-
Quantity of energy transferred in water/heat energy required to increase temp of mass of water by particular amount.q=m*C*ΔT (q in joules=mass grams*SHC*change in temp in degrees C)
-
Reasons for heat lost in calorimetryPoor insulation, heat lost to surroundings and value measured for ΔT will be lower
-
What does calibration factor tell you?How much energy required to change the temp of water in calorimeter by 1 degree C
-
Equation for electrical energyE=VIt (volts*amps*seconds)
-
Equation for calibration factorCF=E/ΔT
-
Define fuelA substance with stored energy that can be released relatively easily for use as heat or power
-
When is a fuel considered non-renewable. Give 3 examples.A fuel is considered to be non-renewable if it cannot be replenished at the rate at which it is consumed. Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas are considered non-renewable
-
How are fossil fuels formed.Fossil fuels are produced over millions of years by the breakdown of biomass at high temperatures and pressures underground.
-
When is a fuel considered renewable. Give 3 examplesA fuel is considered to be renewable if it can be replenished at the rate at which it is consumed. Biofuels such as biogas, bioethanol and biodiesel are renewable.
-
How is biogas formed?Biogas is formed by the anaerobic breakdown of organic waste.
-
How is bioethanol produced?Bioethanol can be produced by the fermentation of starches and sugars
-
How is biodiesel produced.Biodiesel is produced in a reaction between a vegetable oil or animal fat, and a small alcohol molecule such as methanol.
-
What sort of fuels undergo combustion reactions, and what are the productsPetrol, natural gas, biogas, and bioethanol undergo combustion in excess oxygen to form CO2 and H2O
-
How do coal-fired stations work, and how efficient are they?Thermal energy creates steam, which turns a turbine. 30-40% efficient
-
What pollutants do fuels produceCO, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulates
-
Advantages/disadvantages of coalLarge reserves, relatively high energy contentNon-renewable, high level of emmisions
-
Advantages/disadvantages of natural gasMore efficient than coal, easy to transport, relatively high energy contentNon-renewable, limited reserves, polluting but less than coal and petrol
-
Advantages/disadvantages of biogasRenewable, made from waste, reduces waste disposal, low running costsLow energy content, supply of waste raw materials limited
-
Advantages/disadvantages of petrolHigh energy content, ease of transportNon-renewable, polluting but less than coal, limited reserves
-
Advantages/disadvantages of bioethanolRenewable, can be made from waste, CO2 absorbed during photosynthesis, burns smoothly, fewer particulates than petrolLimited supply of raw materials from which to produce it, lower energy than petrol, may require use of farmland otherwise used for food production
-
Advantages/disadvantages of LPGLow cost, easily seperated from natural gas, relatively high energy content, fewer particulates than petrolNon-renewable, polluting but less than petrol
-
How does a diesel engine compare to petrol engines?Better fuel economy due to higher energy efficiency, and higher energy per litre10-20% less CO2 emissions
-
Petrodiesel production and makeupPetrodiesel is non-renewablePetrodiesel is seperated from crude oil by fractional distillation.Composed 75% alkanes containing 10-15 carbon atoms, 25% aromatic compounds
-
Biodiesel production and makeup
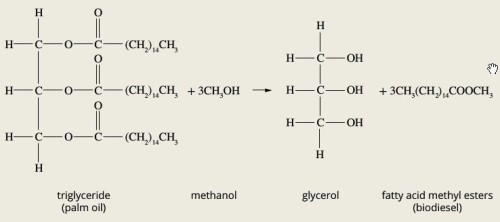 Biodiesel is renewableBiodiesel produced from triglycerides in animal fats or plant oils. The triglycerides reaction with methanol in a transesterification reaction to form biodiesel.Can be described as fatty acid esters
Biodiesel is renewableBiodiesel produced from triglycerides in animal fats or plant oils. The triglycerides reaction with methanol in a transesterification reaction to form biodiesel.Can be described as fatty acid esters -
Petrodiesel vs biodiesel (renewability, energy content, viscosity, cold flow, emissions, environmental impact of production)1. Biodiesel is renewable2. marginally lower energy content3. higher viscosity4 more likely to need antifreeze additives in cold climates,5. produces CO2 but is consumed in production of tryglycerides used to make the fuel. Fewer particulates. Produces other pollutants. 6. Biodiesel produced from farm crops can add to land degradation and might lead to higher food prices. Biodiesel made from waste products such as used booking oil have a positive impact on the environment1. Petrodiesel is non-renewable2. marginally higher energy content3. lower viscosity4. can be used without additives at lower temps than biodiesel, 5. produces CO2, particulates and other pollutants6. Oil fields prone to spills and damage to local habitats. Oil refineries produce emissions that have a negative impact on local regions.
-
Compare J to kJ and MJJ=10^-3kJ=10^-6MJ
-
Where is the chemical energy stored?In the bonds between atoms and molecules
-
Endothermic vs exothermicA chemical reaction that releases energy to the surroundings is called an exothermic reaction. A chemical reaction in which energy is absorbed from the surroundings is called an endothermic reaction.
-
Are combustion reactions endo or exothermicExothermic
-
What does the ΔH value indicateThe magnitude of the energy change and whether energy is absorbed (postive value) or released (negative)
-
What does doubling the coefficients in a chemical reaction do to the ΔH value, and why?Doubles it as twice as many reactants react to produce or absorb twice as much energy.
-
Why must states of matter be included in thermochemical equations?Because changes of state involve enthalpy changes
-
What is activation energyThe energy that must be absorbed to break the bonds in the reactants so that a chemical reaction can proceed.
-
Do combustion reactions have a pos or neg ΔH value?Negative
-
What is ΔHc and what are common unitsΔHc is heat of combustion, and indicates maz amount of energy that can be released when a specified amount of fuel undergoes complete combustions. Common units are kJ/mol, kJ/g and KJ/tonne.
-
When does incomplete combustion occur?Incomplete combustion occors when a substance undergoes combustion in a limited supply of oxygen.
-
Equation for energy when you have ΔHc in kJ/molE=n*ΔHc (n=number of moles)
-
What does n representNumber of moles
-
Specific heat capacity of water4.187 kJ/kg/K
-
Define specific heat capacitySpecific heat capacity of a substance measures the quantity of energy needed to increase the temperature of a specified quantity of that substance by 1 degree C
-
Define mmass (in grams)
-
1L in mL and cm^31L=1000mL=1000cm^3
-
1m^3 in cm^3, mL, and L1m^3=1*10^6cm^3=1*10^6mL=1000L
-
Define pressureForce per unit area
-
1 bar in kPa and Pa1 bar = 100 kPa = 1.00*10^5Pa
-
1 atm in mmHg, Pa, kPa and bar1 atm = 760 mmHg = 1.013*10^5 Pa = 101.3kPa = 1.013 bar
-
V proportionality to pressure, temp and amountV∝nV∝1/PV∝T
-
Standard lab conditions (SLC)25C (298K) and 100 kPa
-
Standard temperature and pressure (STP)0C (273K) and 100 kPa
-
What is the molar volume of a gas, and equationn=V/Vm
-
Value of Vm at SLC24.8 L/mol
-
Value of Vm at STP22.7L/mol
-
Universal gas equation and value of universal gas constantPV=nRt R=8.31J/K/mol
-
Number of moles of substance using mass providedn=m/M
-
What does M representMolar mass of substance

