-
Hamiltonian by perturbation order expansion
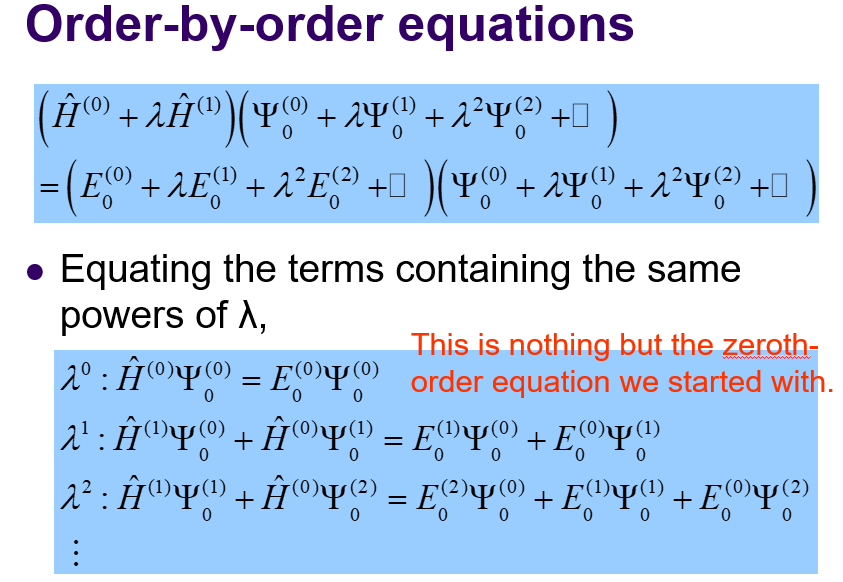
-
Fermi Golden Rule; what is it describing and formula
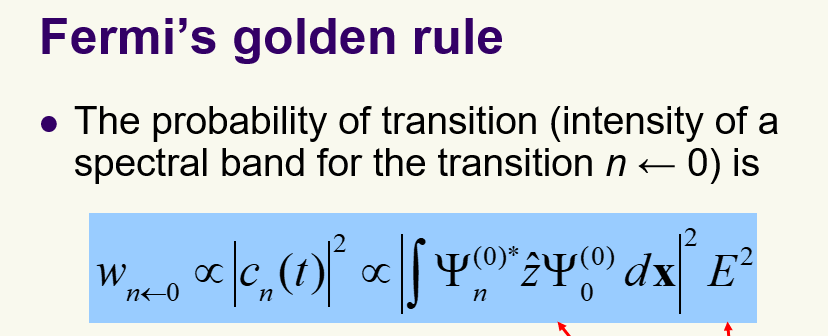
-
absorption excitation & emission deexcitation energy (energy of transition)
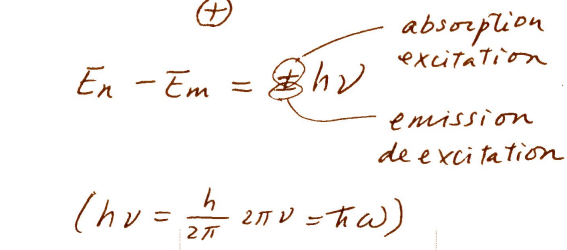
-
Tunneling, what are wavefunctions at different points? what is transmission ratio?
