-
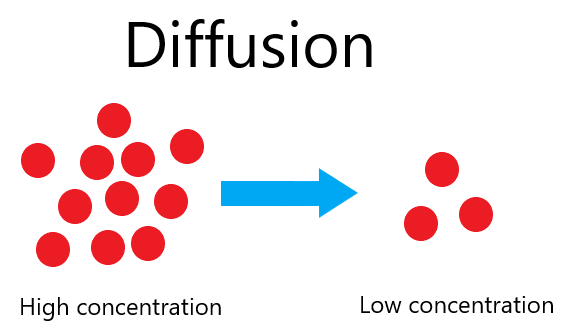
DefenitionDiffusion is where particles of a gas or liquid spread from high concentration. This happens until an equilibrium is reached. E.g: smells in a room or squash and water.
-
Key pointsDiffusion is a passive process, meaning it does not require energy. Molecules move around randomly, but their ne movement will be from a high to a low concentration until an equilibrium is reached. This movement occurs across a partially permable membrane.
-
TemperatureAs temperature increases the rate of diffusion also increases. Molecules gain more kinetic energy and move around faster. As a result more of the molecules move down the concentration gradient in a given time.
-
Surface areaThe larger the surface area, the faster the rate of diffusion. In our bodies structures such as the alveoli in the lungs and the villi in the small intestine help increasethe diffusion of oxygen and digested food respectively.
-
Concentration gradientThe steeper the concentraion gradient, the faster diffusion will take place. The bigger the difference in the concentration of the substance acroos the partially permable membrane, the quicker diffusion will take place.
-
Diffusion distanceThe shorter the diffusion distance, the faster the rate of diffusion wil be. Many diffusion surfaces in our body are relatively thin in order to allow diffusion to take place as efficiently as possible.
-
Osmosis defenitionOsmosis is the movement of the substance from an area of high water concentration (no/little solute) to an area of low water concentration (more solute) acroos a partially permable membrane
-
Useful molecules that diffuse into cellsGlucose and oxygen.
-
Harmful molecules that diffuse out of cellsCarbon dioxide and urea.
-
Surfaces where diffusion happens are usually:- Thin - Have a large surface area - Moist
-
OsmosisOsmosis is a special case of diffusion. It is the net (overall) movement of water across a selectively permable membrane from a high concentration to a low concentration.
-
What is a selectively permable membrane?The cell mebrane has a very small holes in it. Water molecules can pass through, but larger ones can't. We say it is selectively permable.