-
Gilbert syndrome
-autosomal recessive disorder
-defects in UGT1A1 metabolism
-main symptom is jaundice
-
Carboxylesterase; SN-38; SN-38G; UGT1A1
Irinotecan is a prodrug converted to its active form via ___________. It's active metabolite is called _______. The inactive metabolite is called _________. It is transformed via __________.
-
a, d
What are adverse effects associated with irinotecan toxicity?
a) diarrhea
b) headaches
c) jaundice
d) Neutropenia
-
promoter mutation; 7 TA repeats instead of 6
What type of mutation is UGT1A1 *? How does this mutation affect the code?
-
-28insTA
What is the nomenclature for UGT1A1 mutation?
-
quantity of mRNA & protein; protein structure
UGT1A1 mutation reduces ________; does not change _______
-
inversely related to repeat length
The UGT1A1 polymorphism is associated with enzyme quantity and activity is ______________.
-
bilirubin
People with UGT1A1 polymorphism will also exhibit high levels of _________; this means we can predict irinotecan toxicity without genotyping.
-
this genotype is only relevant for irinotecan doses > 250mg/m2
UGT1A1 genotype is not used to guide therapy at St. Jude hospital. Why is that?
-
Invader UGT1A1 Molecular Assay
-in vitro diagnostic (IVD) used to detect UGT1A1 polymorphisms (TA repeats)
- uses peripheral blood
-
only metabolic reaction that increases logP
What is unique about methyltransferases?
-
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Thiopurines are oral anticancer agent used mainly in the treatment of ___________.
-
HPRT; triphosphates; incorporated into growing strand of DNA which will result in chain termination
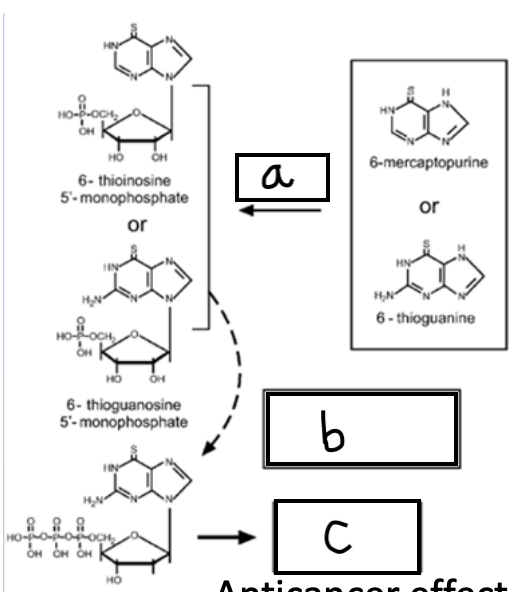
What enzyme is acting at A?
What is added at B?
What happens at C?
-
d
Thiopurine methylatransferase (TPMT) are found in :
a) liver
b) kidney
c) neutrophils
d) red blood cells
-
6-mercaptopurine; azathioprine
TPMT-deficient individuals cannot tolerate thiopurine drugs such as ________ & _________.
-
1/10th - 1/15th
Patients homozygous for TPMT mutant alleles should be treated with ____________ of the standard dose.
-
SN-38
Elevated levels of ________ metabolite will need to myelosuppresive effects.
-
Camptothecin
-natural product obtained from oriental tree, camptotheca acuminata.
-synthetic analogs of this were made to produce topotecan and ironotecan (topoisomerase I inhibitors)
-
PAPS
What cofactor is associated with Sulfonlytransferase?
-
UDP-GA
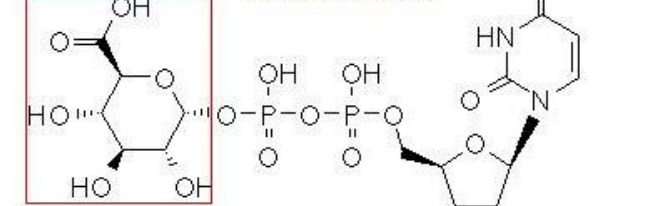
What cofactor is associated with this metabolite?
