-
OLE DB
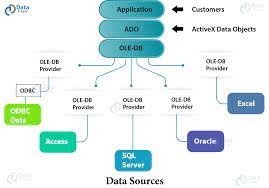
OLE DB stands for Object Linking and Embedding, Database. It is an API designed by Microsoft, that allows users to access a variety of data sources in a uniform manner.
-
GUID

Describes a globally unique identifier (GUID)
-
VLAN
Virtual LAN
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_LAN
!!!!!!!! READ ARTICLE AND EXPAND DEFINITION!!!!
!!!!!! RESEARCH & INSERT HELPFUL DIAGRAM !!!!!!
-
LAN
Local Area Network
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_area_network
!!!!!!!!! READ ARTICLE & EXPAND DEFINITION!!!!!!!
!!!!!! RESEARCH & INSERT HELPFUL DIAGRAM !!!!!!
-
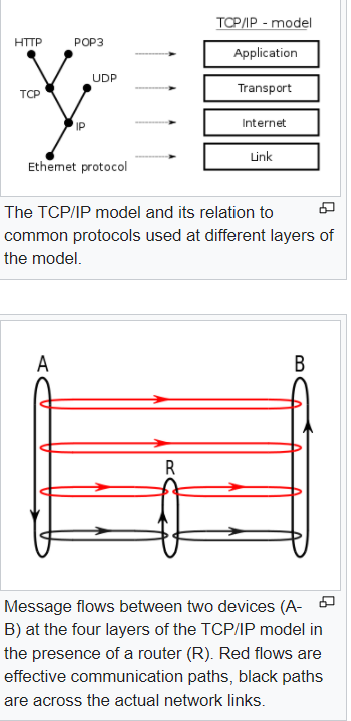
Internet Protocol
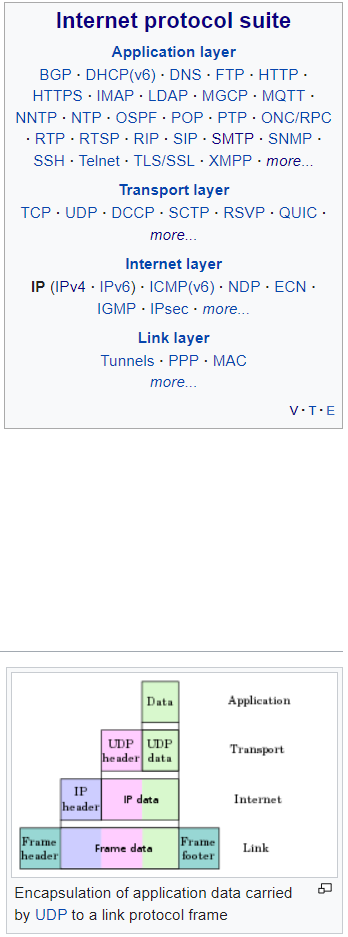
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Protocol
!!!!!!!!! READ ARTICLE & EXPAND DEFINITION!!!!!!!
1) Look at the OSI Model Diagram & examples for each layer in photo--------------------------------------------------->>>>>>>>>>>>
2) Research Wikipedia and make a FLASHCARD each for IPv4 and IPv6
-
UEFI
UNITED EXTENSIBLE FIRMWARE INTERFACE
a SPECIFICATION
that defines a
-
PI
PLATFORM INITIALIZATION
-
Education relevant to software development
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Outline_of_software_development
Bachelor's Degree in Computer Science –
type of bachelor's degree awarded for study of computer science, emphasizing the mathematical and theoretical foundations of computing, rather than teaching specific technologies that may quickly become outdated.
A Bachelor of Computer Science degree is a common initial bachelor's degree for those entering the field of software development.
-
Software Development Topics & Examples
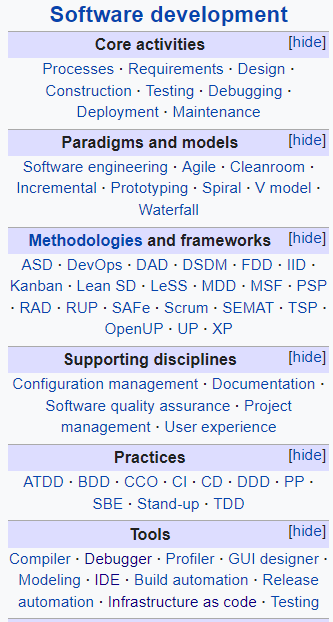
LOOK AT PHOTO & LIST THE MAJOR CONCEPTS--------------->>>>>>>>
!!!!!!!!! MAYBE CREATE A FLASHCARD FOR EACH MAJOR CONCEPT !!!!!!!!!!
