-
What are the milestones in the international response to climate change?
first world climate conference: Geneva 1979
IPCC established 1988
First IPCC Report 1990
UNFCCC Framework Convention ClimChnge 1992
entered into force 1994)
COPs Conferences of Parties annual meetings begin 1995
Kyoto Protocol 1997
ratified 2005-reduce emissions relative to 1990 by 5% by 2012
Durban Platform 2011
terms established by 2015, implemented 2020 (plan)
Paris Climate Agreement 2015
opened for signature: april 22 2016 (earth day)
entered into force: nov. 4 2016
2020: countries submit plans for climate action
2023: accurate reports on climate progress "global stockade" begin.
-
What does IPCC stand for, and how and when was it created?
IPCC: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
estatblished 1988
created by UN environment program(UNEP) and WMO (world meterological org)
policy neutral and politically neutral
-
How many IPCC reports have been published so far?
6
ar1 1990 (beginnings of climate modeling-planet seems to be warming. didn't have a lot of data).
ar2 1995
ar3 2001
ar4 2007
ar5 2014
ar6 march 2023
-
What is RCP?
representative concentration pathway
different levels of greenhouse gases resulting in diff radiative forcing
-
What does COP stand for, and how often do the COP meetings take place?
COP
Conferences of Parties
began in 1995
annual climate conferences (each year)
-
What is the Kyoto Protocol,
Third COP, 1997
Kyoto Japan
first international treaty directly addressing climate change
Ratified in 2005
GOALS:
reduce GHG emissions relative to 1990 by 5% by 2012
specific GHG: CO2, CH4, N2O, HFC, PFC, SF6
(carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbon, sulphur hexafluoride)
Developing nations (eg India, China) didn't
different targets to different nations (eg 7% reduction USA)
CAN withdrew 2011, USA never ratified/agreed
-
What are the three Kyoto mechanisms?
1. emissions trading
2. joint implementation
3. clean development
emission trading
countries sell or purchase assigned units of emissions
"cap and trade"
ETS (eu emission trending system)
used today, corporations financial incentive to cut emissions to sell
joint implementation
industrialized countries to invest in projects that reduce emissions in another industrialized country
think projects where location matters (eg windfarms)
clean development mechanism
allows industrialized countries to offset emissions by financing projects that reduce global emissions in developing world
-
Durban Platform
Durban Platform 2011
agreement to be part of legally binding treaty
The terms of the future treaty are to be defined
by 2015 and become effective in 2020.
first time include dev countries (and USA)
for the interim: follow kyoto protocal
-
Paris Climate Agreement
Paris Climate Agreement 2015
consensus of 196 parties
opened for signature: april 22 2016 (earth day)
entered into force: nov. 4 2016
GOALS
zero net anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions by second half of 21st century
limit warming to below 2C relative to preindustrial levels
no specific timetable, no country specific goals
no enforcement mechaisms
-
After paris climate agreement
representatives go back to country to negotiate and attempt implement policy
plan for 5-yr cycle of increasingle ambitious climate action
every 5 yr stocktakes of progress
2020:
countries submit their plans for climate action (nationally determined contributions = NDC)
long term low GHG emission strategies (LT-LEDs) submit
GLOBAL STOCKTAKE begin in 2023
happen every 5 years
countries honest report on progress
-
Post-Paris Agreement Results/Predictions
increasing trend GHG emissions
dip in emissions at 2020 (COVID) then increase back to previous
potentially stabilizing emissions
NDC (nationallly determined contributions) stillabove the 2C threshold (likely between SSP2-4.5 and SSP1-2.6)
most optimistic: 1.5C
indc indicared ndc above ndc
even in most optimistic full implementation of announced targets, warming likely to be above paris agreement goal (most likely in optimistic 1.8)
real world action indicares 2.7C
-
Global Emissions
GLOBAL CO2
china biggest emitter (>10 billions tons)
high emitters from: north america, europe, asia
doesnt exactly matter where they come from because mix
new high, 425ppm observed at mauna loa
india and china co2 rising
per capita co2 emissions -> us highest
overtime/cumulative: US > 250 billion tons
-
Which countries are the top three CO2 emitters?
China, USA, European Union, (India close behind)
-
How do per capita emissions differ from global CO2 emissions?
per capita emissions:
1. USA
2. China
3. European Union
4. UK
5. World
6. India
world:
china
usa
eu
-
What are SSPs? Which one is the "most optimistic" SSP and why?
shared socioeconomic pathway
1: a world sustainability focused growth and equality. optimistic for human development. well functioning institutions based on sustainab;e practices (optimistic)
2: middle of the road, historical patterns
3: fragmented "resurgent nationalism" pessimistic trends for human development. inequality. big population
4: increasing inequality. pessimistic for humanity
5: rapid unconstrained growth in use and outpit. optimistic for human development. rapid economic growth. fossil fuel economy. not sustainably.
-
What would be the lowest radiative forcing reached for the baseline SSPs?
none reaches radiative forcing below 5 w/m2 by 2100 (therefore: none meeting paris climate agreements)
(different from RCP radiative forcing hypotheticals)
-
What is the difference between climate mitigation and adaptation?
Mitigation: combat climate change reduction of greenhouse gas emissions through technological advances
Adaptation: “live with” climate change by relocating, building protective structures, growind different crops, etc
-
Which are the two sectors that produce most greenhouse gases in the US/globally?
Sources of US GHG emissions
1. transportation (29%)
2. electricity (25%)
3. industry (23%)
Sources of WORLD GHG emissions
1. Electricity/Heat production (25%)
2. Agriculture/land use (24%)
3. Industry (21%)
-
Which are the two major fossil fuel sources for electricity generation? How do their efficiencies compare?
1. Coal (33% efficient)
2. Gas
-typical gas fired power plant (42% efficient)
-typical natural gas combined-cycle power plant (60%)
-
Why is coal widely used in southeast Asia?
- inexpensive in SoutheastAsia (China, India) and thus widely used there
- dirty, its mining causes destruction, and it pollutes the atmosphere
-
Where does most natural gas in the US now come from?
reserved of shale recovered through fracking (formation fracturing)
natural gas production by state:
TX and Pennyslvania are highest in US
-
What is fracking
Last ten years fracking boom.
Over 60% modern from fracking
Vertical role burrows down, then turns horizontal, pumps fracking material into the deep earth (fracking chemicals and a tremendous amount of water) leaving cracks allowing for natural gas extraction
Uses a lot of drinking water and can contaminate nearby dribkingwater-we aren’t even sure of all the consequences
Vast reserves of shale gas are now being recovered through formation
Old drill holes, waste water left in the ground. Cause earthquakes through finding old faults.
Texas, and pennsylvania.
Gas is tight;y bound in these dense shale layers can o nly bee retrieved from breaking the layers
-
Hydropower; different forms?
Dams/Diversion Systems most common
(flow through turbines in dams and produce electricity)
Three Gorges Dam: biggest dam in world
Norway gets most electricity from hydropower
About 20% of global electricity generation
Less common: wave power
Rance ridal power station, pelamis wave energy converter
Wind is always a way of the atmosphere to equalize pleasure, technically because sun’s heating
On top of waves, move on top of waves and magnets inside there, generate electricity
-
Wind power
Plentiful in various locations
Differs by place because different air masses used to harvest wind
Used in texas and midwest
Needs to be stored or transpoered
(yeah sun won’t last forever but for pur purposes right now we can just act like it is)
Wind turbines
Wind farms, more complicated than old prairie windmills.
Wind turbine blades, assymetrical so the air pressure is uneven and spins blades. Then spins shaft
New wind tech designs: bladeless wind turbine, sails or kites, floating wind farm
Not always located where electricity is needed, wind isn’t always blowing, need way to store
-
How can solar energy be used?
Solar energy is plentiful in various locations
Needs to be stored or transported
About 3.5% global
Solar panels can be on top of homes
Concentrated solar towers: movvable mirrors, steam turbine generates electricity. Solar updtaft towers: make use of thermal updraft
Concentrating solar power: (csp) focuses suns energy through mirrors and troughs: heats liquid that hears water that creates steam. Reflector, absorber tube, solar field, piping.
photovoltaic solar panels
-
What are photovoltaic cells? And where in the US is the photovoltaic solar resource the greatest?
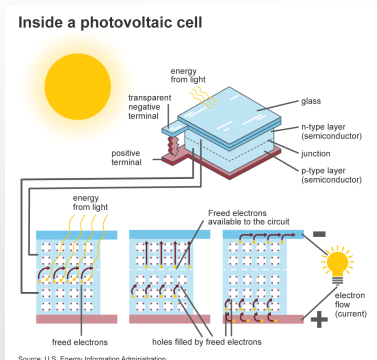
Solar panels use: solar photovoltaic (pv) effect
Sunlight made of tiny packets of energy photons, photons strike the cells and frees electrons in semiconductor material multiplied by number of sells in each panel
No emissions and can be used anywhere the sun shines
Southwest US greatest uses
-
What is geothermal power, and how can it be used?
Radiate outward from interior of the earth
Radioactive decay in earth’s interior. As we go deeper into earth’s crust it goes hotter. Depends on how thick the earth is in certain places
California produces 3-4% of its electricity geothermally because high geothermal gradient (largest geothermal powerplant in california “the geysers”)
-
Which is the primary fuel for transport?
Oil
-
What is a fuel cell?
Fuel cells powered by hydrogen
Still very limited network of fueling stations
Not completely clean unless the hydrogen is gotten through clean measures
Lots of the hydrogen we get now from fossil fuel byproducts
Still cleaner than other fuels honestly
In california biggest sales of these, but no real big push (sales have gone down from 2021-2022)
Hydrogen good for storing energy
Fuel cell: two plates from membrane ions and electrons
-
What might be an option for sustainable aviation fuels?
renewable biomass and waste products
Hardest to replace with non fossil fuel based fuels
Develop sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) from renewable biomass and waste products
Using biomass fermentation
-
What does CCS or CCUS stand for?
Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS)
(or Carbon Capture Storage CCS)
take out co2 already in atmosphere
Capturing co2 from fossil or biomass fueled power stations, industrial factories, or directly in air.
Needs to be transported. Moving compressed co2 by ship or pipeline from place of capture to point of use or storage
CCUS - carbon capture, use, and storage (CCS- carbon capture and storage)
Global increase in carbon capture in past decade. But compared to how much carbon emitted it’s very small
About 44million tons captured 2021 (we release like 37 billion a year)
-
How can carbon be stored?
Injection of captures co2 into underground geological reservoir
Porous rock covered by impermeable rock
Deep saline formation (co2 dissolves)
Depleted oil and gas reservoirs (co2 gets trapped in pore spaces)
Basalt (co2 reacts with rock to form stable minerals)
-
What are some measures to achieve "negative emissions"?
Carbon capture and storage “negative emissions”
Just CCUS not enough
BECCS-bioenergy carbon capture and storage
Biomass burned to generate electricity. Co2 captured and stored.
Carbon scrubbber
DAC- direct air capture and storage of CO2
Orca Plant-iceland-carbon captured and turned into stone
-
Geoengineering approaches, e.g. SRM (what does that stand for?)
Fertilizing oceans w/ iron dust
Spur production of phytoplankton growth
Has not been very successful. Bad ramifications
SRM-solar radiation management
Altering reflectivity of earth’s surface
3 levels
In space (reflectors in orbit)
Expensive, potential unintended consequences
Atmosphere based (more clouds? Brighter clouds?)
Tried above great barrier reef. Still in trial phase
Surface based (increasing albedo of various surfaces)
-
Which of the following is NOT considered to be a renewable energy source?
Nuclear, biomass, ocean tides, hydropower?
Nuclear not renewable. The uranium used in nuclear power may last another 90 years ish. cannot be remade
-
In a fuel cell, _____ is used as a fuel to produce electricity.
hydrogen
-
early milestones in policy
first world climate conference: Geneva 1979
WMO (world meterological org.) (part of UN)
IPCC established 1988
est UN/WMO-policy/politic neutral
First IPCC Report 1990
planet warming/humans prob responsible
didn't have a lot of data
UNFCCC Framework Convention ClimChnge 1992
Rio. signed by 154 nations (entered into force 1994)
COPs Conferences of Parties annual meetings begin 1995


