-
Heat vs. temperature
Heat = The exchange (transfer) of thermal energy
Temperature = A measure of thermal energy
-
System vs. surroundings
System = The chemical reaction of interest
Surroundings = Everything around the system that it can potentially interact and exchange energy with
-
KJ → J
1 KJ = 1000 J
1 J = 0.001 KJ
-
"Energy"
Anything that has the capacity to do work
-
How are heat and work related to energy
Heat and work are two different ways an object can exchange energy with other objects
-
Change in energy formula
ΔE = q + w
- q is heat/thermal energy
- w is work
-
What does a positive q value mean (what are words associated with it)
System is gaining thermal energy
- Thermal energy added
- Absorbed
- Temperature increase
-
What does a negative q value mean (what are words associated with it)
System is losing thermal energy
- Cooled
- Thermal energy removed
- Releases (thermal energy)
-
What does a positive w value mean (what words are associated with it)
Work is being done on the system
- Forced
- Compressed
- Applied
-
What does a negative w value mean (what are words associated with it)
Work is being done by the system
- System performing
- Expanding
- Produces
-
A +ΔE value means ___
A -ΔE value means ___
+ΔE = Energy is flowing into the system
-ΔE = energy is flowing out of the system
-
Specific heat capacity
The heat/thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1C°
-
Temperature change formula
q = m · Cs · ΔT
- q in J
- m in g
- Cs is specific heat capacity
- T in K
-
Thermal energy transfer formula
m · Cs · (Tf - Ti) = m · Cs · (Tf - Ti)
- Where each side is a different substance from the problem
-
1. What is an exothermic reaction
2. What is its ΔHrxn
3. Common exothermic reactions (5)
Heat is released out of the system
- Negative (-) ΔHrxn value
- making chemical bonds - combustion - oxidation - freezing - condensation
-
1. What is an endothermic reaction
2. What is its ΔHrxn
3. Common endothermic reactions (5)
Heat is absorbed into the system
- Positive (+) ΔHrxn value
- breaking chemical bonds - melting - photosynthesis - evaporation - dissolving