-
Programming Tools: definition
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Programming_tool
also called SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT TOOL
a computer program
that software developers use to:
1) create,
2) debug,
3) maintain,
4) support
other:
1) programs
2) applications.
-
Programming Tools: fundamentals
The most basic TOOLS are:
1) a SOURCE CODE EDITOR
and
2) a COMPILER or INTERPRETER,
The 2 TOOLS are used:
1) For ALL ACTIONS
and
2) CONTINOUSLY.
-
Functional Consultant: Definition
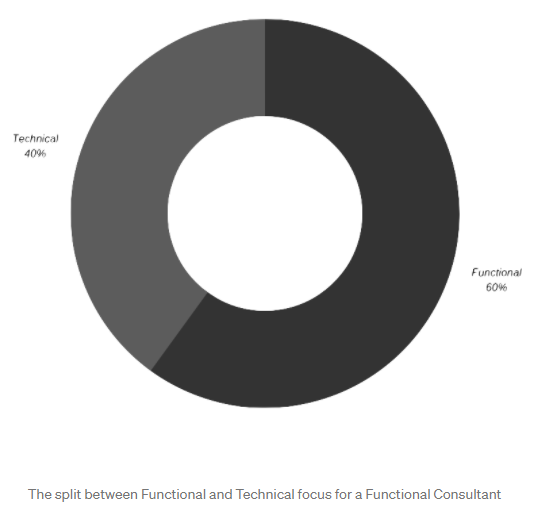
https://medium.com/capgemini-microsoft-team/what-is-a-functional-consultant-49a4dafb0d0e
!!!!!!!!! READ ARTICLE & EXPAND DEFINITION!!!!!!!
A Functional Consultant is
a product and/or industry expert, often in a specialist field, who understands their product on a technical level, knowing limitations, and how to take advantage of out of the box functionality. It’s this in-depth knowledge that sets a Functional Consultant apart, allowing them to best advise clients on the right solution and approach to meet their needs.
-
Motherboards: Purpose
Google "motherboard vs processor"->pediaa.com
A MOTHERBOARD
the main Printed Circuit Board in the computer.
It is also known as the:
mainboard,
logic board
system board.
It consists of components
that allow COMMUNICATION between components such as:
1) processor,
2) memory
and
3) the buses, or electrical pathways,
that allow data
to travel between computer COMPONENTS.
4) peripherals.
-
Motherboards: Components
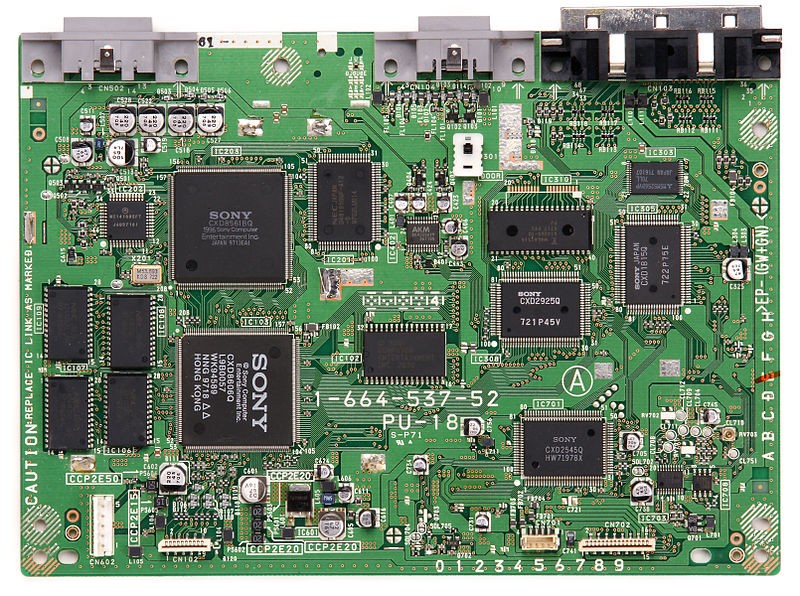
Google "is a cpu a part of motherboard?"->.com
The MOTHERBOARD
contains the following COMPONENTS:
1) CHIPSET,
2) MEMORY CONTROLLERS,
3) INTERFACE CARDS such as:
sound cards,
video cards,
network cards, and
other components
The MOTHERBOARD integrates all these COMPONENTS together.
