-
Define relation
A two dimensional table within the relational model
-
In a relation: columns are called _______, rows are called _______
attributes, tuples
-
Define (relation) schema
The name of a relation and the set of attributes for it (including their data types, constraints(?) etc)
-
________ = picking certain rows. _________ = picking certain columns
Selection, projection
-
Product between two relations notes
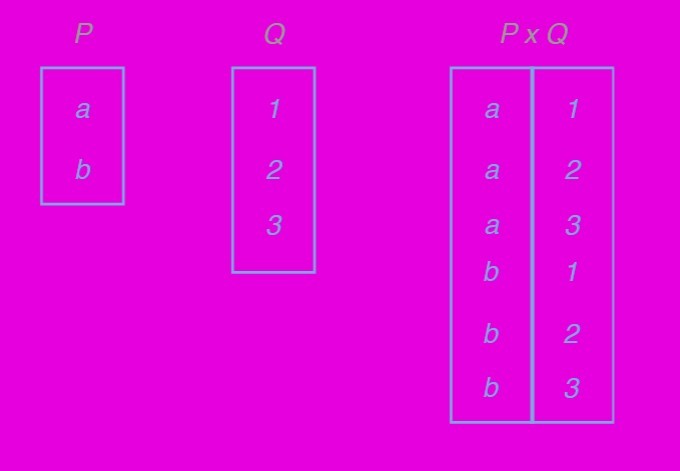
-
Define database schema
Set of all relation schemas in the database
-
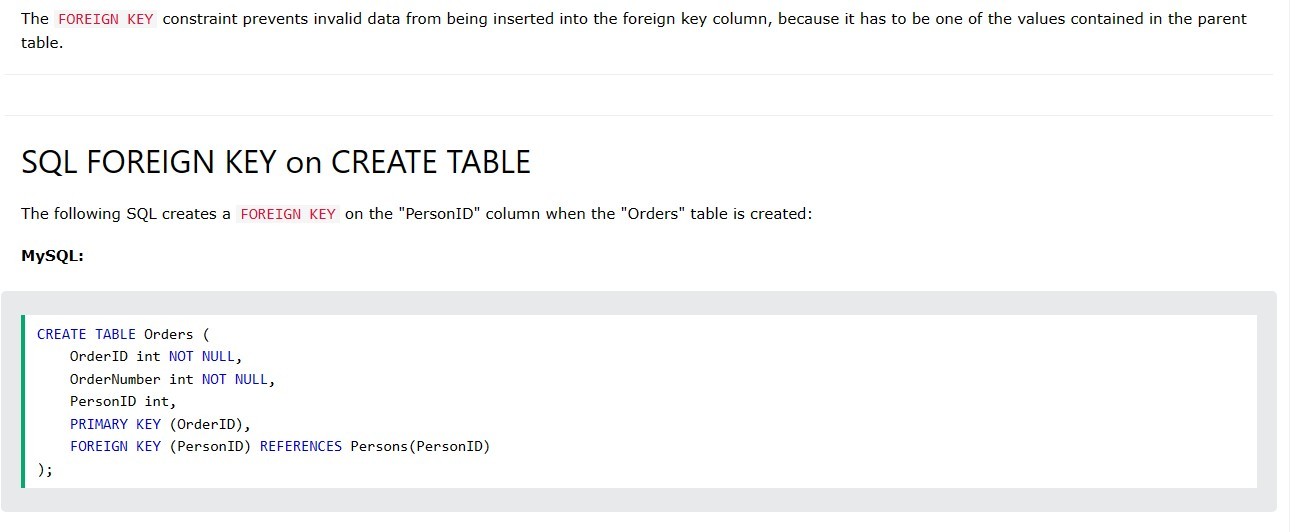
Creating a relation SQL notes

-
Multi-attribute primary key notes
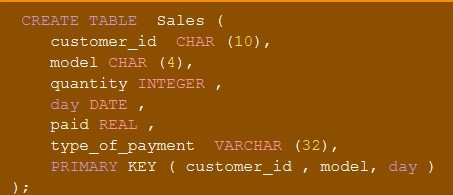
-
Joins notes
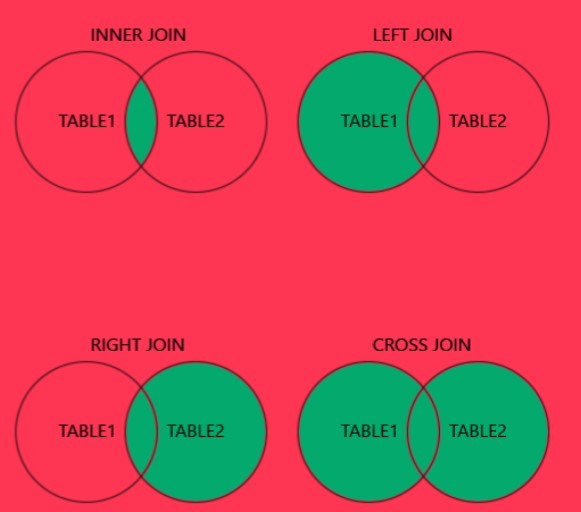
-
USING clause example
table1 JOIN table2 USING (a_1 ,a_2 ,...,a_n )
-
not equal to operator SQL
<>
-
EXISTS operator notes

-
ANY operator notes

-
HAVING clause example
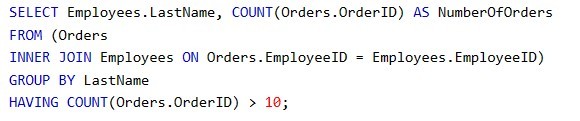
-
Do set operators (UNION, INTERSECT, MINUS) work with relations with different schema?
NO. Although you may be able to circumvent this by making selections from those relations so that you select equal schemas
-
UNION vs UNION ALL
Union deletes duplicate tuples, UNION ALL suppresses this
-
Two kinds of views
Virtual, materialized (in mySQL there is only virtual)
-
Define view
A relation (table) defined in terms of other relations already in the database. So you essentially make a selection and assign it as a view.
-
Foreign key notes
-
ACID transaction properties for database systems
Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability (and Access Control)
-
ACID transaction principles: define consistency