-
more polar
Phase II metabolic reactions are designed to make drug :
-
liver & GI tract
UGT1A1 is most expressed in what organs?
-
methyltransferase
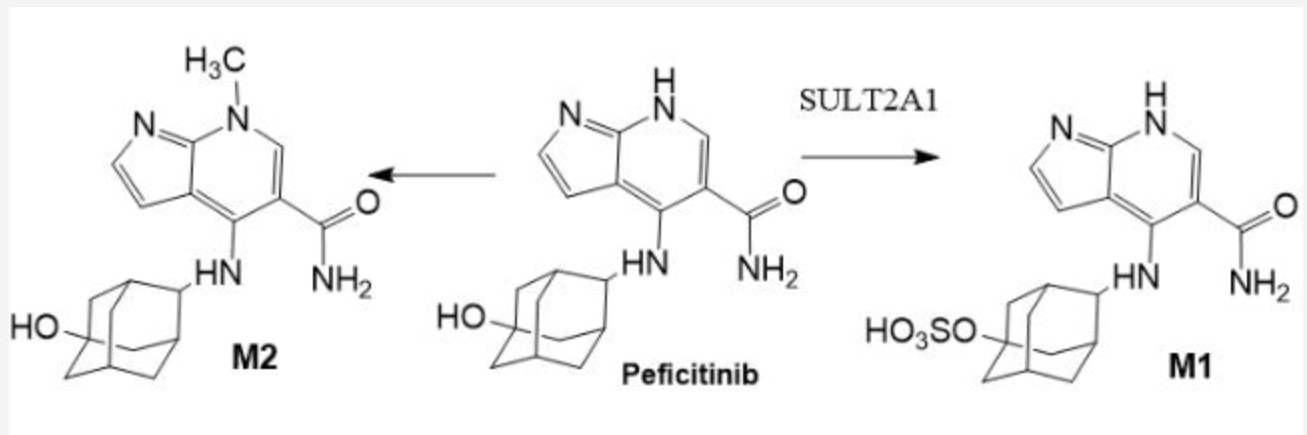
M2 is catalyzed by:
-
PAPS
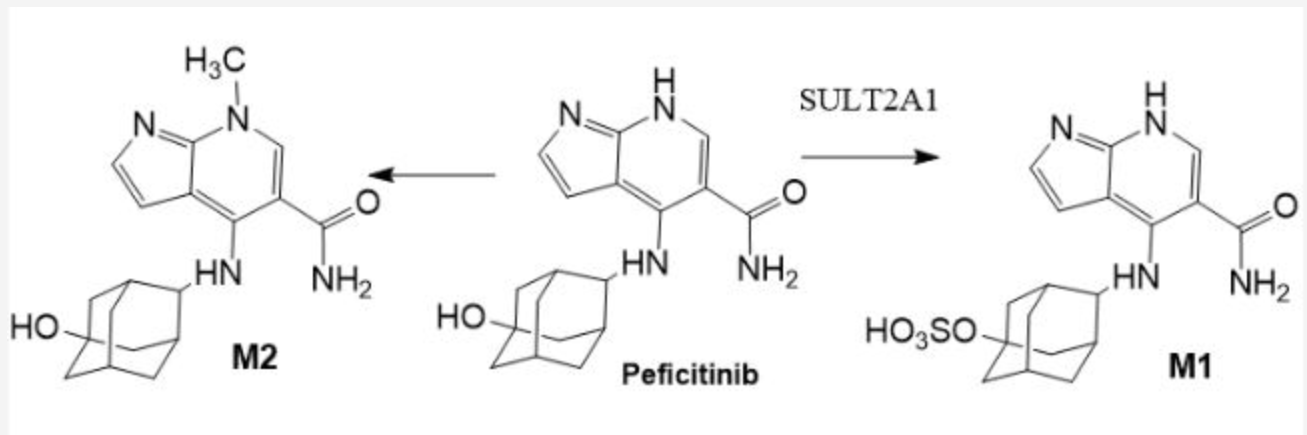
M1 is catalyzed by:

