-
Sampling
Recording a signal at regular intervals
-
Sampling frequency
Num of samples obtained per second
-
Greater sampling frequency means
Better quality but bigger file size
-
Sample size
How many bits are available for each sample - bit depth
-
Bit rate formula
Sample frequency x bit depth
-
File size formula
sample frequency x bit depth x time
-
Lossy compression
Some data is removed from the file
-
Lossless compression
Rearranged data to make it more efficient
-
RLE - compress 'yyyybbbpppprr' where y is yellow b is blue etc
4y3b4p2r
-
NOT gate
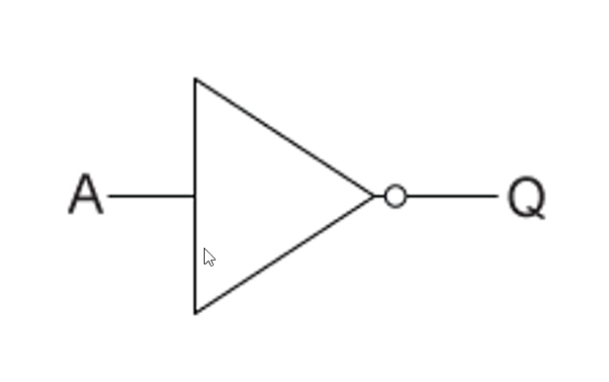
Reverses input
-
OR gate
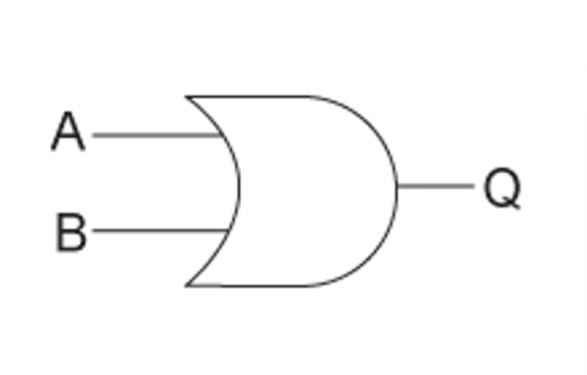
Returns true if either / both input are true
-
AND gate
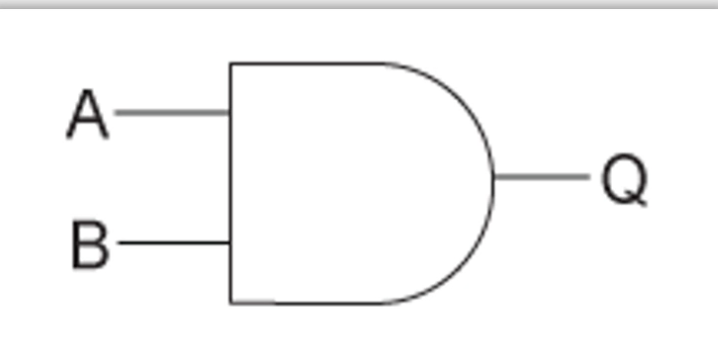
Returns true if both inputs are true
-
XOR gate
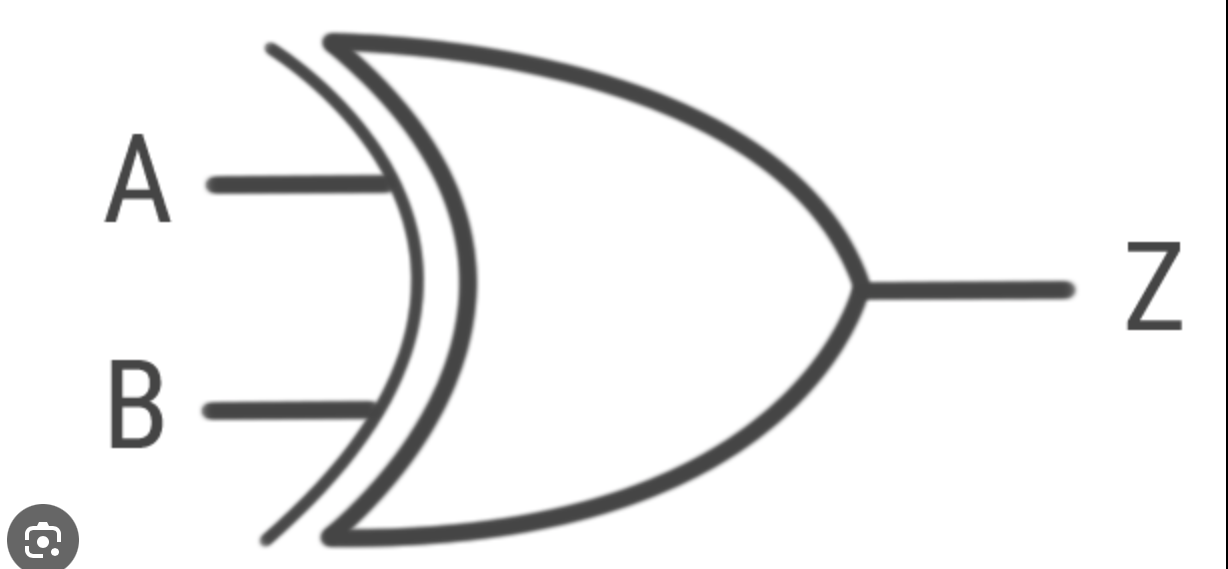
Returns true if either (not both) are true
-
Application software
Used to carry out tasks on a computer e.g web browsers
-
System software
Peforms tasks need to operate the hardware e.g operating system, utility software
-
Operatig system
Manages computer system e.g linux
-
Machine code (low level)
Binary
-
Assembly code (low level)
Communicates with computer
-
High level code
Like Python
-
High level vs Low level
programmer understands vs computer understands
-
Translators and why their needed
Converts code from one language to another - all code needs to be translated to machine code
-
Assembler
Converts assembly to machine code
-
Compiler
Converts high level to machine code translates the whole block
-
Interpreter
Converts high level to machine code translates line by line and slower than compiler
-
ALU
Perform arithmetic and logic operations
-
Control Unit
Coordinates the CPU
-
Register
Quick small stores of data in cpu
-
Clock
Provide signals to synchronise internal components
-
RAM is (non volatile / volatile)
Volatile memory that can be read/write to
-
ROM is (non volatile / volatile)
Non volatile memory that can only be read to
-
Cache
Fast but small memory that stores frequently used data
-
Cores
Processing units
-
Optical storage
Binary data
Light is shined and light that hits a land reflects differently to when it hits a pit. E.g pits can be read as 0 and lands as 1. Data is written with a laser burning the pits into the disk
-
Optical 1 disadvantage 2 advantage
Small capacity
Reliable
Very portable
-
Magnetic storage
Parts of the surface are either magnetised (1) or demagnetised (0) by the electromagnets in the head.
-
Magnetic 1 disadvantage 2 advantage
Can be noisy and generate heat
Large capacity
Cheap
-
Solid State Storage
Form of flash memory
-
SSD 1 disadvantage 2 advantage
Expensive
Silent
Reliable as non-mechanical
-
Embedded system
A special purpose computer
-
Network
Connection between devices to share resources
-
Protocols
Set of rules for communication
-
Application layer protocols
HTTP/S, FTP, SMTP, IMAP
-
Transport layer protocols
TCP, UDP
-
Internet layer protocols
IP
-
Link layer protocols
Ethernet, Wifi
-
Application layer
Where the network applications operate
-
Transport layer
Sets up communication between two hosts
-
Internet layer
Handles and routes data
-
Link layer
Where hardware operates
-
Viruses
Insert themselves in normal programs
-
Adware
Generates unwanted adverts
-
Trojans
Disguised as a desirable software but there is malware hidden within it
-
Spyware
Collects data about the user
-
Blagging
Inventing a scenario to gain a victim trust
-
Phishing
Obtaining private info through a fake link often pretending to be something your not
-
Pharming
Cyberattack where websites traffic is redirected to a fake site
-
Shouldering
Viewing private info over the person shoulder
-
Firewalls
Monitor network traffic and filter packets based on rules
-
White box penetration test
Attempting to gain access with some knowledge and basic credentials - simulating an inside attack
-
Black box penetration test
Attempting to gain access with no knowledge - simulating an outside attack
-
HTTPS use
used for accessing webpages from a server and uses encryption to secure data
-
SMTP VS IMAP
handling out bound email vs handling in bound email
-
TCP VS UDP 1 similarity and 3 differences each
Similarity; exists to deal with connection between devices
Differences; TCP - two way connection splits and slower and more reliable
UDP - sends data one way and faster and less reliable
-
IP protocol use
Enables communication over the internet
-
2 enviromental issues of computing
too much energy use and finite resource use
-
2 cultural issues of computing
changing the job market and social media also makes it easier to spread abuse and hold politicians accountable
-
2 ethical issues of computing
the right to privacy conflicting with the government ensuring public safety e. g FBI asking apple to hack into a phone
-
2 legal issues of computing
Blackmail , stealing of financial info


