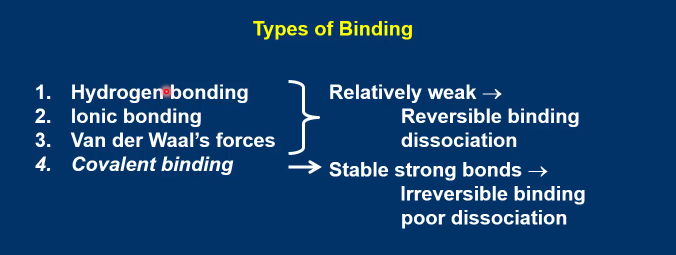
Why is the binding reversible?
Weak bonds
-
Name the 4 main bonds and describe their strengths and dissociations
-
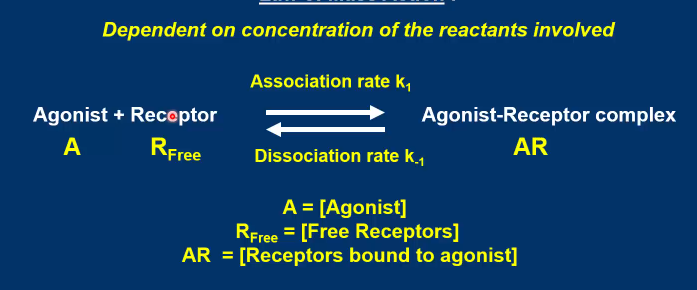
Reversible binding of an agonist to a receptor is governed by what law?
Law of mass action
-
Picture demonstrating how reversible binding is dependent on concentration of the reactants involved
-
What is the Bmax?
The maximum amount of receptor binding
-
Each drug has its own what value?
Kd value
-
What is Kd?
Kd (Affinity) is the ability of a drug molecule to bind to a receptor site: Concentration of the drug where 50% of max number of receptors are bound by the drug
Kd is inversely correlated with affinity. The lower the Kd, the higher the affinity
-
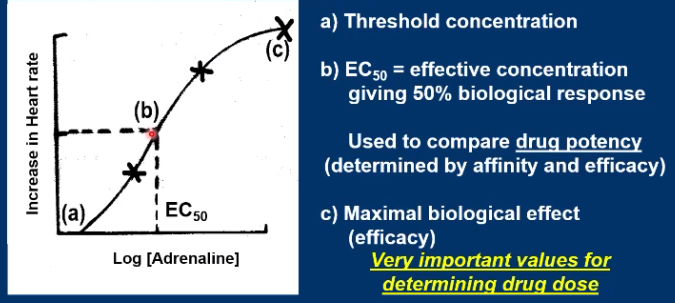
What is Efficacy?
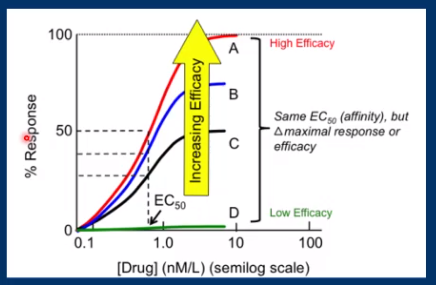
Refers to the effect of the drug/ the biological effect, the more effect the drug has the more efficacious. e.g. increase in heart rate
-
Picture outlining efficacy: