-
What are joints?
sites where two bones meet
-
What are the functions of Joints?
skeleton mobility
hold skeleton together
-
what are the 3 functional classifications of joints?
synarthrosis (immovable)
amphiarthroses (slightly movable)
diarthroses (freely movable)
-
what are the 3 structural classifications of joints?
-fibrous
-cartilaginous
-synovial (contains joint cavity)
-
what is a fibrous joint?
what are the three fibrous joints?
bones joined by ligaments
sutures
syndesmosis
gomphosis
-
what are sutures?
how moveable are they?
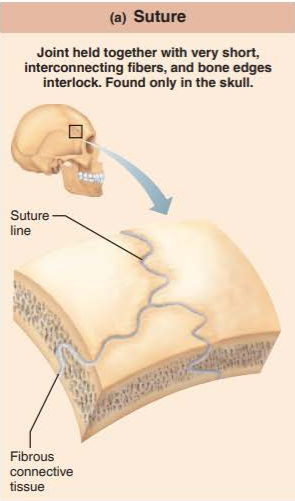
short seams of collagen fibers that connect bones of the skull
synarthrosis
-
what are syndesmosis?
how movable are they?
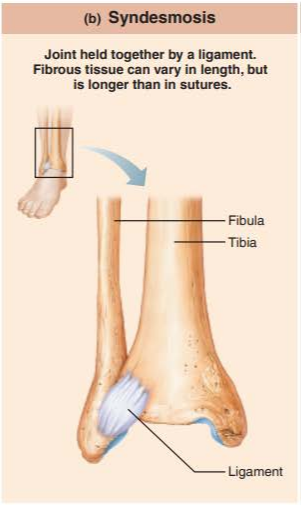
bones connected by ligaments, bands of fibrous tissue
amphiarthrosis limited by length of ligaments
-
what is gomphosis?
how moveable are they?
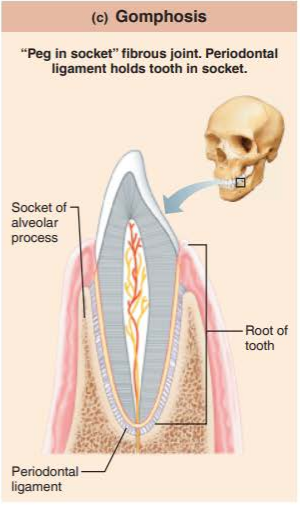
a peg-in socket fibrous joint
synarthrosis
-
what are are cartilaginous joints?
what are the two types?
articulating bones connected by cartilage
synchondroses
symphyses
-
what are synchondroses?
how moveable is it?
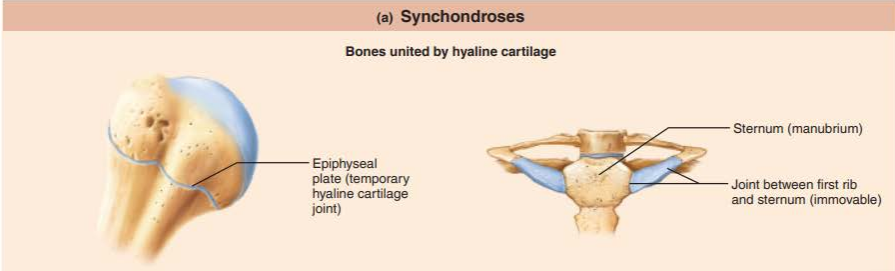
a plate of hyaline cartilage that unites the bones
synarthrosis
-
what is a symphysis?
how moveable is it?
name a function of this joint
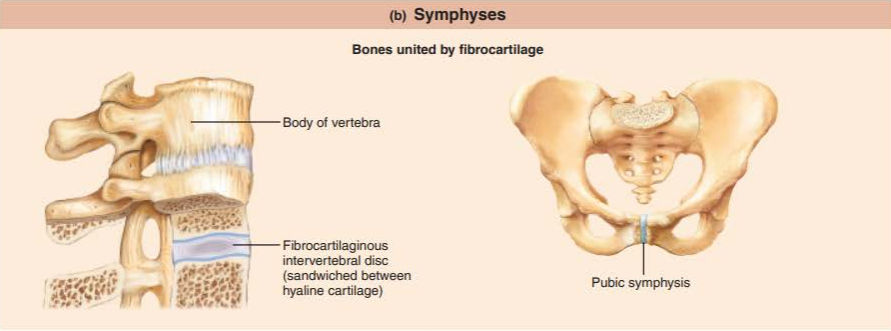
a joint where fibrocartilage unites the bone
amphiarthroses
shock absorber
-
what are synovial joints?
how moveable is it?
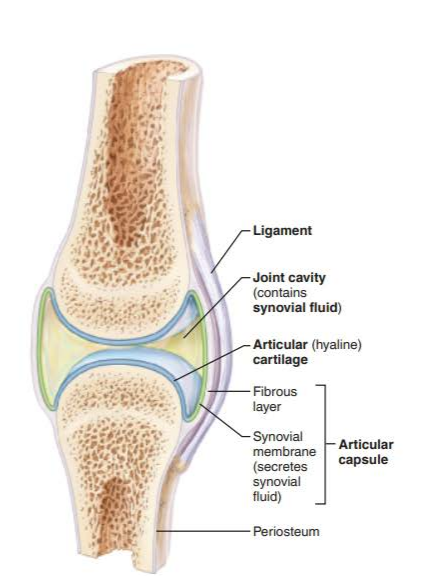
2 or more bones meet separated by a joint cavity that is lined with a synovial membrane and the cavity is filled with synovial fluid
diarthrosis
-
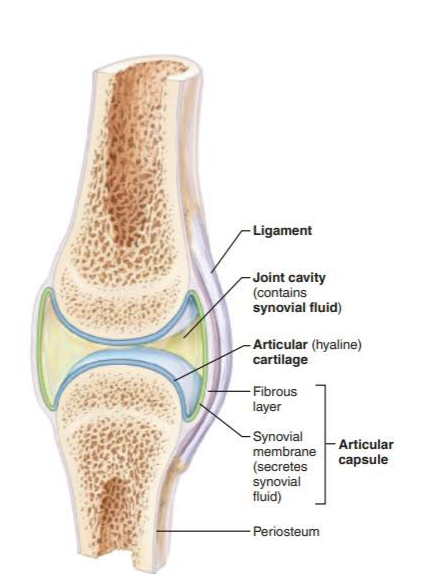
what are the major structural features of synovial joints?
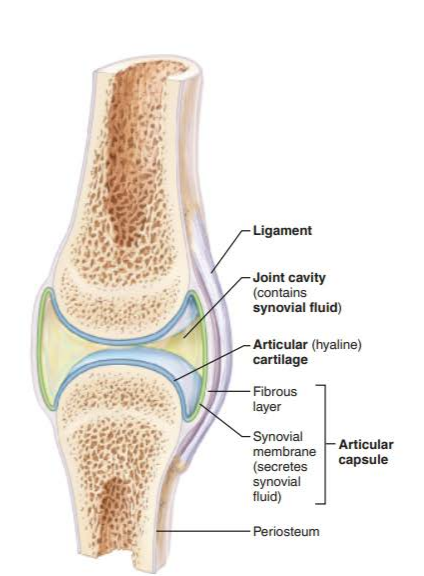
-joint cavity
-articular capsule
-synovial fluid
-articular cartilage
-reinforcing ligaments
-nerves and blood vessels
-
what is the articular capsule?
what is the outer layer made of?
the inner layer?
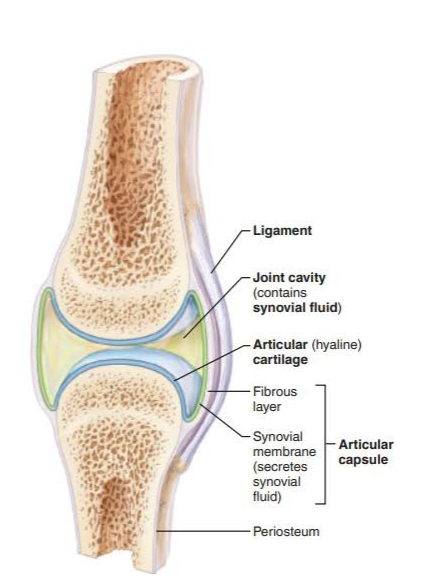
major feature of synovial joints
outer layer is dense irregular connective tissue
inner layer is synovial membrane made of loose connective tissue
-
what does the synovial membrane do?
makes synovial fluid
-
what does synovial fluid do
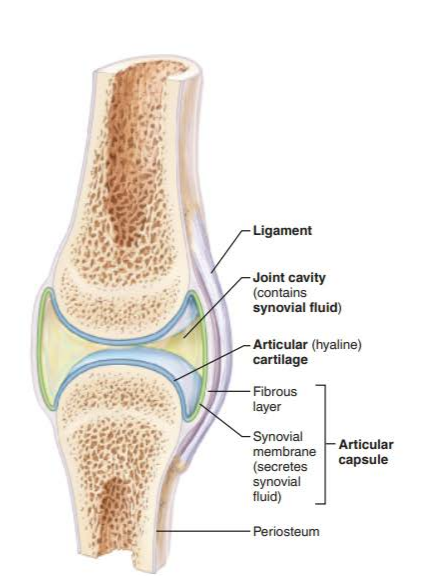
provides a slippery weight-bearing film that reduces friction between cartilages
-
describe the articular cartilage of synovial joints
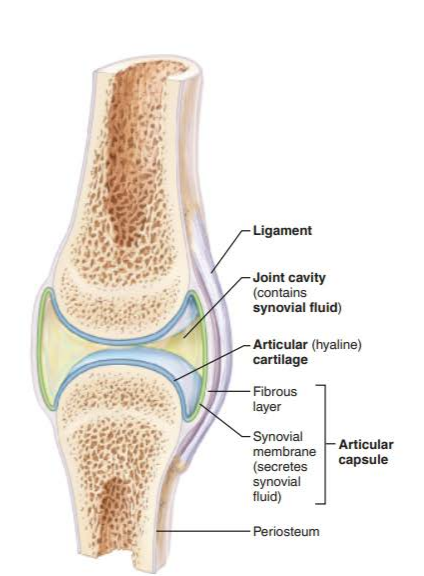
glassy smooth hyaline cartilage that covers the opposing bone surfaces
filled with synovial fluid
spongy cushions that absorb compression
-
what are Bursae?
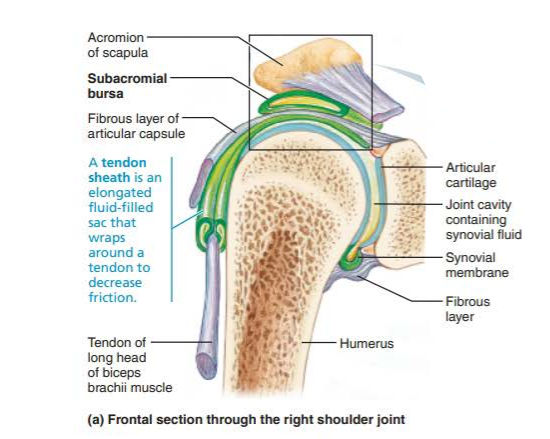
flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane
contains thin film of synovial fluid
-
what is a tendon sheathe?
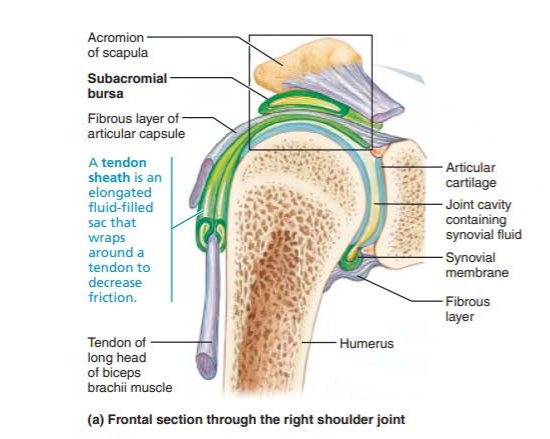
elongated bursa
wraps completely around a tendon subjected to friction
-
what are the 6 synovial joints?
hinge
saddle
planar
pivot
condyloid
ball and socket
-
what axial movements are involved with hinge joints?
name the two specific motions
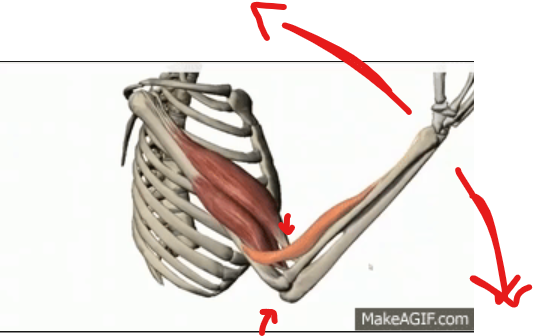
uniaxial movement
flexion
extension
-
what axial movements are allowed with pivot joints?
name the one specific motion
uniaxial movement
rotation
-
what axial movements are allowed with ball and socket joints?
name the six specific motions
multiaxial movement
flexion
extension
abduction
adduction
rotation
circumduction
-
what axial movements are allowed with condylar joints?
name the 5 specific movements
biaxial movement
flexion
extension
abduction
adduction
circumduction
-
what axial movements are allowed with a saddle joint?
name the 6 specific movements
biaxial movement
flexion
extension
abduction
adduction
slightly rotate
circumduction
-
what axial movements are allowed with a plane joint?
name the 1 specific movement
nonaxial
.gliding movements
-
give a location where you would find a saddle joint
carpometacarpal joint of digit 1
-
give two locations where you would find a ball and socket joint
shoulder joint
hip joint
-
why do menisci tear easily?
menisci are only attached at their outer margins
-
what are the 3 joints within the knee?
medial tibiofemoral joint
lateral tibiofemoral joint
femoropatellar joint
-
describe the functions of the menisci
deepens shallow tibial articular surfaces
prevents side to side rocking of the femur on the tibia
absorbs shock transmitted to the knee
-
what are the bones that form the shoulder joint
scapula articulating with the humerus
-
why is the shoulder easily dislocated?
structures reinforcing this joint are weakest anteriorly and inferiorly
head of the humerus easily dislocates forwards and downwards
-
describe the function of the tibiofemoral joint
diarthrotic
flexion and extension of the leg
some rotation when partially flexed
-
describe the structure of the tibiofemoral joint
synovial modified hinge
-
describe the structure of the femoropatellar joint
synovial plane
-
describe the function of the femoropatellar joint
diarthrotic
gliding of patella
-
what tissue is the medial and lateral menisci made of?
fibrocartilage
-
name 3 bursae associated with the knee
deep infrapatellar bursa
subcutaneous prepatellar bursa
suprapatellar bursa
-
Describe the function of the tendon sheath associated with the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle
secures the head of the humerus to the glenoid cavity
-
Where is the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle relative to this joint?
-travels through the joint cavity and runs within the anterior intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
-
Where are the bursae located in the shoulder joint?
subacromial bursa
subscapular bursa
-
what are the bones connected by the medial collateral ligament
tibia
femur
-
Name the structures connected by the quadriceps tendon
patella
quadriceps femoris muscle
-
Name the structures connected by the patellar ligament
patella
tibia
-
describe Flexion
bending movement that decreases the angle of the joint and brings articulating bones closer together
-
describe Extension
reverse of flexion that increases the angle between articulating bones
-
Hyperextension
continuation of the extension movement past anatomical position
-
describe Rotation
turning a bone along its own long axis
-
describe Circumduction
moving a limb that traces a cone in space
-
describe Abduction
movement of the limb away from the midline of the body
-
describe Adduction
movement of the limb towards the midline of the body
-
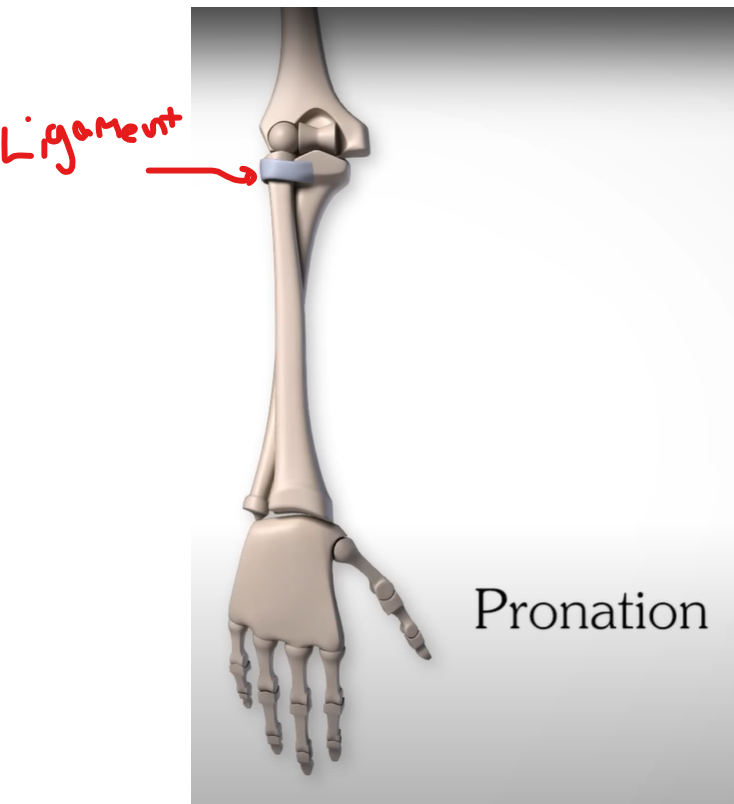
describe Supination (hand)
palms facing anteriorly
-
describe Pronation (hand)
palms facing posteriorly
-
describe Eversion (foot)
sole of the foot turning laterally
-
describe Inversion (foot)
sole of the foot turning medially
-
describe Dorsiflexion (foot)
lifting the foot so that its superior surface approaches the shin
-
describe Plantar flexion (foot)
depressing the foot so that the superior surface moves away from the shin
-
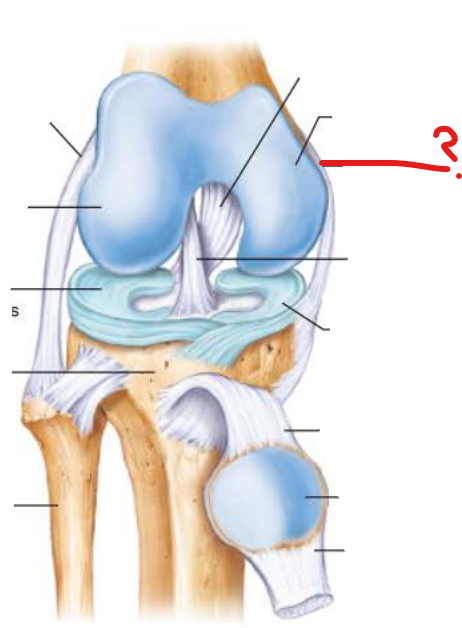
medial collateral ligament
-
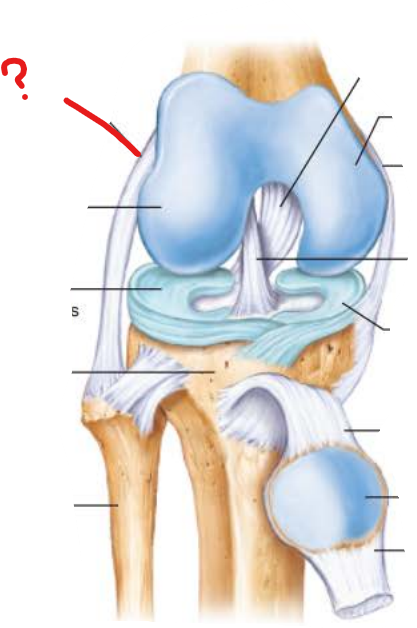
lateral collateral ligament
-
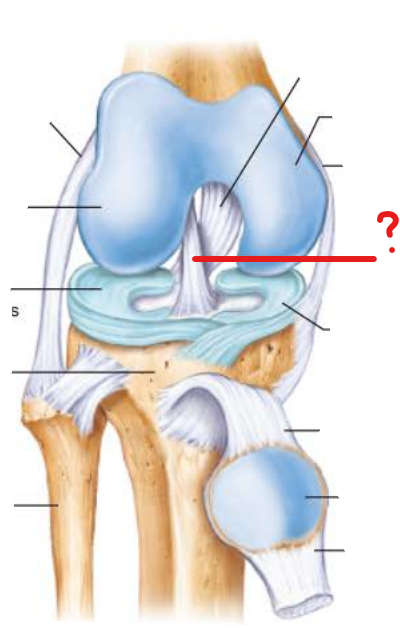
anterior cruciate ligament
-
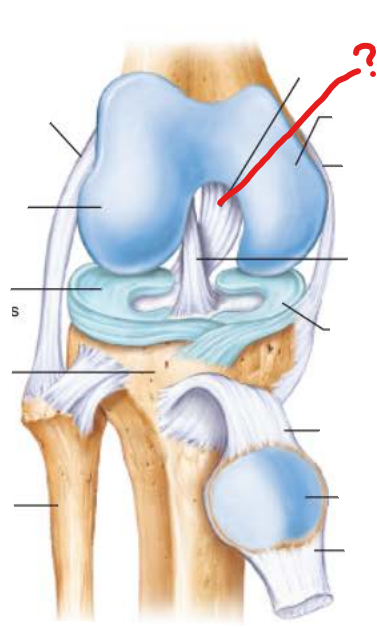
posterior cruciate ligament
-
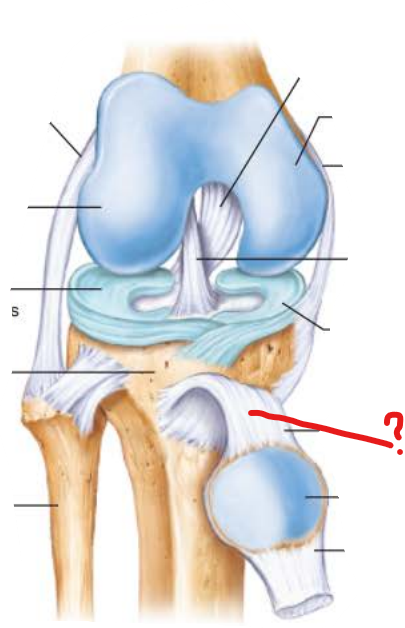
patellar ligament
-
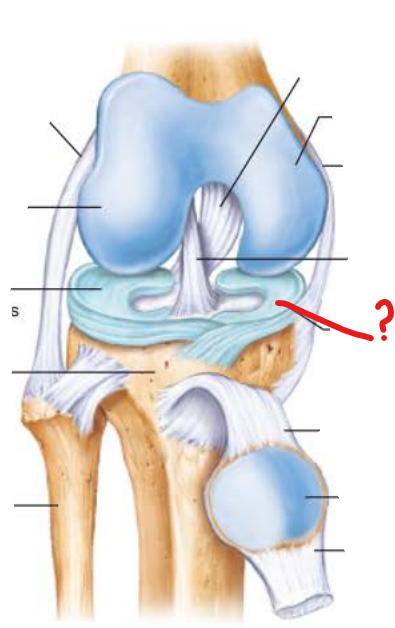
medial meniscus
-
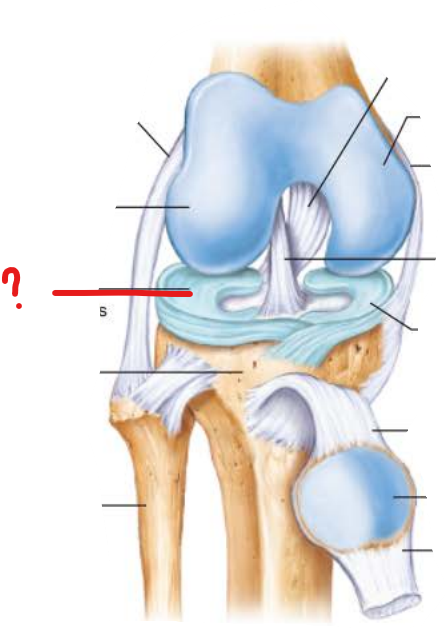
lateral meniscus
-
what three structures of the knee are commonly injured when lateral force is applied to the knee?
medial collateral ligament
medial meniscus
anterior cruciate ligament