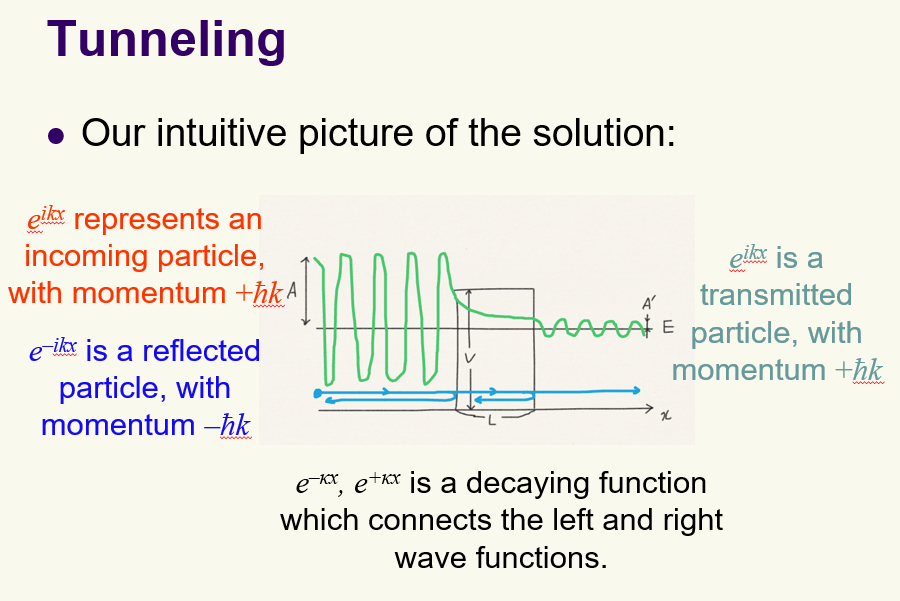
Transition ratio = |A'|^2 / |A|^2 proportional to e^(-2kL)
-
Tunneling: What are the boundary conditions the wave function must satisfy?
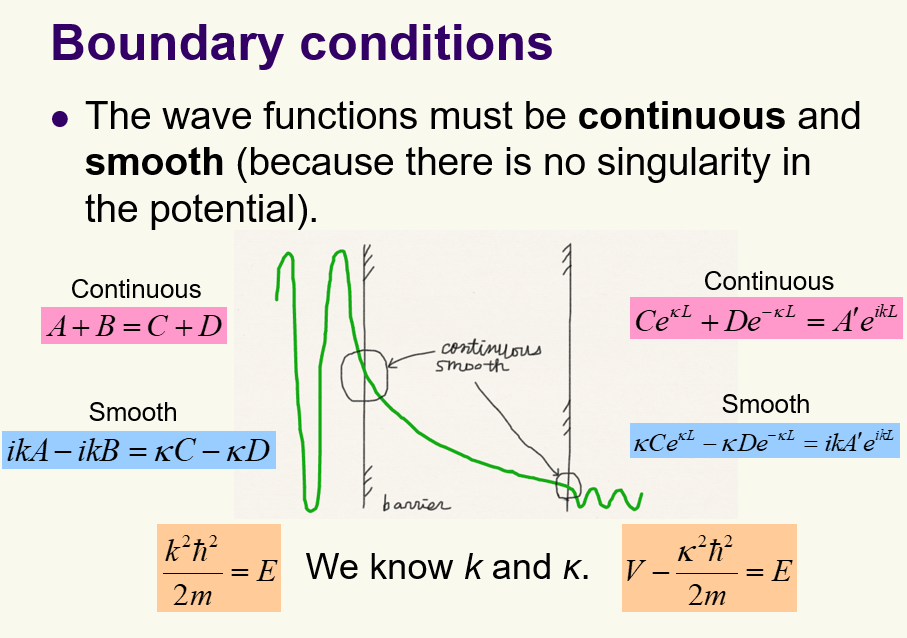
-
Coulombs potential: what is it and formula?