-
Functional Consultant: Necessary Qualities
https://medium.com/capgemini-microsoft-team/what-is-a-functional-consultant-49a4dafb0d0e
!!!!!!!!! READ ARTICLE & EXPAND DEFINITION!!!!!!!
Being able to translate business requirements into technical tasks is another differentiator — a Functional Consultant can write detailed user stories that both the client and developers can understand. This allows developers to task out stories, that would have previously required a back-and-forth with the client and involved a Business Analyst middleperson.
The combination of understanding client pain-points and long term goals, paired with a strong vendor ecosphere knowledge, allows Functional Consultants to spot up-sell/cross-sell opportunities.
-
Motherboards: Memory
consist of
NONVOLATILE MEMORY, to:
1) initialize the system
2) to load some startup software.
COMMON SETUPS:
1) Some have ROM (Read-Only Memory) chips
MOUNTED in SOCKETS ON the MOTHERBOARD'
2) Modern MOTHERBOARDS use a BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) chip
==> which is STORED in an EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) chip
SOLDERED TO/SOCKETED ON the MOTHERBOARD
-
Motherboards: Form Factor
The motherboard accommodates the central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), expansion slots, heat sink and fan assembly, basic input/output system (BIOS) chip, chipset, and the circuitry that interconnects the motherboard components. Sockets, internal and external connectors, and various ports are also placed on the motherboard. The form factor of motherboards pertains to the size and shape of the board. It also describes the physical layout of the different components and devices on the motherboard. The form factor determines how individual components attach to the motherboard and the shape of the computer case. Various form factors exist for motherboards, as shown in this chart.
-
Volatile Memory
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volatile_memory
-
Non-Volatile Memory
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-volatile_memory
-
PUA
Potentially Unwanted Program
MALWARE
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potentially_unwanted_program
-
FTP
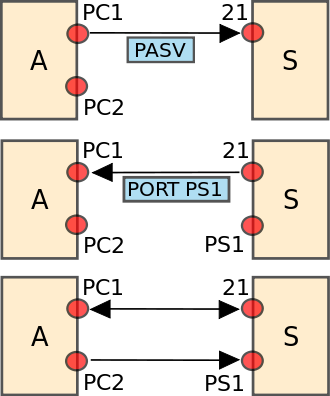
a STANDARD COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL
used for the TRANSFER of
COMPUTER FILES from a SERVER to
a CLIENT.
-
COMPUTER NETWORK:
a FTP occurs on a
COMPUTER NETWORK:
a set of COMPUTERS
SHARING RESOURCES LOCATED ON / OR PROVIDED BY
NETWORK NODES { either a REDISTRIBUTION POINT or a COMMUNICATION ENDPOINT. Definition=f(NETWORK LAYER, PROTOCOL LAYER).
-
Network Nodes
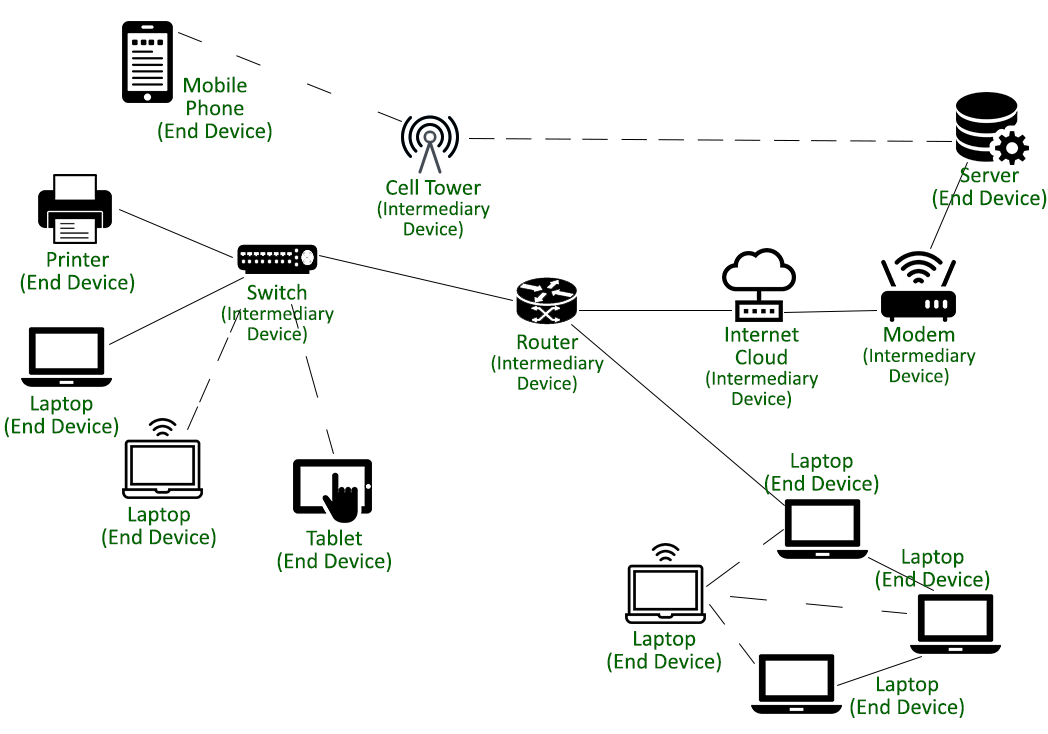
1) a REDISTRIBUTION POINT or
2) a COMMUNICATION ENDPOINT.
=f( NETWORK LAYER, PROTOCOL LAYER)
a PHYSICAL NETWORK NODE
is an ELECTRONIC DEVICE
that is ATTACHED to a NETWORK,
and capable of:
1) CREATING
2) RECEIVING or
3) TRANSMITTING
INFORMATION over a
COMMUNICATION CHANNEL.
PHOTO->> Nodes = End Devices + Intermediary Devices ->>
-
TELECOMMUNICATIONS EXAMPLE - DTE

DATA CIRCUIT-TERMINATING EQUIPMENT = a DEVICE that sits between the DATA TERMINAL EQUIPMENT (DTE) and a DATA TRANSMISSION CIRCUIT.
Usually, the DATA TERMINAL EQUIPMENT (DTE) is a "TERMINAL". so think of DTE's as the terminal in an airport: planes either slow down to a dead stop to let out the passengers/"information".... or, they wait until they have the passengers/"information" they need, and take off to reach a different airport to let the passengers/"information" off there.
Technically, a DATA TERMINAL EQUIPMENT is an
END INSTRUMENT that either:
1) CONVERTS
USER INFORMATION
into SIGNALS
2) RECONVERTS/DECODES
RECEIVED
SIGNALS
into INFORMATION
that is usable for the USER.
A COMPUTER is a type of DATA TRANSMITTER EQUIPMENT.
-
TELECOMMUNICATIONS EXAMPLE - DCE Part 1

DCE = many names
1) DATA CARRIER EQUIPMENT=
after INFORMATION is placed correctly onto the TERMINAL, the 'plane" that actually gets the everyone where they need to go is the DCE. It CARRIES or COMMUNICATES the information across the open skies so it can reach it's right audience.
2) DATA COMMUNICATION EQUIPMENT =
same reason as above
-
TELECOMMUNICATIONS EXAMPLE - DCE Part 2
3) DATA CIRCUIT-TERMINATING EQUIPMENT =
in the plane analogy, it doesn't simply reach Paris from New York instantly.
1) Air traffic has to make sure it's path is clear at all times,
2) Weather must be constantly monitored and dealt with and
3) the plane's Gasoline level and overall Structural quality are a major factor as to whether that INFO/DATA makes it to the correct TERMINAL.
-
TELECOMMUNICATIONS EXAMPLE - DCE Part 3
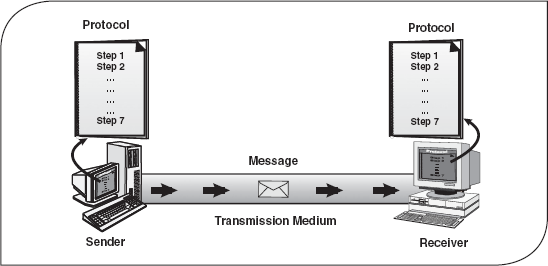
For DATA to travel from one TERMINAL to another TERMINAL, it must travel through a huge NETWORK.
This NETWORK is really just an elaborate CIRCUIT
=> Once the plane lands, or the DATA reaches the DCE, the CIRCUIT, or "traveling", is over
=> thereby giving it the name DATA CIRCUIT-TERMINATING EQUIPMENT.
-
TELECOMMUNICATIONS EXAMPLE - DCE Part 4 = MODEMS 1
DCE are usually found in the form of a
MODEM:
it CONVERTS DATA->from a DIGITAL format-> into something like RADIO or TELEVISION.
This is because these FORMATS->are suitable for an: ANALOG_TRANSMISSION_MEDIUM.
A modem transmits data by modulating one or more carrier wave signals to encode digital information, while the receiver demodulates the signal to recreate the original digital information.
-
Modulation Part 2
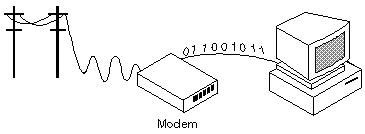
The frequency band occupied by the modulation signal is called the baseband, while the higher frequency band occupied by the modulated carrier is called the passband.
In analog modulation an analog modulation signal is impressed on the carrier. Examples are amplitude modulation (AM) in which the amplitude (strength) of the carrier wave is varied by the modulation signal, and frequency modulation (FM) in which the frequency of the carrier wave is varied by the modulation signal. These were the earliest types of modulation, and are used to transmit an audio signal representing sound, in AM and FM radio broadcasting.
-
Modulation Part 3
More recent systems use digital modulation, which impresses a digital signal consisting of a sequence of binary digits (bits), a bitstream, on the carrier. In frequency-shift keying (FSK) modulation, used in computer buses and telemetry, the carrier signal is periodically shifted between two frequencies that represent the two binary digits. In digital baseband modulation (line coding) used to transmit data in serial computer bus cables and wired LAN computer networks such as Ethernet, the voltage on the line is switched between two amplitudes (voltage levels) representing the two binary digits, 0 and 1, and the carrier (clock) frequency is combined with the data. A more complicated digital modulation method that employs multiple carriers, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), is used in WiFi networks, digital radio stations and digital cable television transmission.