-
Pressure-volume work formula
w = - P · ΔV
- w in J
- p is external pressure
- V is (final volume - initial volume) in L
-
In pressure-volume work when gas does the work on its surroundings, the volume ___ and the work done is ___
- The volume increases (think expansion)
- The work done is negative (because work is being done by the system)
-
In pressure-volume work when work is done on the gas by the surroundings, the volume ___ and the work done is ___
- The volume decreases (think compression)
- The work done is positive (because work is being done on the system)
-
Steps for calculating ΔHrxn algebraically
If an equation is a sum of steps then the ΔHrxn for the total equation is the sum of the ΔHrxn from each step
- If the reaction is reversed = - ΔH
- If the reaction is multiplied = ( ) · ΔH
- If the reaction is divided = ( ) ÷ ΔH
-
Steps for calculating ΔHrxn using bond enthalpies
∑(ΔHrxn of bonds broken) - ∑(ΔHrxn of bonds formed)
1. Draw Lewis structure
2. Determine the ΔHrxn of all bonds broken (reactant side)
3. Determine the ΔHrxn of all bonds formed (product side)
4. Plug these values into the formula
-
Steps for calculating ΔHrxn using bond enthalpies of formation
∑nΔHrxn(products) - ∑nΔHrxn(reactants)
1. Determine what formations compose the molecules on the reactant side, find their ΔHf° using the table
2. Determine what formations compose the molecules on the product side, find their ΔHf° using the table
3. add the reactant and product formations together and plug into the formula
-
What is a standard enthalpy change
The enthalpy change when all reactants and products are in their standard state
-
What is a standard enthalpy of formation
The enthalpy change of a reaction that forms 1 mole of a pure compound from its constituent elements
-
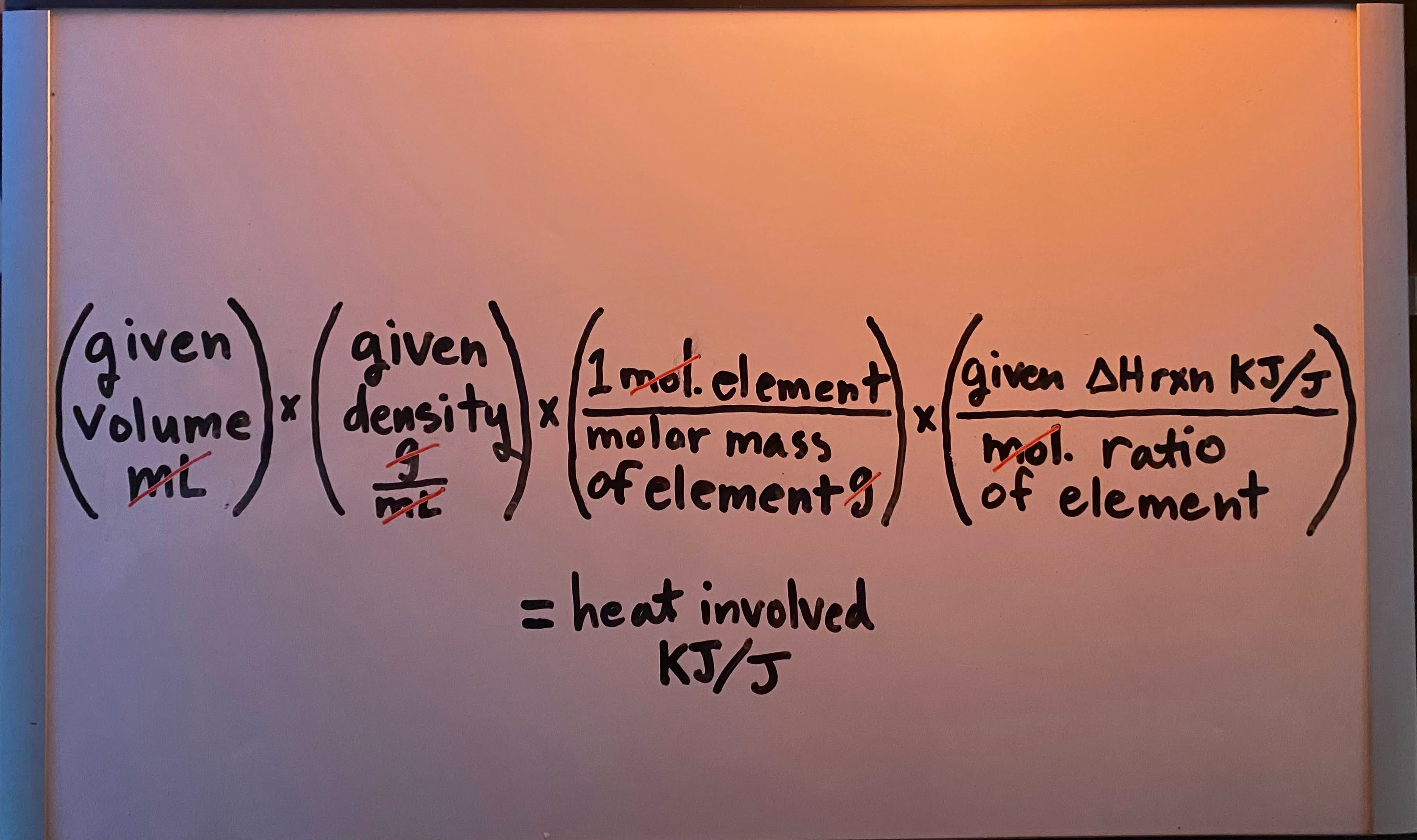
Constant-pressure (calorimetry for ΔHrxn) formula
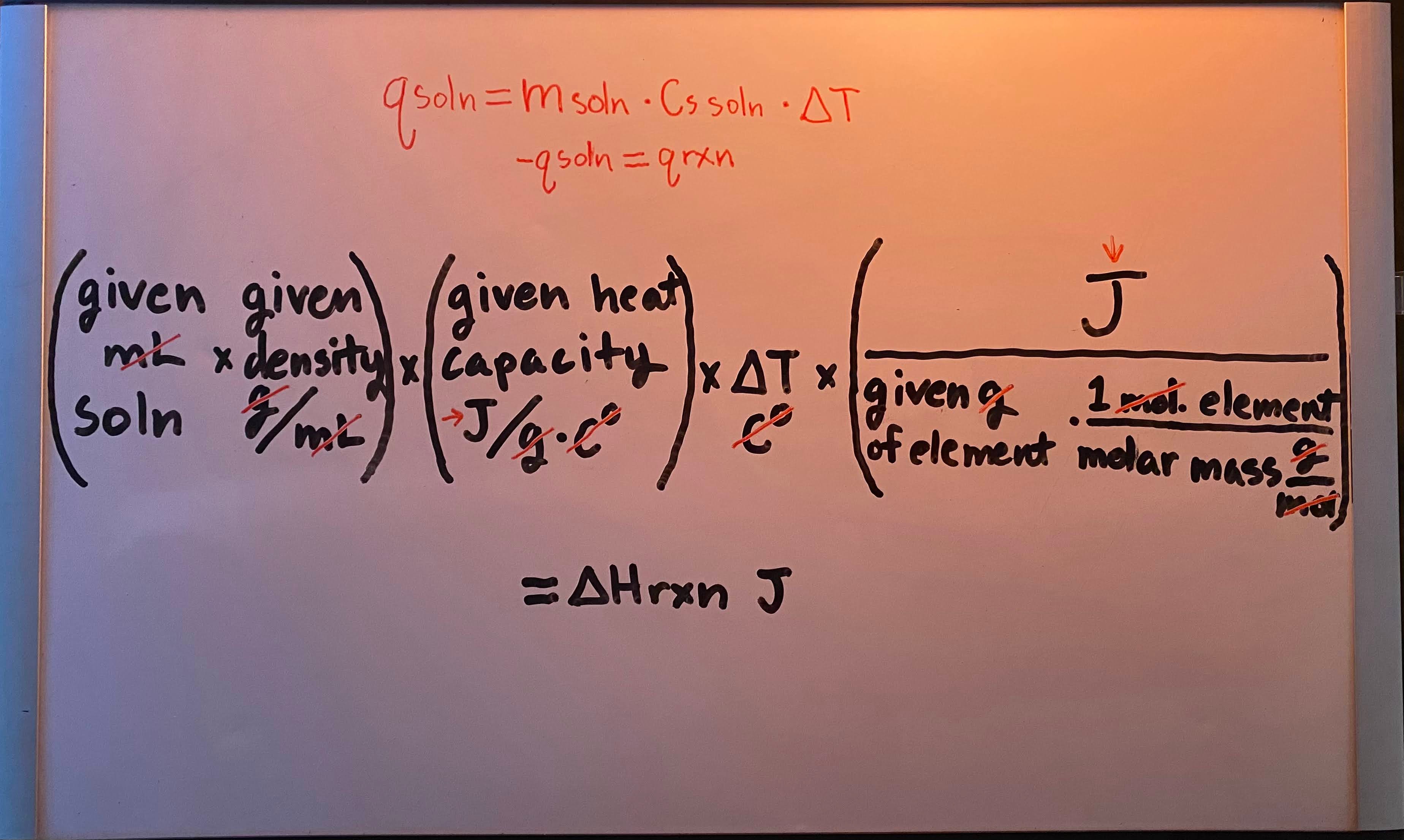
-
Heat produced/released by a complete reaction" when given mass (kg/g)
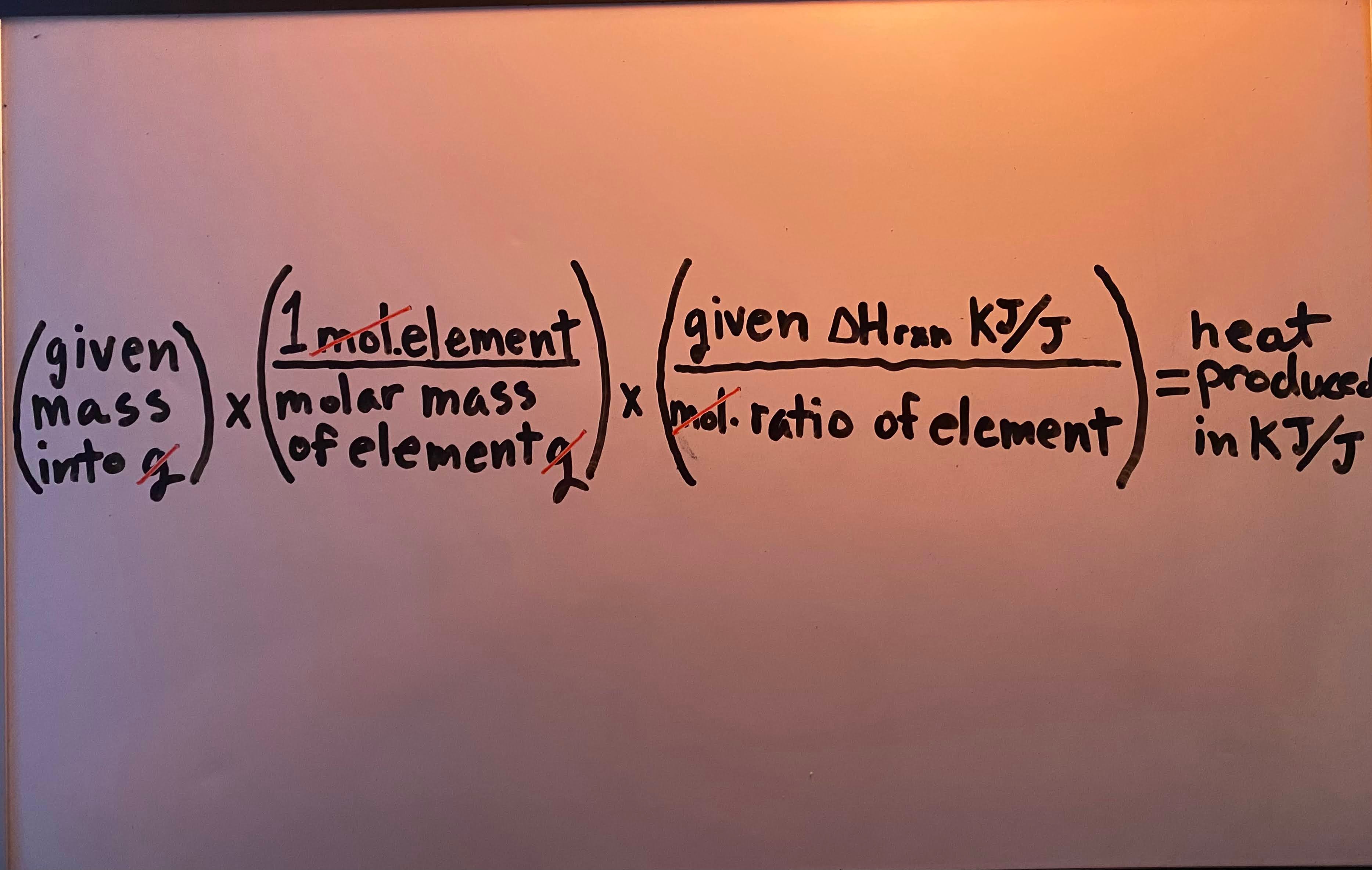
-
Heat produced/released by a complete reaction" when given volume (mL/L)