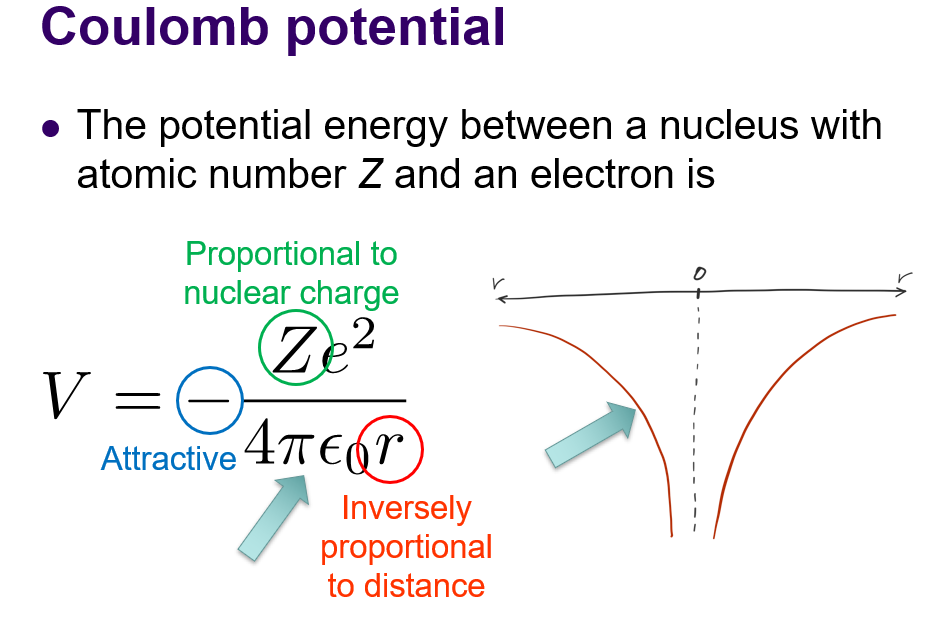
-
Schrodinger Eqn of a hydrogenic atom
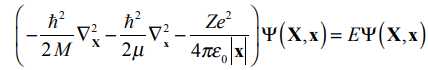
-
angular, centrifugal force(last arrow): of S.E eqn. mu is reduced mass = M1M2/(M1+M2)
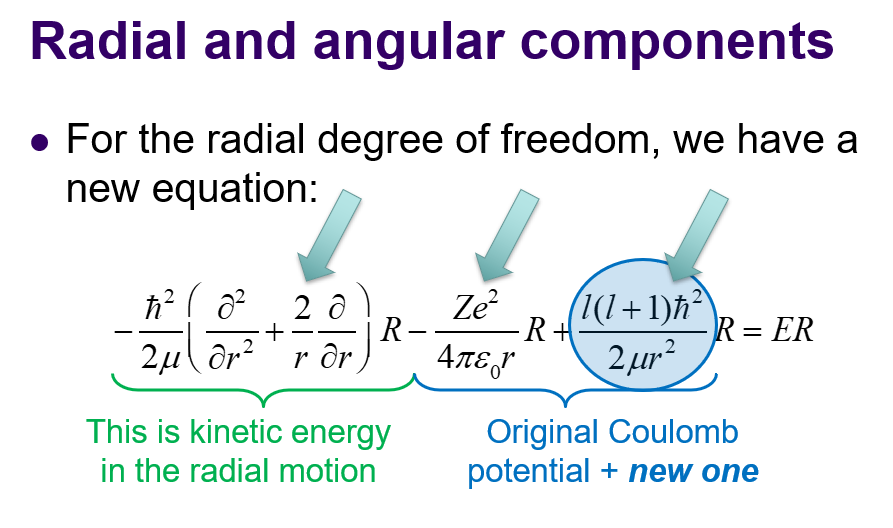
-
energy eigenval of hydrogenic atom
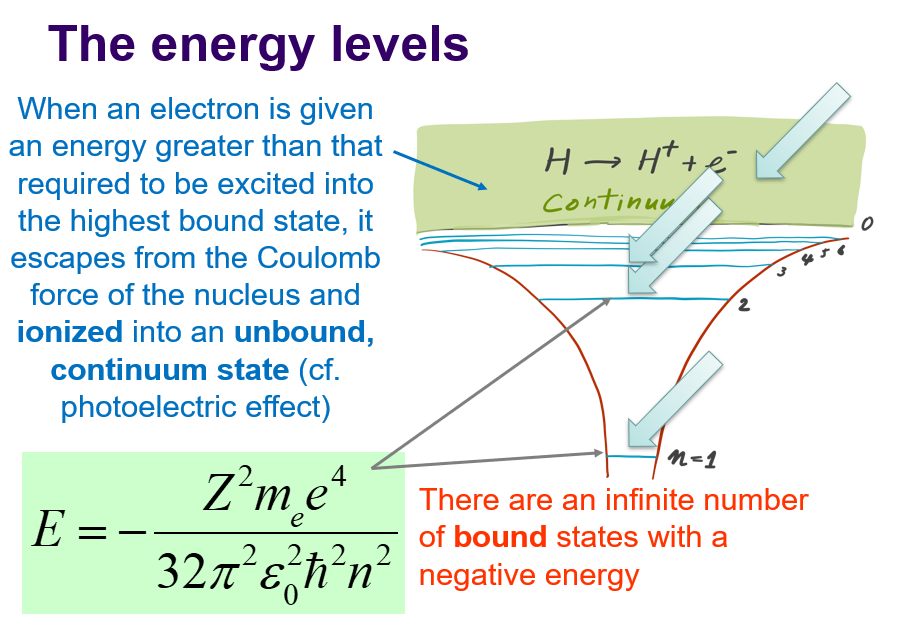
-
What is 1 bohr, and 1 Rydberg?
1 Bohr = 0.529A, 1 Rydberg = 13.6eV
-
average radius
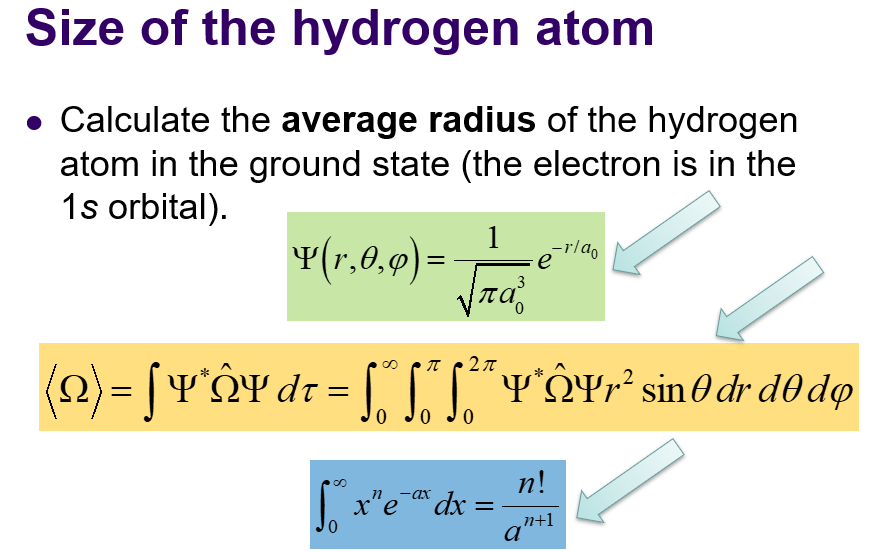
-
allowable domains of three quantum numbers of the hydrogenic atom and, on that basis, explain the atomic shell structure

-
electronic Schrödinger equation of the helium atom
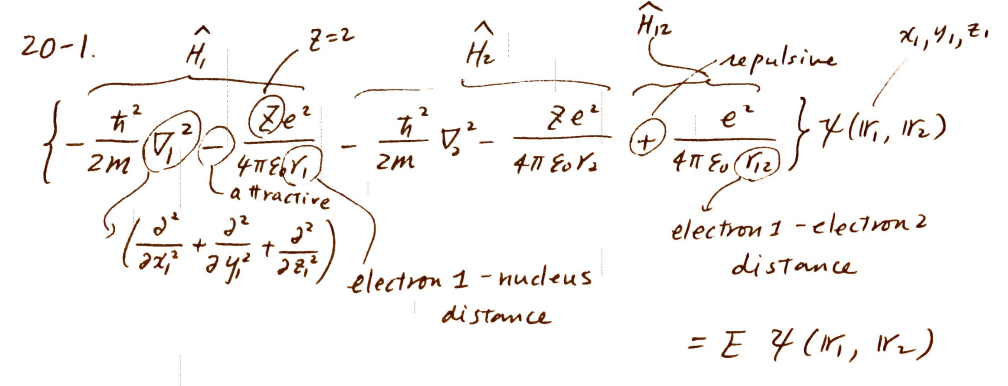
-
1) singlet wave function of the helium atom with both electrons in the 1s orbital within the orbital approximation.
2) singlet and 3 triplet wave functions of the helium atom with one electron in the 1s orbital and the other electron in the 2s orbital.
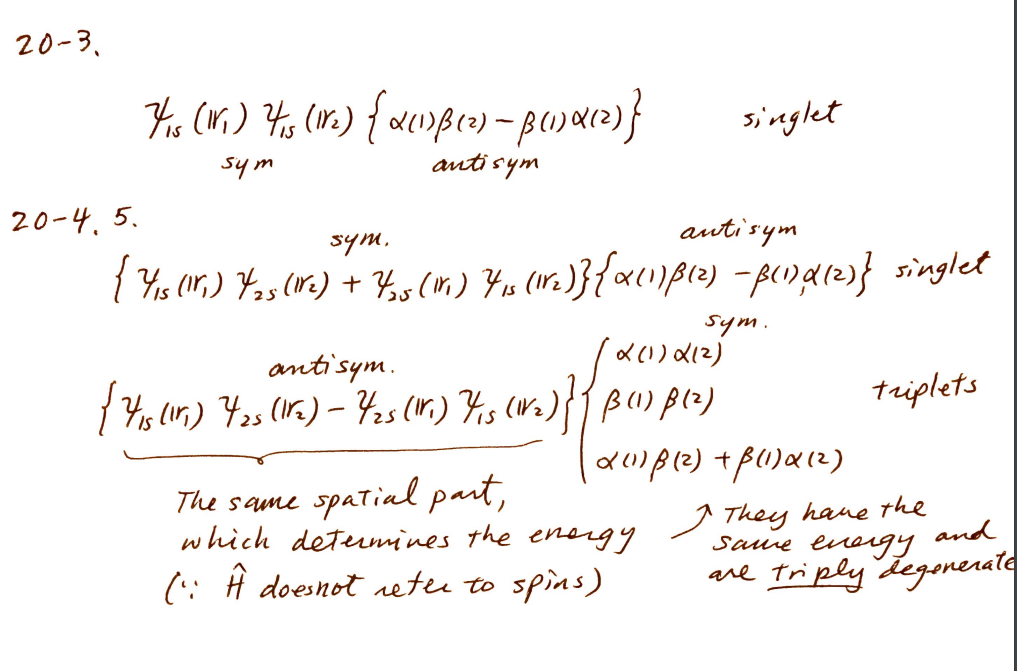
-
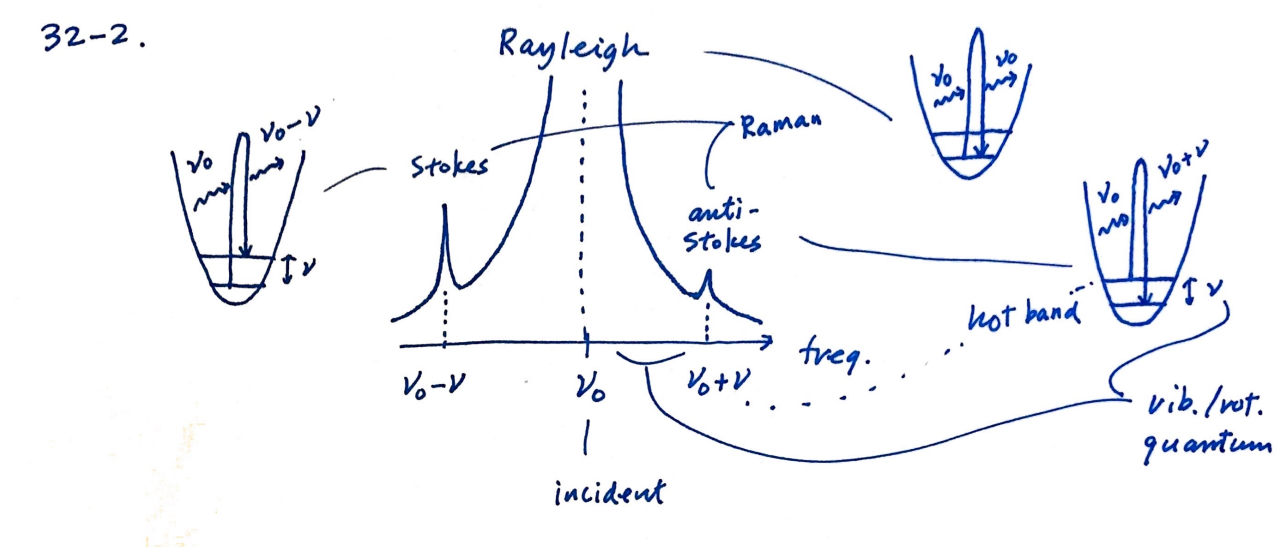
Define the Rayleigh scattering, Stokes Raman scattering, and anti-Stokes Raman scattering. Draw a typical Raman spectrum and explain the temperature dependence of the spectral lines
-
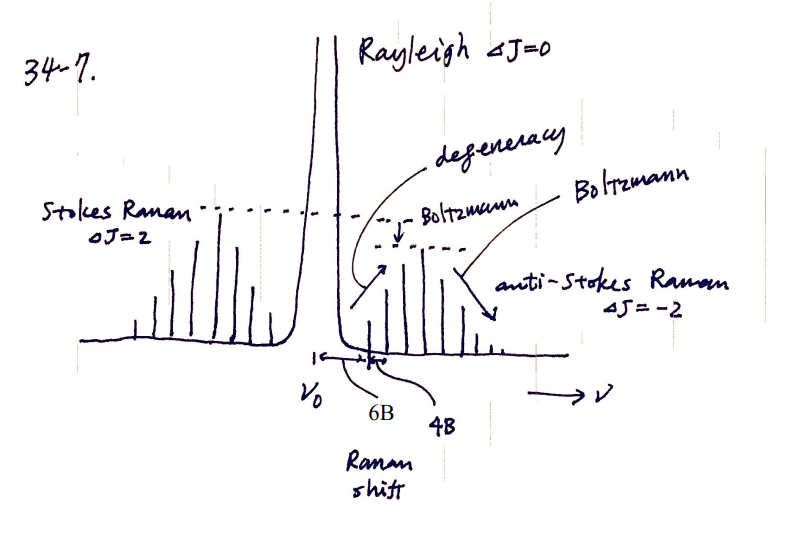
Draw a pure rotational Raman spectrum of a linear rotor. Name the three branches, explain their relative intensities, rationalize the shape of branch envelope, and give line spacing in terms of the rotational constant B.
-
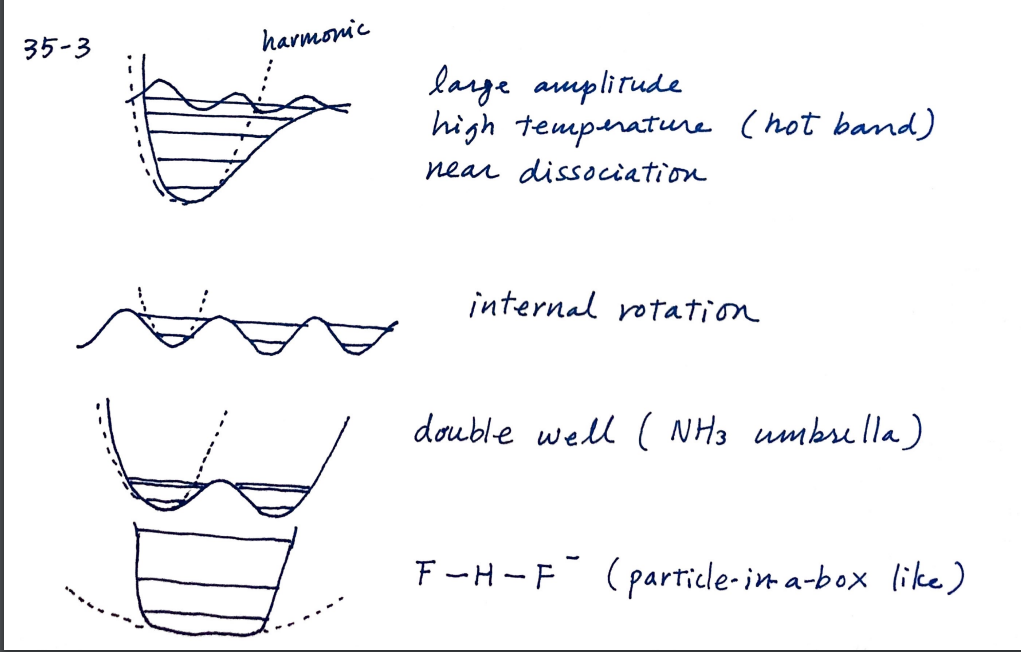
In what circumstances, the harmonic approximation to molecular vibrational problem becomes a poor approximation?
-
Starting from the transition dipole moment, derive the gross and specific selection rules of infrared absorption due to pure vibrational transitions in the harmonic approximation