-
OSI Model
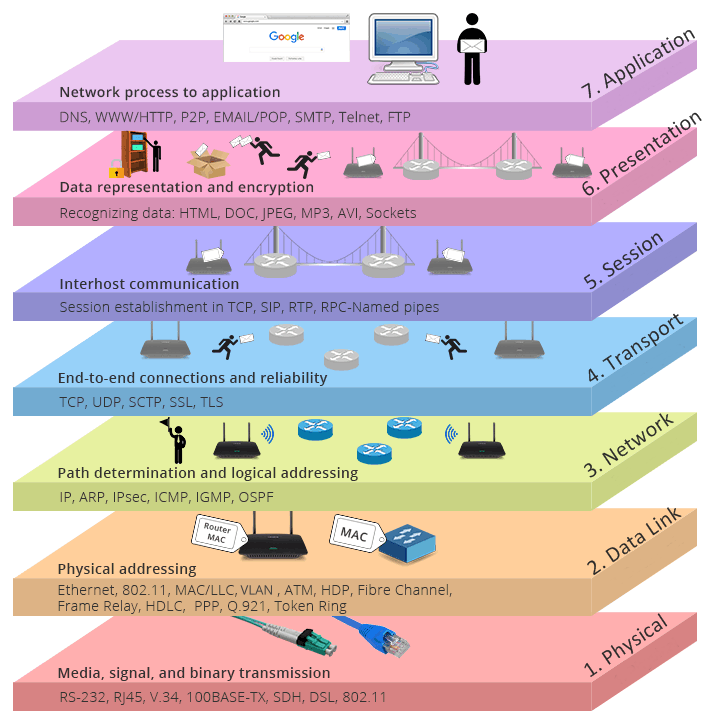
PHOTO----------------->>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
-
Form Factor
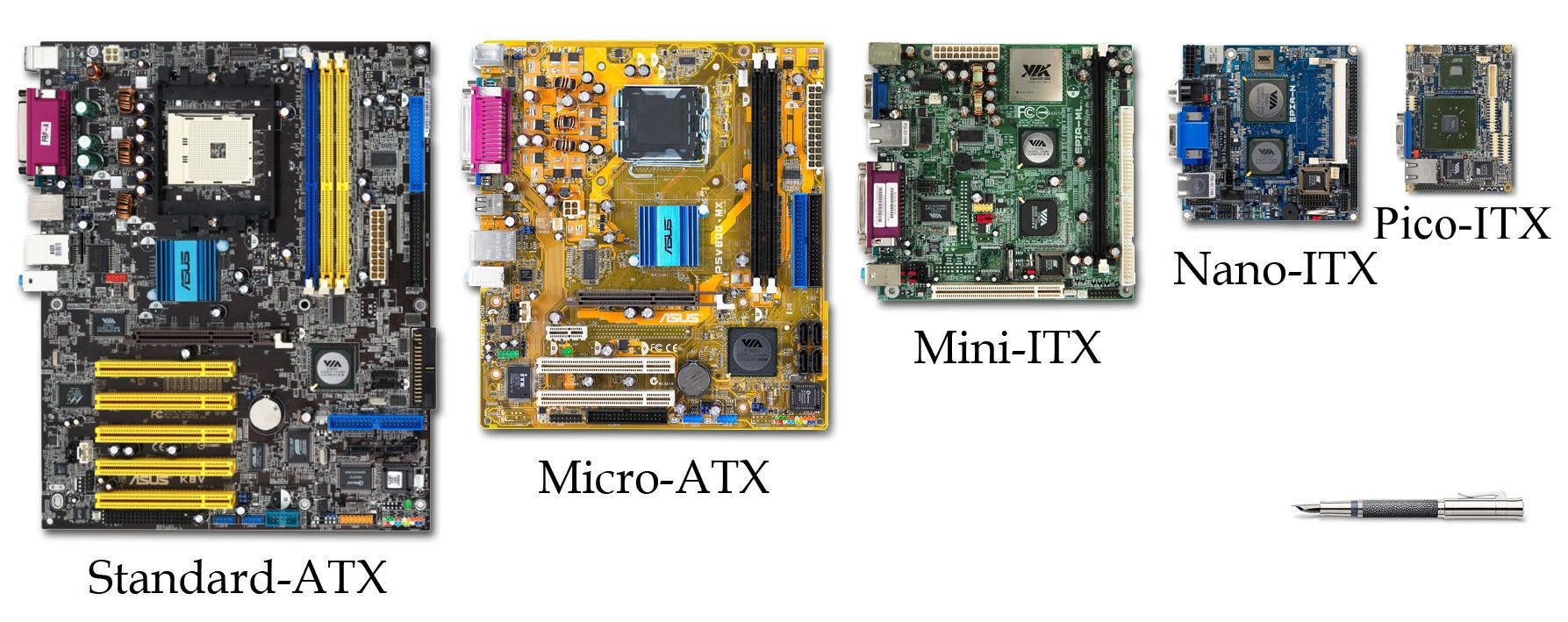
a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics.
form factors have historically been slower to evolve than individual components. Standardization of form factors is vital for compatibility of hardware from different manufacturers.
-
Motherboard form factor Part 1
![the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc.The most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the computer case. [A computer case, also known as a computer chassis, is the enclosure that contains most of the components of a personal computer (usually excluding the display, keyboard, and mouse). ]](/flashcards/cardimage2/5f22efd6/275/7275976_back.png)
the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc.
The most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the computer case. [A computer case, also known as a computer chassis, is the enclosure that contains most of the components of a personal computer (usually excluding the display, keyboard, and mouse). ]
-
Motherboard form factor Part 2
The list of components required on a motherboard changes far more slowly than the components
The current industry standard ATX (Advanced Technology Extended), which still governs the size and design of the motherboard in most modern PCs.
A PC motherboard is the main circuit board within a typical desktop computer, laptop or server. Its main functions are as follows:
To serve as a central backbone to which all other modular parts such as CPU, RAM, and hard drives can be attached as required to create a computer
To be interchangeable (in most cases) with different components (in particular CPU and expansion cards) for the purposes of customization and upgrading
To distribute power to other circuit boards
To electronically co-ordinate and interface the operation of the components