Maintain data in a valid state at all times. -eg. no two operations share a name."–
-
ACID transaction principles: define isolation
Keeping transaction steps separate to prevent conflict and maintain integrity /// The partial effects of incomplete transactions should not be visible to other transactions
-
Database management system (DBMS) definition
The software that manages and controls access to the database, ie MySQL
-
Data structures used to implement data in the computer (for the database) are referred to as ____________, as opposed to conceptual models
physical data models
-
Three parts of a data model
Structure of the data, operations on the data, constraints on the data
-
Can any type of value be null in SQL?
Yes
-
which is correct?
1)DROP function selectMax;
2)DROP function selectMax();
1). The brackets are only used when declaring.
-
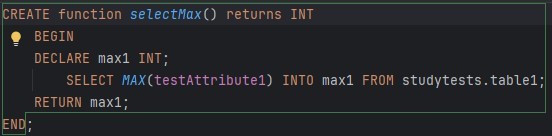
What is wrong here?
Missing 'READS SQL DATA' before begin
-
5 Aggregate functions
SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX
-
Can aggregate functions be used in the where clause?
No, only in the select clause
-
Relational algebra: symbol for selection
σ
-
Translate to relational algebra: selects rows in the table occupation where the company name is City Bank
σ(company-name = "city bank")(occupation)
-
π meaning in relational algebra
Projection, ie where you define which columns you want
-
translate into relational algebra: SELECT first_name, last_name FROM employees WHERE department = 'Sales';
π(first_name, last_name)(σ(employees)(department = 'Sales'))
-
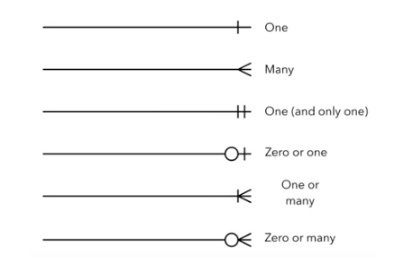
ERD cardinality symbols
-
What operator do you use to find the difference between two relations of equal schema?
MINUS
-
Using a table customers: find the names of all customerswho live in Dublin and have 'Jervis St.' theiraddress:
SELECT firstname, lastname FROM Customers WHERE city = 'Dublin' AND address LIKE '%Jervis St.%';
-
Using a table sales: find all details about salesmade in December (any year)
SELECT * FROM Sales WHERE day LIKE ' ____ -12%';
-
3 values in sql logic
TRUE, FALSE, UNKNOWN
-
Logiucally comparing any value with NULL yields ________
UNKNOWN
-
When you don't specify a type of join, an _____ join is used
INNER
-
is 'NOT IN' correct as an operator?
yes
-
What's wrong with this query? SELECT model FROM PCs WHERE hd <= 250 AND speed = MAX (speed);
MAX can only be used within a select clause. You could use a subquery.
-
select unique values query
SELECT DISTINCT attributeFROM table;
-
Do nulls contribute to averages?
No
-
Do nulls contribute to counts?
No
-
If all the values in a column are null, what is the result of an aggregation?
NULL
-
Does the aggregate function here act on all the values of the column at once? Or for each group separately? SELECT customer_id , SUM (paid)FROM Sales GROUP BY customer_id
for each group separately
-
Fill in the blank: UPDATE PCs ____ price = 1999.0 WHERE model = '1001';
SET
-
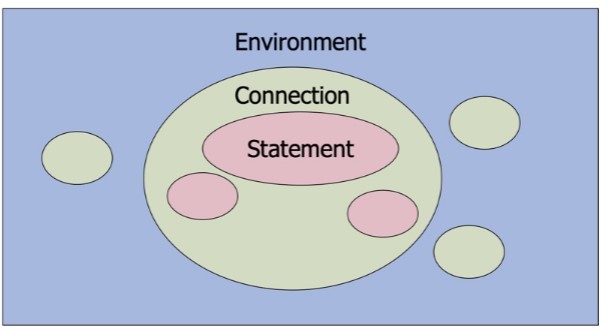
Three tiers in architecture for database environments
First tier – Client (front-end)– User Interface–Second Tier - Application server (back-end)– Business logic– Data processing logic–
Third Tier - Database server– Data validation– Database access–
-
Database environment blob diagram
-
Cascade definition within a foreign key
If the referenced value changes/gets deleted, perform the same action on the value that references it.
-
possibilities after ON UPDATE or ON DELETE in a foreign key
CASCADE, SET NULL, RESTRICT (don't allow it to be changed)
-
What is the default policy of a foreign key in case of changes or deletions to the referenced value?
RESTRICT (reject)
-
How to declare a foreign key
FOREIGN KEY (attribute) REFERENCES Table(referenced_attribute)
-
What are CHECKS (not in MySQL) similar to in MySQL?
Foreign keys
-
How to define assertions (not supported in MySQL)
CREATE ASSERTION <name>CHECK (<condition>);
-
1NF requirements
values are atomic, columns are unique, and rows are unique
-
2NF Requirements
There are no partial dependencies
-
Define partial dependency
a non-key attribute of a table depends on only a part of the primary key (it is allowed to have another functional dependency with part of the primary key along with another attribute on the LHS, but not just the primary key alone)
-
3NF Requirements
2NF and there are no transitive dependencies. /// for each nontrivial FD X -> A that holds in R , either X is a superkey of R or A is prime
-
BCNF Requirements
3NF and for all non-trivial FDs A-> B, A is a superkey
-
Transitive dependency definition
a non-prime attribute depends on another non-prime attribute through a series of functional dependencies
-
Requirement for a superkey to be a candidate key
No proper subset is a superkey
-
Define update anomaly
When you change one occurrence of a fact in the database,but other occurrences of the same fact remain unchanged
-
Define deletion anomaly
By deleting one fact from the database weunintentionally delete other facts as well
-
Violating 2FA leads to a risk of ______ anomalies
deletion
-
If a functional dependency X -> Y is trivial , then ___ is in ___
Y, X
-
Does bcnf decomposition automatically achieve 2NF and/or 3NF?
Yes
-
BCNF decomposition steps
1) look for a FD X with a BCNF violation
2) Compute {X}+
3) Replace the relation R by two relations with schemas: R1 = X+ ; R2 = R - (X+ - X)
-
BCNF Limitations
separation of data that usually goes together can make FDs impossible to enforce
-
3NF Synthesis algorithm
Step 0. Find all keys of R and check if any FD in Fviolates 3NF. If a violation is present then proceed with Step 1. Otherwise stop.
Step 1. Find a minimal basis G.
Step 2. For each left side of the FDs in the minimal basis, create a new relation with attributes being the closure of the left side.
-
Reflexivity Inference rule
Reflexivity : if B ⊆ A then A → B
-
Augmentation inference rule
Augmentation : if A → B then AC → B
-
Pseudo-transitivity inference rule
if A → B and BC → D then AC → D
-
Negatives of using indexes
Data modification takes longer, as indexes need to be adjusted too
-
4 data structures used for indexes
B+ trees, B-trees, Bitmap indexes, Hash tables
-
Key-pointer pair in a b tree definition
the key is the representation of the value in the tree, the pointer points to the location of the actual value in the table
-
How is a b+ tree different from a b-tree?
1) Internal nodes only contain keys, no pointers.
2) Leaf nodes contain key-pointer pairs AND pointers to their right sibling
3) all keys appear in leaf nodes and some keys appear in internal nodes
-
B+ trees are _____ (faster/slower) than B trees for sequential access
faster
-
Bitmap index pros and cons compared to B+ trees
+ Faster access time
+ Less storage space
- Slower update time
-
Transaction definition
a logical unit of work on the database, which should transform it from one consistent state to another
-
The SQL statement COMMIT causes a transaction to __________
complete
-
The SQL statement ROLLBACK causes a transaction to __________
end, by aborting (no changes are made)
-
Serial schedule definition
a schedule where the operations of each transaction are executed consecutively without any interleaved operations from other transactions.
-
Nonserial Schedule definition
a schedule where the operations from a set of concurrent transactions are interleaved
-
Serializable Schedule definition
a nonserial schedule that produces the same result as some serial schedule
-
Concurrency control: locking definition
When one transaction is accessing the database, a lock may deny access to other transactions to prevent incorrect results
-
Concurrency control: 2 types of locks
Shared (transaction with the lock can read but not update), and exclusive (only the transaction with the lock can read and update)
-
Concurrency control: timestamp definition
A unique identifier created by the DBMS that indicates the relative starting time of a transaction
-
What does PSM stand for?
persistent stored modules
-
Persistent stored modules (non-relational) function
allows for the storage of procedures as database schema elements
-
create TRIGGER notation
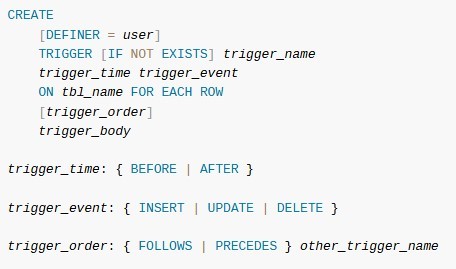
-
create FUNCTION and PROCEDURE notation

-
input parameters in a function notation
(IN testInput type, IN testInput2 type)
-
prime attribute definition
An attribute that is part of a candidate key
-
how do you declare a variable within a function?
DECLARE testVar type;
-
How do you assign the result of a query to a variable you declared in a function?
SELECT ______ INTO variable FROM ______ WHERE
-
What should you put before BEGIN in functions/procedures?
MODIFIES SQL DATA / READS SQL DATA / DETERMINISTIC

